

Travel Past Tense
Commonwealth travelled, US traveled past tense of travel is Commonwealth travelled, US traveled.
Travel verb forms
Conjugation of travel.
- What is the past tense of tup in English?
- What is the second form of verb TUPE?
- What is the third form of verb turbanize in English?
- What is the conjugation of turbinate in English?
- Conjugate turbocharge in English?
- turkey-trot
PastTenses is a database of English verbs. One can check verbs forms in different tenses. Use our search box to check present tense, present participle tense, past tense and past participle tense of desired verb.
Conjugation verb travel
Model : cancel
Auxiliary : have , be
Other forms: travel oneself / not travel
Contractions
in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings
The verb has several variants of conjugation, which may correspond to different meanings. Please use the menu to select one or all variants.
- he/she/it travels
- they travel
- I travelled/traveled
- you travelled/traveled
- he/she/it travelled/traveled
- we travelled/traveled
- they travelled/traveled
Present continuous
- I am travelling/traveling
- you are travelling/traveling
- he/she/it is travelling/traveling
- we are travelling/traveling
- they are travelling/traveling
Present perfect
- I have travelled/traveled
- you have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it has travelled/traveled
- we have travelled/traveled
- they have travelled/traveled
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he/she/it will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Future perfect
- I will have travelled/traveled
- you will have travelled/traveled
- he/she/it will have travelled/traveled
- we will have travelled/traveled
- they will have travelled/traveled
Past continous
- I was travelling/traveling
- you were travelling/traveling
- he/she/it was travelling/traveling
- we were travelling/traveling
- they were travelling/traveling
Past perfect
- I had travelled/traveled
- you had travelled/traveled
- he/she/it had travelled/traveled
- we had travelled/traveled
- they had travelled/traveled
Future continuous
- I will be travelling/traveling
- you will be travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will be travelling/traveling
- we will be travelling/traveling
- they will be travelling/traveling
Present perfect continuous
- I have been travelling/traveling
- you have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it has been travelling/traveling
- we have been travelling/traveling
- they have been travelling/traveling
Past perfect continuous
- I had been travelling/traveling
- you had been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it had been travelling/traveling
- we had been travelling/traveling
- they had been travelling/traveling
Future perfect continuous
- I will have been travelling/traveling
- you will have been travelling/traveling
- he/she/it will have been travelling/traveling
- we will have been travelling/traveling
- they will have been travelling/traveling
- let's travel
- travelling/traveling
- travelled/traveled
Perfect participle
- having travelled/traveled
Helping millions of people and large organizations communicate more efficiently and precisely in all languages.
Online Language Dictionaries
Perfect tenses, continuous (progressive) and emphatic tenses, compound continuous (progressive) tenses, conditional, subjunctive.
*Blue letters in conjugations are irregular forms. ( example ) *Red letters in conjugations are exceptions to the model. ( example )
Report a problem.

Past Tense of Travel: Traveling Back in Time
By: Author Oliver
Posted on Last updated: August 12, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Welcome to our article on the past tense of travel! If you’re learning English grammar, you know that understanding verb tenses is an essential part of the language. The past tense is particularly important, as it allows us to talk about events and experiences that have already happened. In this article, we’ll explore the basics of English tenses, give an overview of the past tense, and focus specifically on how to use the past tense when talking about travel.
Travel is one of the most common topics of conversation, and being able to talk about past trips is a great way to connect with others and share experiences. However, using the past tense correctly can be tricky, especially when it comes to irregular verbs and complex sentence structures. In this article, we’ll provide plenty of examples and exercises to help you master the past tense of travel. We’ll also cover some common mistakes to avoid and provide additional resources for further learning.
So whether you’re planning your next trip or just want to improve your English skills, read on to learn everything you need to know about the past tense of travel!
Key Takeaways
- The past tense is essential for talking about past events and experiences, past tense of ‘travel’ is ‘traveled’
- By practicing with examples and exercises, you can improve your use of the past tense of travel and avoid common mistakes.

