Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 24 February 2024

Modeling the link between tourism and economic development: evidence from homogeneous panels of countries
- Pablo Juan Cárdenas-García ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1779-392X 1 ,
- Juan Gabriel Brida 2 &
- Verónica Segarra 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 308 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1029 Accesses
Metrics details
- Development studies
Having previously analyzed the relationship between tourism and economic growth from distinct perspectives, this paper attempts to fill the void existing in scientific research on the relationship between tourism and economic development, by analyzing the relationship between these variables using a sample of 123 countries between 1995 and 2019. The Dumistrescu and Hurlin adaptation of the Granger causality test was used. This study takes a critical look at causal analysis with heterogeneous panels, given the substantial differences found between the results of the causal analysis with the complete panel as compared to the analysis of homogeneous country groups, in terms of their dynamics of tourism specialization and economic development. On the one hand, a one-way causal relationship exists from tourism to development in countries having low levels of tourism specialization and development. On the other hand, a one-way causal relationship exists by which development contributes to tourism in countries with high levels of development and tourism specialization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Gravity models do not explain, and cannot predict, international migration dynamics
Robert M. Beyer, Jacob Schewe & Hermann Lotze-Campen
The coordination pattern of tourism efficiency and development level in Guangdong Province under high-quality development
Lijuan Zhang, Azizan Marzuki & Zhenjie Liao
Analysis of spatial-temporal pattern, dynamic evolution and influencing factors of health tourism development in China
Huadi Wang, Yue Feng, … Nianxing Zhou
Introduction
Across the world, tourism is one of the most important sectors. It has undergone exponential growth since the mid-1900s and is currently experiencing growth rates that exceed those of other economic sectors (Yazdi, 2019 ).
Today, tourism is a major source of income for countries that specialize in this sector, generating 5.8% of the global GDP (5.8 billion US$) in 2021 (UNWTO, 2022 ) and providing 5.4% of all jobs (289 million) worldwide. Although its relevance is clear, tourism data have declined dramatically due to the recent impact of the Covid-19 health crisis. In 2019, prior to the pandemic (UNWTO, 2020 ), tourism represented 10.3% of the worldwide GDP (9.6 billion US$), with the number of tourism-related jobs reaching 10.2% of the global total (333 million). With the evolution of the pandemic and the regained trust of tourists across the globe, it is estimated that by 2022, approximately 80% of the pre-pandemic figures will be attained, with a full recovery being expected by 2024 (UNWTO, 2022 ).
Given the importance of this economic activity, many countries consider tourism to be a tool enabling economic growth (Corbet et al., 2019 ; Ohlan, 2017 ; Xia et al., 2021 ). Numerous works have analyzed the relationship between increased tourism and economic growth; and some systematic reviews have been carried out on this relationship (Brida et al., 2016 ; Ahmad et al., 2020 ), examining the main contributions over the first two decades of this century. These reviews have revealed evidence in this area: in some cases, it has been found that tourism contributes to economic growth while, in other cases, the economic cycle influences tourism expansion. Moreover, other works offer evidence of a bi-directional relationship between these variables.
Distinct international organizations (OECD, 2010 ; UNCTAD, 2011 ) have suggested that not only does tourism promote economic growth, it also contributes to socio-economic advances in the host regions. This may be the real importance of tourism, since the ultimate objective of any government is to improve a country’s socio-economic development (UNDP, 1990 ).
The development of economic and other policies related to the economic scope of tourism, in addition to promoting economic growth, are also intended to improve other non-economic factors such as education, safety, and health. Improvements in these factors lead to a better life for the host population (Lee, 2017 ; Todaro and Smith, 2020 ).
Given tourism’s capacity as an instrument of economic development (Cárdenas-García et al., 2015 ), distinct institutions such as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa, the United Nations World Tourism Organization and the World Bank, have begun funding projects that consider tourism to be a tool for improved socio-economic development, especially in less advanced countries (Carrillo and Pulido, 2019 ).
This new trend within the scientific literature establishes, firstly, that tourism drives economic growth and, secondly, that thanks to this economic growth, the population’s economic conditions may be improved (Croes et al., 2021 ; Kubickova et al., 2017 ). However, to take advantage of the economic growth generated by tourism activity to boost economic development, specific policies should be developed. These policies should determine the initial conditions to be met by host countries committed to tourism as an instrument of economic development. These conditions include regulation, tax system, and infrastructure provision (Cárdenas-García and Pulido-Fernández, 2019 ; Lejárraga and Walkenhorst, 2013 ; Meyer and Meyer, 2016 ).
Therefore, it is necessary to differentiate between the analysis of the relationship between tourism and economic growth, whereby tourism boosts the economy of countries committed to tourism, traditionally measured through an increase in the Gross Domestic Product (Alcalá-Ordóñez et al., 2023 ; Brida et al., 2016 ), and the analysis of the relationship between tourism and economic development, which measures the effect of tourism on other factors (not only economic content but also inequality, education, and health) which, together with economic criteria, serve as the foundation to measure a population’s development (Todaro and Smith, 2020 ).
However, unlike the analysis of the relationship between tourism and economic growth, few empirical studies have examined tourism’s capacity as a tool for development (Bojanic and Lo, 2016 ; Cárdenas-García and Pulido-Fernández, 2019 ; Croes, 2012 ).
To help fill this gap in the literature analyzing the relationship between tourism and economic development, this work examines the contribution of tourism to economic development, given that the relationship between tourism and economic growth has been widely analyzed by the scientific literature. Moreover, given that the literature has demonstrated that tourism contributes to economic growth, this work aims to analyze whether it also contributes to economic development, considering development in the broadest possible sense by including economic and socioeconomic variables in the multi-dimensional concept (Wahyuningsih et al., 2020 ).
Therefore, based on the results of this work, it is possible to determine whether the commitment made by many international organizations and institutions in financing tourism projects designed to improve the host population’s socioeconomic conditions, especially in countries with lower development levels, has, in fact, resulted in improved development levels.
It also presents a critical view of causal analyses that rely on heterogeneous panels, examining whether the conclusions reached for a complete panel differ from those obtained when analyzing homogeneous groups within the panel. As seen in the literature review analyzing the relationship between tourism and economic development, empirical works using panel data from several countries tend to generalize the results obtained to the entire panel, without verifying whether, in fact, they are relevant for all of the analyzed countries or only some of the same. Therefore, this study takes an innovative approach by examining the panel countries separately, analyzing the homogeneous groups distinctly.
Therefore, this article presents an empirical analysis examining whether a causal relationship exists between tourism and economic development, with development being considered to be a multi-dimensional variable including a variety of factors, distinct from economic ones. Panel data from 123 countries during the 1995–2019 period was considered to examine the causal relationship between tourism and economic development. For this, the Granger causality test was performed, applying the adaptation of this test made by Dumistrescu and Hurlin. First, a causal analysis was performed collectively for all of the countries of the panel. Then, a specific analysis was performed for each of the homogeneous groups of countries identified within the panel, formed according to levels of tourism specialization and development.
This article provides information on tourism’s capacity to serve as an instrument of development, helping to fill the gap in scientific research in this area. It critically examines the use of causal analyses based on heterogeneous samples of countries. This work offers the following main novelties as compared to prior works on the same topic: firstly, it examines the relationship between tourism and economic development, while the majority of the existing works only analyze the relationship between tourism and economic growth; secondly, it analyzes a large sample of countries, representing all of the global geographic areas, whereas the literature has only considered works from specific countries or a limited number of nations linked to a specific country in a specific geographical area, and; thirdly, it analyzes the panel both individually and collectively, for each of the homogenous groups of countries identified, permitting the adoption of specific policies for each group of countries according to the identified relationship, as compared to the majority of works that only analyze the complete panel, generalizing these results for all countries in the sample.
Overall, the results suggest that a relationship exists between tourism and development in all of the analyzed countries from the sample. A specific analysis was performed for homogeneous country groups, only finding a causal relationship between tourism and development in certain country groups. This suggests that the use of heterogeneous country samples in causal analyses may give rise to inappropriate conclusions. This may be the case, for example, when finding causality for a broad panel of countries, although, in fact, only a limited number of panel units actually explain this causal relationship.
The remainder of the document is organized as follows: the next section offers a review of the few existing scientific works on the relationship between tourism and economic development; section three describes the data used and briefly explains the methodology carried out; section four details the results obtained from the empirical analysis; and finally, the conclusions section discusses the main implications of the work, also providing some recommendations for economic policy.
Tourism and economic development
Numerous organizations currently recognize the importance of tourism as an instrument of economic development. It was not until the late 20th century, however, when the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), in its Manila Declaration, established that the development of international tourism may “help to eliminate the widening economic gap between developed and developing countries and ensure the steady acceleration of economic and social development and progress, in particular of the developing countries” (UNWTO, 1980 ).
From a theoretical point of view, tourism may be considered an effective activity for economic development. In fact, the theoretical foundations of many works are based on the relationship between tourism and development (Ashley et al., 2007 ; Bolwell and Weinz, 2011 ; Dieke, 2000 ; Sharpley and Telfer, 2015 ; Sindiga, 1999 ).
The link between tourism and economic development may arise from the increase in tourist activity, which promotes economic growth. As a result of this economic growth, policies may be developed to improve the resident population’s level of development (Alcalá-Ordóñez and Segarra, 2023 ).
Therefore, it is essential to identify the key variables permitting the measurement of the level of economic development and, therefore, those variables that serve as a basis for analyzing whether tourism results in improved the socioeconomic conditions of the host population (Croes et al., 2021 ). Since economic development refers not only to economic-based variables, but also to others such as inequality, education, or health (Todaro and Smith, 2020 ), when analyzing the economic development concept, it has been frequently linked to human development (Pulido-Fernández and Cárdenas-García, 2021 ). Thus, we wish to highlight the major advances resulting from the publication of the Human Development Index (HDI) when measuring economic development, since it defines development as a multidimensional variable that combines three dimensions: health, education, and income level (UNDP, 2023 ).
However, despite the importance that many organizations have given to tourism as an instrument of economic development, basing their work on the relationship between these variables, a wide gap continues to exist in the scientific literature for empirical studies that examine the existence of a relationship between tourism and economic development, with very few empirical analyses analyzing this relationship.
First, a group of studies has examined the causal relationship between tourism and economic development, using heterogeneous samples, and without previously grouping the subjects based on homogeneous characteristics. Croes ( 2012 ) analyzed the relationship between tourism and economic development, measured through the HDI, finding that a bidirectional relationship exists for the cases of Nicaragua and Costa Rica. Using annual data from 2001 to 2014, Meyer and Meyer ( 2016 ) performed a collective analysis of South African regions, determining that tourism contributes to economic development. For a panel of 63 countries worldwide, and once again relying on the HDI to define economic development, it was determined that tourism contributes to economic development. Kubickova et al. ( 2017 ), using annual data for the 1995–2007 period, analyzed Central America and Caribbean nations, determining the existence of this relationship by which tourism influences the level of economic development and that the level of development conditions the expansion of tourism. Another work examined nine micro-states of America, Europe, and Africa (Fahimi et al., 2018 ); and 21 European countries in which human capital was measured, as well as population density and tourism income, analyzing panel data and determining that tourism results in improved economic development. Finally, within this first group of works, Chattopadhyay et al. ( 2022 ), using a broad panel of destinations, (133 countries from all geographic areas of the globe) determined that there is no relationship between tourism and economic development.
Studies performed with large country samples that attempt to determine the causal relationship between tourism and economic development by analyzing countries that do not necessarily share homogeneous characteristics, may lead to erroneous conclusions, establishing causality (or not) for panel sets even when this situation is actually explained by a small number of panel units.
Second, another group of studies have analyzed the causal relationship between tourism and economic development, considering the previous limitation, and has grouped the subjects based on their homogeneous characteristics. Cárdenas-García et al. ( 2015 ) used annual data from 1990–2010, in a collective analysis of 144 countries, making a joint panel analysis and then examining two homogeneous groups of countries based on their level of economic development. They determined that tourism contributes to economic development, but only in the most developed group of countries. They determined that tourism contributes to economic development, both for the total sample and for the homogeneous groups analyzed. Pulido-Fernández and Cárdenas-García ( 2021 ), using annual data for the 1993–2017 period, performed a joint analysis of 143 countries, followed by a specific analysis for three groups of countries sharing homogeneous characteristics in terms of tourism growth and development level. They determined that tourism contributes to economic development and that development level conditions tourism growth in the most developed countries.
Finally, another group of studies has analyzed the causal relationship between tourism and economic development in specific cases examined on an individual basis. In a specific analysis by Aruba et al. ( 2016 ), it was determined that tourism contributes to human development. Analyzing Malaysia, Tan et al. ( 2019 ) determined that tourism contributes to development, but only over the short term, and that level of development does not influence tourism growth. Similar results were obtained by Boonyasana and Chinnakum ( 2020 ) in an analysis carried out in Thailand. In this case of Thailand (Boonyasana and Chinnakum, 2020 ), which relied on the HDI, the relationship with economic growth was also analyzed, finding that an increase in tourism resulted in improved economic development. Finally, Croes et al. ( 2021 ), in a specific analysis of Poland, determined that tourism does not contribute to development.
As seen from the analysis of the most relevant publications detailed in Table 1 , few empirical works have considered the relationship between tourism and economic development, in contrast to the numerous works from the scientific literature that have examined the relationship between tourism and economic growth. Most of the works that have empirically analyzed the relationship between tourism and economic development have determined that tourism positively influences the improved economic development in host destinations. To a lesser extent, some studies have found a bidirectional relationship between these variables (Croes, 2012 ; Kubickova et al., 2017 ; Pulido-Fernández and Cárdenas-García, 2021 ) while others have found no relationship between tourism and economic development (Chattopadhyay et al., 2022 ; Croes et al., 2021 ).
Furthermore, in empirical works relying on panel data, the results have tended to be generalized to the entire panel, suggesting that tourism improves economic development in all countries that are part of the panel. This has been the case in all of the examined works, with the exception of two studies that analyzed the panel separately (Cárdenas-García et al., 2015 ; Pulido-Fernández and Cárdenas-García, 2021 ).
Thus, it may be suggested that the use of very large country panels and, therefore, including very heterogeneous destinations, as was the case in the works of Biagi et al. ( 2017 ) using a panel of 63 countries, as well as that of Chattopadhyay et al. ( 2022 ) working with a panel of 133 countries, may lead to error, given that this relationship may only arise in certain destinations of the panel, although it is generalized to the entire panel.
This work serves to fill this gap in the literature by analyzing the panel both collectively and separately, for each of the homogenous groups of countries that have been previously identified.
The lack of relevant works on the relationship between tourism and development, and of studies using causal analyses to examine these variables based on heterogeneous panels, may lead to the creation of rash generalizations regarding the entirety of the analyzed countries. Thus, conclusions may be reached that are actually based on only specific panel units. Therefore, we believe that this study is justified.
Methodological approach
Given the objective of this study, to determine whether a causal relationship exists between tourism and socio-economic development, it is first necessary to identify the variables necessary to measure tourism activity and development level. Thus, the indicators are highly relevant, given that the choice of indicator may result in distinct results (Rosselló-Nadal and He, 2020 ; Song and Wu, 2021 ).
Table 2 details the measurement variables used in this work. Specifically, the following indicators have been used in this paper to measure tourism and economic development:
Measurement of tourist activity. In this work, we decided to consider tourism specialization, examining the number of international tourists received by a country with regard to its population size as the measurement variable.
This information on international tourists at a national level has been provided annually by the United Nations World Tourism Organization since 1995 (UNWTO, 2023 ). This variable has been relativized based on the country’s population, according to information provided by the World Bank on the residents of each country (WB, 2023 ).
Tourism specialization is considered to be the level of tourism activity, specifically, the arrival of tourists, relativized based on the resident population, which allows for comparisons to be made between countries. It accurately measures whether or not a country is specialized in this economic activity. If the variable is used in absolute values, for example, the United States receives more tourists than Malta, so based on this variable it may be that the first country is more touristic than the second. However, in reality, just the opposite happens, Malta is a country in which tourist activity is more important for its economy than it is in the United States, so the use of tourist specialization as a measurement variable classifies, correctly, both Malta as a country with high tourism specialization and to the United States as a country with low tourism specialization.
Therefore, most of the scientific literature establishes the need to use the total number of tourists relativized per capita, given that this allows for the determination of the level of tourism specialization of a tourism destination (Dritsakis, 2012 ; Tang and Abosedra, 2016 ); furthermore, this indicator has been used in works analyzing the relationship between tourism and economic development (for example, Biagi et al., 2017 ; Boonyasana and Chinnakum; 2020 ; Croes et al., 2021 ; Fahimi et al., 2018 ).
Although some works have used other variables to measure tourism, such as tourism income, exports, or tourist spending, these variables are not available for all of the countries making up the panel, so the sample would have been significantly reduced. Furthermore, the data available for these alternative variables do not come from homogeneous databases, and therefore cannot be compared.
Measurement of economic development. In this work, the Human Development Index has been used to measure development.
This information is provided by the United Nations Development Program, which has been publishing it annually at the country level since 1990 (UNDP, 2023 ).
The selection of this indicator to measure economic development is in line with other works that have defended its use to measure the impact on development level (for example, Jalil and Kamaruddin, 2018 ; Sajith and Malathi, 2020 ); this indicator has also been used in works analyzing the relationship between tourism and economic development (for example, Meyer and Meyer, 2016 ; Kubickova et al., 2017 ; Pulido-Fernández and Cárdenas-García, 2021 ).
Although some works have used other variables, such as poverty or inequality, to measure development, these variables are not available for all of the countries forming the panel. Therefore the sample would have been considerably reduced and the data available for these alternative variables do not come from homogenous databases, and therefore comparisons cannot be made.
These indicators are available for a total of 123 countries, across the globe. Thus, these countries form part of the sample analyzed in this study.
As for the time frame considered in this work, two main issues were relevant when determining this period: on the one hand, there is an initial time restriction for the analyzed series, given that information on the arrival of international tourists is only available as of 1995, the first year when this information was provided by the UNWTO. On the other hand, it was necessary to consider the effect of the Covid-19 pandemic and the resulting tourism sector crisis, which also affected the global economy as a whole. Therefore, our time series ended as of 2019, with the overall time frame including data from 1995 to 2019, a 25-year period.
Previous considerations
Caution should be taken when considering causality tests to determine the relationships between two variables, especially in cases in which large heterogeneous samples are used. This is due to the fact that generalized conclusions may be reached when, in fact, the causality is only produced by some of the subjects of the analyzed sample. This study is based on this premise. While heterogeneity in a sample is clearly a very relevant aspect, in some cases, it may lead to conclusions that are less than appropriate.
In this work, a collective causal analysis has been performed on all of the countries of the panel, which consists of 123 countries. However, given that it is a broad sample including countries having major differences in terms of size, region, development level, or tourism performance, the conclusions obtained from this analysis may lead to the generalization of certain conclusions for the entire sample set, when in fact, these relationships may only be the case for a very small portion of the sample. This has been the case in other works that have made generalized conclusions from relatively large samples in which the sample’s homogeneity regarding certain patterns was not previously verified (Badulescu et al., 2021 ; Ömer et al., 2018 ; Gedikli et al., 2022 ; Meyer and Meyer, 2016 ; Xia et al., 2021 ).
Therefore, after performing a collective analysis of the entire panel, the causal relationship between tourism and development was then determined for homogeneous groups of countries that share common patterns of tourism performance and economic development level, to analyze whether the generalized conclusions obtained in the previous section differ from those made for the individual groups. This was in line with strategies that have been used in other works that have grouped countries based on tourism performance (Min et al., 2016 ) or economic development level (Cárdenas-García et al., 2015 ), prior to engaging in causal analyses. To classify the countries into homogeneous groups based on tourism performance and development level, a previous work was used (Brida et al., 2023 ) which considered the same sample of 123 countries, relying on the same data to measure tourism and development level and the same time frame. This guarantees the coherence of the results obtained in this work.
From the entire panel of 123 countries, a total of six country groups were identified as having a similar dynamic of tourism and development, based on qualitative dynamic behavior. In addition, an “outlier” group of countries was found. These outlier countries do not fit into any of the groups (Brida et al., 2023 ). The three main groups of countries were considered, discarding three other groups due to their small size. Table 3 presents the group of countries sharing similar dynamics in terms of tourism performance and economic development level.
Applied methodology
As indicated above, this work uses the Tourist Specialization Rate (TIR) and the Human Development Index (HDI) to measure tourism and economic development, respectively. In both cases, we work with the natural logarithm (l.TIR and l.HDI) as well as the first differences between the variables (d.l.TIR and d.l.HDI), which measure the growth of these variables.
A complete panel of countries is used, consisting of 123 countries. The three main groups indicated in the previous section are also considered (the first of the groups contains 36 countries, the second contains 29 and the last group contains 43).
The Granger causality test ( 1969 ) is used to analyze the relationships between tourism specialization and development level; this test shows if one variable predicts the other, but this should not be confused with a cause-effect relationship.
In the context of panel data, different tests may be used to analyze causality. Most of these tests differ with regard to the assumptions of homogeneity of the panel unit coefficients. While the standard form of the Granger causality test for panels assumes that all of the coefficients are equal between the countries forming part of the panel, the Dumitrescu and Hurlin test (2012) considers that the coefficients are different between the countries forming part of the panel. Therefore, in this work, Granger’s causality is analyzed using the Dumitrescu and Hurlin test (2012). In this test, the null hypothesis is of no homogeneous causality; in other words, according to the null hypothesis, causality does not exist for any of the countries of the analyzed sample whereas, according to the alternative hypothesis, in which the regression model may be different in the distinct countries, causality is verified for at least some countries. The approach used by Dumitrescu and Hurlin ( 2012 ) is more flexible in its assumptions since although the coefficients of the regressions proposed in the tests are constant over time, the possibility that they may differ for each of the panel elements is accepted. This approach has more realistic assumptions, given that countries exhibit different behaviors. One relevant aspect of this type of tests is that they offer no information on which countries lead to the rejection of the lack of causality.
Given the specific characteristics of this type of tests, the presence of very heterogeneous samples may lead to inappropriate conclusions. For example, causality may be assumed for a panel of countries, when only a few of the panel’s units actually explain this relationship. Therefore, this analysis attempts to offer novel information on this issue, revealing that the conclusions obtained for the complete set of 123 countries are not necessarily the same as those obtained for each homogeneous group of countries when analyzed individually.
Given the nature of the variables considered in this work, specifically, regarding tourism, it is expected that a shock taking place in one country may be transmitted to other countries. Therefore, we first analyze the dependency between countries, since this may lead to biases (Pesaran, 2006 ). The Pesaran cross-sectional dependence test (2004) is used for the total sample and for each of the three groups individually.
First, a dependence analysis is performed for the countries of the sample, verifying the existence of dependence between the panel subjects. A cross-sectional dependence test (Pesaran, 2004 ) is used, first for the overall set of countries in the sample and second, for each of the groups of countries sharing homogeneous characteristics.
The results are presented in Table 4 , indicating that the test is statistically significant for the two variables, both for all of the countries in the sample and for each of the homogeneous country clusters, for the variables taken in logarithms as well as their first differences.
Upon rejecting the null hypothesis of non-cross-sectional dependence, it is assumed that a shock occurs in a country that may be transmitted to other countries in the sample. In fact, the lack of dependence between the variables, both tourism and development, is natural in this type of variables, given the economic cycle through the globalization of the economic activity, common regions visited by tourists, the spillover effect, etc.
Second, the stationary nature of the series is tested, given that cross-sectional dependence has been detected between the variables. First-generation tests may present certain biases in the rejection of the null hypothesis since first-generation unit root tests do not permit the inclusion of dependence between countries (Pesaran, 2007 ). On the other hand, second-generation tests permit the inclusion of dependence and heterogeneity. Therefore, for this analysis, the augmented IPS test (CIPS) proposed by Pesaran ( 2007 ) is used. This second-generation unit root test is the most appropriate for this case, given the cross-sectional dependence.
The results are presented in Table 5 , showing the statistics of the CIPS test for both the overall set of countries in the sample and in each of the homogeneous clusters of countries. The results are presented for models with 1, 2, and 3 delays, considering both the variables in the logarithm and their first differences.
As observed, the null hypothesis of unit root is not rejected for the variables in levels, but it is rejected for the first differences. This result is found in all of the cases, for both the total sample and for each of the homogeneous groups, with a significance of 1%. Therefore, the variables are stationary in their first differences, that is, the variables are integrated at order 1. Given that the causality test requires stationary variables, in this work it is used with the variation or growth rate of the variables, that is, the variable at t minus the variable at t−1.
Finally, to analyze Granger’s causality, the test by Dumitrescu and Hurlin ( 2012 ) is used. This test is used to analyze the causal relationship in both directions; that is, whether tourism contributes to economic development and whether the economic development level conditions tourism specialization. Statistics are calculated considering models with 1, 2, and 3 delays. Considering that cross-sectional dependence exists, the p-values are corrected using bootstrap techniques (making 500 replications). Given that the test requires stationary variables, primary differences of both variables were considered.
Table 6 presents the result of the Granger causality analysis using the Dumitrescu and Hurlin test (2012), considering the null hypothesis that tourism does not condition development level, either for all of the countries or for each homogeneous country cluster.
For the entire sample of countries, the results suggest that the null hypothesis of no causality from tourism to development was rejected when considering 3 delays (in other works analyzing the relationship between tourism and development, the null hypothesis was rejected with a similar level of delay: Rivera ( 2017 ) when considering 3–4 delays or Ulrich et al. ( 2018 ) when considering 3 delays). This suggests that for the entire panel, one-way causality exists whereby tourism influences economic development, demonstrating that tourism specialization contributes positively to improving the economic development of countries opting for tourism development. This is in line with the results of Meyer and Meyer ( 2016 ), Ridderstaat et al. ( 2016 ); Biagi et al. ( 2017 ); Fahimi et al. ( 2018 ); Tan et al. ( 2019 ), or Boonyasana and Chinnakum ( 2020 ).
However, the previous conclusion is very general, given that it is based on a very large sample of countries. Therefore, it may be erroneous to generalize that tourism is a tool for development. In fact, the results indicate that, when analyzing causality by homogeneous groups of countries, sharing similar dynamics in both tourism and development, the null hypothesis of no causality from tourism to development is only rejected for the group C countries, when considering three delays. Therefore, the development of generalized policies to expand tourism in order to improve the socioeconomic conditions of any destination type should consider that this relationship between tourism and economic development does not occur in all cases. Thus, it should first be determined if the countries opting for this activity have certain characteristics that will permit a positive relationship between said variables.
In other words, it may be a mistake to generalize that tourism contributes to economic development for all countries, even though a causal relationship exists for the entire panel. Instead, it should be understood that tourism permits an improvement in the level of development only in certain countries, in line with the results of Cárdenas-García et al. ( 2015 ) or Pulido-Fernández and Cárdenas-García ( 2021 ). In this specific work, this positive relationship between tourism and development only occurs in countries from group C, which are characterized by a low level of tourism specialization and a low level of development. Some works have found similar results for countries from group C. For example, Sharma et al. ( 2020 ) found the same relationship for India, while Nonthapot ( 2014 ) had similar findings for certain countries in Asia and the Pacific, which also made up group C. Some recent works have analyzed the relationship between tourism specialization and economic growth, finding similar results. This has been the case with Albaladejo et al. ( 2023 ), who found a relationship from tourism to economic growth only for countries where income is low, and the tourism sector is not yet developed.
These countries have certain limitations since even when tourism contributes to improved economic development, their low levels of tourism specialization do not allow them to reach adequate host population socioeconomic conditions. Therefore, investments in tourism are necessary there in order to increase tourism specialization levels. This increase in tourism may allow these countries to achieve development levels that are similar to other countries having better population conditions.