Past Tense of Travel
Travel is a verb that is commonly used in the past tense. In this section, we will cover the formation and usage examples of the past tense of travel.
To form the past tense of travel, we add “-ed” to the base form of the verb. For example:
- I traveled to Europe last summer.
- She traveled to Asia for business.
- We traveled to South America for vacation.
Simple Past
The simple past is used to describe a completed action in the past. Regular verbs like travel are formed by adding -ed to the base form. For example:
- I traveled to Paris last year.
Past Continuous
The past continuous is used to describe an action that was in progress at a specific point in the past. It is formed by using the past tense of “to be” (was/were) and the present participle (-ing) of the main verb. Here are some examples:
- I was traveling to Paris when I got a call from my boss.
Usage Examples
The past tense of travel is used to talk about a completed action in the past. Here are some examples:
- I traveled to Japan last year and had an amazing time.
- She traveled to Italy for her honeymoon and fell in love with the country.
- We traveled to Mexico for our anniversary and enjoyed the beautiful beaches.
We can also use the past tense of travel to talk about a past habit or routine. For example:
- When I was younger, I traveled to different countries every summer.
- She traveled for work every week and got used to living out of a suitcase.
- We traveled to visit our family every holiday season.
In conclusion, the past tense of travel is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb and is used to talk about completed actions or past habits. Practice using the past tense of travel in your own sentences to improve your English grammar skills.
Common Mistakes with Past Tense of Travel
If you are learning English, you might be struggling with the past tense of the verb “travel.” Here are some common mistakes people make and how to avoid them.
Mixing Past and Present Tenses
One of the most common mistakes is mixing past and present tenses. For example, saying “I travel to Paris last year” instead of “I traveled to Paris last year.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Present Participle
Another mistake is using the present participle instead of the past tense. For example, saying “I am traveling to London last week” instead of “I traveled to London last week.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the past tense of “travel” when referring to something that happened in the past.
Using the Wrong Auxiliary Verb
Using the wrong auxiliary verb is also a common mistake. For example, saying “I was travel to Rome” instead of “I traveled to Rome.” To avoid this mistake, remember to use the correct auxiliary verb (in this case, “did”) when forming the past tense.
Example Sentences
Here are some example sentences to help you practice using the past tense of “travel” correctly:
- I traveled to Japan last summer.
- She visited her grandparents in Florida last month.
- They took a road trip across the United States.
- We flew to Paris for our honeymoon.
- He backpacked through Europe after college.
Remember, practice makes perfect! Keep practicing using the past tense of “travel” correctly, and soon it will become second nature.
Exercises to Practice Past Tense of Travel
Learning English grammar can be challenging, especially when it comes to mastering the past tense of travel. To help you improve your skills, we have compiled a list of exercises that you can use to practice and perfect your past tense of travel.
Interactive Exercises
Interactive exercises are a great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to engage with the material and receive immediate feedback on your progress. Here are a few interactive exercises you can try:
- Fill in the Blank: In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a blank space where the past tense verb should go. Your task is to fill in the blank with the correct past tense verb. For example, “I ___ to Paris last year.” The correct answer would be “went.”
- Matching: In this exercise, you will be given a list of past tense verbs and a list of travel-related words. Your task is to match the past tense verb with the correct travel-related word. For example, “flew” would match with “airplane.”
Written Exercises
Written exercises are another great way to practice the past tense of travel. They allow you to focus on the material and practice at your own pace. Here are a few written exercises you can try:
- Sentence Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a travel-related word, and your task is to write a sentence using the correct past tense verb. For example, “train” could be used in the sentence, “I ___ to New York on a train.”
- Paragraph Writing: In this exercise, you will be given a prompt related to travel, and your task is to write a paragraph using the correct past tense verbs. For example, “Write a paragraph about your last vacation.” You could write, “Last summer, I ___ to Hawaii with my family. We ___ on the beach, ___ in the ocean, and ___ at some amazing restaurants.”
By practicing these exercises, you will improve your understanding and mastery of the past tense of travel. Keep practicing, and before you know it, you’ll be a pro at English grammar!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the past tense of travel?
The past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second “l” in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?
As mentioned above, both spellings are correct. The difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English.
Which is correct travel or travelling?
Both “travel” and “travelling” are correct, but “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
What’s the difference between travel and Travelled?
“Travel” is the present tense of the verb, while “travelled” is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
What is the V2 form of travel?
The V2 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
What is the V3 form of travel?
The V3 form of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is “traveled” in American English and “travelled” in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, “traveling” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “travelling” is the preferred spelling in British English.
The past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, but American English tends to drop the second \"l\" in the past tense and past participle forms of the verb.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Is it spelled Travelled or traveled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Which is correct travel or travelling?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Both \"travel\" and \"travelling\" are correct, but \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What's the difference between travel and Travelled?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
\"Travel\" is the present tense of the verb, while \"traveled\" is the past tense. The difference between the two is the time frame in which the action occurs.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V2 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V2 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the V3 form of travel?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The V3 form of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English.
In summary, the past tense of travel is \"traveled\" in American English and \"travelled\" in British English. Both spellings are correct, and the difference in spelling is due to the variation in American and British English. Additionally, \"traveling\" is the preferred spelling in American English, while \"travelling\" is the preferred spelling in British English.
- Recent Posts
- Plural of Safe: What It Is and How to Use It Correctly - October 3, 2023
- Purple Color Names: Different Hues of Purple - October 2, 2023
- Addition Transition Words for Clear and Cohesive Writing - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- Past Tense of Buy: How to Use them Correctly in English Grammar
- Mastering English Grammar: The Definitive Guide to Understanding the Past Tense of Cost
- Past Tense of Drag: Dragged Through Time
- Hoped or Hoped For? Mastering the Past Tense of Hope with Ease
To support our work, we invite you to accept cookies or to subscribe.
You have chosen not to accept cookies when visiting our site.
The content available on our site is the result of the daily efforts of our editors. They all work towards a single goal: to provide you with rich, high-quality content. All this is possible thanks to the income generated by advertising and subscriptions.
By giving your consent or subscribing, you are supporting the work of our editorial team and ensuring the long-term future of our site.
If you already have purchased a subscription, please log in
How to conjugate "to travel" in English?
English "to travel" conjugation.
- traveled; travelled
Full conjugation of "to travel"
Translations for "to travel", present continuous, simple past, past continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, conditional present, conditional present progressive, conditional perfect, conditional perfect progressive, subjunctive, present subjunctive, past subjunctive, past perfect subjunctive, present participle, past participle.
Translations for "to travel" in our English dictionaries
Popular English verbs
Find out the most frequently used verbs in English.
Social Login
Here are the past tense forms of the verb travel
👉 Forms of verb travel in future and past simple and past participle. ❓ What is the past tense of travel.
Travel: Past, Present, and Participle Forms
What are the 2nd and 3rd forms of the verb travel.
🎓 What are the past simple, future simple, present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect forms of the base form (infinitive) ' travel '? 👉 It's quite simple -->
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'
- the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses.
- the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense.
- the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
What are the past tense and past participle of travel?
What is the past tense of travel.
The past tense of the verb "travel" is "travelled (BrE)", or "traveled (AmE)", and the past participle is "travelled (BrE)" or "traveled (AmE)".
Verb Tenses
Past simple — travel in past simple travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (V2) . Future simple — travel in future simple is travel (will + V1) . Present Perfect — travel in present perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (have/has + V3) . Past Perfect — travel in past perfect tense is travelled (BrE), traveled (AmE) (had + V3) .
travel regular or irregular verb?
👉 Is 'travel' a regular or irregular verb? The verb 'travel' is regular verb .
Examples of Verb travel in Sentences
- These days we travelled 1400 km (Past Simple)
- We didn't travel that long (Past Simple)
- She has travelled extensively in the Philippines (Present Perfect)
- I can't travel without you (Present Simple)
- We usually travel to work by bus (Present Simple)
- A plane travels faster than a train (Present Simple)
- They are travelling together since 2018 (Present Continuous)
- You can travel by foot, why not? (Present Simple)
- Unfortunately you can't travel without a ticket, so please proceed to the ticket office (Present Simple)
- How many countries have you travelled to? (Present Perfect)
Along with travel, words are popular give and tell .
Verbs by letter: r , d , u , c , m , p , b , w , h , a , e , g , s , q , j , l , t , f , o , n , k , i , v , y , z .
English verbs
- 318 Irregular verbs
- 904 Regular verbs
- 5 Modal verbs
- 407 Phrasal verb
Online verb dictionary
We are currently working to add new verbs and examples to our website, along with detailed descriptions. Please send us a message if you have any requests or suggestions, and we will add them as quickly as we can. Thank you for your interest in our website!
our editor - Peter (Certified TEFL Tutor with over 8 years experience)
Have a question or find mistake?
- Slovenščina
- FAQ Technical Questions
- Text Translation
- Vocabulary Trainer
- Online Dictionary
- Login
- Online dictionary
- Products & Shop
- Conjugation
- Vocabulary trainer
- Dictionary API
- Add to home screen
- Browse the dictionaries
- Terms and conditions of use
- Supply chain
- Data Protection Declaration
- Legal notice
- Privacy Settings
- EN');"> English
- FR');"> French
- DE');"> German
- LA');"> Latin
- ES');"> Spanish
Verb Table for travel
- Simple tenses
- Continuous tenses
Conditional
Simple tenses • continuous tenses • conditional • imperative • impersonal, present perfect, past perfect, will -future, going to -future, future perfect, conditional past, past participle, browse the conjugations (verb tables), look up "travel" in other languages, links to further information.
You can suggest improvements to this PONS entry here:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
My search history
- Most popular
- English ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ French
- German ⇄ Greek
- German ⇄ Polish
- Arabic ⇄ English
- Arabic ⇄ German
- Bulgarian ⇄ English
- Bulgarian ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ English
- Chinese ⇄ French
- Chinese ⇄ German
- Chinese ⇄ Spanish
- Croatian ⇄ German
- Czech ⇄ German
- Danish ⇄ German
- Dutch ⇄ German
- Elvish ⇄ German
- English ⇄ Arabic
- English ⇄ Bulgarian
- English ⇄ Chinese
- English ⇄ French
- English ⇄ Italian
- English ⇄ Polish
- English ⇄ Portuguese
- English ⇄ Russian
- English → Serbian
- English ⇄ Spanish
- Finnish ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Chinese
- French ⇄ English
- French ⇄ German
- French ⇄ Italian
- French ⇄ Polish
- French ⇄ Slovenian
- French ⇄ Spanish
- German ⇄ Arabic
- German ⇄ Bulgarian
- German ⇄ Chinese
- German ⇄ Croatian
- German ⇄ Czech
- German ⇄ Danish
- German ⇄ Dutch
- German ⇄ Elvish
- German ⇄ English
- German ⇄ Finnish
- German ⇄ Hungarian
- German → Icelandic
- German ⇄ Italian
- German ⇄ Japanese
- German ⇄ Latin
- German ⇄ Norwegian
- German ⇄ Persian
- German ⇄ Portuguese
- German ⇄ Romanian
- German ⇄ Russian
- German → Serbian
- German ⇄ Slovakian
- German ⇄ Slovenian
- German ⇄ Swedish
- German ⇄ Turkish
- Dictionary of German Spelling
- Greek ⇄ German
- Hungarian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ English
- Italian ⇄ French
- Italian ⇄ German
- Italian ⇄ Polish
- Italian ⇄ Slovenian
- Italian ⇄ Spanish
- Japanese ⇄ German
- Latin ⇄ German
- Norwegian ⇄ German
- Persian ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ English
- Polish ⇄ French
- Polish ⇄ German
- Polish ⇄ Italian
- Polish ⇄ Russian
- Polish ⇄ Spanish
- Portuguese ⇄ English
- Portuguese ⇄ German
- Portuguese ⇄ Spanish
- Romanian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ English
- Russian ⇄ German
- Russian ⇄ Polish
- Slovakian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ English
- Slovenian ⇄ French
- Slovenian ⇄ German
- Slovenian ⇄ Italian
- Slovenian ⇄ Spanish
- Spanish ⇄ Chinese
- Spanish ⇄ English
- Spanish ⇄ French
- Spanish ⇄ German
- Spanish ⇄ Italian
- Spanish ⇄ Polish
- Spanish ⇄ Portuguese
- Spanish ⇄ Slovenian
- Swedish ⇄ German
- Turkish ⇄ German
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->

Select your English level
To personalize your experience.
- To Travel Conjugation
In the US the spelling 'traveling' and 'traveled' are preferred.
Continuous Perfect
Conditional.
We notice you're using an ad blocker.
Linguasorb is free and ad supported, without ad revenue we can't exist. Certain features such as audio, directly cost us money and so are disabled for ad block users.
Please disable your ad blocker for this site if you wish to use the premium features.
Alternatively you can become a supporter and remove the ads completely .
Onlymyenglish.com
Learn English
Travel Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Table of Contents
Travel past tense
Travel past participle, travel verb forms v1 v2 v3 v4, conjugation of travel, more verb past tense, you might also like.

Identify Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Welcome Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Get Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

See Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Itch Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3

Press Verb Forms – Past Tense, Past Participle & V1V2V3
Conjugation English verb to travel
Simple present, present progressive/continuous, simple past, past progressive/continuous, present perfect simple, present perfect progressive/continuous, past perfect, past perfect progressive/continuous, future progressive/continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous, conditional, progressive, perfect progressive, translation to travel.
Verb "travel"
For the settings to take effect, you must restart the trainer Restart
Conjugation
Simple tense.
Present Simple
- he, she travels
- they travel
Past Simple
- I traveled ; travelled
- you traveled ; travelled
- he, she traveled ; travelled
- we traveled ; travelled
- they traveled ; travelled
Future Simple
- I will travel
- you will travel
- he, she will travel
- we will travel
- they will travel
Continuous Tense
Present Simple Continuous
- I am traveling ; travelling
- you are traveling ; travelling
- he, she is traveling ; travelling
- we are traveling ; travelling
- they are traveling ; travelling
Past Simple Continuous
- I was traveling ; travelling
- you were traveling ; travelling
- he, she was traveling ; travelling
- we were traveling ; travelling
- they were traveling ; travelling
Future Simple Continuous
- I will be traveling ; travelling
- you will be traveling ; travelling
- he, she will be traveling ; travelling
- we will be traveling ; travelling
- they will be traveling ; travelling
Perfect Tense
Present Perfect
- I have traveled ; travelled
- you have traveled ; travelled
- he, she has traveled ; travelled
- we have traveled ; travelled
- they have traveled ; travelled
Past Perfect
- I had traveled ; travelled
- you had traveled ; travelled
- he, she had traveled ; travelled
- we had traveled ; travelled
- they had traveled ; travelled
Future Perfect
- I will have traveled ; travelled
- you will have traveled ; travelled
- he, she will have traveled ; travelled
- we will have traveled ; travelled
- they will have traveled ; travelled
Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Continuous
- I have been traveling ; travelling
- you have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she has been traveling ; travelling
- we have been traveling ; travelling
- they have been traveling ; travelling
Past Perfect Continuous
- I had been traveling ; travelling
- you had been traveling ; travelling
- he, she had been traveling ; travelling
- we had been traveling ; travelling
- they had been traveling ; travelling
Future Perfect Continuous
- I will have been traveling ; travelling
- you will have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she will have been traveling ; travelling
- we will have been traveling ; travelling
- they will have been traveling ; travelling
Conditional
- I would travel
- you would travel
- he, she would travel
- we would travel
- they would travel
- I would have traveled ; travelled
- you would have traveled ; travelled
- he, she would have traveled ; travelled
- we would have traveled ; travelled
- they would have traveled ; travelled
Present Continuous
- I would be traveling ; travelling
- you would be traveling ; travelling
- he, she would be traveling ; travelling
- we would be traveling ; travelling
- they would be traveling ; travelling
Perfect Continuous
- I would have been traveling ; travelling
- you would have been traveling ; travelling
- he, she would have been traveling ; travelling
- we would have been traveling ; travelling
- they would have been traveling ; travelling
- we Let's travel
Other verbs
Be the first to comment.
Add comment
- English Tense Converter
- Basic English
- Parts of speech
- Daily tasks
- Verb of the day
- Quiz of the day
- Top 500 verbs list
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and conditions

Simple past tense of Travel | ltsenglish.com
Travel verb forms, simple past tense of travel.