Therefore, in this group, consisting of 43 countries, a causal relationship exists, given that these countries are characterized by a low level of tourism specialization. However, the weakness of this activity, due to its low relevance in the country, prevents it from increasing the level of economic development. In these countries (details of these countries can be found in Table 3 , specifically, the countries included in Group C), policymakers have to develop policies to improve tourism infrastructure as a prior step to improving their levels of development.
On the other hand, in Table 7 , the results of Granger’s causal analysis based on the Dumitrescu and Hurlin test (2012) are presented, considering the null hypothesis that development level does not condition an increase in tourism, both in the overall sample set and in each of the homogeneous country clusters.
The results indicate that, for the entire country sample, the null hypothesis of no causality from development to tourism is not rejected, for any type of delay. This suggests that, for the entire panel, one-way causality does not exist, with level of development influencing the level of tourism specialization. This is in line with the results of Croes et al. ( 2021 ) in a specific analysis in Poland.
Once again, this conclusion is quite general, given that it has been based on a very broad sample of countries. Therefore, it may be erroneous to generalize that the development level does not condition tourism specialization. Past studies using a large panel of countries, such as the work of Chattopadhyay et al. ( 2022 ) analyzing panel data from 133 countries, have been generalized to all of the analyzed countries, suggesting that economic development level does not condition the arrival of tourists to the destination, although, in fact, this relationship may only exist in specific countries within the analyzed panel.
In fact, the results indicate that, when analyzing causality by homogeneous country groups sharing a similar dynamic, for both tourism and development, the null hypothesis of no causality from development to tourism is only rejected for country group A when considering 2–3 delays. Although the statistics of the test differ, when the sample’s time frame is small, as in this case, the Z-bar tilde statistic is more appropriate.
Thus, development level influences tourism growth in Group A countries, which are characterized by a high level of development and tourism specialization, in accordance with the prior results of Pulido-Fernández and Cárdenas-García ( 2021 ).
These results, suggesting that tourism is affected by economic development level, but only in the most developed countries, imply that the existence of better socioeconomic conditions in these countries, which tend to have better healthcare systems, infrastructures, levels of human resource training, and security, results in an increase in tourist arrivals to these countries. In fact, when traveling to a specific tourist destination, if this destination offers attractive factors and a higher level of economic development, an increase in tourist flows was fully expected.
In this group, consisting of 36 countries, the high development level, that is, the proper provision of socio-economic factors in their economic foundations (training, infrastructures, safety, health, etc.) has led to the attraction of a large number of tourists to their region, making their countries having high tourism specialization.
Although international organizations have recognized the importance of tourism as an instrument of economic development, based on the theoretical relationship between these two variables, few empirical studies have considered the consequences of the relationship between tourism and development.
Furthermore, some hasty generalizations have been made regarding the analysis of this relationship and the analysis of the relationship of tourism with other economic variables. Oftentimes, conclusions have been based on heterogeneous panels containing large numbers of subjects. This may lead to erroneous results interpretation, basing these results on the entire panel when, in fact, they only result from specific panel units.
Given this gap in the scientific literature, this work attempts to analyze the relationship between tourism and economic development, considering the panel data in a complete and separate manner for each of the previously identified country groups.
The results highlight the need to adopt economic policies that consider the uniqueness of each of the countries that use tourism as an instrument to improve their socioeconomic conditions, given that the results differ according to the specific characteristics of the analyzed country groups.
This work provides precise results regarding the need for policymakers to develop public policies to ensure that tourism contributes to the improvement of economic development, based on the category of the country using this economic activity to achieve greater levels of economic development.
Specifically, this work has determined that tourism contributes to economic development, but only in countries that previously had a lower level of tourism specialization and were less developed. This highlights the need to invest in tourism to attract more tourists to these countries to increase their economic development levels. Countries having major natural attraction resources or factors, such as the Dominican Republic, Egypt, India, Morocco, and Vietnam, need to improve their positioning in the international markets in order to attain a higher level of tourism specialization, which will lead to improved development levels.
Furthermore, the results of this study suggest that a greater past economic development level of a country will help attract more tourists to these countries, highlighting the need to invest in security, infrastructures, and health in order for these destinations to be considered attractive and increase tourist arrival. In fact, given their increased levels of development, countries such as Spain, Greece, Italy, Qatar, and Uruguay have become attractive to tourists, with soaring numbers of visitors and high levels of tourism specialization.
Therefore, the analysis of the relationship between tourism and economic development should focus on the differentiated treatment of countries in terms of their specific characteristics, since working with panel data with large samples and heterogenous characteristics may lead to incorrect results generalizations to all of the analyzed destinations, even though the obtained relationship in fact only takes place in certain countries of the sample.
Conclusions and policy implications
Within this context, the objective of this study is twofold: on the one hand, it aims to contribute to the lack of empirical works analyzing the causal relationship between tourism and economic development using Granger’s causality analysis for a broad sample of countries from across the globe. On the other hand, it critically examines the use of causality analysis in heterogeneous samples, by verifying that the results for the panel set differ from the results obtained when analyzing homogeneous groups in terms of tourism specialization and development level.
In fact, upon analyzing the causal relationship from tourism to development, and the causal relationship from development to tourism, the results from the entire panel, consisting of 123 countries, differ from those obtained when analyzing causality by homogeneous country groups, in terms of tourism specialization and economic development dynamics of these countries.
On the one hand, a one-way causality relationship is found to exist, whereby tourism influences economic development for the entire sample of countries, although this conclusion cannot be generalized, since this relationship is only explained by countries belonging to Group C (countries with low levels of tourism specialization and low development levels). This indicates that, although a causal relationship exists by which tourism contributes to economic development in these countries, the low level of tourism specialization does not permit growth to appropriate development levels.
The existence of a causal relationship whereby the increase in tourism precedes the improvement of economic development in this group of countries having a low level of tourism specialization and economic development, suggests the appropriateness of the focus by distinct international organizations, such as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development or the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa, on funding tourism projects (through the provision of tourism infrastructure, the stimulation of tourism supply, or positioning in international markets) in countries with low economic development levels. This work has demonstrated that investment in tourism results in the attracting of a greater flow of tourists, which will contribute to improved economic development levels.
Therefore, both international organizations financing projects and public administrations in these countries should increase the funding of projects linked to tourism development, in order to increase the flow of tourism to these destinations. This, given that an increase in tourism specialization suggests an increased level of development due to the demonstrated existence of a one-way causal relationship from tourism to development in these countries, many of which form part of the group of so-called “least developed” countries. However, according to the results obtained in this work, this relationship is not instantaneous, but rather, a certain delay exists in order for economic development to improve as a result of the increase in tourism. Therefore, public managers must adopt a medium and long-term vision of tourism activity as an instrument of development, moving away from short-term policies seeking immediate results, since this link only occurs over a broad time horizon.
On the other hand, this study reveals that a one-way causal relationship does not exist, by which the level of development influences tourism specialization level for the entire sample of countries. However, this conclusion, once again, cannot be generalized given that in countries belonging to Group A (countries with a high development level and a high tourism specialization level), a high level of economic development determines a higher level of tourism specialization. This is because the socio-economic structure of these countries (infrastructures, training or education, health, safety, etc.) permits their shaping as attractive tourist destinations, thereby increasing the number of tourists visiting them.
Therefore, investments made by public administrations to improve these factors in other countries that currently do not display this causal relationship implies the creation of the necessary foundations to increase their tourism specialization and, therefore, as shown in other works, tourism growth will permit economic growth, with all of the associated benefits for these countries.
Therefore, to attract tourist flows, it is not only important for a country to have attractive factors or resources, but also to have an adequate level of prior development. In other words, the tourists should perceive an adequate level of security in the destination; they should be able to use different infrastructures such as roads, airports, or the Internet; and they should receive suitable services at the destination from personnel having an appropriate level of training. The most developed countries, which are the destinations having the greatest endowment of these resources, are the ones that currently receive the most tourist flows thanks to the existence of these factors.
Therefore, less developed countries that are committed to tourism as an instrument to improve economic development should first commit to the provision of these resources if they hope to increase tourist flows. If this increase in tourism takes place in these countries, their economic development levels have been demonstrated to improve. However, since these countries are characterized by low levels of resources, cooperation by organizations financing the necessary investments is key to providing them with these resources.
Thus, a critical perspective is necessary when considering the relationship between tourism and economic development based on global causal analysis using heterogeneous samples with numerous subjects. As in this case, carrying out analyses on homogeneous groups may offer interesting results for policymakers attempting to suitably manage population development improvements due to tourism growth and tourism increases resulting from higher development levels.
One limitation of this work is its national scope since evidence suggests that tourism is a regional and local activity. Therefore, it may be interesting to apply this same approach on a regional level, using previously identified homogeneous groups.
And given that the existence of a causal relationship (in either direction) between tourism and development has only been determined for a specific set of countries, future works could consider other country-specific factors that may determine this causal relationship, in addition to the dynamics of tourism specialization and development level.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Ahmad N, Menegaki AN, Al-Muharrami S (2020) Systematic literature review of tourism growth nexus: An overview of the literature and a content analysis of 100 most influential papers. J Econ Surv 34(5):1068–1110. https://doi.org/10.1111/joes.12386
Article Google Scholar
Albaladejo I, Brida G, González M y Segarra V (2023) A new look to the tourism and economic growth nexus: a clustering and panel causality analysis. World Econ https://doi.org/10.1111/twec.13459
Alcalá-Ordóñez A, Brida JG, Cárdenas-García PJ (2023) Has the tourism-led growth hypothesis been confirmed? Evidence from an updated literature review. Curr Issues Tour https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2023.2272730
Alcalá-Ordóñez A, Segarra V (2023) Tourism and economic development: a literature review to highlight main empirical findings. Tour Econom https://doi.org/10.1177/13548166231219638
Ashley C, De Brine P, Lehr A, Wilde H (2007) The role of the tourism sector in expanding economic opportunity. Kennedy School of Government, Harvard University, Cambridge MA
Google Scholar
Biagi B, Ladu MG, Royuela V (2017) Human development and tourism specialization. Evidence from a panel of developed and developing countries. Int J Tour Res 19(2):160–178. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.2094
Badulescu D, Simut R, Mester I, Dzitac S, Sehleanu M, Bac DP, Badulescu A (2021) Do economic growth and environment quality contribute to tourism development in EU countries? A panel data analysis. Technol Econom Dev Econ 27(6):1509–1538. https://doi.org/10.3846/tede.2021.15781
Bojanic DC, Lo M (2016) A comparison of the moderating effect of tourism reliance on the economic development for islands and other countries. Tour Manag 53:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.10.00
Bolwell D, Weinz W (2011) Poverty reduction through tourism. International Labour Office, Geneva
Boonyasana P, Chinnakum W (2020) Linkages among tourism demand, human development, and CO 2 emissions in Thailand. Abac J 40(3):78–98
Brida JG, Cárdenas-García PJ, Segarra V (2023) Turismo y Desarrollo Económico: una Exploración Empírica. Red Nacional de Investigadores en Economía (RedNIE), Working Papers, 283
Brida JG, Cortes-Jimenez I, Pulina M (2016) Has the tourism-led growth hypothesis been validated? A literature review. Curr Issues Tour 19(5):394–430. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2013.868414
Cárdenas-García PJ, Pulido-Fernández JI (2019) Tourism as an economic development tool. Key factors. Curr Issues Tour 22(17):2082–2108. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2017.1420042
Cárdenas-García PJ, Sánchez-Rivero M, Pulido-Fernández JI (2015) Does tourism growth influence economic development? J Travel Res 54(2):206–221. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287513514297
Carrillo I, Pulido JI, (2019) Is the financing of tourism by international financial institutions inclusive? A proposal for measurement. Curr Issues Tour 22:330–356. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2016.1260529
Chattopadhyay M, Kumar A, Ali S, Mitra SK (2022) Human development and tourism growth’s relationship across countries: a panel threshold analysis. J Sustain Tour 30(6):1384–1402. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2021.1949017
Corbet S, O’Connell JF, Efthymiou M, Guiomard C, Lucey B (2019) The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Ann Tour Res 75:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2018.12.012
Croes R (2012) Assessing tourism development from Sen’s capability approach. J Travel Res 51(5):542–554. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287511431323
Article ADS Google Scholar
Croes R, Ridderstaat J, Bak M, Zientara P (2021) Tourism specialization, economic growth, human development and transition economies: the case of Poland. Tour Manag 82:104181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104181
Dieke P (2000) The political economy of tourism development in Africa. Cognizant, New York
Dritsakis N (2012) Tourism development and economic growth in seven Mediterranean countries: a panel data approach. Tour Econ 18(4):801–816. https://doi.org/10.5367/te.2012.0140
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econom Model 29(4):1450–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2012.02.014
Fahimi A, Saint Akadiri S, Seraj M, Akadiri AC (2018) Testing the role of tourism and human capital development in economic growth. A panel causality study of micro states. Tour Manag Perspect 28:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2018.08.004
Gedikli A, Erdoğan S, Çevik EI, Çevik E, Castanho RA, Couto G(2022) Dynamic relationship between international tourism, economic growth and environmental pollution in the OECD countries: evidence from panel VAR model. Econom Res 35:5907–5923. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2022.2041063
Granger CWJ (1969) Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 37(3):424–438. https://doi.org/10.2307/1912791
Jalil SA, Kamaruddin MN (2018) Examining the relationship between human development index and socio-economic variables: a panel data analysis. J Int Bus Econ Entrepreneurship 3(2):37–44. https://doi.org/10.24191/jibe.v3i2.14431
Kubickova M, Croes R, Rivera M (2017) Human agency shaping tourism competitiveness and quality of life in developing economies. Tour Manag Perspect 22:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2017.03.002
Lee YS (2017) General theory of law and development. Cornell Int Law Rev 50(3):432–435
CAS Google Scholar
Lejárraga I, Walkenhorst P (2013) Economic policy, tourism trade and productive diversification. Int Econ 135:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inteco.2013.09.001
Meyer DF, Meyer N (2016) The relationship between the tourism sector and local economic development (Led): the case of the Vaal Triangle region. South Afr J Environ Manag Tour 3(15):466–472
Min CK, Roh TS, Bak S (2016) Growth effects of leisure tourism and the level of economic development. Appl Econ 48(1):7–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2015.1073838
Nonthapot S (2014) The relationship between tourism and economic development in the Greater Mekong Subregion: panel cointegration and Granger causality. J Adv Res Law Econ 1(9):44–51
OECD (2010) Tourism trends & policies 2010. Paris: Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
Ohlan R (2017) The relationship between tourism, financial development and economic growth in India. Future Bus J 3(1):9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbj.2017.01.003
Ömer Y, Muhammet D, Kerem K (2018) The effects of international tourism receipts on economic growth: evidence from the first 20 highest income earning countries from tourism in the world (1996–2016). Montenegrin J Econ 14(3):55–71
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. Cambridge Working Papers in Economics No: 0435. Faculty of Economics, University of Cambridge
Pesaran MH (2006) Estimation and inference in large heterogeneous panels with a multifactor error structure. Econometrica 74(4):967–1012. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0262.2006.00692.x
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22:265–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.951
Pulido-Fernández JI, Cárdenas-García PJ (2021) Analyzing the bidirectional relationship between tourism growth and economic development. J Travel Res 60(3):583–602. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287520922316
Ridderstaat J, Croes R, Nijkamp P (2016) The tourism development–quality of life nexus in a small island destination. J Travel Res 55(1):79–94. https://doi.org/10.1177/0047287514532372
Rivera MA (2017) The synergies between human development, economic growth, and tourism within a developing country: an empirical model for Ecuador. J Destination Mark Manag 6:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdmm.2016.04.002
Rosselló-Nadal J, He J (2020) Tourist arrivals versus tourist expenditures in modelling tourism demand. Tour Econ 26(8):1311–1326. https://doi.org/10.1177/1354816619867810
Sajith GG, Malathi K (2020) Applicability of human development index for measuring economic well-being: a study on GDP and HDI indicators from Indian context. Indian Econom J 68(4):554–571. https://doi.org/10.1177/0019466221998620
Sharma M, Mohapatra G, Giri AK (2020) Beyond growth: does tourism promote human development in India? Evidence from time series analysis. J Asian Financ Econ Bus 7(12):693–702
Sharpley R, Telfer D (2015) Tourism and development: concepts and issues. Routledge, New York
Sindiga I (1999) Tourism and African development: change and challenge of tourism in Kenya. Ashgate, Leiden
Song H, Wu DC (2021) A critique of tourism-led economic growth studies. J Travel Res 61(4):719–729. https://doi.org/10.1177/004728752110185
Tan YT, Gan PT, Hussin MYM, Ramli N (2019) The relationship between human development, tourism and economic growth: evidence from Malaysia. Res World Econ 10(5):96–103. https://doi.org/10.5430/rwe.v10n5p96
Tang C, Abosedra S (2016) Does tourism expansion effectively spur economic growth in Morocco and Tunisia? Evidence from time series and panel data. J Policy Res Tour Leis Events 8(2):127–145. https://doi.org/10.1080/19407963.2015.1113980
Todaro MP, Smith SC (2020) Economic development. 13th Edition. Boston: Addison Wesley
Ulrich G, Ceddia MG, Leonard D, Tröster B (2018) Contribution of international ecotourism to comprehensive economic development and convergence in the Central American and Caribbean region. Appl Econ 50(33):3614–3629. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2018.1430339
UNCTAD (2011) Fourth United Nations Conference on least developed countries. Geneva: United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
UNDP (1990) Human Development Report 1990. Concept and measurement of human development.United Nations Development Programme, NY
UNDP (2023) Human Development Reports 2021/2022.United Nations Development Programme, NY
UNWTO (1980) Manila Declaration on World Tourism. United Nations World Tourism Organization, Madrid
UNWTO (2020) World Tourism Barometer. January 2020. United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), Madrid
UNWTO (2022) World Tourism Barometer. January 2022. United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), Madrid
UNWTO (2023) UNWTO Tourism Data Dashboard. United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), Madrid
Wahyuningsih D, Yunaningsih A, Priadana MS, Wijaya A, Darma DC, Amalia S (2020) The dynamics of economic growth and development inequality in Borneo Island, Indonesia. J Appl Econom Sci 1(67):135–143. https://doi.org/10.14505/jaes.v15.1(67).12
World Bank (2023) World Bank Open Data. World Bank, Washington DC
Xia W, Doğan B, Shahzad U, Adedoyin FF, Popoola A, Bashir MA (2021) An empirical investigation of tourism-led growth hypothesis in the European countries: evidence from augmented mean group estimator. Port Econom J 21(2):239–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10258-021-00193-9
Yazdi SK (2019) Structural breaks, international tourism development and economic growth. Econom Res 32(1):1765–1776. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2019.1638279
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, University of Jaén, Campus Las Lagunillas s/n, 23071, Jaén, Spain
Pablo Juan Cárdenas-García
GIDE, Faculty of Economics, Universidad de la República, Gonzalo Ramirez 1926, 11200, Montevideo, Uruguay
Juan Gabriel Brida & Verónica Segarra
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Author 1: conceptualization, funding acquisition, investigation, project administration, resources, supervision, validation, writing original draft, writing review & editing. Author 2: conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, validation, visualization. Author 3: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, software, validation, writing original draft.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pablo Juan Cárdenas-García .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Researchdata-tourism+hdi, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cárdenas-García, P.J., Brida, J.G. & Segarra, V. Modeling the link between tourism and economic development: evidence from homogeneous panels of countries. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 308 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02826-8
Download citation
Received : 03 September 2023
Accepted : 13 February 2024
Published : 24 February 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02826-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Open access
- Published: 05 January 2021
The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: a panel cointegration analysis
- Haroon Rasool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0083-4553 1 ,
- Shafat Maqbool 2 &
- Md. Tarique 1
Future Business Journal volume 7 , Article number: 1 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
120k Accesses
87 Citations
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Tourism has become the world’s third-largest export industry after fuels and chemicals, and ahead of food and automotive products. From last few years, there has been a great surge in international tourism, culminates to 7% share of World’s total exports in 2016. To this end, the study attempts to examine the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth by using the panel data over the period 1995–2015 for five BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) countries. The results of panel ARDL cointegration test indicate that tourism, financial development and economic growth are cointegrated in the long run. Further, the Granger causality analysis demonstrates that the causality between inbound tourism and economic growth is bi-directional, thus validates the ‘feedback-hypothesis’ in BRICS countries. The study suggests that BRICS countries should promote favorable tourism policies to push up the economic growth and in turn economic growth will positively contribute to international tourism.
Introduction
World Tourism Day 2015 was celebrated around the theme ‘One Billion Tourists; One Billion Opportunities’ highlighting the transformative potential of one billion tourists. With more than one billion tourists traveling to an international destination every year, tourism has become a leading economic sector, contributing 9.8% of global GDP and represents 7% of the world’s total exports [ 59 ]. According to the World Tourism Organization, the year 2013 saw more than 1.087 billion Foreign Tourist Arrivals and US $1075 billion foreign tourism receipts. The contribution of travel and tourism to gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to reach 10.8% at the end of 2026 [ 61 ]. Representing more than just economic strength, these figures exemplify the vast potential of tourism, to address some of the world´s most pressing challenges, including socio-economic growth and inclusive development.
Developing countries are emerging as the important players, and increasingly aware of their economic potential. Once essentially excluded from the tourism industry, the developing world has now become its major growth area. These countries majorly rely on tourism for their foreign exchange reserves. For the world’s forty poorest countries, tourism is the second-most important source of foreign exchange after oil [ 37 ].
The BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) countries have emerged as a potential bloc in the developing countries which caters the major tourists from developed countries. Tourism becomes major focus at BRICS Xiamen Summit 2017 held in China. These countries have robust growth rate, and are focal destinations for global tourists. During 1990 to 2014, these countries stride from 11% of the world’s GDP to almost 30% [ 17 ]. Among BRICS countries, China is ranked as an important destination followed by Brazil, Russia, India and South Africa [ 60 ].
The importance of inbound tourism has grown exponentially, because of its growing contribution to the economic growth in the long run. It enhances economic growth by augmenting the foreign exchange reserves [ 38 ], stimulating investments in new infrastructure, human capital and increases competition [ 9 ], promoting industrial development [ 34 ], creates jobs and hence to increase income [ 34 ], inbound tourism also generates positive externalities [ 1 , 14 ] and finally, as economy grows, one can argue that growth in GDP could lead to further increase in international tourism [ 11 ].
The tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) proposed by Balaguer and Cantavella-Jorda [ 3 ], states that expansion of international tourism activities exerts economic growth, hence offering a theoretical and empirical link between inbound tourism and economic growth. Theoretically, the TLGH was directly derived from the export-led growth hypothesis (ELGH) that postulates that economic growth can be generated not only by increasing the amount of labor and capital within the economy, but also by expanding exports.
The ‘new growth theory,’ developed by Balassa [ 4 ], suggests that export expansion can trigger economic growth, because it promotes specialization and raises factors productivity by increasing competition, creating positive externalities by advancing the dispersal of specialized information and abilities. Exports also enhance economic growth by increasing the level of investment. International tourism is considered as a non-standard type of export, as it indicates a source of receipts and consumption in situ. Given the difficulties in measuring tourism activity, the economic literature tends to focus on primary and manufactured product exports, hence neglecting this economic sector. Analogous to the ELGH, the TLGH analyses the possible temporal relationship between tourism and economic growth, both in the short and long run. The question is whether tourism activity leads to economic growth or, alternatively, economic expansion drives tourism growth, or indeed a bi-directional relationship exists between the two variables.
To further substantiate the nexus, the study will investigate the plausible linkages between economic growth and international tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. Financial markets are considered a key factor in producing strong economic growth, because they contribute to economic efficiency by diverting financial funds from unproductive to productive uses. The origin of this role of financial development may is traced back to the seminal work of Schumpeter [ 50 ]. In his study, Schumpeter points out that the banking system is the crucial factor for economic growth due to its role in the allocation of savings, the encouragement of innovation, and the funding of productive investments. Early works, such as Goldsmith [ 18 ], McKinnon [ 39 ] and Shaw [ 51 ] put forward considerable evidence that financial development enhances growth performance of countries. The importance of financial development in BRICS economies is reflected by the establishment of the ‘New Development Bank’ aimed at financing infrastructure and sustainable development projects in these and other developing countries. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no attempt has been made so far to investigate the long-run relationship Footnote 1 between tourism, financial development and economic growth in case of BRICS countries. Hence, the present study is an attempt to fill the gap in the existing literature.
Review of past studies
From last few decades there has been a surge in the research related to tourism-growth nexus. The importance of growth and development and its determinants has been studied extensively both in developed and developing countries. Extant literature has recognized tourism as an important determinant of economic growth. The importance of tourism has grown exponentially, courtesy to its manifold advantages in form of employment, foreign exchange production household income and government revenues through multiplier effects, improvements in the balance of payments and growth in the number of tourism-promoted government policies [ 21 , 41 , 53 ]. Empirical findings on tourism and economic development have produced mixed finding and sometimes conflicting results despite the common choice of time series techniques as a research methodology. On empirical grounds, four hypotheses have been explored to determine the link between tourism and economic growth [ 12 ]. The first two hypotheses present an account on the unidirectional causality between the two variables, either from tourism to economic growth (Tourism-led economic growth hypothesis-TLGH) or its reserve (economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis-EDTH). The other two hypotheses support the existence of bi-directional hypothesis, (bi-directional causality hypothesis-BC) or that there is no relationship at all (no causality hypothesis-NC), respectively. According to TLEG hypothesis, tourism creates an array of benefits which spillover though multiple routes to promote the economic growth [ 55 ]. In particular, it is believed that tourism (1) increases foreign exchange earnings, which in turn can be used to finance imports [ 38 ], (2) it encourages investment and drives local firms toward greater efficiency due to the increased competition [ 3 , 31 ], (3) it alleviates unemployment, since tourism activities are heavily based on human capital [ 10 ] and (4) it leads to positive economies of scale thus, decreasing production costs for local businesses [ 1 , 14 ]. Other recent studies which find evidence in favor of the TLGH hypothesis include [ 44 , 52 ]. Even though literature is dominated by TLGH, few studies produce a result in support of EDTH [ 40 , 41 , 45 ]. Payne and Mervar [ 45 ] posit that tourism growth of a country is mobilized by the stability of well-designed economic policies, governance structures and investments in both physical and human capital. This positive and vibrant environment creates a series of development activities which proliferate and flourish the tourism. Pertaining to the readily available information, bi-directional causality could also exist between tourism income and economic growth [ 34 , 49 ]. From a policy view, a reciprocal tourism–economic growth relationship implies that government agendas should cater for promoting both areas simultaneously. Finally, there are some studies that do not offer support to any of the aforementioned hypotheses, suggesting that the impact between tourism and economic growth is insignificant [ 25 , 47 , 57 ]. There is a vast literature examining the relationship between tourism and growth as a result, only a selective literature review will be presented here.
Banday and Ismail [ 5 ] used ARDL cointegration model to test the relationship between tourism revenue and economic growth in BRICS countries from the time period of (1995–2013). The study validates the tourism-led growth hypothesis for BRICS countries, which evinces that tourism has positive influence on economic growth.
Savaş et al. [ 54 ] evaluated the tourism-led growth hypothesis in the context of Turkey. The study employed gross domestic product, real exchange rate, real total expenditure and international tourism arrivals to sketch out the causality among variables. The result reveals a unidirectional relationship between tourism and real exchange rate. The findings suggest that tourism is the driving force for economic growth, which in turn helps turkey to culminate its current account deficit.
Dhungel [ 15 ] made an effort to investigate causality between tourism and economic growth, In Nepal for the period of (1974–2012), by using Johansen’s cointegration and Error correction model. The result states that unidirectional causality exists in the long run, while in short run no causality exists between two constructs. The study emphasized that strategies should be devised to attain causality running from tourism to economic growth.