© Copyright 2020 ltsenglish.com

'travel' conjugation table in English
Past participle, present participle, present continuous, present perfect, present perfect continuous, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous, future continuous, future perfect, future perfect continuous.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

All ENGLISH words that begin with 'T'
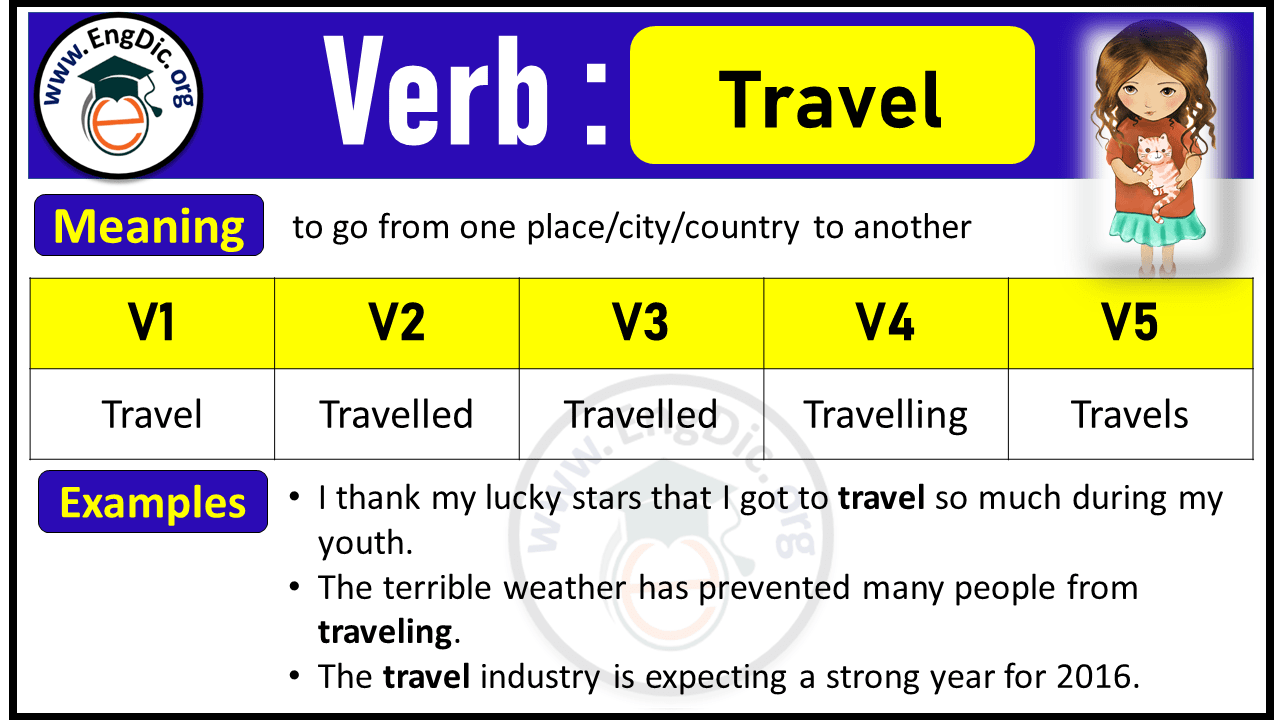
Travel Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Meaning: to go from one place/city/country to another
Table of Contents

Travel Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
Travel past tense:.
Past Tense of Travel is Traveled .
Example: Sarah Traveled by Train.
Travel Past Participle:
Past Participle Form of Travel is Traveled .
Example: Sarah has Traveled by Train.
Travel Present Participle:
Present Participle Form of Travel is Travelling .
Example: Sarah is Travelling by Train.
Travel 3rd Person Singular:
3rd Person Singular of Travel is Travels .
Example: Sarah Travels by Train.
Travel Conjugation
Indefinite / simple present tense.
- I Travel by Train.
- We/You/They Travel by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam Travels by Train.
Present Continuous Tense
- I am Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They are Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam is Travelling by Train.
Present Perfect Tense
- I have Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They have Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam has Traveled by Train.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- I have been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They have been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam has been Travelling by Train.
Indefinite / Simple Past Tense
- I Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam Traveled by Train.
Past Continuous Tense
- I was Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They were Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam was Travelling by Train.
Past Perfect Tense
- I had Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They had Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam had Traveled by Train.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- I had been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They had been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam had been Travelling by Train.
Indefinite / Simple Future Tense
- I will Travel by Train.
- We/You/They will Travel by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will Travel by Train.
Future Continuous Tense
- I will be Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They will be Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will be Travelling by Train.
Future Perfect Tense
- I will have Traveled by Train.
- We/You/They will have Traveled by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will have Traveled by Train.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- I will have been Travelling by Train.
- We/You/They will have been Travelling by Train.
- He/She/It/Adam will have been Travelling by Train.
Past Tense of Travel Phrasal Verbs
Explore Other Verb Forms:
What is the Future Tense of Travel?
Future Tense of Travel is “ will Travel” .
What is the Present Tense of Travel?
Present Tense of Travel is “ Travel + s/es or ing” .
What is the Past Perfect Tense of Travel?
Past perfect tense of take is “ had Traveled ”.
Last updated on May 24th, 2023 at 02:22 am
Related Posts

Submit Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

Oppress Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Fall Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
Saponify Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

Sprout Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)