Mallick et al. [ 36 ] analyzed the nexus between economic growth and tourism in 23 Indian states over a period of 14 years (1997–2011). Using panel autoregressive distributed lag model based on three alternative estimators such as mean group estimator, pooled mean group and dynamic fixed effects, Research found that tourism exerts positive influence on economic growth in the long run.
Belloumi [ 8 ] examines the causal relationship between international tourism receipts and economic growth in Tunisia by using annual time series data for the period 1970–2007. The study uses the Johansen’s cointegration methodology to analyze the long-run relationship among the concerned variables. Granger causality based Vector error correction mechanism approach indicates that the revenues generated from tourism have a positive impact on economic growth of Tunisia. Thus, the study supports the hypothesis of tourism-driven economic growth, which is specific to developing countries that base their foreign exchange earnings on the existence of a comparative advantage in certain sectors of the economy.
Tang et al. [ 58 ] explored the dynamic Inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India for the period 1971–2012. The study employed Bounds testing approach to cointegration and generalized variance decomposition methods to analyze the relationship. The bounds testing and the Gregory-Hansen test for cointegration with structural breaks consistently reveals that energy consumption, tourism and economic growth in India are cointegrated. The study demonstrated that tourism and economic growth have positive impact on energy consumption, while tourism and economic growth are interrelated; with tourism exert significant influence on economic growth. Consequently, this study validates the tourism-led growth hypothesis in the Indian context.
Kadir and Karim [ 24 ]) examined the causal nexus between tourism and economic growth in Malaysia by applying panel time series approach for the period 1998–2005. By applying Padroni’s panel cointegration test and panel Granger causality test, the result indicated both short and long-run relationship. Further, the panel causality shows unidirectional causality directing from tourism receipts to economic growth. The result provides evidence of the significant contribution of tourism industry to Malaysia’s economic growth, thereby justifying the necessity of public intervention in providing tourism infrastructure and facilities.
Antonakakis et al. [ 2 ] test the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe by using a newly introduced spillover index approach. Based on monthly data for 10 European countries over the period 1995–2012, the findings suggested that the tourism–economic growth relationship is not stable over time in terms of both magnitude and direction, indicating that the tourism-led economic growth (TLEG) and the economic-driven tourism growth (EDTG) hypotheses are time-dependent. Thus, the findings of the study suggest that the same country can experience tourism-led economic growth or economic-driven tourism growth at different economic events.
Oh [ 41 ] verifies the contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy by applying Engle and Granger two-stage approach and a bivariate Vector Autoregression model. He claimed that economic expansion lures tourists in the short run only, while there is no such long-run stable relationship between international tourism and economic development in Korea.
Empirical studies have pronouncedly focused on the literature that tourism promotes economic growth. To further substantiate the nexus, the study will investigate the plausible linkages between economic growth and international tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. The inclusion of financial development in the examination of tourism-growth nexus is a unique feature of this study, which have an influencing role in economic growth as financial development has been theoretically and empirically recognized as source of comparative advantage [ 22 ].
This study employs panel ARDL cointegration approach to verify the existence of long-run association among the variables. Further, study estimated the long-run and short-run coefficients of the ARDL model. Subsequently, Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] panel Granger causality test has been employed to check the direction of causality between tourism, financial development and economic growth among BRICS countries.
Database and methodology
Data and variables.
The study is analytical and empirical in nature, which intends to establish the relationship between economic growth and inbound tourism in BRICS countries. For the BRICS countries, limited studies have been conducted depicting the present scenario. Therefore, present study tries to verify the relevance of tourism in economic growth to further enhance the understanding of economic dynamics in BRICS countries. The data used in the study are annual figures for the period stretching from 1995 to 2015, consisting of one endogenous variable (GDP per capita, a proxy for economic growth) and two exogenous variables (international tourism receipts per capita and financial development). The variables employed in the study are based on the economic growth theory, proposed by Balassa [ 4 ], which states that export expansion has a relevant contribution in economic growth. Further, this study incorporates financial development in the model to reduce model misspecification as it is considered to have an influencing role in economic growth both theoretically and empirically [ 22 , 33 ].
The annual data for all the variables have been collected from the World Development Indicators (WDI, 2016) database. The variables used in the study includes gross domestic product per capita (GDP) in constant ($US2010) used as a proxy for economic growth (EG), international tourism receipts per capita (TR) in current US$ as it is widely accepted that the most adequate proxy of inbound tourism in a country is tourism expenditure normally expressed in terms of tourism receipts [ 32 ] and financial development (FD). In line with a recent study on the relationship between financial development and economic growth by Hassan et al. [ 19 ], financial development is surrogated by the ratio of the broad money (M3) to real GDP for all BRICS countries. Here we use the broadest definition of money (M3) as a proportion of GDP– to measure the liquid liabilities of the banking system in the economy. We use M3 as a financial depth indicator, because monetary aggregates, such as M2 or M1, may be a poor proxy in economies with underdeveloped financial systems, because they ‘are more related to the ability of the financial system to provide transaction services than to the ability to channel funds from savers to borrowers’ [ 26 ]. A higher liquidity ratio means higher intensity in the banking system. The assumption here is that the size of the financial sector is positively associated with financial services [ 29 ]. All the variables have been taken into log form.
Unit root test
To verify the long-run relationship between tourism and economic growth through Bounds testing approach, it is necessary to test for stationarity of the variables. The stationarity of all the variables can be assessed by different unit root tests. The study utilizes panel unit root test proposed by Levin et al. [ 35 ] henceforth LLC and Im et al. [ 23 ] henceforth IPS based on traditional augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) test. The LLC allows for heterogeneity of the intercepts across members of the panel under the null hypothesis of presence of unit root, while IPS allows for heterogeneity in intercepts as well as in the slope coefficients [ 48 ].
Panel ARDL approach to Cointegration
After checking the stationarity of the variables the study employs panel ARDL technique for Cointegration developed by Pesaran et al. [ 23 ]. Pesaran et al. [ 23 ] have introduced the pooled mean group (PMG) approach in the panel ARDL framework. According to Pesaran et al. [ 23 ], the homogeneity in the long-run relationship can be attributed to several factors such as arbitration condition, common technologies, or the institutional development which was covered by all groups. The panel ARDL bounds test [ 46 ] is more appropriate by comparing other cointegration techniques, because it is flexible regarding unit root properties of variables. This technique is more suitable when variables are integrated at different orders but not I (2). Haug [ 20 ] has argued that panel ARDL approach to cointegration provides better results for small sample data set such as in our case. The ARDL approach to cointegration estimates both long and short-run parameters and can be applied independently of variable order integration (independent of whether repressors are purely I (0), purely I(1) or combination of both. The ARDL bounds test approach used in this study is specified as follows:
where Δ is the first-difference operator, \(\alpha_{0}\) stands for constant, t is time element, \(\omega_{1} , \omega_{2} \;\;{\text{and}}\;\; \omega_{3}\) represent the short-run parameters of the model, \(\emptyset_{1} , \emptyset_{2} ,and \emptyset_{3}\) are long-run coefficients, while \(V_{it}\) is white noise error term and lastly, it represents country at a particular time period. In the ARDL model, the bounds test is applied to determine whether the variables are cointegrated or not.
This test is based on the joint significance of F -statistic and the χ 2 statistic of the Wald test. The null hypothesis of no cointegration among the variables under study is examined by testing the joint significance of the F -statistic of \(\omega_{1} , \omega_{2} ,\omega_{3}\) .
In case series variables are cointegrated, an error correction mechanism (ECM) can be developed as Eq. ( 2 ), to assess the short-run influence of international tourism and financial development on economic growth.
where ECT is the error correction term, and \(\varPhi\) is its coefficient which shows how fast the variables attain long-term equilibrium if there is any deviation in the short run. The error correction term further confirms the existence of a stable long-run relationship among the variables.
Panel granger causality test
To examine the direction of causality Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] test is employed. Instead of pooled causality, Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] proposed a causality based on the individual Wald statistic of Granger non-causality averaged across the cross section units. Dumitrescu and Hurlin [ 16 ] assert that traditional test allows for homogeneous analysis across all panel sets, thereby neglecting the specific causality across different units.
This approach allows heterogeneity in coefficients across cross section panels. The two statistics Wbar-statistics and Zbar-statistics provides standardized version of the statistics and is easier to compute. Wbar-statistic, takes an average of the test statistics, while the Zbar-statistic shows a standard (asymptotic) normal distribution.
They proposed an average Wald statistic that tests the null hypothesis of no causality in a panel subgroup against an alternative hypothesis of causality in at least one panel. Following equations will be used to check the direction of causality between the variables.
Estimation, results and Discussion
Descriptive statistics.
Table 1 presents descriptive statistics of variables selected for the period 1995–2015. The variable set includes GDP, FD and TR for all BRICS countries. Brazil tops the list with GDP per capita of 4.18, while India lagging behind all BRICS nations. In the recent economic survey by International Monetary Fund (IMF report 2016), India was ranked 126 for its per capita GDP. India’s GDP per capita went up to $7170 against all other BRICS countries which were placed in the above $10,000 bracket. China has the highest tourism receipts in comparison to other BRICS countries. China is a very popular country for foreign tourists, which ranks third after France and USA. In 2014, China invested $136.8 billion into its tourist infrastructure, a figure second only to the United States ($144.3 billion). Tourism, based on direct, indirect, and induced impact, accounted for near 10% in the GDP of China (WTTC report 2017).
Stationarity results
Primarily, we employed LLC and IPS unit root test to assess the integrated properties of the series. The results of IPS and PP tests are presented in Table 2 . Panel unit root test result evinces that FD and TR are stationary at level, while GDP per capita is integrated variable of order 1. The result exemplifies that GDP per capita, Tourism receipts and Financial Development are integrated at 1(0) and 1(1). Consequently, the panel ARDL approach to cointegration can be applied.
Cointegration test results
In view of the above results with a mixture of order integration, the panel ARDL approach to cointegration is the most appropriate technique to investigate whether there exists a long-run relationship among the variables [ 42 ]. Table 3 illustrates that the estimated value of F-statistics, which is higher than the lower and upper limit of the bound value, when InEG is used as a dependent variable. Hence, we reject the null hypothesis of no cointegration \(H_{0 } : \emptyset_{1} = \emptyset_{2} = \emptyset_{3} = 0\) of Eq. ( 1 ). Therefore, the result asserts that international tourism, financial development and economic growth are significantly cointegrated over the period (1995–2015).
Subsequently, the study investigates the long-run and short-run impact of international tourism and financial development on economic growth. Lag length is selected on the principle of minimum Bayesian information criterion (SBC) value, which is 2 in our case. The long-run coefficients of financial development and tourism receipts with respect to economic growth in Table 4 indicate that tourism growth and financial development exerts positive influence on economic growth in the long run. In other words, an increase in volume of tourism receipts per capita and financial depth spurs economic growth and both the coefficients are statistically significant in case of BRICS nations in the long run. The results are interpreted in detail as below:
The elasticity coefficient of economic growth with respect to tourism shows that 1% rise in international tourism receipts per capita would imply an estimated increase of almost 0.31% domestic real income in the long run, all else remaining the same. Thus, the earnings in the form of foreign exchange from international tourism affect growth performance of BRICS nations positively. This finding of our study is in consonance with the empirical results of Kreishan for Jordan [ 30 ], Balaguer and Cantavella-Jordá [ 3 ] for Spain and Ohlan [ 43 ] for India.
Further our finding lend support to the wide applicability of the new growth theory proposed by Balassa which states that export expansion promote growth performance of nations. Thus, validates TLGH coined by Balaguer and Cantavell-Jorda [ 3 ] which states that inbound tourism acts a long-run economic growth factor. The so called tourism-led growth hypothesis suggests that the development of a country’s tourism industry will eventually lead to higher economic growth and, by extension, further economic development via spillovers and other multiplier effects.
Likewise, financial development as expected is found to be positively associated with economic growth. The coefficient of financial development states that 1% improvement in financial development will push up economic growth by 0.22% in the long run, keeping all other variables constant. The empirical results are consistent with the finding of Hassan et al. [ 19 ] for a panel of South Asian countries. Well-regulated and properly functioning financial development enhances domestic production through savings, borrowings & investment activities and boosts economic growth. Further, it promotes economic growth by increasing efficiency [ 7 ]. Levine [ 33 ] believes that financial intermediaries enhance economic efficiency, and ultimately growth, by helping allocation of capital to its best use. Modern growth theory identifies two specific channels through which the financial sector might affect long-run growth; through its impact on capital accumulation and through its impact on the rate of technological progress. The sub-prime crisis which depressed the economic growth worldwide in 2007 further substantiates the growth-financial development nexus.
In the third and final step of the bounds testing procedure, we estimate short-run dynamics of variables by estimating an error correction model associated with long-run estimates. The empirical finding indicates that the coefficient of error correction term (ECT) with one period lag is negative as well as statistically significant. This finding further substantiates the earlier cointegration results between tourism, financial development and economic growth, and indicates the speed of adjustment from the short-run toward long-run equilibrium path. The coefficient of ECT reveals that the short-run divergences in economic growth from long-run equilibrium are adjusted by 43% every year following a short-run shock.
The short-run parameters in Table 5 demonstrates that tourism and financial development acts as an engine of economic growth in the short run as well. The coefficient of both tourism receipts per capita and financial development with one period lag is also found to be progressive and significant in the short run. These results highlight the role of earnings from international tourism and financial stability as an important driving force of economic growth in BRICS nations in the short run as well.
Further, a comparison between short-run and long-run elasticity coefficients evince that long-run responsiveness of economic growth with respect to tourism and financial development is higher than that of short run. It exemplifies that over time higher international tourism receipts and well-regulated financial system in BRICS nations give more boost to economic growth.
Analysis of causality
At this stage, we investigate the causality between tourism, financial development and economic growth presented in Table 6 . The result shows bi-directional causal relationship between tourism and economic growth, thereby validates ‘feedback hypothesis’ and consequently supported both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) and its reciprocal, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis (EDTH). The bi-directional causality between inbound tourism and GDP, which directs the level of economic activity and tourism growth, mutually influences each other in that a high volume of tourism growth leads to a high level of economic development and reverse also holds true. These results replicate the findings of Banday and Ismail [ 5 ] in the context of BRICS countries, Yazdi et al. [ 27 ] for Iran and Kim et al. [ 28 ] for Taiwan. One of the channels through which tourism spurs economic growth is through the use of receipts earned in the form of foreign currency. Thus, growth in foreign earnings may allow the import of technologically advances goods that will favor economic growth and vice versa. Thus, results demonstrate that international tourism promotes growth and in turn economic expansion is necessary for tourism development in case of BRICS countries. With respect to policy context, this finding suggests that the BRICS nations should focus on economic policies to promote tourism as a potential source of economic growth which in turn will further promote tourism growth.
Similarly, in case of economic growth and financial development, the findings demonstrate the presence of bi-directional causality between two constructs. The findings validate thus both ‘demand following’ and supply leading’ hypothesis. The findings suggests that indeed financial development plays a crucial role in promoting economic activity and thus generating economic growth for these countries and reverse also holds. Our findings are in line with Pradhan [ 48 ] in case of BRICS countries and Hassan et al. [ 19 ] for low and middle-income countries. This suggests that finance development can be used as a policy variable to foster economic growth in the five BRICS countries and vice versa. The study emphasizes that the current economic policies should recognize the finance-growth nexus in BRICS in order to maintain sustainable economic development in the economy. The empirical results in this paper are in line with expectations, confirming that the emerging economies of the BRICS are benefiting from their finance sectors.
Finally, two-sided causal relationship is found between tourism receipts and financial development. That is, tourism might contribute to financial development and, in return, financial development may positively contribute to tourism. This means that financial depth and tourism in BRICS have a reinforcing interaction. The positive impact of tourism on financial development can be attributed to the fact that inflows of foreign exchange via international tourism not only increases income levels but also leads to rise in official reserves of central banks. This in turn enables central banks to adapt expansionary monetary policy. The positive contribution of financial sector to tourism is further characterized by supply leading hypothesis. Further, better financial and market conditions will attract tourism entrepreneurship, because firms will be able to use more capital instead of being forced to use leveraging [ 13 ]. Hence, any shocks in money supply could adversely affect tourism industry in these countries. Song and Lin [ 56 ] found that global financial crisis had a negative impact on both inbound and outbound tourism in Asia. This result is in consistent with Başarir and Çakir [ 6 ] for Turkey and four European countries.
Stability tests
In addition, to test the stability of parameters estimated and any structural break in the model CUSUM and CUSUMSQ tests are employed. Figs. 1 and 2 show blue line does not transcend red lines in both the tests, thus provides strong evidence that our estimated model is fit and valid policy implications can be drawn from the results.
Plot of CUSUM
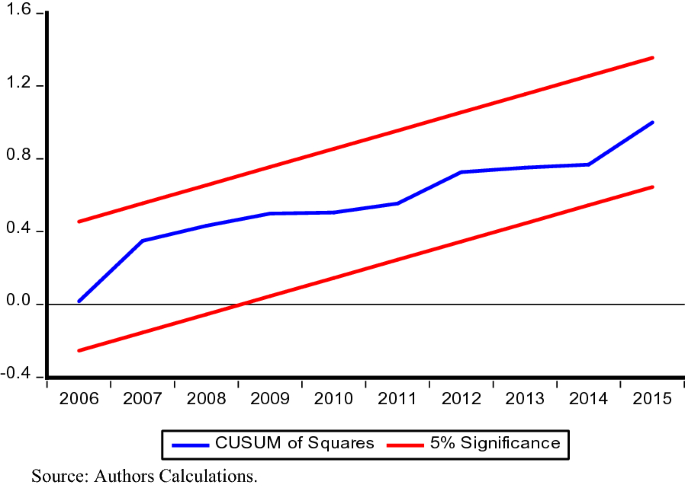
Plot of CUSUMQ
Summary and concluding remarks
A rigorous study of the relationship between tourism and economic growth, through the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) perspective has remained a debatable issue in the economic growth literature. This study aims to empirically investigate the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth in BRICS countries by utilizing the panel data over the period 1995–2015. The study employs the panel ARDL approach to cointegration and Dumitrescu-Hurlin panel Granger causality test to detect the direction of causation.
To the best of authors’ knowledge, this is the first study which explored the relationship between economic growth and tourism while considering the relative importance of financial development in the context of BRICS nations. The empirical results of ARDL model posits that in BRICS countries inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth are significantly cointegrated, i.e., variables have stable long-run relationship. This methodology has allowed obtaining elasticities of economic growth with respect to tourism and financial development both in the long run and short run. The result reveals that international tourism growth and financial development positively affects economic growth both in the long run and short run. The coefficient of tourism indicates that with a 1% rise in tourism receipts per capita, GDP per capita of BRICS economies will go up by 0.31% in the long run. This finding lends support to TLGH coined by Balaguer and Cantavell-Jorda [ 3 ] which states that inbound tourism acts a long-run economic growth factor. The so called tourism-led growth hypothesis suggests that the development of a country’s tourism industry will eventually lead to higher economic growth and, by extension, further economic development via spillovers and other multiplier effects.
Likewise, 1% improvement in financial development, on average, will increase economic growth in BRICS countries by 0.22% in the long run. The result seems logical as modern growth theory identifies two channels through which the financial sector might affect long-run growth: first, through its impact on capital accumulation and secondly, through its impact on the rate of technological progress. The sub-prime crisis which hit the economic growth Worldwide in 2007 further substantiates the growth-financial development nexus.
The negative and statistically significant coefficient of lagged error correction term (ECT) further substantiates the long-run equilibrium relationship among variables. The negative coefficient of ECT also shows the speed of adjustment toward long-run equilibrium is 43% per annum if there is any short-run deviation. The estimates of parameters are found to be stable by applying CUSUM and CUSUMQ for the time period under consideration. Therefore, inbound tourism earnings and financial institutions can be used as a channel to increase economic growth in BRICS economies.
Further, Granger causality test result indicates the bi-directional causation in all cases. Hence, the causal relationship between international tourism and economic growth is bi-directional. And, consequently this empirical finding lends support to both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH) and its reciprocal, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis (EDTH). This means that tourism is not only an engine for economic growth, but the economic outcome on itself can play an important role in providing growth potential to tourism sector.
The Granger causality findings provide useful information to governments to examine their economic policy, to adjust priorities regarding economic investment, and boost their economic growth with the given limited resources. Thus, it is suggested that more resources should be allocated to tourism industry and tourism-related industries if the tourism-led growth hypothesis holds true. On the other side, if economic-driven tourism growth is supported then more resources should be diverted to leading industries rather than the travel and tourism sector, and the tourism industry will in turn benefit from the resulting overall economic growth. And, when bi-directional causality is detected, a balanced allocation of economic resources for the travel and tourism sector and other industries is important and necessary. The policy implication is that resource allocation supporting both the tourism and tourism-related industries could benefit both tourism development and economic growth.
To sum up, the major finding of this study lends support to wide applicability of the tourism-led growth hypothesis in case of BRICS countries. Thus, in the Policy context, significant impact of tourism on BRICS economy rationalizes the need of encouraging tourism. Tourism can spur economic prosperity in these countries and for this reason; policymakers should give serious consideration toward encouraging tourism industry or inbound tourism. BRICS countries should focus more on tourism infrastructure, such as, convenient transportation, alluring destinations, suitable tax incentives, viable hostels and proper security arrangements to attract the potential tourists. Most of these countries are devoid of rich facilities and popular tourist incentives, to get promoted as important destination and in the long-run promotes economic growth. Further, they need a staunch support from all sections of authorities, non-government organizations (NGOs), and private and allied industries, in the endeavor to attain sustainable growth in tourism. Both state and non-state actors must recognize this growing industry and its positive implication on economy.
For future research, we suggest that researchers should consider the nonlinear factor in the dynamic relationship of tourism and economic growth in case of BRICS countries. Further one can go for comparative study to examine the TLGH in BRICS countries.
Availability of data and materials
Data used in the study can be provided by the corresponding author on request.
There are no fixed definitions of short, medium and long run and generally in macroeconomics, short run can be viewed as 1 to 2 or 3 years, medium up to 5 years and long run from 5 years to 20 or 25 years.
Abbreviations
autoregressive distributed lag model
Brazil, Russia, India, China and South-Africa
United Nations World Tourism Organization
World Travel & Tourism Council
gross domestic product
world development indicators
tourism-led growth hypothesis
export-led growth hypothesis
economic-driven tourism hypothesis
augmented Dickey–Fuller test
error correction model
error correction term
Andriotis K (2002) Scale of hospitality firms and local economic development—evidence from Crete. Tourism Manag 23(4):333–341
Google Scholar
Antonakakis N, Dragouni M, Filis G (2015) How strong is the linkage between tourism and economic growth in Europe? Econ Modell 44:142–155
Balaguer J, Cantavella-Jorda M (2002) Tourism as a long-run economic growth factor: the Spanish case. Appl Econ 34(7):877–884
Balassa B (1978) Exports and economic growth: further evidence. J Dev Econ 5(2):181–189
Banday UJ, Ismail S (2017) Does tourism development lead positive or negative impact on economic growth and environment in BRICS countries? A panel data analysis. Econ Bull 37(1):553–567
Basarir C, Çakir YN (2015) Causal interactions between CO 2 emissions, financial development, energy and tourism. Asian Econ Financ Rev 5(11):1227
Bell C, Rousseau PL (2001) Post-independence India: a case of finance-led industrialization? J Dev Econ 65(1):153–175
Belloumi M (2010) The relationship between tourism receipts, real effective exchange rate and economic growth in Tunisia. Int J Tour Res 12(5):550–560
Blake A, Sinclair MT, Soria JAC (2006) Tourism productivity: evidence from the United Kingdom. Ann Tourism Res 33(4):1099–1120
Brida JG, Pulina M (2010) A literature review on the tourism-led-growth hypothesis. Working paper CRENoS201017. Centre for North South Economic Research, Sardinia
Brida JG, Cortes-Jimenez I, Pulina M (2016) Has the tourism-led growth hypothesis been validated? A literature review. Curr Issues Tourism 19(5):394–430
Chatziantoniou I, Filis G, Eeckels B, Apostolakis A (2013) Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: a structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Manag 36:331–341
Chen M-H (2010) The economy, tourism growth and corporate performance in the Taiwanese hotel industry. Tourism Manag 31:665–675
Croes R (2006) A paradigm shift to a new strategy for small island economies: embracing demand side economics for value enhancement and long term economic stability. Tourism Manag 27:453–465
Dhungel KR (2015) An econometric analysis on the relationship between tourism and economic growth: empirical evidence from Nepal. Int J Econ Financ Manag 3(2):84–90
Dumitrescu EI, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Modell 29(4):1450–1460
Daniel Mminele (2016) The role of BRICS in the global economy. Speech at the Bundesbank Regional Office in North Rhine-Westphalia, Düsseldorf, Germany. https://www.bis.org/review/r160720c.pdf
Goldsmith RW (1969) Financial structure and development (No. HG174 G57)
Hassan MK, Sanchez B, Yu JS (2011) Financial development and economic growth: new evidence from panel data. Quart Rev Econ Financ 51(1):88–104
Haug AA (2002) Temporal aggregation and the power of cointegration tests: A Monte Carlo study. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 64:399–412
Henry EW, Deane B (1997) The contribution of tourism to the economy of Ireland in 1990 and 1995. Tourism Manag 18(8):535–553
Hur J, Raj M, Riyanto YE (2006) Finance and trade: a cross-country empirical analysis on the impact of financial development and asset tangibility on international trade. World Dev 34(10):1728–1741
Im KS, Pesaran MH, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econ 115(1):53–74
Kadir N, Karim MZA (2012) Tourism and economic growth in Malaysia: evidence from tourist arrivals from Asean-S countries. Econ Res Ekonomska istraživanja 25(4):1089–1100
Katircioglu S (2009) Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis: the case of Malta. Acta Oeconomica 59(3):331–343
Khan M, Senhadji A (2003) Financial development and economic growth: a review and new evidence. J Afr Econ 12:89–110
Khoshnevis Yazdi S, Homa Salehi K, Soheilzad M (2017) The relationship between tourism, foreign direct investment and economic growth: evidence from Iran. Curr Issues Tourism 20(1):15–26
Kim HJ, Chen MH (2006) Tourism expansion and economic development: the case of Taiwan. Tourism Manag 27(5):925–933
King R, Levine R (1993) Finance, entrepreneurship, and growth: theory and evidence. J Monet Econ 32:513–542
Kreishan FM (2010) Tourism and economic growth: the case of Jordan. Eur J Soc Sci 15:229–234
Krueger A (1980) Trade policy as an input to development. Am Econ Rev 70:188–292
Kumar RR (2014) Exploring the role of technology, tourism and financial development: an empirical study of Vietnam. Qual Quant 48(5):2881–2898
Levine R (1997) Financial development and economic growth: views and agenda. J Econ Lit 35(2):688–726
Lee CC, Chang CP (2008) Tourism development and economic growth: a closer look at panels. Tourism Manag 29(1):180–192
Levin A, Lin CF, Chu CSJ (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econ 108(1):1–24
Mallick L, Mallesh U, Behera J (2016) Does tourism affect economic growth in Indian states? Evidence from panel ARDL model. Theor Appl Econ 23(1):183–194
Mastny L (2001) Treading lightly: new paths for international tourism. In: Peterson JA (ed) World Watch Paper 159. World Watch Institute
McKinnon RI (1964) Foreign exchange constraints in economic development and efficient aid allocation. Econ J 74(294):388–409
McKinnon RI (1973) Money and capital in economic development. The Brookings Institution, Washington
Narayan PK (2004) Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Econ 10(4):419–433
Oh CO (2005) The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Manag 26(1):39–44
Ohlan R (2015) The impact of population density, energy consumption, economic growth and trade openness on CO 2 emissions in India. Nat Hazards 79(2):1409–1428
Ohlan R (2017) The relationship between tourism, financial development and economic growth in India. Future Bus J 3(1):9–22
Parrilla JC, Font AR, Nadal JR (2007) Tourism and long-term growth a Spanish perspective. Ann Tourism Res 34(3):709–726
Payne JE, Mervar A (2010) Research note: the tourism-growth nexus in Croatia. Tourism Econ 16(4):1089–1094
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Econ 16(3):289–326
Po WC, Huang BN (2008) Tourism development and economic growth—a nonlinear approach. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 387(22):5535–5542
Pradhan RP, Dasgupta P, Bele S (2013) Finance, development and economic growth in BRICS: a panel data analysis. J Quant Econ 11(1–2):308–322
Ridderstaat J, Oduber M, Croes R, Nijkamp P, Martens P (2014) Impacts of seasonal patterns of climate on recurrent fluctuations in tourism demand: evidence from Aruba. Tourism Manag 41:245–256
Schumpeter JA (1911) The theory of economic development: an inquiry into profits, capital, credit, interest, and the business cycle. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, p 1934
Shaw ES (1973) Financial deepening in economic development. Oxford University Press, London
Sugiyarto G, Blake A, Sinclair MT (2003) Tourism and globalization: economic impact in Indonesia. Ann Tourism Res 30(3):683–701
Szivas E, Riley M (1999) Tourism employment during economic transition. Ann Tourism Res 26(4):747–771
Savaş B, Beşkaya A, Şamiloğlu F (2010) Analyzing the impact of international tourism on economic growth in Turkey. Uluslararası Yönetim İktisat ve İşletme Dergisi 6(12):121–136
Schubert SF, Brida JG, Risso WA (2011) The impacts of international tourism demand on economic growth of small economies dependent on tourism. Tourism Manag 32(2):377–385
Song H, Lin S (2010) Impacts of the financial and economic crisis on tourism in Asia. J Travel Res 49(1):16–30
Tang CF (2013) Temporal Granger causality and the dynamics relationship between real tourism receipts, real income and real exchange rates in Malaysia. Int J Tourism Res 15(3):272–284
Tang CF, Tiwari AK, Shahbaz M (2016) Dynamic inter-relationships among tourism, economic growth and energy consumption in India. Geosyst Eng 19(4):158–169
United Nations World Tourism Report (2014) Annual report 2014
World Travel & Tourism Council (2012) Travel & Tourism Economic Impact. World, London: World Travel & Tourism Council.
World Travel and Tourism Council (2016) Global travel and tourism economic impact update August 2016
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research has received no specific funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Haroon Rasool & Md. Tarique
Department of Commerce, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Shafat Maqbool
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HR has written introduction, research methodology and results and discussion part. Review of literature and data analysis was done by SM. Conclusion was written jointly by HR and SM. MT has provided useful inputs and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Haroon Rasool .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Rasool, H., Maqbool, S. & Tarique, M. The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: a panel cointegration analysis. Futur Bus J 7 , 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00048-3
Download citation
Received : 02 August 2019
Accepted : 30 November 2020
Published : 05 January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00048-3

Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Economic growth
- Inbound tourism
- Financial development
- Cointegration
- Panel granger causality
JEL Classification
This website uses cookies.
By clicking the "Accept" button or continuing to browse our site, you agree to first-party and session-only cookies being stored on your device to enhance site navigation and analyze site performance and traffic. For more information on our use of cookies, please see our Privacy Policy .
- American Economic Review
- Tourism and Economic Development: Evidence from Mexico's Coastline
Tourism and Economic Development: Evidence from Mexico's Coastline
- Benjamin Faber
- Cecile Gaubert
- Article Information
Additional Materials
- Replication Package (87.66 KB)
- Online Appendix (711.99 KB)
- Author Disclosure Statement(s) (151.51 KB)
JEL Classification
- Z32 Tourism and Development
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Agriculture and the Environment
- Case Studies
- Chemistry and Toxicology
- Environment and Human Health
- Environmental Biology
- Environmental Economics
- Environmental Engineering
- Environmental Ethics and Philosophy
- Environmental History
- Environmental Issues and Problems
- Environmental Processes and Systems
- Environmental Sociology and Psychology
- Environments
- Framing Concepts in Environmental Science
- Management and Planning
- Policy, Governance, and Law
- Quantitative Analysis and Tools
- Sustainability and Solutions
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
The role of tourism in sustainable development.
- Robert B. Richardson Robert B. Richardson Community Sustainability, Michigan State University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780199389414.013.387
- Published online: 25 March 2021
Sustainable development is the foundational principle for enhancing human and economic development while maintaining the functional integrity of ecological and social systems that support regional economies. Tourism has played a critical role in sustainable development in many countries and regions around the world. In developing countries, tourism development has been used as an important strategy for increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, creating jobs, and improving food security. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of biological diversity, natural resources, and cultural heritage sites that attract international tourists whose local purchases generate income and support employment and economic development. Tourism has been associated with the principles of sustainable development because of its potential to support environmental protection and livelihoods. However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is multifaceted, as some types of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, many of which are borne by host communities.
The concept of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which involves the participation of large numbers of people, often in structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has been associated with economic leakage and dependence, along with negative environmental and social impacts. Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to these economic, environmental, and social impacts. Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms. Tourism has played an important role in sustainable development in some countries through the development of alternative tourism models, including ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others that aim to enhance livelihoods, increase local economic growth, and provide for environmental protection. Although these models have been given significant attention among researchers, the extent of their implementation in tourism planning initiatives has been limited, superficial, or incomplete in many contexts.
The sustainability of tourism as a global system is disputed among scholars. Tourism is dependent on travel, and nearly all forms of transportation require the use of non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels for energy. The burning of fossil fuels for transportation generates emissions of greenhouse gases that contribute to global climate change, which is fundamentally unsustainable. Tourism is also vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include the impacts of natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and civil unrest. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to global shocks include the impacts of climate change, economic crisis, global public health pandemics, oil price shocks, and acts of terrorism. It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, debatable, and potentially contradictory.
- conservation
- economic development
- environmental impacts
- sustainable development
- sustainable tourism
- tourism development
Introduction
Sustainable development is the guiding principle for advancing human and economic development while maintaining the integrity of ecosystems and social systems on which the economy depends. It is also the foundation of the leading global framework for international cooperation—the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (United Nations, 2015 ). The concept of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future (World Commission on Environment and Development [WCED], 1987 , p. 29), which defined it as “paths of human progress that meet the needs and aspirations of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.” Concerns about the environmental implications of economic development in lower income countries had been central to debates about development studies since the 1970s (Adams, 2009 ). The principles of sustainable development have come to dominate the development discourse, and the concept has become the primary development paradigm since the 1990s.
Tourism has played an increasingly important role in sustainable development since the 1990s, both globally and in particular countries and regions. For decades, tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, non-extractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ). Many developing countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development is increasingly viewed as an important tool in increasing economic growth, alleviating poverty, and improving food security. Tourism enables communities that are poor in material wealth, but rich in history and cultural heritage, to leverage their unique assets for economic development (Honey & Gilpin, 2009 ). More importantly, tourism offers an alternative to large-scale development projects, such as construction of dams, and to extractive industries such as mining and forestry, all of which contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and the cultural values of Indigenous Peoples.
Environmental quality in destination areas is inextricably linked with tourism, as visiting natural areas and sightseeing are often the primary purpose of many leisure travels. Some forms of tourism, such as ecotourism, can contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the protection of ecosystem functions in destination areas (Fennell, 2020 ; Gössling, 1999 ). Butler ( 1991 ) suggests that there is a kind of mutual dependence between tourism and the environment that should generate mutual benefits. Many developing countries are in regions that are characterized by high levels of species diversity, natural resources, and protected areas. Such ideas imply that tourism may be well aligned with the tenets of sustainable development.
However, the relationship between tourism and the environment is complex, as some forms of tourism have been associated with negative environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, freshwater use, land use, and food consumption (Butler, 1991 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ; Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Assessments of the sustainability of tourism have highlighted several themes, including (a) parks, biodiversity, and conservation; (b) pollution and climate change; (c) prosperity, economic growth, and poverty alleviation; (d) peace, security, and safety; and (e) population stabilization and reduction (Buckley, 2012 ). From a global perspective, tourism contributes to (a) changes in land cover and land use; (b) energy use, (c) biotic exchange and extinction of wild species; (d) exchange and dispersion of diseases; and (e) changes in the perception and understanding of the environment (Gössling, 2002 ).
Research on tourism and the environment spans a wide range of social and natural science disciplines, and key contributions have been disseminated across many interdisciplinary fields, including biodiversity conservation, climate science, economics, and environmental science, among others (Buckley, 2011 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Given the global significance of the tourism sector and its environmental impacts, the role of tourism in sustainable development is an important topic of research in environmental science generally and in environmental economics and management specifically. Reviews of tourism research have highlighted future research priorities for sustainable development, including the role of tourism in the designation and expansion of protected areas; improvement in environmental accounting techniques that quantify environmental impacts; and the effects of individual perceptions of responsibility in addressing climate change (Buckley, 2012 ).
Tourism is one of the world’s largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020 ). As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national economies, and it represents a large and growing share of world trade (Hunter, 1995 ). Global tourism has had an average annual increase of 6.6% over the past half century, with international tourist arrivals rising sharply from 25.2 million in 1950 to more than 950 million in 2010 . In 2019 , the number of international tourists reached 1.5 billion, up 4% from 2018 (Fennell, 2020 ; United Nations World Tourism Organization [UNWTO], 2020 ). European countries are host to more than half of international tourists, but since 1990 , growth in international arrivals has risen faster than the global average, in both the Middle East and the Asia and Pacific region (UNWTO, 2020 ).
The growth in global tourism has been accompanied by an expansion of travel markets and a diversification of tourism destinations. In 1950 , the top five travel destinations were all countries in Europe and the Americas, and these destinations held 71% of the global travel market (Fennell, 2020 ). By 2002 , these countries represented only 35%, which underscores the emergence of newly accessible travel destinations in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and the Pacific Rim, including numerous developing countries. Over the past 70 years, global tourism has grown significantly as an economic sector, and it has contributed to the economic development of dozens of nations.
Given the growth of international tourism and its emergence as one of the world’s largest export sectors, the question of its impact on economic growth for the host countries has been a topic of great interest in the tourism literature. Two hypotheses have emerged regarding the role of tourism in the economic growth process (Apergis & Payne, 2012 ). First, tourism-led growth hypothesis relies on the assumption that tourism is an engine of growth that generates spillovers and positive externalities through economic linkages that will impact the overall economy. Second, the economic-driven tourism growth hypothesis emphasizes policies oriented toward well-defined and enforceable property rights, stable political institutions, and adequate investment in both physical and human capital to facilitate the development of the tourism sector. Studies have concluded with support for both the tourism-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Durbarry, 2004 ; Katircioglu, 2010 ) and the economic-led growth hypothesis (e.g., Katircioglu, 2009 ; Oh, 2005 ), whereas other studies have found support for a bidirectional causality for tourism and economic growth (e.g., Apergis & Payne, 2012 ; Lee & Chang, 2008 ).
The growth of tourism has been marked by an increase in the competition for tourist expenditures, making it difficult for destinations to maintain their share of the international tourism market (Butler, 1991 ). Tourism development is cyclical and subject to short-term cycles and overconsumption of resources. Butler ( 1980 ) developed a tourist-area cycle of evolution that depicts the number of tourists rising sharply over time through periods of exploration, involvement, and development, before eventual consolidation and stagnation. When tourism growth exceeds the carrying capacity of the area, resource degradation can lead to the decline of tourism unless specific steps are taken to promote rejuvenation (Butler, 1980 , 1991 ).
The potential of tourism development as a tool to contribute to environmental conservation, economic growth, and poverty reduction is derived from several unique characteristics of the tourism system (UNWTO, 2002 ). First, tourism represents an opportunity for economic diversification, particularly in marginal areas with few other export options. Tourists are attracted to remote areas with high values of cultural, wildlife, and landscape assets. The cultural and natural heritage of developing countries is frequently based on such assets, and tourism represents an opportunity for income generation through the preservation of heritage values. Tourism is the only export sector where the consumer travels to the exporting country, which provides opportunities for lower-income households to become exporters through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists. Tourism is also labor intensive; it provides small-scale employment opportunities, which also helps to promote gender equity. Finally, there are numerous indirect benefits of tourism for people living in poverty, including increased market access for remote areas through the development of roads, infrastructure, and communication networks. Nevertheless, travel is highly income elastic and carbon intensive, which has significant implications for the sustainability of the tourism sector (Lenzen et al., 2018 ).
Concerns about environmental issues appeared in tourism research just as global awareness of the environmental impacts of human activities was expanding. The United Nations Conference on the Human Environment was held in Stockholm in 1972 , the same year as the publication of The Limits to Growth (Meadows et al., 1972 ), which highlighted the concerns about the implications of exponential economic and population growth in a world of finite resources. This was the same year that the famous Blue Marble photograph of Earth was taken by the crew of the Apollo 17 spacecraft (Höhler, 2015 , p. 10), and the image captured the planet cloaked in the darkness of space and became a symbol of Earth’s fragility and vulnerability. As noted by Buckley ( 2012 ), tourism researchers turned their attention to social and environmental issues around the same time (Cohen, 1978 ; Farrell & McLellan, 1987 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Young, 1973 ).
The notion of sustainable development is often associated with the publication of Our Common Future , the report of the World Commission on Environment and Development, also known as the Brundtland Commission (WCED, 1987 ). The report characterized sustainable development in terms of meeting “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (WCED, 1987 , p. 43). Four basic principles are fundamental to the concept of sustainability: (a) the idea of holistic planning and strategy making; (b) the importance of preserving essential ecological processes; (c) the need to protect both human heritage and biodiversity; and (d) the need to develop in such a way that productivity can be sustained over the long term for future generations (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ). In addition to achieving balance between economic growth and the conservation of natural resources, there should be a balance of fairness and opportunity between the nations of the world.
Although the modern concept of sustainable development emerged with the publication of Our Common Future , sustainable development has its roots in ideas about sustainable forest management that were developed in Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries (Blewitt, 2015 ; Grober, 2007 ). Sustainable forest management is concerned with the stewardship and use of forests in a way that maintains their biodiversity, productivity, and regeneration capacity as well as their potential to fulfill society’s demands for forest products and benefits. Building on these ideas, Daly ( 1990 ) offered two operational principles of sustainable development. First, sustainable development implies that harvest rates should be no greater than rates of regeneration; this concept is known as maximum sustainable yield. Second, waste emission rates should not exceed the natural assimilative capacities of the ecosystems into which the wastes are emitted. Regenerative and assimilative capacities are characterized as natural capital, and a failure to maintain these capacities is not sustainable.
Shortly after the emergence of the concept of sustainable development in academic and policy discourse, tourism researchers began referring to the notion of sustainable tourism (May, 1991 ; Nash & Butler, 1990 ), which soon became the dominant paradigm of tourism development. The concept of sustainable tourism, as with the role of tourism in sustainable development, has been interpreted in different ways, and there is a lack of consensus concerning its meaning, objectives, and indicators (Sharpley, 2000 ). Growing interest in the subject inspired the creation of a new academic journal, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , which was launched in 1993 and has become a leading tourism journal. It is described as “an international journal that publishes research on tourism and sustainable development, including economic, social, cultural and political aspects.”
The notion of sustainable tourism development emerged in contrast to mass tourism, which is characterized by the participation of large numbers of people, often provided as structured or packaged tours. Mass tourism has risen sharply in the last half century. International arrivals alone have increased by an average annual rate of more than 25% since 1950 , and many of those trips involved mass tourism activities (Fennell, 2020 ; UNWTO, 2020 ). Some examples of mass tourism include beach resorts, cruise ship tourism, gaming casinos, golf resorts, group tours, ski resorts, theme parks, and wildlife safari tourism, among others. Little data exist regarding the volume of domestic mass tourism, but nevertheless mass tourism activities dominate the global tourism sector. Mass tourism has been shown to generate benefits to host countries, such as income and employment generation, although it has also been associated with economic leakage (where revenue generated by tourism is lost to other countries’ economies) and economic dependency (where developing countries are dependent on wealthier countries for tourists, imports, and foreign investment) (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Khan, 1997 ; Peeters, 2012 ). Mass tourism has been associated with numerous negative environmental impacts and social impacts (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Ghimire, 2013 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ). Sustainable tourism development has been promoted in various ways as a framing concept in contrast to many of these economic, environmental, and social impacts.
Much of the early research on sustainable tourism focused on defining the concept, which has been the subject of vigorous debate (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Inskeep, 1991 ; Liu, 2003 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). Early definitions of sustainable tourism development seemed to fall in one of two categories (Sharpley, 2000 ). First, the “tourism-centric” paradigm of sustainable tourism development focuses on sustaining tourism as an economic activity (Hunter, 1995 ). Second, alternative paradigms have situated sustainable tourism in the context of wider sustainable development policies (Butler, 1991 ). One of the most comprehensive definitions of sustainable tourism echoes some of the language of the Brundtland Commission’s definition of sustainable development (WCED, 1987 ), emphasizing opportunities for the future while also integrating social and environmental concerns:
Sustainable tourism can be thought of as meeting the needs of present tourists and host regions while protecting and enhancing opportunity for the future. Sustainable tourism development is envisaged as leading to management of all resources in such a way that we can fulfill economic, social and aesthetic needs while maintaining cultural integrity, essential ecological processes, biological diversity and life support systems. (Inskeep, 1991 , p. 461)
Hunter argued that over the short and long terms, sustainable tourism development should
“meet the needs and wants of the local host community in terms of improved living standards and quality of life;
satisfy the demands of tourists and the tourism industry, and continue to attract them in order to meet the first aim; and
safeguard the environmental resource base for tourism, encompassing natural, built and cultural components, in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.” (Hunter, 1995 , p. 156)
Numerous other definitions have been documented, and the term itself has been subject to widespread critique (Buckley, 2012 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, there have been numerous calls to move beyond debate about a definition and to consider how it may best be implemented in practice (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Liu, 2003 ). Cater ( 1993 ) identified three key criteria for sustainable tourism: (a) meeting the needs of the host population in terms of improved living standards both in the short and long terms; (b) satisfying the demands of a growing number of tourists; and (c) safeguarding the natural environment in order to achieve both of the preceding aims.
Some literature has acknowledged a vagueness of the concept of sustainable tourism, which has been used to advocate for fundamentally different strategies for tourism development that may exacerbate existing conflicts between conservation and development paradigms (Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ). Similar criticisms have been leveled at the concept of sustainable development, which has been described as an oxymoron with a wide range of meanings (Adams, 2009 ; Daly, 1990 ) and “defined in such a way as to be either morally repugnant or logically redundant” (Beckerman, 1994 , p. 192). Sharpley ( 2000 ) suggests that in the tourism literature, there has been “a consistent and fundamental failure to build a theoretical link between sustainable tourism and its parental paradigm,” sustainable development (p. 2). Hunter ( 1995 ) suggests that practical measures designed to operationalize sustainable tourism fail to address many of the critical issues that are central to the concept of sustainable development generally and may even actually counteract the fundamental requirements of sustainable development. He suggests that mainstream sustainable tourism development is concerned with protecting the immediate resource base that will sustain tourism development while ignoring concerns for the status of the wider tourism resource base, such as potential problems associated with air pollution, congestion, introduction of invasive species, and declining oil reserves. The dominant paradigm of sustainable tourism development has been described as introverted, tourism-centric, and in competition with other sectors for scarce resources (McKercher, 1993a ). Hunter ( 1995 , p. 156) proposes an alternative, “extraparochial” paradigm where sustainable tourism development is reconceptualized in terms of its contribution to overall sustainable development. Such a paradigm would reconsider the scope, scale, and sectoral context of tourism-related resource utilization issues.
“Sustainability,” “sustainable tourism,” and “sustainable development” are all well-established terms that have often been used loosely and interchangeably in the tourism literature (Liu, 2003 ). Nevertheless, the subject of sustainable tourism has been given considerable attention and has been the focus of numerous academic compilations and textbooks (Coccossis & Nijkamp, 1995 ; Hall & Lew, 1998 ; Stabler, 1997 ; Swarbrooke, 1999 ), and it calls for new approaches to sustainable tourism development (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Garrod & Fyall, 1998 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Sharpley, 2000 ). The notion of sustainable tourism has been reconceptualized in the literature by several authors who provided alternative frameworks for tourism development (Buckley, 2012 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter, 1995 ; Liu, 2003 ; McKercher, 1993b ; Sharpley, 2000 ).
Early research in sustainable tourism focused on the local environmental impacts of tourism, including energy use, water use, food consumption, and change in land use (Buckley, 2012 ; Butler, 1991 ; Gössling, 2002 ; Hunter & Green, 1995 ). Subsequent research has emphasized the global environmental impacts of tourism, such as greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity losses (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ; Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Additional research has emphasized the impacts of environmental change on tourism itself, including the impacts of climate change on tourist behavior (Gössling et al., 2012 ; Richardson & Loomis, 2004 ; Scott et al., 2012 ; Viner, 2006 ). Countries that are dependent on tourism for economic growth may be particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change (Richardson & Witkoswki, 2010 ).
The early focus on environmental issues in sustainable tourism has been broadened to include economic, social, and cultural issues as well as questions of power and equity in society (Bramwell & Lane, 1993 ; Sharpley, 2014 ), and some of these frameworks have integrated notions of social equity, prosperity, and cultural heritage values. Sustainable tourism is dependent on critical long-term considerations of the impacts; notions of equity; an appreciation of the importance of linkages (i.e., economic, social, and environmental); and the facilitation of cooperation and collaboration between different stakeholders (Elliott & Neirotti, 2008 ).
McKercher ( 1993b ) notes that tourism resources are typically part of the public domain or are intrinsically linked to the social fabric of the host community. As a result, many commonplace tourist activities such as sightseeing may be perceived as invasive by members of the host community. Many social impacts of tourism can be linked to the overuse of the resource base, increases in traffic congestion, rising land prices, urban sprawl, and changes in the social structure of host communities. Given the importance of tourist–resident interaction, sustainable tourism development depends in part on the support of the host community (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ).
Tourism planning involves the dual objectives of optimizing the well-being of local residents in host communities and minimizing the costs of tourism development (Sharpley, 2014 ). Tourism researchers have paid significant attention to examining the social impacts of tourism in general and to understanding host communities’ perceptions of tourism in particular. Studies of the social impacts of tourism development have examined the perceptions of local residents and the effects of tourism on social cohesion, traditional lifestyles, and the erosion of cultural heritage, particularly among Indigenous Peoples (Butler & Hinch, 2007 ; Deery et al., 2012 ; Mathieson & Wall, 1982 ; Sharpley, 2014 ; Whitford & Ruhanen, 2016 ).
Alternative Tourism and Sustainable Development
A wide body of published research is related to the role of tourism in sustainable development, and much of the literature involves case studies of particular types of tourism. Many such studies contrast types of alternative tourism with those of mass tourism, which has received sustained criticism for decades and is widely considered to be unsustainable (Cater, 1993 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Fennell, 2020 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Liu, 2003 ; Peeters, 2012 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ). Still, some tourism researchers have taken issue with the conclusion that mass tourism is inherently unsustainable (Sharpley, 2000 ; Weaver, 2007 ), and some have argued for developing pathways to “sustainable mass tourism” as “the desired and impending outcome for most destinations” (Weaver, 2012 , p. 1030). In integrating an ethical component to mass tourism development, Weaver ( 2014 , p. 131) suggests that the desirable outcome is “enlightened mass tourism.” Such suggestions have been contested in the literature and criticized for dubious assumptions about emergent norms of sustainability and support for growth, which are widely seen as contradictory (Peeters, 2012 ; Wheeller, 2007 ).
Models of responsible or alternative tourism development include ecotourism, community-based tourism, pro-poor tourism, slow tourism, green tourism, and heritage tourism, among others. Most models of alternative tourism development emphasize themes that aim to counteract the perceived negative impacts of conventional or mass tourism. As such, the objectives of these models of tourism development tend to focus on minimizing environmental impacts, supporting biodiversity conservation, empowering local communities, alleviating poverty, and engendering pleasant relationships between tourists and residents.
Approaches to alternative tourism development tend to overlap with themes of responsible tourism, and the two terms are frequently used interchangeably. Responsible tourism has been characterized in terms of numerous elements, including
ensuring that communities are involved in and benefit from tourism;
respecting local, natural, and cultural environments;
involving the local community in planning and decision-making;
using local resources sustainably;
behaving in ways that are sensitive to the host culture;
maintaining and encouraging natural, economic, and cultural diversity; and
assessing environmental, social, and economic impacts as a prerequisite to tourism development (Spenceley, 2012 ).
Hetzer ( 1965 ) identified four fundamental principles or perquisites for a more responsible form of tourism: (a) minimum environmental impact; (b) minimum impact on and maximum respect for host cultures; (c) maximum economic benefits to the host country; and (d) maximum leisure satisfaction to participating tourists.
The history of ecotourism is closely connected with the emergence of sustainable development, as it was born out of a concern for the conservation of biodiversity. Ecotourism is a form of tourism that aims to minimize local environmental impacts while bringing benefits to protected areas and the people living around those lands (Honey, 2008 ). Ecotourism represents a small segment of nature-based tourism, which is understood as tourism based on the natural attractions of an area, such as scenic areas and wildlife (Gössling, 1999 ). The ecotourism movement gained momentum in the 1990s, primarily in developing countries in Latin America and sub-Saharan Africa, and nearly all countries are now engaged in some form of ecotourism. In some communities, ecotourism is the primary economic activity and source of income and economic development.
The term “ecotourism” was coined by Hector Ceballos-Lascuráin and defined by him as “tourism that consists in travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring, and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 13). In discussing ecotourism resources, he also made reference to “any existing cultural manifestations (both past and present) found in these areas” (Ceballos-Lascuráin, 1987 , p. 14). The basic precepts of ecotourism had been discussed long before the actual use of the term. Twenty years earlier, Hetzer ( 1965 ) referred to a form of tourism “based principally upon natural and archaeological resources such as caves, fossil sites (and) archaeological sites.” Thus, both natural resources and cultural resources were integrated into ecotourism frameworks from the earliest manifestations.
Costa Rica is well known for having successfully integrated ecotourism in its overall strategy for sustainable development, and numerous case studies of ecotourism in Costa Rica appear in the literature (Chase et al., 1998 ; Fennell & Eagles, 1990 ; Gray & Campbell, 2007 ; Hearne & Salinas, 2002 ). Ecotourism in Costa Rica has been seen as having supported the economic development of the country while promoting biodiversity conservation in its extensive network of protected areas. Chase et al. ( 1998 ) estimated the demand for ecotourism in a study of differential pricing of entrance fees at national parks in Costa Rica. The authors estimated elasticities associated with the own-price, cross-price, and income variables and found that the elasticities of demand were significantly different between three different national park sites. The results reveal the heterogeneity characterizing tourist behavior and park attractions and amenities. Hearne and Salinas ( 2002 ) used choice experiments to examine the preferences of domestic and foreign tourists in Costa Rica in an ecotourism site. Both sets of tourists demonstrated a preference for improved infrastructure, more information, and lower entrance fees. Foreign tourists demonstrated relatively stronger preferences for the inclusion of restrictions in the access to some trails.
Ecotourism has also been studied extensively in Kenya (Southgate, 2006 ), Malaysia (Lian Chan & Baum, 2007 ), Nepal (Baral et al., 2008 ), Peru (Stronza, 2007 ), and Taiwan (Lai & Nepal, 2006 ), among many other countries. Numerous case studies have demonstrated the potential for ecotourism to contribute to sustainable development by providing support for biodiversity conservation, local livelihoods, and regional development.
Community-Based Tourism
Community-based tourism (CBT) is a model of tourism development that emphasizes the development of local communities and allows for local residents to have substantial control over its development and management, and a major proportion of the benefits remain within the community. CBT emerged during the 1970s as a response to the negative impacts of the international mass tourism development model (Cater, 1993 ; Hall & Lew, 2009 ; Turner & Ash, 1975 ; Zapata et al., 2011 ).
Community-based tourism has been examined for its potential to contribute to poverty reduction. In a study of the viability of the CBT model to support socioeconomic development and poverty alleviation in Nicaragua, tourism was perceived by participants in the study to have an impact on employment creation in their communities (Zapata et al., 2011 ). Tourism was seen to have had positive impacts on strengthening local knowledge and skills, particularly on the integration of women to new roles in the labor market. One of the main perceived gains regarding the environment was the process of raising awareness regarding the conservation of natural resources. The small scale of CBT operations and low capacity to accommodate visitors was seen as a limitation of the model.
Spenceley ( 2012 ) compiled case studies of community-based tourism in countries in southern Africa, including Botswana, Madagascar, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. In this volume, authors characterize community-based and nature-based tourism development projects in the region and demonstrate how community participation in planning and decision-making has generated benefits for local residents and supported conservation initiatives. They contend that responsible tourism practices are of particular importance in the region because of the rich biological diversity, abundant charismatic wildlife, and the critical need for local economic development and livelihood strategies.
In Kenya, CBT enterprises were not perceived to have made a significant impact on poverty reduction at an individual household level, in part because the model relied heavily on donor funding, reinforcing dependency and poverty (Manyara & Jones, 2007 ). The study identified several critical success factors for CBT enterprises, namely, awareness and sensitization, community empowerment, effective leadership, and community capacity building, which can inform appropriate tourism policy formulation in Kenya. The impacts of CBT on economic development and poverty reduction would be greatly enhanced if tourism initiatives were able to emphasize independence, address local community priorities, enhance community empowerment and transparency, discourage elitism, promote effective community leadership, and develop community capacity to operate their own enterprises more efficiently.
Pro-Poor Tourism
Pro-poor tourism is a model of tourism development that brings net benefits to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ; Harrison, 2008 ). Although its theoretical foundations and development objectives overlap to some degree with those of community-based tourism and other models of AT, the key distinctive feature of pro-poor tourism is that it places poor people and poverty at the top of the agenda. By focusing on a very simple and incontrovertibly moral idea, namely, the net benefits of tourism to impoverished people, the concept has broad appeal to donors and international aid agencies. Harnessing the economic benefits of tourism for pro-poor growth means capitalizing on the advantages while reducing negative impacts to people living in poverty (Ashley et al., 2001 ). Pro-poor approaches to tourism development include increasing access of impoverished people to economic benefits; addressing negative social and environmental impacts associated with tourism; and focusing on policies, processes, and partnerships that seek to remove barriers to participation by people living in poverty. At the local level, pro-poor tourism can play a very significant role in livelihood security and poverty reduction (Ashley & Roe, 2002 ).
Rogerson ( 2011 ) argues that the growth of pro-poor tourism initiatives in South Africa suggests that the country has become a laboratory for the testing and evolution of new approaches toward sustainable development planning that potentially will have relevance for other countries in the developing world. A study of pro-poor tourism development initiatives in Laos identified a number of favorable conditions for pro-poor tourism development, including the fact that local people are open to tourism and motivated to participate (Suntikul et al., 2009 ). The authors also noted a lack of development in the linkages that could optimize the fulfilment of the pro-poor agenda, such as training or facilitation of local people’s participation in pro-poor tourism development at the grassroots level.
Critics of the model have argued that pro-poor tourism is based on an acceptance of the status quo of existing capitalism, that it is morally indiscriminate and theoretically imprecise, and that its practitioners are academically and commercially marginal (Harrison, 2008 ). As Chok et al. ( 2007 ) indicate, the focus “on poor people in the South reflects a strong anthropocentric view . . . and . . . environmental benefits are secondary to poor peoples’” benefits (p. 153).
Harrison ( 2008 ) argues that pro-poor tourism is not a distinctive approach to tourism as a development tool and that it may be easier to discuss what pro-poor tourism is not than what it is. He concludes that it is neither anticapitalist nor inconsistent with mainstream tourism on which it relies; it is neither a theory nor a model and is not a niche form of tourism. Further, he argues that it has no distinctive method and is not only about people living in poverty.
Slow Tourism
The concept of slow tourism has emerged as a model of sustainable tourism development, and as such, it lacks an exact definition. The concept of slow tourism traces its origin back to some institutionalized social movements such as “slow food” and “slow cities” that began in Italy in the 1990s and spread rapidly around the world (Fullagar et al., 2012 ; Oh et al., 2016 , p. 205). Advocates of slow tourism tend to emphasize slowness in terms of speed, mobility, and modes of transportation that generate less environmental pollution. They propose niche marketing for alternative forms of tourism that focus on quality upgrading rather than merely increasing the quantity of visitors via the established mass-tourism infrastructure (Conway & Timms, 2010 ).
In the context of the Caribbean region, slow tourism has been promoted as more culturally sensitive and authentic, as compared to the dominant mass tourism development model that is based on all-inclusive beach resorts dependent on foreign investment (Conway & Timms, 2010 ). Recognizing its value as an alternative marketing strategy, Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) make the case for rebranding alternative tourism in the Caribbean as a means of revitalizing the sector for the changing demands of tourists in the 21st century . They suggest that slow tourism is the antithesis of mass tourism, which “relies on increasing the quantity of tourists who move through the system with little regard to either the quality of the tourists’ experience or the benefits that accrue to the localities the tourist visits” (Conway & Timms, 2010 , p. 332). The authors draw on cases from Barbados, the Grenadines, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago to characterize models of slow tourism development in remote fishing villages and communities near nature preserves and sea turtle nesting sites.
Although there is a growing interest in the concept of slow tourism in the literature, there seems to be little agreement about the exact nature of slow tourism and whether it is a niche form of special interest tourism or whether it represents a more fundamental potential shift across the industry. Conway and Timms ( 2010 ) focus on the destination, advocating for slow tourism in terms of a promotional identity for an industry in need of rebranding. Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 77) discusses the implementation of slow tourism in terms of “encouraging visitors to make slower choices when planning and enjoying their holidays.” It is not clear whether slow tourism is a marketing strategy, a mindset, or a social movement, but the literature on slow tourism nearly always equates the term with sustainable tourism (Caffyn, 2012 ; Conway & Timms, 2010 ; Oh et al., 2016 ). Caffyn ( 2012 , p. 80) suggests that slow tourism could offer a “win–win,” which she describes as “a more sustainable form of tourism; keeping more of the economic benefits within the local community and destination; and delivering a more meaningful and satisfying experience.” Research on slow tourism is nascent, and thus the contribution of slow tourism to sustainable development is not well understood.
Impacts of Tourism Development
The role of tourism in sustainable development can be examined through an understanding of the economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism. Tourism is a global phenomenon that involves travel, recreation, the consumption of food, overnight accommodations, entertainment, sightseeing, and other activities that simultaneously intersect the lives of local residents, businesses, and communities. The impacts of tourism involve benefits and costs to all groups, and some of these impacts cannot easily be measured. Nevertheless, they have been studied extensively in the literature, which provides some context for how these benefits and costs are distributed.
Economic Impacts of Tourism
The travel and tourism sector is one of the largest components of the global economy, and global tourism has increased exponentially since the end of the Second World War (UNWTO, 2020 ). The direct, indirect, and induced economic impact of global travel accounted for 8.9 trillion U.S. dollars in contribution to the global gross domestic product (GDP), or 10.3% of global GDP. The global travel and tourism sector supports approximately 330 million jobs, or 1 in 10 jobs around the world. From an economic perspective, tourism plays a significant role in sustainable development. In many developing countries, tourism has the potential to play a unique role in income generation and distribution relative to many other industries, in part because of its high multiplier effect and consumption of local goods and services. However, research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been fully realized (Liu, 2003 ).
Numerous studies have examined the impact of tourism expenditure on GDP, income, employment, and public sector revenue. Narayan ( 2004 ) used a computable general equilibrium model to estimate the economic impact of tourism growth on the economy of Fiji. Tourism is Fiji’s largest industry, with average annual growth of 10–12%; and as a middle-income country, tourism is critical to Fiji’s economic development. The findings indicate that an increase in tourism expenditures was associated with an increase in GDP, an improvement in the country’s balance of payments, and an increase in real consumption and national welfare. Evidence suggests that the benefits of tourism expansion outweigh any export effects caused by an appreciation of the exchange rate and an increase in domestic prices and wages.
Seetanah ( 2011 ) examined the potential contribution of tourism to economic growth and development using panel data of 19 island economies around the world from 1990 to 2007 and revealed that tourism development is an important factor in explaining economic performance in the selected island economies. The results have policy implications for improving economic growth by harnessing the contribution of the tourism sector. Pratt ( 2015 ) modeled the economic impact of tourism for seven small island developing states in the Pacific, the Caribbean, and the Indian Ocean. In most states, the transportation sector was found to have above-average linkages to other sectors of the economy. The results revealed some advantages of economies of scale for maximizing the economic contribution of tourism.
Apergis and Payne ( 2012 ) examined the causal relationship between tourism and economic growth for a panel of nine Caribbean countries. The panel of Caribbean countries includes Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, and Trinidad and Tobago. The authors use a panel error correction model to reveal bidirectional causality between tourism and economic growth in both the short run and the long run. The presence of bidirectional causality reiterates the importance of the tourism sector in the generation of foreign exchange income and in financing the production of goods and services within these countries. Likewise, stable political institutions and adequate government policies to ensure the appropriate investment in physical and human capital will enhance economic growth. In turn, stable economic growth will provide the resources needed to develop the tourism infrastructure for the success of the countries’ tourism sector. Thus, policy makers should be cognizant of the interdependent relationship between tourism and economic growth in the design and implementation of economic policy. The mixed nature of these results suggest that the relationship between tourism and economic growth depends largely on the social and economic context as well as the role of tourism in the economy.