Subscribe Verb Forms: Past Tense and Past Participle (V1 V2 V3)
About the author.
Hi, I'm USMI, engdic.org's Author & Lifestyle Linguist. My decade-long journey in language and lifestyle curation fuels my passion for weaving words into everyday life. Join me in exploring the dynamic interplay between English and our diverse lifestyles. Dive into my latest insights, where language enriches every aspect of living.
- English Grammar
Level: intermediate
There are two tenses in English – past and present.
The past tense in English is used:
- to talk about the past
- to talk about hypotheses (when we imagine something)
- for politeness .
There are four past tense forms in English:
We use these forms:
- to talk about the past :
He worked at McDonald's. He had worked there since July. He was working at McDonald's. He had been working there since July.
- to refer to the present or future in hypotheses :
It might be dangerous. Suppose they got lost.
This use is very common in wishes:
I wish it wasn't so cold.
and in conditions with if :
He could get a new job if he really tried . If Jack was playing , they would probably win.
For hypotheses, wishes and conditions in the past, we use the past perfect:
It was very dangerous. What if you had got lost? I wish I hadn't spent so much money last month. I would have helped him if he had asked .
and also to talk about the present in a few polite expressions :
Excuse me, I was wondering if this was the train for York. I just hoped you would be able to help me.
MultipleChoice_MTYzMjA=
GapFillTyping_MTYzMjE=
Hi Jonathan, Thanks so much for your super clear explanation. I give you below the complete paragraph written in my book : Quote : A) He had served in the army for ten years; then he retired and married. His children were now at school.
Note : If we put the last verb in this sentence into the present tense, the other tenses will change to the simple past :
B) He served in the army for ten years; then he retired and married. His children are now at school. Unquote.
Questions : 1) From the whole paragraph above, would you interpret that the use of "were now" in A refers to the past, or to "currently/at this present moment" just like "are now" in B ?
2) If "were now" in A bears the same meaning as "are now" in B (meaning "currently"), I think we can change "were" in A to "are", but why do the authors give a special note saying that if we change "were" in A with "are", the past perfect will change to the past tense ? What is the reason?
Jonathan, please help me clarify this issue. I'd appreciate your detailed explanation.
Best regards,
- Log in or register to post comments
Hi melvinthio,
1) Yes, I still think "were now" is describing the past. The meaning of "now" in this example is "used in stories or reports of past events to describe a new situation or event" (source: Cambridge Dictionary - note the emphasis on past events).
2) As mentioned above, I don't think it has the same meaning as "are now". The books seems to be changing the verb into the present tense just as an exercise, or to illustrate how verb tense choices are connected to other ones within the same text. It isn't trying to say that the meaning stays the same.
About the use of the past perfect in A) but not in B). The reason is that A's focal time is the past (as shown by "were now") and B's focal time is the present ("are now"). It is grammatically possible to use the past perfect "had served in the army" in B) as well - however, then there would be four verbs ( had served / retired and married / are now ) moving from past perfect to past to present in very quick succession. This would make the timeframe of the narrative jump forward very quickly from the past to the present, and this is not conventionally done.
Additionally, when it is logically obvious that one past action happened before the other (e.g. ""had served in the army" must logically happen before "retired"), people often simplify the past perfect to the past simple.
I hope that helps.
LearnEnglish team
Hi Peter, Thanks for your reply. I've noticed the following example in my grammar book published by OUP:
"He had served in the army for ten years; then he retired and married. His children were now at school".
Questions: 1) Is it grammatically correct if we replace "were" with "are" in the last sentence (His children are now at school) ?
2) If yes, which one sounds more natural using "are" or "were" ?
3) From the point of grammar, if we write a past story, apart from using the past perfect tense, should we put all the other verbs into the past tense as a default to be consistent although for situations still true in the present ?
I'd highly appreciate your detailed explanation.
I'll try to help.
1) Yes, it is. However, "His children are now at school" is about the present. I suspect that "His children were now at school" is about the past, even though it says "now". The word "now" is sometimes used in past narratives to show a jump forward in the focal time of the narrative, or highlight a change in circumstances, as in this example which jumps forward from his time in the army to the time of his retirement and marriage (still in the past).
2) Both sound natural but as explained above, their meanings differ.
3) Generally, yes. Especially if you are writing a factual and objective past story, this would be the norm. However, story writing may not follow fixed rules like this, so that story writers can convey their ideas to the reader better. For example, story writers commonly use present tenses for story events in order to give the reader a stronger sense of how the character is experiencing and reacting (see Present tense , advanced level section for an example of this), even though those story events happened in the past in the overall timeframe.
Hi Peter, Thanks for your explanation. For my previous two sentences (in 2a and 2b) in the past tense : "there were 3 children in my family" and "my parents had 3 children", I assume they can be used if I tell a past story. e.g. "When we were kids, my parents worked very hard as there were 3 children in our family. They had 3 children while our neighbours had only one or two".
(1) Is it right to use the two sentences in the past tense in the above story ?
(2) In your previous answer to my 2a question, you said "If you say 'There are....' then the listener would understand that all are still alive". Interestingly, I noticed that you used "would" in the first conditional sentence. Please help explain in what situation we can use this type of mixed conditional (the use of "WOULD" in the first conditional) and if possible, please give me some more examples to help me get it more clearly.
I'd highly appreciate your detailed explanations. Best regards,
Hello melvinthio,
(1) Yes, that's fine. Your example is correct.
(2) It's not a standard form, I'm afraid. Native speakers sometimes mix up forms in non-standard ways and this is a sentence which, strictly speaking, is not internally consistent. A better construction would be If you said... a listener would...
The LearnEnglish Team
Hi Peter, I've seen the following sentence : - His father was the second of four children in his family (The use of the past is due to the fact that they're not children anymore now).
My questions:
(1) Can we say this sentence although his father is still alive ?
I have two siblings in my family. We're all adults now and my parents are still alive.
(2) In this case, which one should I say ? Or either the past or the present is grammatically correct ?
a) There were (or are) 3 children in my family.
b) My parents had (or have) 3 children.
I'd appreciate your clear explanation. Thanks. Best regards,
Hi melvinthio,
1) Yes, you can say the sentence even though the father is still alive. As you say, he is no longer a child so the sentence past makes sense, though the present is also possible.
2) a) If you say 'There were' then the implication is that this is no longer true. The listener might infer that one of your siblings died, for example. If you say 'There are' then the listener would understand that all are still alive.
2) b) Both are possible. 'Had' might mean that the parents died; 'have' makes it clear that they are still alive.
Hello The LearnEnglish Team, The selfish giant by Oscar wilde.. Suddenly he rubbed his eyes in wonder and looked and looked. It certainly was a marvellous sight. In the farthest corner of the garden was a tree quite covered with lovely white blossoms. Its branches were golden, and silver fruit hung down from them, and underneath it stood the little boy he had loved. Could you explain why the author has used hung down and stood instead of were hanging and was standing the little boy? Would it be incorrect to use past continuous tense though I think the action was in progress at that time? Jitu_jaga
Hello jitu_jaga,
The simple tenses here suggest that this character views this scene not so much something that is in progress, but as more of a static scene, almost as if it were the background of a painting.
Though please note that I say this without having read either before or after this extract -- my analysis might change if I did read the full context.
The speaker's perspective and intentions are key in the choice of verb forms.
Best wishes, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hi, is this sentence grammatically correct “We hadn’t chicken curry last night”
Hello blaky,
The negative form of have is didn't have . We normally use hadn't (or haven't ) only when it is an auxiliary verb and part of a longer verb phrase such as a perfect form.
Hi , i hope you feeling well. Why we use past perfect here after which why we can’t use simple present?
That this type of writing represents a kind pf literary genre is a point which some critics had failed to notice
sorry i mean simple past not simple present
Hello hanieh1315,