The economic benefits and costs of tourism are frequently distributed unevenly. An analysis of the impact of wildlife conservation policies in Zambia on household welfare found that households located near national parks earn higher levels of income from wage employment and self-employment than other rural households in the country, but they were also more likely to suffer crop losses related to wildlife conflicts (Richardson et al., 2012 ). The findings suggest that tourism development and wildlife conservation can contribute to pro-poor development, but they may be sustainable only if human–wildlife conflicts are minimized or compensated.
Environmental Impacts of Tourism
The environmental impacts of tourism are significant, ranging from local effects to contributions to global environmental change (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Tourism is both dependent on water resources and a factor in global and local freshwater use. Tourists consume water for drinking, when showering and using the toilet, when participating in activities such as winter ski tourism (i.e., snowmaking), and when using swimming pools and spas. Fresh water is also needed to maintain hotel gardens and golf courses, and water use is embedded in tourism infrastructure development (e.g., accommodations, laundry, dining) and in food and fuel production. Direct water consumption in tourism is estimated to be approximately 350 liters (L) per guest night for accommodation; when indirect water use from food, energy, and transport are considered, total water use in tourism is estimated to be approximately 6,575 L per guest night, or 27,800 L per person per trip (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). In addition, tourism contributes to the pollution of oceans as well as lakes, rivers, and other freshwater systems (Gössling, 2002 ; Gössling et al., 2011 ).
The clearing and conversion of land is central for tourism development, and in many cases, the land used for tourism includes roads, airports, railways, accommodations, trails, pedestrian walks, shopping areas, parking areas, campgrounds, vacation homes, golf courses, marinas, ski resorts, and indirect land use for food production, disposal of solid wastes, and the treatment of wastewater (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). Global land use for accommodation is estimated to be approximately 42 m 2 per bed. Total global land use for tourism is estimated to be nearly 62,000 km 2 , or 11.7 m 2 per tourist; more than half of this estimate is represented by land use for traffic infrastructure.
Tourism and hospitality have direct and indirect links to nearly all aspects of food production, preparation, and consumption because of the quantities of food consumed in tourism contexts (Gössling et al., 2011 ). Food production has significant implications for sustainable development, given the growing global demand for food. The implications include land conversion, losses to biodiversity, changes in nutrient cycling, and contributions to greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change (Vitousek et al., 1997 ). Global food use for tourism is estimated to be approximately 39.4 megatons 1 (Mt), about 38% than the amount of food consumed at home. This equates to approximately 1,800 grams (g) of food consumed per tourist per day.
Although tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, (Gössling, 2000 ), assessments reveal that such pursuits have a significant carbon footprint, as tourism is significantly more carbon intensive than other potential areas of economic development (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). Tourism is dependent on energy, and virtually all energy use in the tourism sector is derived from fossil fuels, which contribute to global greenhouse emissions that are associated with global climate change. Energy use for tourism has been estimated to be approximately 3,575 megajoules 2 (MJ) per trip, including energy for travel and accommodations (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). A previous estimate of global carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emissions from tourism provided values of 1.12 gigatons 3 (Gt) of CO 2 , amounting to about 3% of global CO 2 -equivalent (CO 2 e) emissions (Gössling & Peeters, 2015 ). However, these analyses do not cover the supply chains underpinning tourism and do not therefore represent true carbon footprints. A more complete analysis of the emissions from energy consumption necessary to sustain the tourism sector would include food and beverages, infrastructure construction and maintenance, retail, and financial services. Between 2009 and 2013 , tourism’s global carbon footprint is estimated to have increased from 3.9 to 4.5 GtCO 2 e, four times more than previously estimated, accounting for about 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions (Lenzen et al., 2018 ). The majority of this footprint is exerted by and within high-income countries. The rising global demand for tourism is outstripping efforts at decarbonization of tourism operations and as a result is accelerating global carbon emissions.
Social Impacts of Tourism
The social impacts of tourism have been widely studied, with an emphasis on residents’ perceptions in the host community (Sharpley, 2014 ). Case studies include research conducted in Australia (Faulkner & Tideswell, 1997 ; Gursoy et al., 2010 ; Tovar & Lockwood, 2008 ), Belize (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ), China (Gu & Ryan, 2008 ), Fiji (King et al., 1993 ), Greece (Haralambopoulos & Pizam, 1996 ; Tsartas, 1992 ), Hungary (Rátz, 2000 ), Thailand (Huttasin, 2008 ), Turkey (Kuvan & Akan, 2005 ), the United Kingdom (Brunt & Courtney, 1999 ; Haley et al., 2005 ), and the United States (Andereck et al., 2005 ; Milman & Pizam, 1988 ), among others. The social impacts of tourism are difficult to measure, and most published studies are mainly concerned with the social impacts on the host communities rather than the impacts on the tourists themselves.
Studies of residents’ perceptions of tourism are typically conducted using household surveys. In most cases, residents recognize the economic dependence on tourism for income, and there is substantial evidence to suggest that working in or owning a business in tourism or a related industry is associated with more positive perceptions of tourism (Andereck et al., 2007 ). The perceived nature of negative effects is complex and often conveys a dislike of crowding, traffic congestion, and higher prices for basic needs (Deery et al., 2012 ). When the number of tourists far exceeds that of the resident population, negative attitudes toward tourism may manifest (Diedrich & Garcia-Buades, 2008 ). However, residents who recognize negative impacts may not necessarily oppose tourism development (King et al., 1993 ).
In some regions, little is known about the social and cultural impacts of tourism despite its dominance as an economic sector. Tourism is a rapidly growing sector in Cuba, and it is projected to grow at rates that exceed the average projected growth rates for the Caribbean and the world overall (Salinas et al., 2018 ). Still, even though there has been rapid tourism development in Cuba, there has been little research related to the environmental and sociocultural impacts of this tourism growth (Rutty & Richardson, 2019 ).
In some international tourism contexts, studies have found that residents are generally resentful toward tourism because it fuels inequality and exacerbates racist attitudes and discrimination (Cabezas, 2004 ; Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Mbaiwa, 2005 ). Other studies revealed similar narratives and recorded statements of exclusion and socioeconomic stratification (Sanchez & Adams, 2008 ). Local residents often must navigate the gaps in the racialized, gendered, and sexualized structures imposed by the global tourism industry and host-country governments (Cabezas, 2004 ).
However, during times of economic crisis, residents may develop a more permissive view as their perceptions of the costs of tourism development decrease (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018 ). This increased positive attitude is not based on an increase in the perception of positive impacts of tourism, but rather on a decrease in the perception of the negative impacts.
There is a growing body of research on Indigenous and Aboriginal tourism that emphasizes justice issues such as human rights and self-empowerment, control, and participation of traditional owners in comanagement of destinations (Jamal & Camargo, 2014 ; Ryan & Huyton, 2000 ; Whyte, 2010 ).
Sustainability of Tourism
A process or system is said to be sustainable to the extent that it is robust, resilient, and adaptive (Anderies et al., 2013 ). By most measures, the global tourism system does not meet these criteria for sustainability. Tourism is not robust in that it cannot resist threats and perturbations, such as economic shocks, public health pandemics, war, and other disruptions. Tourism is not resilient in that it does not easily recover from failures, such as natural disasters or civil unrest. Furthermore, tourism is not adaptive in that it is often unable to change in response to external conditions. One example that underscores the failure to meet all three criteria is the dependence of tourism on fossil fuels for transportation and energy, which are key inputs for tourism development. This dependence itself is not sustainable (Wheeller, 2007 ), and thus the sustainability of tourism is questionable.
Liu ( 2003 ) notes that research related to the role of tourism in sustainable development has emphasized supply-side concepts such as sustaining tourism resources and ignored the demand side, which is particularly vulnerable to social and economic shocks. Tourism is vulnerable to both localized and global shocks. Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to localized shocks include disaster vulnerability in coastal Thailand (Calgaro & Lloyd, 2008 ), bushfires in northeast Victoria in Australia (Cioccio & Michael, 2007 ), forest fires in British Columbia, Canada (Hystad & Keller, 2008 ); and outbreak of foot and mouth disease in the United Kingdom (Miller & Ritchie, 2003 ).
Like most other economic sectors, tourism is vulnerable to the impacts of earthquakes, particularly in areas where tourism infrastructure may not be resilient to such shocks. Numerous studies have examined the impacts of earthquake events on tourism, including studies of the aftermath of the 1997 earthquake in central Italy (Mazzocchi & Montini, 2001 ), the 1999 earthquake in Taiwan (Huan et al., 2004 ; Huang & Min, 2002 ), and the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in western Sichuan, China (Yang et al., 2011 ), among others.
Tourism is vulnerable to extreme weather events. Regional economic strength has been found to be associated with lower vulnerability to natural disasters. Kim and Marcoullier ( 2015 ) examined the vulnerability and resilience of 10 tourism-based regional economies that included U.S. national parks or protected seashores situated on the Gulf of Mexico or Atlantic Ocean coastline that were affected by several hurricanes over a 26-year period. Regions with stronger economic characteristics prior to natural disasters were found to have lower disaster losses than regions with weaker economies.
Tourism is extremely sensitive to oil spills, whatever their origin, and the volume of oil released need not be large to generate significant economic losses (Cirer-Costa, 2015 ). Studies of the vulnerability of tourism to the localized shock of an oil spill include research on the impacts of oil spills in Alaska (Coddington, 2015 ), Brazil (Ribeiro et al., 2020 ), Spain (Castanedo et al., 2009 ), affected regions in the United States along the Gulf of Mexico (Pennington-Gray et al., 2011 ; Ritchie et al., 2013 ), and the Republic of Korea (Cheong, 2012 ), among others. Future research on the vulnerability of tourist destinations to oil spills should also incorporate freshwater environments, such as lakes, rivers, and streams, where the rupture of oil pipelines is more frequent.
Significant attention has been paid to assessing the vulnerability of tourist destinations to acts of terrorism and the impacts of terrorist attacks on regional tourist economies (Liu & Pratt, 2017 ). Such studies include analyses of the impacts of terrorist attacks on three European countries, Greece, Italy, and Austria (Enders et al., 1992 ); the impact of the 2001 terrorist attacks on the United States (Goodrich, 2002 ); terrorism and tourism in Nepal (Bhattarai et al., 2005 ); vulnerability of tourism livelihoods in Bali (Baker & Coulter, 2007 ); the impact of terrorism on tourist preferences for destinations in the Mediterranean and the Canary Islands (Arana & León, 2008 ); the 2011 massacres in Olso and Utøya, Norway (Wolff & Larsen, 2014 ); terrorism and political violence in Tunisia (Lanouar & Goaied, 2019 ); and the impact of terrorism on European tourism (Corbet et al., 2019 ), among others. Pizam and Fleischer ( 2002 ) studied the impact of acts of terrorism on tourism demand in Israel between May 1991 and May 2001 , and they confirmed that the frequency of acts of terrorism had caused a larger decline in international tourist arrivals than the severity of these acts. Most of these are ex post studies, and future assessments of the underlying conditions of destinations could reveal a deeper understanding of the vulnerability of tourism to terrorism.
Tourism is vulnerable to economic crisis, both local economic shocks (Okumus & Karamustafa, 2005 ; Stylidis & Terzidou, 2014 ) and global economic crisis (Papatheodorou et al., 2010 ; Smeral, 2010 ). Okumus and Karamustafa ( 2005 ) evaluated the impact of the February 2001 economic crisis in Turkey on tourism, and they found that the tourism industry was poorly prepared for the economic crisis despite having suffered previous impacts related to the Gulf War in the early 1990s, terrorism in Turkey in the 1990s, the civil war in former Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, an internal economic crisis in 1994 , and two earthquakes in the northwest region of Turkey in 1999 . In a study of the attitudes and perceptions of citizens of Greece, Stylidis and Terzidou ( 2014 ) found that economic crisis is associated with increased support for tourism development, particularly out of self-interest. Economic crisis diminishes residents’ concern for environmental issues. In a study of the behavior of European tourists amid an economic crisis, Eugenio-Martin and Campos-Soria ( 2014 ) found that the probability of households cutting back on travel expenditures depends largely on the climate and economic conditions of tourists’ home countries, and households that do reduce travel spending engage in tourism closer to home.
Becken and Lennox ( 2012 ) studied the implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism in New Zealand, and they estimate that a doubling of oil prices is associated with a 1.7% decrease in real gross national disposable income and a 9% reduction in the real value of tourism exports. Chatziantoniou et al. ( 2013 ) investigated the relationship among oil price shocks, tourism variables, and economic indicators in four European Mediterranean countries and found that aggregate demand oil price shocks generated a lagged effect on tourism-generated income and economic growth. Kisswani et al. ( 2020 ) examined the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts and the sensitive susceptibility of tourism to oil price changes using nonlinear analysis. The findings document a long-run asymmetrical effect for most countries, after incorporating the structural breaks, suggesting that governments and tourism businesses and organizations should interpret oil price fluctuations cautiously.
Finally, the sustainability of tourism has been shown to be vulnerable to the outbreak of infectious diseases, including the impact of the Ebola virus on tourism in sub-Saharan Africa (Maphanga & Henama, 2019 ; Novelli et al., 2018 ) and in the United States (Cahyanto et al., 2016 ). The literature also includes studies of the impact of swine flu on tourism demand in Brunei (Haque & Haque, 2018 ), Mexico (Monterrubio, 2010 ), and the United Kingdom (Page et al., 2012 ), among others. In addition, rapid assessments of the impacts of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 have documented severe disruptions and cessations of tourism because of unprecedented global travel restrictions and widespread restrictions on public gatherings (Gössling et al., 2020 ; Qiu et al., 2020 ; Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Hotels, airlines, cruise lines, and car rentals have all experienced a significant decrease globally because of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the shock to the industry is significant enough to warrant concerns about the long-term outlook (Sharma & Nicolau, 2020 ). Qiu et al. ( 2020 ) estimated the social costs of the pandemic to tourism in three cities in China (Hong Kong, Guangzhou, and Wuhan), and they found that most respondents were willing to pay for risk reduction and action in responding to the pandemic crisis; there was no significant difference between residents’ willingness to pay in the three cities. Some research has emphasized how lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic can prepare global tourism for an economic transformation that is needed to mitigate the impacts of climate change (Brouder, 2020 ; Prideaux et al., 2020 ).
It is clear that tourism has contributed significantly to economic development globally, but its role in sustainable development is uncertain, contested, and potentially paradoxical. This is due, in part, to the contested nature of sustainable development itself. Tourism has been promoted as a low-impact, nonextractive option for economic development, particularly for developing countries (Gössling, 2000 ), and many countries have managed to increase their participation in the global economy through development of international tourism. Tourism development has been viewed as an important sector for investment to enhance economic growth, poverty alleviation, and food security, and the sector provides an alternative opportunity to large-scale development projects and extractive industries that contribute to emissions of pollutants and threaten biodiversity and cultural values. However, global evidence from research on the economic impacts of tourism has shown that this potential has rarely been realized (Liu, 2003 ).
The role of tourism in sustainable development has been studied extensively and with a variety of perspectives, including the conceptualization of alternative or responsible forms of tourism and the examination of economic, environmental, and social impacts of tourism development. The research has generally concluded that tourism development has contributed to sustainable development in some cases where it is demonstrated to have provided support for biodiversity conservation initiatives and livelihood development strategies. As an economic sector, tourism is considered to be labor intensive, providing opportunities for poor households to enhance their livelihood through the sale of goods and services to foreign tourists.
Nature-based tourism approaches such as ecotourism and community-based tourism have been successful at attracting tourists to parks and protected areas, and their spending provides financial support for biodiversity conservation, livelihoods, and economic growth in developing countries. Nevertheless, studies of the impacts of tourism development have documented negative environmental impacts locally in terms of land use, food and water consumption, and congestion, and globally in terms of the contribution of tourism to climate change through the emission of greenhouse gases related to transportation and other tourist activities. Studies of the social impacts of tourism have documented experiences of discrimination based on ethnicity, gender, race, sex, and national identity.
The sustainability of tourism as an economic sector has been examined in terms of its vulnerability to civil conflict, economic shocks, natural disasters, and public health pandemics. Most studies conclude that tourism may have positive impacts for regional development and environmental conservation, but there is evidence that tourism inherently generates negative environmental impacts, primarily through pollutions stemming from transportation. The regional benefits of tourism development must be considered alongside the global impacts of increased transportation and tourism participation. Global tourism has also been shown to be vulnerable to economic crises, oil price shocks, and global outbreaks of infectious diseases. Given that tourism is dependent on energy, the movement of people, and the consumption of resources, virtually all tourism activities have significant economic, environmental, and sustainable impacts. As such, the role of tourism in sustainable development is highly questionable. Future research on the role of tourism in sustainable development should focus on reducing the negative impacts of tourism development, both regionally and globally.
Further Reading
- Bramwell, B. , & Lane, B. (1993). Sustainable tourism: An evolving global approach. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 1–5.
- Buckley, R. (2012). Sustainable tourism: Research and reality. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (2), 528–546.
- Butler, R. W. (1991). Tourism, environment, and sustainable development. Environmental Conservation , 18 (3), 201–209.
- Butler, R. W. (1999). Sustainable tourism: A state‐of‐the‐art review. Tourism Geographies , 1 (1), 7–25.
- Clarke, J. (1997). A framework of approaches to sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (3), 224–233.
- Fennell, D. A. (2020). Ecotourism (5th ed.). Routledge.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 (4), 283–302.
- Honey, M. (2008). Ecotourism and sustainable development: Who owns paradise? (2nd ed.). Island Press.
- Inskeep, E. (1991). Tourism planning: An integrated and sustainable development approach . Routledge.
- Jamal, T. , & Camargo, B. A. (2014). Sustainable tourism, justice and an ethic of care: Toward the just destination. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 22 (1), 11–30.
- Liburd, J. J. , & Edwards, D. (Eds.). (2010). Understanding the sustainable development of tourism . Oxford.
- Liu, Z. (2003). Sustainable tourism development: A critique. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 11 (6), 459–475.
- Sharpley, R. (2020). Tourism, sustainable development and the theoretical divide: 20 years on. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 28 (11), 1932–1946.
- Adams, W. M. (2009). Green development: Environment and sustainability in a developing world (3rd ed.). Routledge.
- Andereck, K. L. , Valentine, K. M. , Knopf, R. A. , & Vogt, C. A. (2005). Residents’ perceptions of community tourism impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 1056–1076.
- Andereck, K. , Valentine, K. , Vogt, C. , & Knopf, R. (2007). A cross-cultural analysis of tourism and quality of life perceptions. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 483–502.
- Anderies, J. M. , Folke, C. , Walker, B. , & Ostrom, E. (2013). Aligning key concepts for global change policy: Robustness, resilience, and sustainability . Ecology and Society , 18 (2), 8.
- Apergis, N. , & Payne, J. E. (2012). Tourism and growth in the Caribbean–evidence from a panel error correction model. Tourism Economics , 18 (2), 449–456.
- Arana, J. E. , & León, C. J. (2008). The impact of terrorism on tourism demand. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 (2), 299–315.
- Ashley, C. , & Roe, D. (2002). Making tourism work for the poor: Strategies and challenges in southern Africa. Development Southern Africa , 19 (1), 61–82.
- Ashley, C. , Roe, D. , & Goodwin, H. (2001). Pro-poor tourism strategies: Making tourism work for the poor: A review of experience (No. 1). Overseas Development Institute.
- Baker, K. , & Coulter, A. (2007). Terrorism and tourism: The vulnerability of beach vendors’ livelihoods in Bali. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (3), 249–266.
- Baral, N. , Stern, M. J. , & Bhattarai, R. (2008). Contingent valuation of ecotourism in Annapurna conservation area, Nepal: Implications for sustainable park finance and local development. Ecological Economics , 66 (2–3), 218–227.
- Becken, S. , & Lennox, J. (2012). Implications of a long-term increase in oil prices for tourism. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 133–142.
- Beckerman, W. (1994). “Sustainable development”: Is it a useful concept? Environmental Values , 3 (3), 191–209.
- Bhattarai, K. , Conway, D. , & Shrestha, N. (2005). Tourism, terrorism and turmoil in Nepal. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 669–688.
- Blewitt, J. (2015). Understanding sustainable development (2nd ed.). Routledge.
- Brouder, P. (2020). Reset redux: Possible evolutionary pathways towards the transformation of tourism in a COVID-19 world. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 484–490.
- Brunt, P. , & Courtney, P. (1999). Host perceptions of sociocultural impacts. Annals of Tourism Research , 26 (3), 493–515.
- Buckley, R. (2011). Tourism and environment. Annual Review of Environment and Resources , 36 , 397–416.
- Butler, R. W. (1980). The concept of a tourist area cycle of evolution: Implications for management of resources. Canadian Geographer/Le Géographe canadien , 24 (1), 5–12.
- Butler, R. , & Hinch, T. (Eds.). (2007). Tourism and indigenous peoples: Issues and implications . Routledge.
- Cabezas, A. L. (2004). Between love and money: Sex, tourism, and citizenship in Cuba and the Dominican Republic. Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society , 29 (4), 987–1015.
- Caffyn, A. (2012). Advocating and implementing slow tourism. Tourism Recreation Research , 37 (1), 77–80.
- Cahyanto, I. , Wiblishauser, M. , Pennington-Gray, L. , & Schroeder, A. (2016). The dynamics of travel avoidance: The case of Ebola in the US. Tourism Management Perspectives , 20 , 195–203.
- Calgaro, E. , & Lloyd, K. (2008). Sun, sea, sand and tsunami: Examining disaster vulnerability in the tourism community of Khao Lak, Thailand. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography , 29 (3), 288–306.
- Castanedo, S. , Juanes, J. A. , Medina, R. , Puente, A. , Fernandez, F. , Olabarrieta, M. , & Pombo, C. (2009). Oil spill vulnerability assessment integrating physical, biological and socio-economical aspects: Application to the Cantabrian coast (Bay of Biscay, Spain). Journal of Environmental Management , 91 (1), 149–159.
- Cater, E. (1993). Ecotourism in the Third World: Problems for sustainable tourism development. Tourism Management , 14 (2), 85–90.
- Ceballos-Lascuráin, H. (1987, January). The future of “ecotourism.” Mexico Journal , 17 , 13–14.
- Chase, L. C. , Lee, D. R. , Schulze, W. D. , & Anderson, D. J. (1998). Ecotourism demand and differential pricing of national park access in Costa Rica. Land Economics , 74 (4), 466–482.
- Chatziantoniou, I. , Filis, G. , Eeckels, B. , & Apostolakis, A. (2013). Oil prices, tourism income and economic growth: A structural VAR approach for European Mediterranean countries. Tourism Management , 36 (C), 331–341.
- Cheong, S. M. (2012). Fishing and tourism impacts in the aftermath of the Hebei-Spirit oil spill. Journal of Coastal Research , 28 (6), 1648–1653.
- Chok, S. , Macbeth, J. , & Warren, C. (2007). Tourism as a tool for poverty alleviation: A critical analysis of “pro-poor tourism” and implications for sustainability. Current Issues in Tourism , 10 (2–3), 144–165.
- Cioccio, L. , & Michael, E. J. (2007). Hazard or disaster: Tourism management for the inevitable in Northeast Victoria. Tourism Management , 28 (1), 1–11.
- Cirer-Costa, J. C. (2015). Tourism and its hypersensitivity to oil spills. Marine Pollution Bulletin , 91 (1), 65–72.
- Coccossis, H. , & Nijkamp, P. (1995). Sustainable tourism development . Ashgate.
- Coddington, K. (2015). The “entrepreneurial spirit”: Exxon Valdez and nature tourism development in Seward, Alaska. Tourism Geographies , 17 (3), 482–497.
- Cohen, E. (1978). The impact of tourism on the physical environment. Annals of Tourism Research , 5 (2), 215–237.
- Conway, D. , & Timms, B. F. (2010). Re-branding alternative tourism in the Caribbean: The case for “slow tourism.” Tourism and Hospitality Research , 10 (4), 329–344.
- Corbet, S. , O’Connell, J. F. , Efthymiou, M. , Guiomard, C. , & Lucey, B. (2019). The impact of terrorism on European tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 75 , 1–17.
- Daly, H. E. (1990). Toward some operational principles of sustainable development. Ecological Economics , 2 (1), 1–6.
- Deery, M. , Jago, L. , & Fredline, L. (2012). Rethinking social impacts of tourism research: A new research agenda. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 64–73.
- Diedrich, A. , & Garcia-Buades, E. (2008). Local perceptions of tourism as indicators of destination decline. Tourism Management , 41 , 623–632.
- Durbarry, R. (2004). Tourism and economic growth: The case of Mauritius. Tourism Economics , 10 , 389–401.
- Elliott, S. M. , & Neirotti, L. D. (2008). Challenges of tourism in a dynamic island destination: The case of Cuba. Tourism Geographies , 10 (4), 375–402.
- Enders, W. , Sandler, T. , & Parise, G. F. (1992). An econometric analysis of the impact of terrorism on tourism. Kyklos , 45 (4), 531–554.
- Eugenio-Martin, J. L. , & Campos-Soria, J. A. (2014). Economic crisis and tourism expenditure cutback decision. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 53–73.
- Farrell, B. , & McLellan, R. (1987). Tourism and physical environment research. Annals of Tourism Research , 14 (1), 1–16.
- Faulkner, B. , & Tideswell, C. (1997). A framework for monitoring community impacts of tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 5 (1), 3–28.
- Fennell, D. A. , & Eagles, P. F. (1990). Ecotourism in Costa Rica: A conceptual framework. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration , 8 (1), 23–34.
- Fullagar, S. , Markwell, K. , & Wilson, E. (Eds.). (2012). Slow tourism: Experiences and mobilities . Channel View.
- Garau-Vadell, J. B. , Gutierrez-Taño, D. , & Diaz-Armas, R. (2018). Economic crisis and residents’ perception of the impacts of tourism in mass tourism destinations. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management , 7 , 68–75.
- Garrod, B. , & Fyall, A. (1998). Beyond the rhetoric of sustainable tourism? Tourism Management , 19 (3), 199–212.
- Ghimire, K. B. (Ed.). (2013). The native tourist: Mass tourism within developing countries . Routledge.
- Goodrich, J. N. (2002). September 11, 2001 attack on America: A record of the immediate impacts and reactions in the USA travel and tourism industry. Tourism Management , 23 (6), 573–580.
- Gössling, S. (1999). Ecotourism: A means to safeguard biodiversity and ecosystem functions? Ecological Economics , 29 , 303–320.
- Gössling, S. (2000). Tourism–sustainable development option? Environmental Conservation , 27 (3), 223–224.
- Gössling, S. (2002). Global environmental consequences of tourism. Global Environmental Change , 12 , 283–302.
- Gössling, S. , & Peeters, P. (2015). Assessing tourism’s global environmental impact 1900–2050. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 23 (5), 639–659.
- Gössling, S. , Peeters, P. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J.‑P. , Dubois, G. , Lehman, L. V. , & Scott, D. (2011). Tourism and water use: Supply, demand and security, and international review. Tourism Management , 33 (1), 16–28.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , & Hall, C. M. (2020). Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 29 (1), 1–20.
- Gössling, S. , Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , Ceron, J. P. , & Dubois, G. (2012). Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Annals of Tourism Research , 39 (1), 36–58.
- Gray, N. J. , & Campbell, L. M. (2007). A decommodified experience? Exploring aesthetic, economic and ethical values for volunteer ecotourism in Costa Rica. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 463–482.
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots—a conceptual history of “sustainable development” (Nachhaltigkeit) . Wissenschaftszentrum Berlin für Sozialforschung.
- Gu, H. , & Ryan, C. (2008). Place attachment, identity and community impacts of tourism—the case of a Beijing hutong. Tourism Management , 29 (4), 637–647.
- Gursoy, D. , Chi, C. G. , & Dyer, P. (2010). Locals’ attitudes toward mass and alternative tourism: The case of Sunshine Coast, Australia. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (3), 381–394.
- Haley, A. J. , Snaith, T. , & Miller, G. (2005). The social impacts of tourism a case study of Bath, UK. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (3), 647–668.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (2009). Understanding and managing tourism impacts: An integrated approach . Routledge.
- Hall, C. M. , & Lew, A. A. (Eds.). (1998). Sustainable tourism: A geographical perspective . Longman.
- Haque, T. H. , & Haque, M. O. (2018). The swine flu and its impacts on tourism in Brunei. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management , 36 , 92–101.
- Haralambopoulos, N. , & Pizam, A. (1996). Perceived impacts of tourism: The case of Samos. Annals of Tourism Research , 23 (3), 503–526.
- Harrison, D. (2008). Pro-poor tourism: A critique. Third World Quarterly , 29 (5), 851–868.
- Hearne, R. R. , & Salinas, Z. M. (2002). The use of choice experiments in the analysis of tourist preferences for ecotourism development in Costa Rica. Journal of Environmental Management , 65 (2), 153–163.
- Hetzer, N. D. (1965). Environment, tourism, culture. Links , 1 (2), 1–3.
- Höhler, S. (2015). Spaceship earth in the environmental age, 1960–1990 . Routledge.
- Honey, M. , & Gilpin, R. (2009). Tourism in the developing world: Promoting peace and reducing poverty . United States Institute for Peace.
- Huan, T. C. , Beaman, J. , & Shelby, L. (2004). No-escape natural disaster: Mitigating impacts on tourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 31 (2), 255–273.
- Huang, J. H. , & Min, J. C. (2002). Earthquake devastation and recovery in tourism: The Taiwan case. Tourism Management , 23 (2), 145–154.
- Hunter, C. (1995). On the need to re-conceptualise sustainable tourism development. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 3 (3), 155–165.
- Hunter, C. , & Green, H. (1995). Tourism and the environment. A sustainable relationship? Routledge.
- Huttasin, N. (2008). Perceived social impacts of tourism by residents in the OTOP tourism village, Thailand. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 13 (2), 175–191.
- Hystad, P. W. , & Keller, P. C. (2008). Towards a destination tourism disaster management framework: Long-term lessons from a forest fire disaster. Tourism Management , 29 (1), 151–162.
- Katircioglu, S. (2009). Tourism, trade and growth: The case of Cyprus. Applied Economics , 41 (21), 2741–2750.
- Katircioglu, S. (2010). Testing the tourism-led growth hypothesis for Singapore: An empirical investigation from bounds test to cointegration and Granger causality tests. Tourism Economics , 16 (4), 1095–1101.
- Khan, M. M. (1997). Tourism development and dependency theory: Mass tourism vs. ecotourism. Annals of Tourism Research , 24 (4), 988–991.
- Kim, H. , & Marcouiller, D. W. (2015). Considering disaster vulnerability and resiliency: The case of hurricane effects on tourism-based economies. The Annals of Regional Science , 54 (3), 945–971.
- King, B. , Pizam, A. , & Milman, A. (1993). Social impacts of tourism: Host perceptions. Annals of Tourism Research , 20 (4), 650–665.
- Kisswani, K. M. , Zaitouni, M. , & Moufakkir, O. (2020). An examination of the asymmetric effect of oil prices on tourism receipts. Current Issues in Tourism , 23 (4), 500–522.
- Kuvan, Y. , & Akan, P. (2005). Residents’ attitudes toward general and forest-related impacts of tourism: The case of Belek, Antalya. Tourism Management , 26 (5), 691–706.
- Lai, P. H. , & Nepal, S. K. (2006). Local perspectives of ecotourism development in Tawushan Nature Reserve, Taiwan. Tourism Management , 27 (6), 1117–1129.
- Lanouar, C. , & Goaied, M. (2019). Tourism, terrorism and political violence in Tunisia: Evidence from Markov-switching models. Tourism Management , 70 , 404–418.
- Lee, C. C. , & Chang, C. P. (2008). Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tourism Management , 29 , 180–192.
- Lenzen, M. , Sun, Y. Y. , Faturay, F. , Ting, Y. P. , Geschke, A. , & Malik, A. (2018). The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nature Climate Change , 8 (6), 522–528.
- Lian Chan, J. K. , & Baum, T. (2007). Ecotourists’ perception of ecotourism experience in lower Kinabatangan, Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (5), 574–590.
- Liu, A. , & Pratt, S. (2017). Tourism’s vulnerability and resilience to terrorism. Tourism Management , 60 , 404–417.
- Manyara, G. , & Jones, E. (2007). Community-based tourism enterprises development in Kenya: An exploration of their potential as avenues of poverty reduction. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 15 (6), 628–644.
- Maphanga, P. M. , & Henama, U. S. (2019). The tourism impact of Ebola in Africa: Lessons on crisis management. African Journal of Hospitality, Tourism and Leisure , 8 (3), 1–13.
- Mathieson, A. , & Wall, G. (1982). Tourism, economic, physical and social impacts . Longman.
- May, V. (1991). Tourism, environment and development—values, sustainability and stewardship. Tourism Management , 12 (2), 112–124.
- Mazzocchi, M. , & Montini, A. (2001). Earthquake effects on tourism in central Italy. Annals of Tourism Research , 28 (4), 1031–1046.
- Mbaiwa, J. E. (2005). The socio-cultural impacts of tourism development in the Okavango Delta, Botswana. Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change , 2 (3), 163–185.
- McKercher, B. (1993a). Some fundamental truths about tourism: Understanding tourism’s social and environmental impacts, Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 1 (1), 6–16.
- McKercher, B. (1993b). The unrecognized threat to tourism: Can tourism survive “sustainability”? Tourism Management , 14 (2), 131–136.
- Meadows, D. H. , Meadows, D. L. , Randers, J. , & Behrens, W. W. (1972). The limits to growth . Universe Books.
- Miller, G. A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2003). A farming crisis or a tourism disaster? An analysis of the foot and mouth disease in the UK. Current Issues in Tourism , 6 (2), 150–171.
- Milman, A. , & Pizam, A. (1988). Social impacts of tourism on central Florida. Annals of Tourism Research , 15 (2), 191–204.
- Monterrubio, J. C. (2010). Short-term economic impacts of influenza A (H1N1) and government reaction on the Mexican tourism industry: An analysis of the media. International Journal of Tourism Policy , 3 (1), 1–15.
- Narayan, P. K. (2004). Economic impact of tourism on Fiji’s economy: Empirical evidence from the computable general equilibrium model. Tourism Economics , 10 (4), 419–433.
- Nash, D. , & Butler, R. (1990). Towards sustainable tourism. Tourism Management , 11 (3), 263–264.
- Novelli, M. , Burgess, L. G. , Jones, A. , & Ritchie, B. W. (2018). “No Ebola . . . still doomed”—the Ebola-induced tourism crisis. Annals of Tourism Research , 70 , 76–87.
- Oh, C. (2005). The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Management , 26 , 39–44.
- Oh, H. , Assaf, A. G. , & Baloglu, S. (2016). Motivations and goals of slow tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 55 (2), 205–219.
- Okumus, F. , & Karamustafa, K. (2005). Impact of an economic crisis evidence from Turkey. Annals of Tourism Research , 32 (4), 942–961.
- Page, S. , Song, H. , & Wu, D. C. (2012). Assessing the impacts of the global economic crisis and swine flu on inbound tourism demand in the United Kingdom. Journal of Travel Research , 51 (2), 142–153.
- Papatheodorou, A. , Rosselló, J. , & Xiao, H. (2010). Global economic crisis and tourism: Consequences and perspectives. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 39–45.
- Peeters, P. (2012). A clear path towards sustainable mass tourism? Rejoinder to the paper “Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence” by David B. Weaver. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1038–1041.
- Pennington-Gray, L. , London, B. , Cahyanto, I. , & Klages, W. (2011). Expanding the tourism crisis management planning framework to include social media: Lessons from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill 2010. International Journal of Tourism Anthropology , 1 (3–4), 239–253.
- Pizam, A. , & Fleischer, A. (2002). Severity versus frequency of acts of terrorism: Which has a larger impact on tourism demand? Journal of Travel Research , 40 (3), 337–339.
- Pratt, S. (2015). The economic impact of tourism in SIDS. Annals of Tourism Research , 52 , 148–160.
- Prideaux, B. , Thompson, M. , & Pabel, A. (2020). Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies , 22 (3), 667–678.
- Qiu, R. T. , Park, J. , Li, S. , & Song, H. (2020). Social costs of tourism during the COVID-19 pandemic . Annals of Tourism Research , 84 , 102994.
- Rátz, T. (2000). Residents’ perceptions of the socio-cultural impacts of tourism at Lake Balaton, Hungary. Tourism and Sustainable Community Development , 7 , 36.
- Ribeiro, L. C. D. S. , Souza, K. B. D. , Domingues, E. P. , & Magalhães, A. S. (2020). Blue water turns black: Economic impact of oil spill on tourism and fishing in Brazilian Northeast . Current Issues in Tourism , 1–6.
- Richardson, R. B. , Fernandez, A. , Tschirley, D. , & Tembo, G. (2012). Wildlife conservation in Zambia: Impacts on rural household welfare. World Development , 40 (5), 1068–1081.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Loomis, J. B. (2004). Adaptive recreation planning and climate change: A contingent visitation approach. Ecological Economics , 50 (1), 83–99.
- Richardson, R. B. , & Witkowski, K. (2010). Economic vulnerability to climate change for tourism-dependent nations. Tourism Analysis , 15 (3), 315–330.
- Ritchie, B. W. , Crotts, J. C. , Zehrer, A. , & Volsky, G. T. (2013). Understanding the effects of a tourism crisis: The impact of the BP oil spill on regional lodging demand. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (1), 12–25.
- Rogerson, C. M. (2011). Urban tourism and regional tourists: Shopping in Johannesburg, South Africa. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie , 102 (3), 316–330.
- Rutty, M. , & Richardson, R. (2019). Tourism research in Cuba: Gaps in knowledge and challenges for sustainable tourism. Sustainability , 11 (12), 3340–3346.
- Ryan, C. , & Huyton, J. (2000). Who is interested in Aboriginal tourism in the Northern Territory, Australia? A cluster analysis. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 53–88.
- Salinas, E. , Mundet, L. , & Salinas, E. (2018). Historical evolution and spatial development of tourism in Cuba, 1919–2017: What is next? Tourism Planning & Development , 15 (3), 216–238.
- Sanchez, P. M. , & Adams, K. M. (2008). The Janus-faced character of tourism in Cuba. Annals of Tourism Research , 35 , 27–46.
- Scott, D. , Hall, C. M. , & Gössling, S. (2012). Tourism and climate change: Impacts, adaptation and mitigation . Routledge.
- Seetanah, B. (2011). Assessing the dynamic economic impact of tourism for island economies. Annals of Tourism Research , 38 (1), 291–308.
- Sharma, A. , & Nicolau, J. L. (2020). An open market valuation of the effects of COVID-19 on the travel and tourism industry . Annals of Tourism Research , 83 , 102990.
- Sharpley, R. (2000). Tourism and sustainable development: Exploring the theoretical divide. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 8 (1), 1–19.
- Sharpley, R. (2014). Host perceptions of tourism: A review of the research. Tourism Management , 42 , 37–49.
- Smeral, E. (2010). Impacts of the world recession and economic crisis on tourism: Forecasts and potential risks. Journal of Travel Research , 49 (1), 31–38.
- Southgate, C. R. (2006). Ecotourism in Kenya: The vulnerability of communities. Journal of Ecotourism , 5 (1–2), 80–96.
- Spenceley, A. (Ed.). (2012). Responsible tourism: Critical issues for conservation and development . Routledge.
- Stabler, M. (Ed.). (1997). Tourism and sustainability: Principles to practice . Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International.
- Stronza, A. (2007). The economic promise of ecotourism for conservation. Journal of Ecotourism , 6 (3), 210–230.
- Stylidis, D. , & Terzidou, M. (2014). Tourism and the economic crisis in Kavala, Greece. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 210–226.
- Suntikul, W. , Bauer, T. , & Song, H. (2009). Pro-poor tourism development in Viengxay, Laos: Current state and future prospects. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research , 14 (2), 153–168.
- Swarbrooke, J. (1999). Sustainable tourism management . CABI.
- Tovar, C. , & Lockwood, M. (2008). Social impacts of tourism: An Australian regional case study. International Journal of Tourism Research , 10 (4), 365–378.
- Tsartas, P. (1992). Socioeconomic impacts of tourism on two Greek isles. Annals of Tourism Research , 19 (3), 516–533.
- Turner, L. , & Ash, J. (1975). The golden hordes: International tourism and the pleasure periphery . Constable.
- United Nations . (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development . Division for Sustainable Development Goals.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2002). Tourism and poverty alleviation . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- United Nations World Tourism Organization . (2020). UNWTO world tourism barometer . United Nations World Tourism Organization.
- Viner, D. (2006). Tourism and its interactions with climate change. Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 14 (4), 317–322.
- Vitousek, P. M. , Mooney, H. A. , Lubchenco, J. , & Melillo, J. M. (1997). Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science , 277 (5325), 494–499.
- World Commission on Environment and Development . (1987). Our common future . Oxford University Press.
- Weaver, D. (2007). Towards sustainable mass tourism: Paradigm shift or paradigm nudge? Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 65–69.
- Weaver, D. B. (2012). Organic, incremental and induced paths to sustainable mass tourism convergence. Tourism Management , 33 (5), 1030–1037.
- Weaver, D. B. (2014). Asymmetrical dialectics of sustainable tourism: Toward enlightened mass tourism. Journal of Travel Research , 53 (2), 131–140.
- Wheeller, B. (2007). Sustainable mass tourism: More smudge than nudge the canard continues. Tourism Recreation Research , 32 (3), 73–75.
- Whitford, M. , & Ruhanen, L. (2016). Indigenous tourism research, past and present: Where to from here? Journal of Sustainable Tourism , 24 (8–9), 1080–1099.
- Whyte, K. P. (2010). An environmental justice framework for indigenous tourism. Environmental Philosophy , 7 (2), 75–92.
- Wolff, K. , & Larsen, S. (2014). Can terrorism make us feel safer? Risk perceptions and worries before and after the July 22nd attacks. Annals of Tourism Research , 44 , 200–209.
- Yang, W. , Wang, D. , & Chen, G. (2011). Reconstruction strategies after the Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan, China. Tourism Management , 32 (4), 949–956.
- Young, G. (1973). Tourism—blessing or blight? Penguin.
- Zapata, M. J. , Hall, C. M. , Lindo, P. , & Vanderschaeghe, M. (2011). Can community-based tourism contribute to development and poverty alleviation? Lessons from Nicaragua. Current Issues in Tourism , 14 (8), 725–749.
1. One megatonne (Mt) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) metric tons.
2. One megajoule (MJ) is equal to 1 million (10 6 ) joules, or approximately the kinetic energy of a 1-megagram (tonne) vehicle moving at 161 km/h.
3. One gigatonne (Gt) is equal to 1 billion (10 9 ) metric tons.
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Environmental Science. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 22 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.148.24.167]
- 185.148.24.167
Character limit 500 /500
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer

share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
Tourism’s Importance for Growth Highlighted in World Economic Outlook Report
- All Regions
- 10 Nov 2023
Tourism has again been identified as a key driver of economic recovery and growth in a new report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). With UNWTO data pointing to a return to 95% of pre-pandemic tourist numbers by the end of the year in the best case scenario, the IMF report outlines the positive impact the sector’s rapid recovery will have on certain economies worldwide.
According to the World Economic Outlook (WEO) Report , the global economy will grow an estimated 3.0% in 2023 and 2.9% in 2024. While this is higher than previous forecasts, it is nevertheless below the 3.5% rate of growth recorded in 2022, pointing to the continued impacts of the pandemic and Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and from the cost-of-living crisis.
Tourism key sector for growth
The WEO report analyses economic growth in every global region, connecting performance with key sectors, including tourism. Notably, those economies with "large travel and tourism sectors" show strong economic resilience and robust levels of economic activity. More specifically, countries where tourism represents a high percentage of GDP have recorded faster recovery from the impacts of the pandemic in comparison to economies where tourism is not a significant sector.
As the report Foreword notes: "Strong demand for services has supported service-oriented economies—including important tourism destinations such as France and Spain".
Looking Ahead
The latest outlook from the IMF comes on the back of UNWTO's most recent analysis of the prospects for tourism, at the global and regional levels. Pending the release of the November 2023 World Tourism Barometer , international tourism is on track to reach 80% to 95% of pre-pandemic levels in 2023. Prospects for September-December 2023 point to continued recovery, driven by the still pent-up demand and increased air connectivity particularly in Asia and the Pacific where recovery is still subdued.
Related links
- Download the News Release on PDF
- UNWTO World Tourism Barometer
- IMF World Economic Outlook
Category tags
Related content.

International Tourism to Reach Pre-Pandemic Levels in 2024

International Tourism to End 2023 Close to 90% of Pre-P...

International Tourism Swiftly Overcoming Pandemic Downturn

Tourism on Track for Full Recovery as New Data Shows St...
Tourism and Sustainable Economic Development: Evidence from Belt and Road Countries
- Published: 22 January 2022
- Volume 14 , pages 503–516, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
- Uktam Umurzakov 1 ,
- Shakhnoza Tosheva 2 &
- Raufhon Salahodjaev 3 , 4 , 5
1192 Accesses
15 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This study is aimed to fill an existing gap in the empirical literature by exploring the effect of tourism on sustainable economic development across Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) countries. BRI is one of the paramount global partnerships as it covers more than 60 percent of the global population and 30 percent of the world’s GDP. Using data from 57 nations over the period of 2000–2018 and applying two-step generalized method of moments (GMM) estimator, we show that tourism has a positive and significant effect on sustainable development, measured by adjusted net national income. In particular, moving from a country with the lowest to highest number of per capita tourist arrivals leads to a 15.2% increase in adjusted per capita income. The results also remain valid using alternative econometric estimation techniques.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Impact of tourism development upon environmental sustainability: a suggested framework for sustainable ecotourism
Qadar Bakhsh Baloch, Syed Naseeb Shah, … Asia Umar Khan
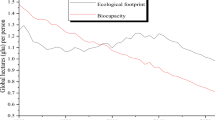
Dynamic linkages between financial development, economic growth, urbanization, trade openness, and ecological footprint: an empirical account of ECOWAS countries
Nazir Muhammad Abdullahi, Adamu Ali Ibrahim, … Xuexi Huo
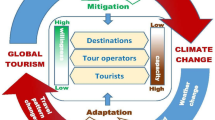
Global tourism, climate change and energy sustainability: assessing carbon reduction mitigating measures from the aviation industry
Walter Leal Filho, Artie W. Ng, … Izabela Rampasso
Ahmad, F., Draz, M. U., Su, L., Ozturk, I., & Rauf, A. (2018). Tourism and environmental pollution: Evidence from the one belt one road provinces of Western China. Sustainability, 10 (10), 3520.
Article Google Scholar
Akinboade, O. A., & Braimoh, L. A. (2010). International tourism and economic development in South Africa: A Granger causality test. International Journal of Tourism Research, 12 (2), 149–163.
Alam, K. J., & Sumon, K. K. (2020). Causal relationship between trade openness and economic growth: A panel data analysis of Asian countries. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 10 (1), 118.
Alhowaish, A. K. (2016) Is tourism development a sustainable economic growth strategy in the long run? Evidence from GCC Countries. Sustainability, 8 (7), 605.
Antonakakis, N., Dragouni, M., Eeckels, B., & Filis, G. (2016). Tourism and economic growth: Does democracy matter? Annals of Tourism Research, 61 , 258–264.
Asongu, S. A., & Odhiambo, N. M. (2020). Foreign direct investment, information technology and economic growth dynamics in Sub-Saharan Africa. Telecommunications Policy , 44 (1), 101838.
Azam, M. (2021). Governance and economic growth: Evidence from 14 Latin America and Caribbean Countries. Journal of the Knowledge Economy , 1–26.
Balli, E., Sigeze, C., Manga, M., Birdir, S., & Birdir, K. (2019). The relationship between tourism, CO2 emissions and economic growth: A case of Mediterranean countries. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 24 (3), 219–232.
Barro, R. J. (1991). Economic growth in a cross section of countries. The quarterly journal of economics, 106 (2), 407–443.
Batuo, M., Mlambo, K., & Asongu, S. (2018). Linkages between financial development, financial instability, financial liberalisation and economic growth in Africa. Research in International Business and Finance, 45 , 168–179.
Belloumi, M. (2010). The relationship between tourism receipts, real effective exchange rate and economic growth in Tunisia. International Journal of Tourism Research, 12 (5), 550–560.
Beladi, H., Chao, C. C., Ee, M. S., & Hollas, D. (2019). Does medical tourism promote economic growth? A cross-country analysis. Journal of Travel Research, 58 (1), 121–135.
Bento, J. P. (2016). Tourism and economic growth in Portugal: An empirical investigation of causal links. Tourism & Management Studies, 12 (1), 164–171.
Bilen, M., Yilanci, V., & Eryüzlü, H. (2017). Tourism development and economic growth: A panel Granger causality analysis in the frequency domain. Current Issues in Tourism, 20 (1), 27–32.
Bouzahzah, M., & El Menyari, Y. (2013). International tourism and economic growth: The case of Morocco and Tunisia. The Journal of North African Studies, 18 (4), 592–607.
Brida, J. G., Gómez, D. M., & Segarra, V. (2020). On the empirical relationship between tourism and economic growth. Tourism Management , 81 , 104131.
Brida, J. G., & Risso, W. A. (2009). Tourism as a factor of long-run economic growth: An empirical analysis for Chile. European Journal of Tourism Research , 2 (2).
Castro-Nuño, M., Molina-Toucedo, J. A., & Pablo-Romero, M. P. (2013). Tourism and GDP: A meta-analysis of panel data studies. Journal of Travel Research, 52 (6), 745–758.
Chou, M. C. (2013). Does tourism development promote economic growth in transition countries? A panel data analysis. Economic Modelling, 33 , 226–232.
Cole, M. A. (2004). Trade, the pollution haven hypothesis and the environmental Kuznets curve: Examining the linkages. Ecological Economics, 48 (1), 71–81.
Corrie, K., Stoeckl, N., & Chaiechi, T. (2013). Tourism and economic growth in Australia: An empirical investigation of causal links. Tourism Economics, 19 (6), 1317–1344.
Cortés-Jiménez, I., Nowak, J. J., & Sahli, M. (2011). Mass beach tourism and economic growth: Lessons from Tunisia. Tourism Economics, 17 (3), 531–547.
Dogru, T., & Bulut, U. (2018). Is tourism an engine for economic recovery? Theory and empirical evidence. Tourism Management, 67 , 425–434.
Dogru, T., Bulut, U., Kocak, E., Isik, C., Suess, C., & Siraka-Turk, E. (2020). The nexus between tourism, economic growth, renewable energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emissions: Contemporary evidence from OECD countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research . https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10110-w
Fayissa, B., Nsiah, C., & Tadasse, B. (2008). Impact of tourism on economic growth and development in Africa. Tourism Economics, 14 (4), 807–818.
Fleurbaey, M. (2009). Beyond GDP: The quest for a measure of social welfare. Journal of Economic Literature, 47 (4), 1029–1075.
Fu, X., Ridderstaat, J., & Jia, H. C. (2020). Are all tourism markets equal? Linkages between market-based tourism demand, quality of life, and economic development in Hong Kong. Tourism Management , 77 , 104015.
Ghardallou, W., & Sridi, D. (2020). Democracy and economic growth: A literature review. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 11 (3), 982–1002.
Haller, A. P., Butnaru, G. I., Hârșan, G. D. T., & Ştefănică, M. (2021). The relationship between tourism and economic growth in the EU-28. Is there a tendency towards convergence?. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja , 34 (1), 1121–1145.
Helali, K. (2021). Markov Switching-Vector Auto Regression Model Analysis of the economic and growth cycles in Tunisia and its main European partners. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00740-x
Holzner, M. (2011). Tourism and economic development: The beach disease? Tourism Management, 32 (4), 922–933.
Hughes, C. G. (1982). The employment and economic effects of tourism reappraised. Tourism Management, 3 (3), 167–176.
Ighodaro, C. A., & Adegboye, A. C. (2020). Long run analysis of tourism and economic growth in Nigeria. International Journal of Economic Policy in Emerging Economies, 13 (3), 286–301.
Isaeva, A., Salahodjaev, R., Khachaturov, A., & Tosheva, S. (2021). The impact of tourism and financial development on energy consumption and carbon dioxide emission: Evidence from post-communist countries. Journal of the Knowledge Economy , 1–14.
Islam, M. S. (2020). Human capital and per capita income linkage in South Asia: A heterogeneous dynamic panel analysis. Journal of the Knowledge Economy , 1–16.
Jin, J. C. (2011). The effects of tourism on economic growth in Hong Kong. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 52 (3), 333–340.
Kadir, N., & Karim, M. Z. A. (2012). Tourism and economic growth in Malaysia: Evidence from tourist arrivals from ASEAN-S countries. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 25 (4), 1089–1100.
Kaiser, C. F., & Vendrik, M. C. (2019). Different versions of the Easterlin Paradox: New evidence for European countries. In The Economics of Happiness (pp. 27–55). Springer, Cham.
Kapera, I. (2018). Sustainable tourism development efforts by local governments in Poland. Sustainable Cities and Society, 40 , 581–588.
Katircioglu, S. T. (2009). Revisiting the tourism-led-growth hypothesis for Turkey using the bounds test and Johansen approach for cointegration. Tourism Management, 30 (1), 17–20.
Khalil, S., Kakar, M. K., & Malik, A. (2007). Role of tourism in economic growth: Empirical evidence from Pakistan economy [with comments]. The Pakistan Development Review , 985–995.
Kim, H. J., & Chen, M. H. (2006). Tourism expansion and economic development: The case of Taiwan. Tourism Management, 27 (5), 925–933.
Kumar, N., Kumar, R. R., Kumar, R., & Stauvermann, P. J. (2020). Is the tourism–growth relationship asymmetric in the Cook Islands? Evidence from NARDL cointegration and causality tests. Tourism Economics, 26 (4), 658–681.
Lee, J. W., & Brahmasrene, T. (2013). Investigating the influence of tourism on economic growth and carbon emissions: Evidence from panel analysis of the European Union. Tourism Management, 38 , 69–76.
Lee, C. C., & Chang, C. P. (2008). Tourism development and economic growth: A closer look at panels. Tourism Management, 29 (1), 180–192.
Lenzen, M., Sun, Y. Y., Faturay, F., Ting, Y. P., Geschke, A., & Malik, A. (2018). The carbon footprint of global tourism. Nature Climate Change, 8 (6), 522–528.
Manzoor, F., Wei, L., & Asif, M. (2019). The contribution of sustainable tourism to economic growth and employment in Pakistan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16 (19), 3785.
Mishra, P. K., Rout, H. B., & Mohapatra, S. S. (2011). Causality between tourism and economic growth: Empirical evidence from India. European Journal of Social Sciences, 18 (4), 518–527.
Google Scholar
Mrabet, Z., AlSamara, M., & Jarallah, S. H. (2017). The impact of economic development on environmental degradation in Qatar. Environmental and Ecological Statistics, 24 (1), 7–38.
Narayan, P. K., Narayan, S., Prasad, A., & Prasad, B. C. (2010). Tourism and economic growth: A panel data analysis for Pacific Island countries. Tourism Economics, 16 (1), 169–183.
Nkoa, B. E. O., & Song, J. S. (2021). Does institutional quality increase inequalities in Africa?. Journal of the Knowledge Economy , 1–32.
Nunkoo, R., Seetanah, B., Jaffur, Z. R. K., Moraghen, P. G. W., & Sannassee, R. V. (2020). Tourism and economic growth: A meta-regression analysis. Journal of Travel Research, 59 (3), 404–423.
Nyasha, S., Odhiambo, N. M., & Asongu, S. A. (2020). The impact of tourism development on economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa. The European Journal of Development Research , 1–22.
Obydenkova, A., Nazarov, Z., & Salahodjaev, R. (2016). The process of deforestation in weak democracies and the role of intelligence. Environmental Research, 148 , 484–490.
Oh, C. O. (2005). The contribution of tourism development to economic growth in the Korean economy. Tourism Management, 26 (1), 39–44.
Ohlan, R. (2017). The relationship between tourism, financial development and economic growth in India. Future Business Journal, 3 (1), 9–22.
Pegkas, P. (2020). Interrelationships between tourism, energy, environment and economic growth in Greece. Anatolia, 31 (4), 565–576.
Proença, S., & Soukiazis, E. (2008). Tourism as an economic growth factor: A case study for Southern European countries. Tourism Economics, 14 (4), 791–806.
Rasool, H., Maqbool, S., & Tarique, M. (2021). The relationship between tourism and economic growth among BRICS countries: A panel cointegration analysis. Future Business Journal, 7 (1), 1–11.
Roudi, S., Arasli, H., & Akadiri, S. S. (2019). New insights into an old issue–Examining the influence of tourism on economic growth: Evidence from selected small island developing states. Current Issues in Tourism, 22 (11), 1280–1300.
Saba, C. S., & Ngepah, N. (2021). ICT Diffusion, industrialisation and economic growth nexus: An international cross-country analysis. Journal of the Knowledge Economy , 1–40.
Sağlam, Y., & EGELİ, H. A. (2018). The nexus between tourism and economic growth: Case of Commonwealth of Independent States. Journal of Multidisciplinary Academic Tourism, 3 (2), 45–51.
Sanchez Carrera, E. J., Brida, J. G., & Risso, W. A. (2008). Tourism’s impact on long-run Mexican economic growth. Economics Bulletin, 23 (21), 1–8.
Santamaria, D., & Filis, G. (2019). Tourism demand and economic growth in Spain: New insights based on the yield curve. Tourism Management, 75 , 447–459.
Shaheen, K., Zaman, K., Batool, R., Khurshid, M. A., Aamir, A., Shoukry, A. M., & Gani, S. (2019). Dynamic linkages between tourism, energy, environment, and economic growth: Evidence from top 10 tourism-induced countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26 (30), 31273–31283.
Shahbaz, M., Ferrer, R., Shahzad, S. J. H., & Haouas, I. (2018). Is the tourism–economic growth nexus time-varying? Bootstrap rolling-window causality analysis for the top 10 tourist destinations. Applied Economics, 50 (24), 2677–2697.
Shahzad, S. J. H., Shahbaz, M., Ferrer, R., & Kumar, R. R. (2017). Tourism-led growth hypothesis in the top ten tourist destinations: New evidence using the quantile-on-quantile approach. Tourism Management, 60 , 223–232.
Schubert, S. F., Brida, J. G., & Risso, W. A. (2011). The impacts of international tourism demand on economic growth of small economies dependent on tourism. Tourism Management, 32 (2), 377–385.
Seetanah, B. (2011). Assessing the dynamic economic impact of tourism for island economies. Annals of Tourism Research, 38 (1), 291–308.
Siddiqui, A., & Rehman, A. U. (2017). The human capital and economic growth nexus: In East and South Asia. Applied Economics , 49 (28), 2697–2710.
Srinivasan, P., Kumar, P. S., & Ganesh, L. (2012). Tourism and economic growth in Sri Lanka: An ARDL bounds testing approach. Environment and Urbanization Asia, 3 (2), 397–405.
Sokhanvar, A. (2019). Does foreign direct investment accelerate tourism and economic growth within Europe? Tourism Management Perspectives, 29 , 86–96.
Sokhanvar, A., & Jenkins, G. P. (2021). Impact of foreign direct investment and international tourism on long-run economic growth of Estonia. Journal of Economic Studies .
Stauvermann, P. J., Kumar, R. R., Shahzad, S. J. H., & Kumar, N. N. (2018). Effect of tourism on economic growth of Sri Lanka: Accounting for capital per worker, exchange rate and structural breaks. Economic Change and Restructuring, 51 (1), 49–68.
Su, Y., Cherian, J., Sial, M. S., Badulescu, A., Thu, P. A., Badulescu, D., & Samad, S. (2021). Does tourism affect economic growth of China? A Panel Granger Causality Approach. Sustainability, 13 (3), 1349.
Sun, X., Chenggang, Y., Khan, A., Hussain, J., & Bano, S. (2021). The role of tourism, and natural resources in the energy-pollution-growth nexus: An analysis of Belt and Road Initiative countries. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 64 (6), 999–1020.
Surugiu, C., & Surugiu, M. R. (2013). Is the tourism sector supportive of economic growth? Empirical evidence on Romanian tourism. Tourism Economics, 19 (1), 115–132.
Tang, C. F., & Abosedra, S. (2014). The impacts of tourism, energy consumption and political instability on economic growth in the MENA countries. Energy Policy, 68 , 458–464.
Tang, C. F. (2021). The threshold effects of educational tourism on economic growth. Current Issues in Tourism, 24 (1), 33–48.
Tecel., A., Katiricioglu, S., Taheri, E., & Bekun, F.V. (2020). Causal interactions among tourism, foreign direct investment, domestic credits, and economic growth: Evidence from selected Mediterranean countries. Portuguese Economic Journal . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10258-020-00181-5
Tugcu, C. T. (2014). Tourism and economic growth nexus revisited: A panel causality analysis for the case of the Mediterranean Region. Tourism Management, 42 , 207–212.
Wu, T. P., & Wu, H. C. (2019). Tourism and economic growth in Asia: A bootstrap multivariate panel Granger causality. International Journal of Tourism Research, 21 (1), 87–96.
Wu, T. P., Wu, H. C., Wu, Y. Y., Liu, Y. T., & Wu, S. T. (2020). Causality between tourism and economic growth. Journal of China Tourism Research , 1–18.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Uktam Umurzakov
ERGO Analytics, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Shakhnoza Tosheva
Tashkent State University of Economics, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Raufhon Salahodjaev
AKFA University, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Tashkent, Uzbekistan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Raufhon Salahodjaev .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Umurzakov, U., Tosheva, S. & Salahodjaev, R. Tourism and Sustainable Economic Development: Evidence from Belt and Road Countries. J Knowl Econ 14 , 503–516 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00872-0
Download citation
Received : 22 January 2021
Accepted : 01 December 2021
Published : 22 January 2022
Issue Date : March 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00872-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Economic growth
- Sustainability
- Belt and Road
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