You can use the simple past here ( ...some critic failed to notice ) as well as the past perfect ( ...some critics had failed to notice ). The past perfect emphasises that the critics failure to notice ended - presumably at a time made clear by the broader context. In other words, the critics did not notice only up until a particular point, and after that they did notice.
got it .Thanks for your answering🌹
Hi, could you please explain to me which one of these following sentences is grammatically correct:
1. She worked there for five years but was fired last week. 2. She had been working there for five years but was fired last week. 3. She had worked there for five years but was fired last week.
I presume that it has something to do with conveying the emphasis in each sentence, but I'm not entirely sure what the actual difference is.
Hello _Chris_,
All three of those are grammatically correct, though the situations we'd use them in are different.
There are so many possibilities here that I can't describe them all, and the differences between the situations are so general it's also difficult to say something useful. But, for example, 1 could be used in lots of situations; it's quite neutral. If I had to choose one of these three on a test, this is the one I'd choose, though I'd also want to ask whoever wrote the test what their thinking was to be sure.
If you can give us any more context for this, perhaps we can explain it better. You're also welcome to propose contexts for each of the three sentences and we can comment on how you see them if you'd like.
All the best, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Could you send some points we must keep in mind while attempting questions related to past and present tenses... Any helpful tips which are useful for scoring 100% in grammar...
Hello SaadBinSiyad2008,
I'm afraid we don't provide long general explanations of grammar points -- for that kind of thing, please see the explanations on our different pages. I'd also recommend trying the exercises and finding out where your weak points are so that you can improve on them.
We're happy to help with specific questions about our explanations or exercises, so please don't hesitate to ask us any of those types of questions.
Hi Petet, Kirk and Jonathan, When I was a child, I lived in France. Would it be incorrect if I wrote was living in France. Please clarify. .
Hello y jitu_jaga,
Both forms are possible. The simple form ( wrote ) suggests that you lived permanently in France - it was your home, at least for a time, and you did not consider it temporary. The continuous form ( was living ) suggests that you saw it as temporary - you knew that you were going to leave. In other words, it's really a question of how the speaker saw the situation, not a question of fact.
Hello Peter, Are there any other verbs which we can use same way?
Hello Team. Could you please help me? In the following sentence, which tense is the correct one or both? Why? - First, my brother (got- had got) a visa. Then, he booked a flight to Canada. Thank you.
Hello Ahmed Imam,
I'd choose 'got' here because the two sentences are clearly narrating a sequence of actions ('first', 'then'). In such cases, we normally use the past simple.
It's possible to use 'had got' in a similar situation ('My brother had got a visa before booking his flight'), but in most cases the past simple is probably best. It really depends on the rest of the situation and the meaning intended, which I can't really speculate about here.
All the best, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
When she got home, she realized that while she ….. someone has stolen her wallet! A. had been walking B. Was working
Hello Alaa El Baddini,
As I said on another page, I'm afraid we don't provide answers for questions from other sources. We're happy to explain points of grammar or answer other questions about the language, but if we began simply giving answers to tasks we would end up doing our users' homework and tests for them, which is not our job!
I wish I heard information soon. I could learning well if I really tried. If I had started 1 year ago I would have a good job. I wonder if these sentences are right ?
Let me make some suggestions.
- The meaning isn't clear for me. If you say this because you want somebody to send you the information, it should be --> "I hope to hear from you soon". If you want to tell somebody that you will get the information soon, it should be --> "I hope to get the information soon."
- Looks good but it should be --> "I could learn well ...". After "could", use the base verb form (not the -ing form).
- Looks good but it's not clear what "started" means. It could be, for example, "If I had started looking for a job one year ago, I would have a good job now".
Hello , During summer i stayed in a hotel. During summer i was staying in a hotel. which one is correct and why? And is "stay" a state verb?
Both the past simple ('I stayed') and the past continuous ('I was staying') are possible here, but we would say one or the other depending on the situation or the meaning we want to convey. It's difficult to explain much more to you because there are so many different reasons that one or the other form would be better that I can't explain them all. Did you have a specific situation in mind?
If not, I'd suggest reading the explanations on the pages I linked to. We're also happy to try to explain a more specific situation if you can tell us more about it.
which is correct?
while i was living in England, i was taking a course on english grammar.
when i was living in England, i took a course on english grammar.
Hello Qirat2004,
Both of those are grammatically correct, but which one is correct for a specific situation depends on the situation and what you want to say. If you can explain the situation and what you mean in more detail, we can help you choose the best form.
Hi Kirk & Peter, She was half listening to the music as she flipped through the magazine. She was half listening to the music as she was flipping through the magazine. Is there any difference in the meaning? Or any one is grammatically incorrect. Could you please explain?
Hello jitu_jaga,
In this case you can use the two forms interchangeably. The context makes it clear that both actions were in progress simultaneously. If another action was being described instead of 'flipping through' then there might be a need to highlight whether or not it was completed during the other action (listening) or in progress.
Hello and happy new year, Culturally, Europe made so many significant advances during the Renaissance that it (would be) impossible to describe them in a brief speech. Why (would be) is used here? I mean the reason? Is it referring to the future? or imaginary? Thank you
Hello Hosseinpour,
Yes, 'would' is used to speak about a hypothetical (imaginary) action here. By saying this, the speaker shows that she is not going to describe them in a brief speech because it is impossible to do so.
Does that make sense?
Thanks a lot sir. Thank you.
please I would like to know which of the following sentences is grammatically correct:
" I thought they have increased the wages" " I thought they had increased the wages"
Hello Haroun,
The second sentence is correct. 'Thought' takes place in a finished past time whereas 'have increased' describes an unfinished past>present time, so they are not logically compatible here.
Peter The LearnEnglish Team
Hi , Could you tell me whether the following sentence is correct: 'As John had been shopping in the duty free area his flight took off.' Or it's better to say As John was shopping in the duty free area his flight took off. Thank you
The second one is better. The past simple action (his flight took off) happened in the middle of the past continuous action (John was shopping).
The first sentence uses past perfect (John had been shopping), but that is used for an action that took place before another action and which had some kind of logical connection to it (e.g., a cause and effect - "As John had been shopping, he arrived at the departure gate late" - it means he arrived late because he had been shopping). But it seems unlikely that his flight took off BECAUSE he had been shopping, so I wouldn't use that here.
Jonathan The LearnEnglish Team
Thank you Jonathan... So, let me see if I understood correctly The passengers had been waiting (not were waiting) in the airport for two hours when a bomb scare occurred. (Logical connection?)
Yes, I think the past perfect continuous version is more likely. Using the past perfect continuous shows that the actions (passengers waiting / bomb scare occurred) happened in sequence, one after the other.
Some people might use the past continuous version, but I think it is less preferable because the phrase "for two hours" suggests the action is complete (rather than ongoing) when the bomb scare occurred. The past continuous would be more likely if the "for two hours" phrase was deleted.
You're asking me: "What did you do yesterday" I'am answering:"I wrote a book" What will you think ? (A) That I wrote some pages of book (didn't finish the book). (B) That I wrote a whole book (finished the book) ? How should I answer in option (A) ?
Hello PeterNosov,
'I wrote a book' would normally mean that you wrote a whole book. If you wrote but didn't finish the book, you could say 'I wrote some pages for my book' or 'I did some writing' or 'I worked on my book'. There are other options, too, but these are some common ways to express that idea.
Thank you, Mr. Kirk !
Hello lexeus,
Yes, it's correct to use an adjective after the verb ' turn ' when it means 'become'. If you follow the link and look at the example sentences under the fourth entry (look for the words ' turn verb (BECOME' in purple), you'll see a sentence very similar to the one you're asking about.
All the best,
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250]
Example: eat, ate, eaten
Past Perfect
Future perfect, present - conditional, perfect - conditional.
Past Tense of travel: Conjugations in Past and Present Participles

What is the past tense of “travel?” Most commonly, the past tense of the word “travel” is “travelled.” Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it’s used. For example, referencing “travel” in the present participle form will change it to “travelling,” but in the infinitive form, will be “travel.”
What is the past tense of the word "travel"
The past tense (past participle) form of “travel” is “travelled.” The infinitive of the word form is “travel.” The present participle form is “travelling.” The past tense form is “travelled” and past participle form is “travelled.”
Understanding verb tenses
The general grammar rules that govern past tenses are as follows. The simple past tense form is created by adding a -ed or -d affix to the root word of the verb. Some verbs use a -t variation where they end in a -t. For example, when "dream" turns into "dreamt."
The past perfect tense is formed for regular verbs (ending in -ed, -d, or -t) by adding "had" followed by the verb. For example, "I had finished ."
The past continuous tense is formed by the verb "be" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, " we were having dinner."
Lastly, the past perfect continuous tense is formed by adding "had been" followed by the affix or ending of -ing. For example, "I had been building a castle with my sister."
For more information on forming all past tenses, visit our " understanding verb tenses " resource.
Sentence examples for the past tense of the word "travel"
- Infinitive: I travel.
- Present participle: She is travelling.
- Past tense: I travelled.
- Past particle: I have travelled.
Verb forms of the word "travel"
Example sentences in all verb forms:
Indefinite present tense
Present continuous tense.
She/he/it is travelling.
Present perfect continuous tense
She/he/it has/had travelled.
Present perfect tense
She/he/it has/had been travelling.
Simple past tense
She/he/it travelled.
Past continuous tense
She/he/it were travelling.
Past perfect tense
Perfect continuous tense.
She/he/it will/shall travel.
Simple future tense
She/he/it will/shall be travelling.
Future perfect tense
She/he/it will/shall have travelled.
Future perfect continuous tense
She/he/it will/shall have been travelling.
Sentence examples in all forms
Sentence examples in all participles and parts of speech :
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
- Slovenščina
- Kundenservice
- Zusatzmaterialien zu meinen Produkten
- Das richtige Wörterbuch für die Schule
- Mein PONS
- Online-Wörterbuch
- Lernen & Üben
- Wissensecke
- Textübersetzung
- Konjugation
- Vokabeltrainer
- Wörterbuch-API
- Translate API
- Zum Homescreen hinzufügen
- Wörterbücher durchsuchen
- Nutzungsbedingungen
- Lieferkette
- Informationen zum Datenschutz
- Privatsphäre-Einstellungen
- Stellenangebote
- Französisch
- DE');"> Deutsch
- EN');"> Englisch
- FR');"> Französisch
- LA');"> Latein
- ES');"> Spanisch
Verbtabelle für travel
- Simple tenses
- Continuous tenses
Conditional
Simple tenses • continuous tenses • conditional • imperative • impersonal, present perfect, past perfect, will -future, going to -future, future perfect, conditional past, past participle, verbtabellen durchsuchen, "travel" auf weiteren sprachen nachschlagen.
- Italienisch
- Portugiesisch
Links zu weiteren Informationen
Hier kannst du uns Verbesserungen dieses PONS-Eintrags vorschlagen:
We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam. We are sorry for the inconvenience.
Mein Suchverlauf
- Beliebteste
- Niederländisch
- Tschechisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Englisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Französisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Spanisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Italienisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Polnisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Latein
- Arabisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Arabisch ⇄ Englisch
- Bulgarisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Bulgarisch ⇄ Englisch
- Chinesisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Chinesisch ⇄ Englisch
- Chinesisch ⇄ Französisch
- Chinesisch ⇄ Spanisch
- Dänisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Deutsch ⇄ Arabisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Bulgarisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Chinesisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Dänisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Elbisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Finnisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Griechisch
- Deutsch → Isländisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Japanisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Kroatisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Niederländisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Norwegisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Persisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Portugiesisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Rumänisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Russisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Schwedisch
- Deutsch → Serbisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Slowakisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Slowenisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Tschechisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Türkisch
- Deutsch ⇄ Ungarisch
- Rechtschreibung und Fremdwörter
- Elbisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Englisch ⇄ Arabisch
- Englisch ⇄ Bulgarisch
- Englisch ⇄ Chinesisch
- Englisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Englisch ⇄ Französisch
- Englisch ⇄ Italienisch
- Englisch ⇄ Polnisch
- Englisch ⇄ Portugiesisch
- Englisch ⇄ Russisch
- Englisch → Serbisch
- Englisch ⇄ Slowenisch
- Englisch ⇄ Spanisch
- Finnisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Französich ⇄ Italienisch
- Französisch ⇄ Chinesisch
- Französisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Französisch ⇄ Englisch
- Französisch ⇄ Polnisch
- Französisch ⇄ Slowenisch
- Französisch ⇄ Spanisch
- Griechisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Italienisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Italienisch ⇄ Englisch
- Italienisch ⇄ Französisch
- Italienisch ⇄ Polnisch
- Italienisch ⇄ Slowenisch
- Italienisch ⇄ Spanisch
- Japanisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Kroatisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Latein ⇄ Deutsch
- Niederländisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Norwegisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Persisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Polnisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Polnisch ⇄ Englisch
- Polnisch ⇄ Französisch
- Polnisch ⇄ Italienisch
- Polnisch ⇄ Russisch
- Polnisch ⇄ Spanisch
- Portugiesisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Portugiesisch ⇄ Englisch
- Portugiesisch ⇄ Spanisch
- Rumänisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Russisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Russisch ⇄ Englisch
- Russisch ⇄ Polnisch
- Schwedisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Slowakisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Slowenisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Slowenisch ⇄ Englisch
- Slowenisch ⇄ Französisch
- Slowenisch ⇄ Italienisch
- Slowenisch ⇄ Spanisch
- Spanisch ⇄ Chinesisch
- Spanisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Spanisch ⇄ Englisch
- Spanisch ⇄ Französisch
- Spanisch ⇄ Italienisch
- Spanisch ⇄ Polnisch
- Spanisch ⇄ Portugiesisch
- Spanisch ⇄ Slowenisch
- Tschechisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Türkisch ⇄ Deutsch
- Ungarisch ⇄ Deutsch
Identified ad region: ALL Identified country code: RU -->