10 Economic impacts of tourism + explanations + examples
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
There are many economic impacts of tourism, and it is important that we understand what they are and how we can maximise the positive economic impacts of tourism and minimise the negative economic impacts of tourism.
Many argue that the tourism industry is the largest industry in the world. While its actual value is difficult to accurately determine, the economic potential of the tourism industry is indisputable. In fact, it is because of the positive economic impacts that most destinations embark on their tourism journey.
There is, however, more than meets the eye in most cases. The positive economic impacts of tourism are often not as significant as anticipated. Furthermore, tourism activity tends to bring with it unwanted and often unexpected negative economic impacts of tourism.
In this article I will discuss the importance of understanding the economic impacts of tourism and what the economic impacts of tourism might be. A range of positive and negative impacts are discussed and case studies are provided.
At the end of the post I have provided some additional reading on the economic impacts of tourism for tourism stakeholders , students and those who are interested in learning more.
Foreign exchange earnings
Contribution to government revenues, employment generation, contribution to local economies, development of the private sector, infrastructure cost, increase in prices, economic dependence of the local community on tourism, foreign ownership and management, economic impacts of tourism: conclusion, further reading on the economic impacts of tourism, the economic impacts of tourism: why governments invest.
Tourism brings with it huge economic potential for a destination that wishes to develop their tourism industry. Employment, currency exchange, imports and taxes are just a few of the ways that tourism can bring money into a destination.
In recent years, tourism numbers have increased globally at exponential rates, as shown in the World Tourism Organisation data below.
There are a number of reasons for this growth including improvements in technology, increases in disposable income, the growth of budget airlines and consumer desires to travel further, to new destinations and more often.

Here are a few facts about the economic importance of the tourism industry globally:
- The tourism economy represents 5 percent of world GDP
- Tourism contributes to 6-7 percent of total employment
- International tourism ranks fourth (after fuels, chemicals and automotive products) in global exports
- The tourism industry is valued at US$1trillion a year
- Tourism accounts for 30 percent of the world’s exports of commercial services
- Tourism accounts for 6 percent of total exports
- 1.4billion international tourists were recorded in 2018 (UNWTO)
- In over 150 countries, tourism is one of five top export earners
- Tourism is the main source of foreign exchange for one-third of developing countries and one-half of less economically developed countries (LEDCs)
There is a wealth of data about the economic value of tourism worldwide, with lots of handy graphs and charts in the United Nations Economic Impact Report .
In short, tourism is an example of an economic policy pursued by governments because:
- it brings in foreign exchange
- it generates employment
- it creates economic activity
Building and developing a tourism industry, however, involves a lot of initial and ongoing expenditure. The airport may need expanding. The beaches need to be regularly cleaned. New roads may need to be built. All of this takes money, which is usually a financial outlay required by the Government.
For governments, decisions have to be made regarding their expenditure. They must ask questions such as:
How much money should be spent on the provision of social services such as health, education, housing?
How much should be spent on building new tourism facilities or maintaining existing ones?
If financial investment and resources are provided for tourism, the issue of opportunity costs arises.
By opportunity costs, I mean that by spending money on tourism, money will not be spent somewhere else. Think of it like this- we all have a specified amount of money and when it runs out, it runs out. If we decide to buy the new shoes instead of going out for dinner than we might look great, but have nowhere to go…!
In tourism, this means that the money and resources that are used for one purpose may not then be available to be used for other purposes. Some destinations have been known to spend more money on tourism than on providing education or healthcare for the people who live there, for example.
This can be said for other stakeholders of the tourism industry too.
There are a number of independent, franchised or multinational investors who play an important role in the industry. They may own hotels, roads or land amongst other aspects that are important players in the overall success of the tourism industry. Many businesses and individuals will take out loans to help fund their initial ventures.
So investing in tourism is big business, that much is clear. What what are the positive and negative impacts of this?

Positive economic impacts of tourism
So what are the positive economic impacts of tourism? As I explained, most destinations choose to invest their time and money into tourism because of the positive economic impacts that they hope to achieve. There are a range of possible positive economic impacts. I will explain the most common economic benefits of tourism below.

One of the biggest benefits of tourism is the ability to make money through foreign exchange earnings.
Tourism expenditures generate income to the host economy. The money that the country makes from tourism can then be reinvested in the economy. How a destination manages their finances differs around the world; some destinations may spend this money on growing their tourism industry further, some may spend this money on public services such as education or healthcare and some destinations suffer extreme corruption so nobody really knows where the money ends up!
Some currencies are worth more than others and so some countries will target tourists from particular areas. I remember when I visited Goa and somebody helped to carry my luggage at the airport. I wanted to give them a small tip and handed them some Rupees only to be told that the young man would prefer a British Pound!
Currencies that are strong are generally the most desirable currencies. This typically includes the British Pound, American, Australian and Singapore Dollar and the Euro .
Tourism is one of the top five export categories for as many as 83% of countries and is a main source of foreign exchange earnings for at least 38% of countries.
Tourism can help to raise money that it then invested elsewhere by the Government. There are two main ways that this money is accumulated.
Direct contributions are generated by taxes on incomes from tourism employment and tourism businesses and things such as departure taxes.
Taxes differ considerably between destinations. I will never forget the first time that I was asked to pay a departure tax (I had never heard of it before then), because I was on my way home from a six month backpacking trip and I was almost out of money!
Japan is known for its high departure taxes. Here is a video by a travel blogger explaining how it works.
According to the World Tourism Organisation, the direct contribution of Travel & Tourism to GDP in 2018 was $2,750.7billion (3.2% of GDP). This is forecast to rise by 3.6% to $2,849.2billion in 2019.
Indirect contributions come from goods and services supplied to tourists which are not directly related to the tourism industry.
Take food, for example. A tourist may buy food at a local supermarket. The supermarket is not directly associated with tourism, but if it wasn’t for tourism its revenues wouldn’t be as high because the tourists would not shop there.
There is also the income that is generated through induced contributions . This accounts for money spent by the people who are employed in the tourism industry. This might include costs for housing, food, clothing and leisure Activities amongst others. This will all contribute to an increase in economic activity in the area where tourism is being developed.
The rapid expansion of international tourism has led to significant employment creation. From hotel managers to theme park operatives to cleaners, tourism creates many employment opportunities. Tourism supports some 7% of the world’s workers.
There are two types of employment in the tourism industry: direct and indirect.
Direct employment includes jobs that are immediately associated with the tourism industry. This might include hotel staff, restaurant staff or taxi drivers, to name a few.
Indirect employment includes jobs which are not technically based in the tourism industry, but are related to the tourism industry. Take a fisherman, for example. He does not have any contact of dealings with tourists. BUT he does sell his fish to the hotel which serves tourists. So he is indirectly employed by the tourism industry, because without the tourists he would not be supplying the fish to the hotel.
It is because of these indirect relationships, that it is very difficult to accurately measure the economic value of tourism.
It is also difficult to say how many people are employed, directly and indirectly, within the tourism industry.
Furthermore, many informal employments may not be officially accounted for. Think tut tut driver in Cambodia or street seller in The Gambia – these people are not likely to be registered by the state and therefore their earnings are not declared.
It is for this reason that some suggest that the actual economic benefits of tourism may be as high as double that of the recorded figures!
All of the money raised, whether through formal or informal means, has the potential to contribute to the local economy.
If sustainable tourism is demonstrated, money will be directed to areas that will benefit the local community most.
There may be pro-poor tourism initiatives (tourism which is intended to help the poor) or volunteer tourism projects.
The government may reinvest money towards public services and money earned by tourism employees will be spent in the local community. This is known as the multiplier effect.
The multiplier effect relates to spending in one place creating economic benefits elsewhere. Tourism can do wonders for a destination in areas that may seem to be completely unrelated to tourism, but which are actually connected somewhere in the economic system.

Let me give you an example.
A tourist buys an omelet and a glass of orange juice for their breakfast in the restaurant of their hotel. This simple transaction actually has a significant multiplier effect. Below I have listed just a few of the effects of the tourist buying this breakfast.
The waiter is paid a salary- he spends his salary on schooling for his kids- the school has more money to spend on equipment- the standard of education at the school increases- the kids graduate with better qualifications- as adults, they secure better paying jobs- they can then spend more money in the local community…
The restaurant purchases eggs from a local farmer- the farmer uses that money to buy some more chickens- the chicken breeder uses that money to improve the standards of their cages, meaning that the chickens are healthier, live longer and lay more eggs- they can now sell the chickens for a higher price- the increased money made means that they can hire an extra employee- the employee spends his income in the local community…
The restaurant purchase the oranges from a local supplier- the supplier uses this money to pay the lorry driver who transports the oranges- the lorry driver pays road tax- the Government uses said road tax income to fix pot holes in the road- the improved roads make journeys quicker for the local community…
So as you can see, that breakfast that the tourist probably gave not another thought to after taking his last mouthful of egg, actually had the potential to have a significant economic impact on the local community!

The private sector has continuously developed within the tourism industry and owning a business within the private sector can be extremely profitable; making this a positive economic impact of tourism.
Whilst many businesses that you will come across are multinational, internationally-owned organisations (which contribute towards economic leakage ).
Many are also owned by the local community. This is the case even more so in recent years due to the rise in the popularity of the sharing economy and the likes of Airbnb and Uber, which encourage the growth of businesses within the local community.
Every destination is different with regards to how they manage the development of the private sector in tourism.
Some destinations do not allow multinational organisations for fear that they will steal business and thus profits away from local people. I have seen this myself in Italy when I was in search of a Starbucks mug for my collection , only to find that Italy has not allowed the company to open up any shops in their country because they are very proud of their individually-owned coffee shops.
Negative economic impacts of tourism
Unfortunately, the tourism industry doesn’t always smell of roses and there are also several negative economic impacts of tourism.
There are many hidden costs to tourism, which can have unfavourable economic effects on the host community.
Whilst such negative impacts are well documented in the tourism literature, many tourists are unaware of the negative effects that their actions may cause. Likewise, many destinations who are inexperienced or uneducated in tourism and economics may not be aware of the problems that can occur if tourism is not management properly.
Below, I will outline the most prominent negative economic impacts of tourism.

Economic leakage in tourism is one of the major negative economic impacts of tourism. This is when money spent does not remain in the country but ends up elsewhere; therefore limiting the economic benefits of tourism to the host destination.
The biggest culprits of economic leakage are multinational and internationally-owned corporations, all-inclusive holidays and enclave tourism.
I have written a detailed post on the concept of economic leakage in tourism, you can take a look here- Economic leakage in tourism explained .

Another one of the negative economic impacts of tourism is the cost of infrastructure. Tourism development can cost the local government and local taxpayers a great deal of money.
Tourism may require the government to improve the airport, roads and other infrastructure, which are costly. The development of the third runway at London Heathrow, for example, is estimated to cost £18.6billion!
Money spent in these areas may reduce government money needed in other critical areas such as education and health, as I outlined previously in my discussion on opportunity costs.

One of the most obvious economic impacts of tourism is that the very presence of tourism increases prices in the local area.
Have you ever tried to buy a can of Coke in the supermarket in your hotel? Or the bar on the beachfront? Walk five minutes down the road and try buying that same can in a local shop- I promise you, in the majority of cases you will see a BIG difference In cost! (For more travel hacks like this subscribe to my newsletter – I send out lots of tips, tricks and coupons!)
Increasing demand for basic services and goods from tourists will often cause price hikes that negatively impact local residents whose income does not increase proportionately.
Tourism development and the related rise in real estate demand may dramatically increase building costs and land values. This often means that local people will be forced to move away from the area that tourism is located, known as gentrification.
Taking measures to ensure that tourism is managed sustainably can help to mitigate this negative economic impact of tourism. Techniques such as employing only local people, limiting the number of all-inclusive hotels and encouraging the purchasing of local products and services can all help.
Another one of the major economic impacts of tourism is dependency. Many countries run the risk of becoming too dependant on tourism. The country sees $ signs and places all of its efforts in tourism. Whilst this can work out well, it is also risky business!
If for some reason tourism begins to lack in a destination, then it is important that the destination has alternative methods of making money. If they don’t, then they run the risk of being in severe financial difficulty if there is a decline in their tourism industry.
In The Gambia, for instance, 30% of the workforce depends directly or indirectly on tourism. In small island developing states, percentages can range from 83% in the Maldives to 21% in the Seychelles and 34% in Jamaica.
There are a number of reasons that tourism could decline in a destination.
The Gambia has experienced this just recently when they had a double hit on their tourism industry. The first hit was due to political instability in the country, which has put many tourists off visiting, and the second was when airline Monarch went bust, as they had a large market share in flights to The Gambia.
Other issues that could result in a decline in tourism includes economic recession, natural disasters and changing tourism patterns. Over-reliance on tourism carries risks to tourism-dependent economies, which can have devastating consequences.

The last of the negative economic impacts of tourism that I will discuss is that of foreign ownership and management.
As enterprise in the developed world becomes increasingly expensive, many businesses choose to go abroad. Whilst this may save the business money, it is usually not so beneficial for the economy of the host destination.
Foreign companies often bring with them their own staff, thus limiting the economic impact of increased employment. They will usually also export a large proportion of their income to the country where they are based. You can read more on this in my post on economic leakage in tourism .
As I have demonstrated in this post, tourism is a significant economic driver the world over. However, not all economic impacts of tourism are positive. In order to ensure that the economic impacts of tourism are maximised, careful management of the tourism industry is required.
If you enjoyed this article on the economic impacts of tourism I am sure that you will love these too-
- Environmental impacts of tourism
- The 3 types of travel and tourism organisations
- 150 types of tourism! The ultimate tourism glossary
- 50 fascinating facts about the travel and tourism industry
- 23 Types of Water Transport To Keep You Afloat
Liked this article? Click to share!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Given tourism's capacity as an instrument of economic development (Cárdenas-García et al., 2015), distinct institutions such as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, the ...
Tourism has become the world's third-largest export industry after fuels and chemicals, and ahead of food and automotive products. From last few years, there has been a great surge in international tourism, culminates to 7% share of World's total exports in 2016. To this end, the study attempts to examine the relationship between inbound tourism, financial development and economic growth ...
Z32 Tourism and Development. Tourism and Economic Development: Evidence from Mexico's Coastline by Benjamin Faber and Cecile Gaubert. Published in volume 109, issue 6, pages 2245-93 of American Economic Review, June 2019, Abstract: Tourism is a fast-growing services sector in developing countries.
After the publication of a significant number of papers analyzing the tourism-led growth hypothesis (TLGH), a new line has arisen within the scientific literature, which attempts to analyze the capacity of tourism as an instrument of economic development, given that this concept has been widely linked to both economic aspects and socio-economic conditions of the resident population.
Cluster 2 is certainly the most heterogeneous among all. Keywords' net suggests a connection between 'economic development' and 'tourism development' and potential negative externalities which governments have to take into account whenever they decide to invest in the tourism sector to boost the economic growth of their countries.
Tourism contributes significantly to economic growth all over the world (Figini & Vici, Citation 2010), has a strong impact on the environment (Hall, Citation 2011), facilitates, when practiced responsibly, sustainable development, and has a remarkable contribution to progress, since there is an overlap between economically developed countries ...
In tourism and regional development, there is only a handful of articles relating to regional economic development and tourism. The so-called tourism led growth hypothesis. Most of these studies are based on the regional growth models in the neoclassical framework first developed by Borts (1960) .
Background. Tourism is one of the world's largest industries, and it has linkages with many of the prime sectors of the global economy (Fennell, 2020).As a global economic sector, tourism represents one of the largest generators of wealth, and it is an important agent of economic growth and development (Garau-Vadell et al., 2018).Tourism is a critical industry in many local and national ...
Economic impact. Much work on tourism development focuses on the economic benefits to host destinations, including increased income, taxes, employment, and economic diversification and regeneration. Tourism, as an economic activity, is being used to help support or bolster an economy and regional development. Tourist spending is a prime source ...
to foster local economic development in economically lagging regions within countries.2 At the same time, much of the existing social sciences literature on tourism has been critical about its long-term economic consequences, especially in developing countries. 3 For example,Honey(1999)
ABSTRACT. Tourism has long been explored through the lens of development theory. David Harrison was one of the earlier academics to do so, subsequently turning his attention to critiquing the relevance of such theory to tourism, concluding that although much tourism research has been framed within it, development theory has contributed little if anything to knowledge and understanding of the ...
10 Nov 2023. Tourism has again been identified as a key driver of economic recovery and growth in a new report by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). With UNWTO data pointing to a return to 95% of pre-pandemic tourist numbers by the end of the year in the best case scenario, the IMF report outlines the positive impact the sector's rapid ...
This study is aimed to fill an existing gap in the empirical literature by exploring the effect of tourism on sustainable economic development across Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) countries. BRI is one of the paramount global partnerships as it covers more than 60 percent of the global population and 30 percent of the world's GDP. Using data from 57 nations over the period of 2000-2018 ...
In the first part, we provide empirical evidence on the local effects of tourism on current-day municipality-level population, employment, local GDP by sector, and Mincerized wages. Tourism in Mexico has had more than half a century to materialize into today's observed distribution of regional economic outcomes.
This article surveys the literature on tourism and economic development, identifying the contribution that tourism can make to development, including foreign currency, income and employment, and the costs that it entails. Single equation and system of equations models for estimating tourism demand are provided, indicating developing countries' potential to benefit from increasing expenditure ...
Tourism Economics is an international peer reviewed journal, covering the business aspects of tourism in the wider context. It takes account of constraints on development, such as social and community interests and the sustainable use of tourism and recreation resources, and inputs into the production process.
According to the data provided by international institutions such as the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism is one of the fundamental bases for global socio-economic development ...
In order to find out more about the channels through which tourism influences economic growth we augment regression A4 by variables used in the Copeland (1991) and the Chao et al. (2006) models that explain the relationship between tourism dependency and economic development. Moreover this task can be seen as a sensitivity analysis to the growth model above.
The development of tourism reallocates factors of production towards services activities, such as gastronomy and hotels, and away from traded sector production with higher potential for agglomeration forces and productivity growth. In this view, tourism could therefore give rise to adverse economic effects in the long run. Tourism in Mexico
Contribution to government revenues. Employment generation. Contribution to local economies. Development of the Private Sector. Negative economic impacts of tourism. Leakage. Infrastructure cost. Increase in prices. Economic dependence of the local community on tourism.
M. Thea Sinclair. This article surveys the literature on tourism and economic development, identifying the contribution that tourism can make to development, including foreign currency, income and employment, and the costs that it entails. Single equation and system of equations models for estimating tourism demand are provided, indicating ...
A research model using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and a multivariate regression analysis was constructed to measure the impact of different sets of attractions on the growth of the tourism industry and regional economic development. Appropriate tests for homoscedasticity, multi-collinearity, and the normality of residuals were performed.
Tourism and Economic Development. All About Cottonwood. Cottonwood, Arizona is The Heart of Arizona Wine Country. Located in Arizona's Verde Valley, this charming community is home to approximately 12,573 residents and serves a greater Verde Valley population of about 40,000. Its 3,300-foot-elevation, mild climate, and natural amenities, such ...