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is the past tense of "travel?". Most commonly, the past tense of the word "travel" is "traveled.". Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it's used. For example, referencing "travel" in the present participle form will change it to "traveling," but in the infinitive form ...
Conjugation of Travel. Simple / Indefinite Present Tense. He/She/It travels . I travel. You/We/They travel. Present Continuous Tense. He/She/It is Commonwealth travelling, US traveling. I am Commonwealth travelling, US traveling. You/We/They are Commonwealth travelling, US traveling.
Conjugate the English verb travel: indicative, past tense, participle, present perfect, gerund, conjugation models and irregular verbs. Translate travel in context, with examples of use and definition. ... Other forms: travel oneself/not travel. Contractions. in the U.K. spelling we double up the 'l' in preterite and participle endings.
travel. 'travel' is the model of its conjugation. In British English, the final consonant is doubled before -ing and -ed. infinitive: present participle: past participle: (to) travel. trave ll ing. trave ll ed.
Travel is a verb that is commonly used in the past tense. In this section, we will cover the formation and usage examples of the past tense of travel. Formation. To form the past tense of travel, we add "-ed" to the base form of the verb. For example: I traveled to Europe last summer. She traveled to Asia for business.
to do. to say. to love. to eat. to make. to like. to tell. to drive. 'to travel' conjugation - English verbs conjugated in all tenses with the bab.la verb conjugator.
Learn the three forms of the English verb 'travel'. the first form (V1) is 'travel' used in present simple and future simple tenses. the second form (V2) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in past simple tense. the third form (V3) is 'travelled (BrE)', 'traveled (AmE)' used in present perfect and past perfect tenses.
Conjugate the verb travel in all tenses: present, past, participle, present perfect, gerund, etc. English Deutsch български Ελληνικά English ... We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched. Otherwise your message will be regarded as spam.
English verb TO TRAVEL conjugated in all forms, with full audio, irregular highlighting, negative forms and contractions. Toggle navigation. English . English Home; ... to travel Gerund: travelling Past participle: travelled Simple past: travelled. Note. In the US the spelling 'traveling' and 'traveled' are preferred. Irregular forms Auxilliary ...
Visit. Travelled is the past tense of the word travel. Travelled is the past participle of the word travel. travel past form, verb forms, v1v2v3, Inf.
Conjugation English verb to travel in several modes, tenses, voices, numbers, persons : indicative mode, subjunctive, imperative mood, conditional, participle form, gerund, present, past, future perfect, progressive. The-conjugation.com. Menu. Other languages available English ... you will have been traveling he will have been traveling we will ...
Conjugation of the verb Travel in all tenses: future, present and past. 🎮 Conjugation trainer for memorizing forms. ... Base Form Past Simple Past Participle Gerund ; travel: traveled: traveled: travelled [ˈtrævl] [ˈtrævəld] [ˈtrævəld] [ˈtrævld] [ˈtræv(ə)l] [ˈtrævəld]
Simple past tense of Travel verb forms learn spoken English course online through Telugu spoken English classes. ... Travel: Past form (v2) Travelled: Past Participle (v3)-ed form: Travelled: Present Participle (v4) 'ing' form: Travelling: Present simple (v5) s / es/ ies : Travels:
Conjugation is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb "break" can be conjugated to form the words break, breaks, broke, broken and breaking. The term conjugation is applied only to the inflection of verbs, and not of other parts of speech (inflection of nouns and adjectives is ...
Present Continuous. I am travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling he/she/it is travelling or traveling we are travelling or traveling you are travelling or traveling they are travelling or traveling.
Travel Past Tense: Past Tense of Travel is Traveled.. Example: Sarah Traveled by Train. Travel Past Participle: Past Participle Form of Travel is Traveled.. Example: Sarah has Traveled by Train. Travel Present Participle: Present Participle Form of Travel is Travelling.. Example: Sarah is Travelling by Train. Travel 3rd Person Singular:
We use these forms: to talk about the past:; He worked at McDonald's.He had worked there since July. He was working at McDonald's.He had been working there since July.. to refer to the present or future in hypotheses:; It might be dangerous. Suppose they got lost.. This use is very common in wishes: I wish it wasn't so cold.. and in conditions with if:. He could get a new job if he really tried.
Answer. The past tense of travel is travelled UK or traveled US (US) . The third-person singular simple present indicative form of travel is travels . The present participle of travel is travelling UK or traveling US .
Simple past. The simple past tense is used when discussing completed past events or actions.. For regular verbs, the simple past tense is formed by adding the suffix "-ed" to the infinitive form of the verb (e.g., "wait" becomes "waited"). For irregular verbs, the formation of the past tense does not follow a single pattern (e.g., "run" becomes "ran," and "bring ...
Look up English verb forms - over 5000 verbs! Excellent resource for students and teachers. verb123.com Home Notes About. Example: eat, ate, eaten ...
Travelled is the past tense and past participle form of the verb "travel." It refers to the act of going from one place to another, typically over a distance. The term "travelled" is commonly used in British English and other English-speaking countries that follow British English conventions. Define Traveled
What is the past tense of "travel?". Most commonly, the past tense of the word "travel" is "travelled.". Although the word form will change based on its participle. And the sentence where it's used. For example, referencing "travel" in the present participle form will change it to "travelling," but in the infinitive form ...
Konjugiere das Verb travel in allen Zeitformen: Present, Past, Participle, Present Perfect, Gerund, etc. ... Simple tenses • Continuous tenses • Conditional • Imperative • Impersonal. Present. I: travel: you: ... We are using the following form field to detect spammers. Please do leave them untouched.