Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Updated: April 17, 2024
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2022? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map at the last second?

The thing is — understanding your customer base can be very challenging. Even when you think you’ve got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

While it isn’t possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a convenient tool for keeping track of critical milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I’ll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents

What is the customer journey?
What is a customer journey map, benefits of customer journey mapping, customer journey stages.
- What’s included in a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
Steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Customer Journey Design
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer’s journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I’ve worked with were confused about the differences between the customer’s journey and the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don’t wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process of considering, evaluating, and purchasing a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand’s place within the buyer’s journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer’s journey. When you create a customer journey map, you’re taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey instead of leaving it up to chance.
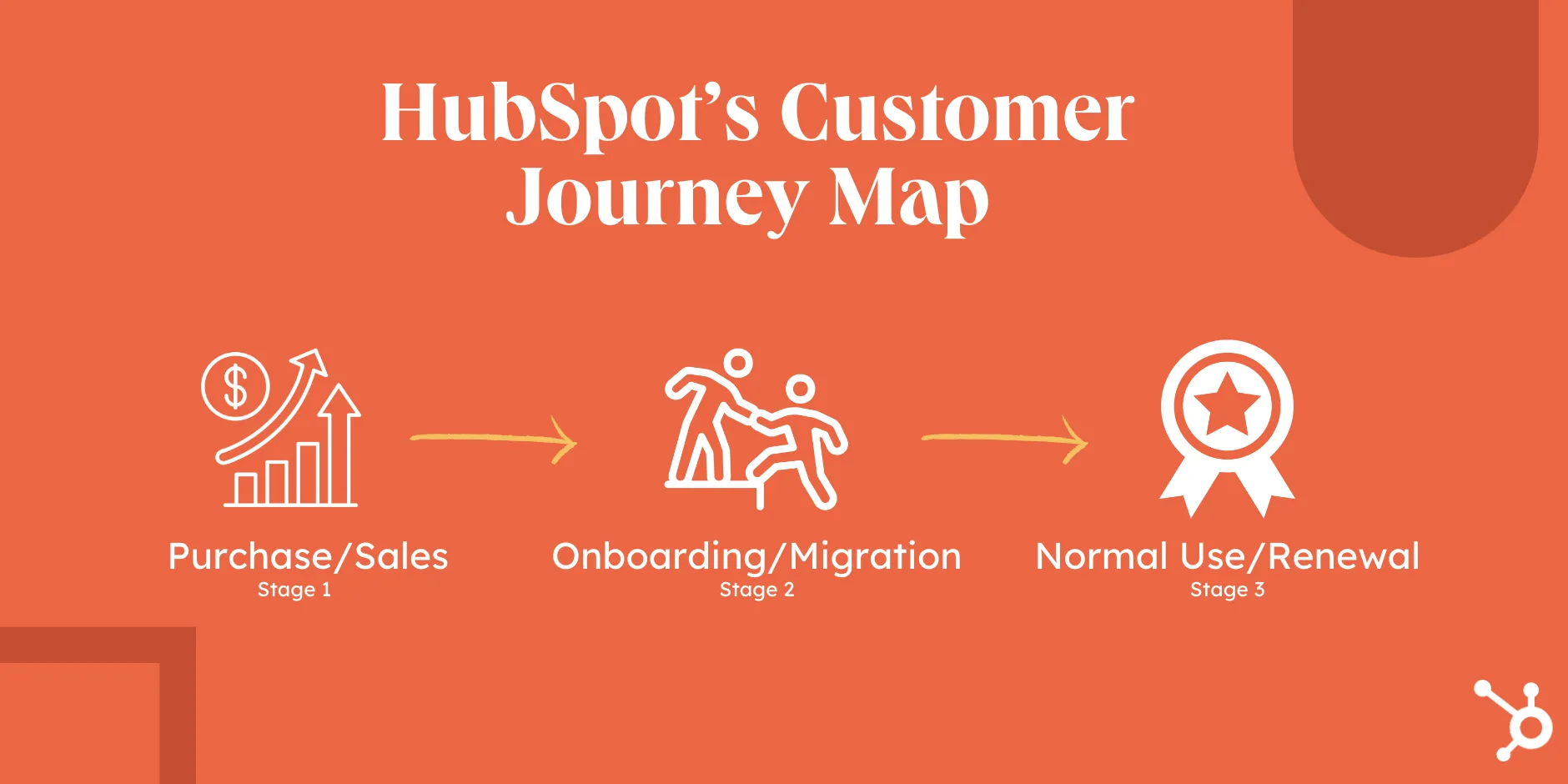
For example, at HubSpot, our customer’s journey is divided into three stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
1. Use customer journey map templates.
Why make a customer journey map from scratch when you can use a template? Save yourself some time by downloading HubSpot’s free customer journey map templates .
This has templates that map out a buyer’s journey, a day in your customer’s life, lead nurturing, and more.
These templates can help sales, marketing, and customer support teams learn more about your company’s buyer persona. This will improve your product and customer experience.
2. Set clear objectives for the map.
Before you dive into your customer journey map, you need to ask yourself why you’re creating one in the first place.
What goals are you directing this map towards? Who is it for? What experience is it based upon?
If you don’t have one, I recommend creating a buyer persona . This persona is a fictitious customer with all the demographics and psychographics of your average customer. This persona reminds you to direct every aspect of your customer journey map toward the right audience.
3. Profile your personas and define their goals.
Next, you should conduct research. This is where it helps to have customer journey analytics ready.
Don’t have them? No worries. You can check out HubSpot’s Customer Journey Analytics tool to get started.
Questionnaires and user testing are great ways to obtain valuable customer feedback. The important thing is to only contact actual customers or prospects.
You want feedback from people interested in purchasing your products and services who have either interacted with your company or plan to do so.
Some examples of good questions to ask are:
- How did you hear about our company?
- What first attracted you to our website?
- What are the goals you want to achieve with our company? In other words, what problems are you trying to solve?
- How long have you/do you typically spend on our website?
- Have you ever made a purchase with us? If so, what was your deciding factor?
- Have you ever interacted with our website to make a purchase but decided not to? If so, what led you to this decision?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how easily can you navigate our website?
- Did you ever require customer support? If so, how helpful was it, on a scale of 1 to 10?
- Can we further support you to make your process easier?
You can use this buyer persona tool to fill in the details you procure from customer feedback.
4. Highlight your target customer personas.
Once you’ve learned about the customer personas that interact with your business, I recommend narrowing your focus to one or two.
Remember, a customer journey map tracks the experience of a customer taking a particular path with your company. If you group too many personas into one journey, your map won’t accurately reflect that experience.
When creating your first map, it’s best to pick your most common customer persona and consider the route they would typically take when engaging with your business for the first time.
You can use a marketing dashboard to compare each and determine the best fit for your journey map. Don’t worry about the ones you leave out, as you can always go back and create a new map specific to those customer types.
5. List out all touchpoints.
Begin by listing the touchpoints on your website.
What is a touchpoint in a customer journey map?
A touchpoint in a customer journey map is an instance where your customer can form an opinion of your business. You can find touchpoints in places where your business comes in direct contact with a potential or existing customer.
For example, if I were to view a display ad, interact with an employee, reach a 404 error, or leave a Google review, all of those interactions would be considered a customer touchpoint.
Your brand exists beyond your website and marketing materials, so you must consider the different types of touchpoints in your customer journey map. These touchpoints can help uncover opportunities for improvement in the buying journey.
Based on your research, you should have a list of all the touchpoints your customers are currently using and the ones you believe they should be using if there’s no overlap.
This is essential in creating a customer journey map because it provides insight into your customers’ actions.
For instance, if they use fewer touchpoints than expected, does this mean they’re quickly getting turned away and leaving your site early? If they are using more than expected, does this mean your website is complicated and requires several steps to reach an end goal?
Whatever the case, understanding touchpoints help you understand the ease or difficulties of the customer journey.
Aside from your website, you must also look at how your customers might find you online. These channels might include:
- Social channels.
- Email marketing.
- Third-party review sites or mentions.
Run a quick Google search of your brand to see all the pages that mention you. Verify these by checking your Google Analytics to see where your traffic is coming from. Whittle your list down to those touchpoints that are the most common and will be most likely to see an action associated with it.
At HubSpot, we hosted workshops where employees from all over the company highlighted instances where our product, service, or brand impacted a customer. Those moments were recorded and logged as touchpoints. This showed us multiple areas of our customer journey where our communication was inconsistent.
The proof is in the pudding — you can see us literally mapping these touch points out with sticky notes in the image below.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![prepare a customer journey map for online shopping How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![prepare a customer journey map for online shopping How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![prepare a customer journey map for online shopping Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2023
![prepare a customer journey map for online shopping How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience

11 Best Practices for B2B Customer Experience
![prepare a customer journey map for online shopping Customer Experience vs. User Experience: What’s the Difference? [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/customer-experience-vs-user-experience_2.webp)
Customer Experience vs. User Experience: What’s the Difference? [+ Examples]
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Learn / Guides / Ecommerce guide
Back to guides
How to create an ecommerce customer journey map (with examples)
In the highly competitive world of ecommerce, selling great products is not always enough. Customers expect fantastic experiences during every interaction with you—and if you don’t deliver them, your competitors will.
Last updated
Reading time.

So: how do you find the best opportunities to optimize your funnel, improve conversions, and grow your ecommerce business? With a little help from your new friend, the customer journey map .
Find new ways to grow ecommerce sales
Hotjar shows you what key user segments are doing on your site, so you can fix the problems hurting your conversions.
What are ecommerce customer journey maps?
Customer journey maps visualize the steps your customers take when moving through your conversion funnel .
A basic map, like the one below, simply shows the key touchpoints customers go through on their journey.
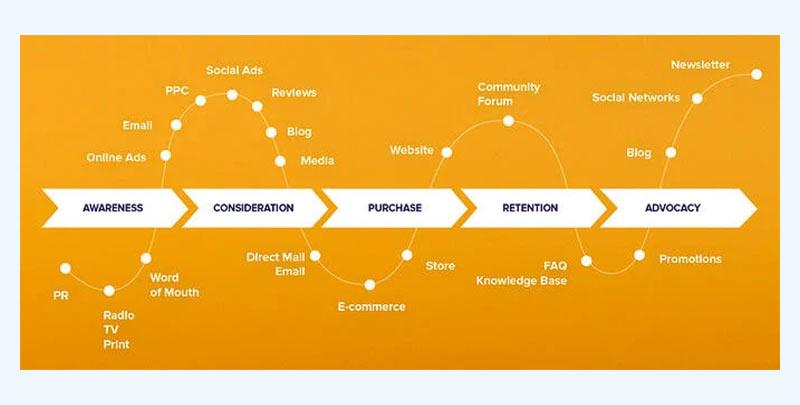
An example of a simple customer journey map from CartsGuru
More sophisticated maps integrate detailed insights about the customer, such as their actions, thoughts, and needs, at different touchpoints. This allows you to take a walk in your customer’s shoes and find ways to improve your ecommerce user experience (UX) .
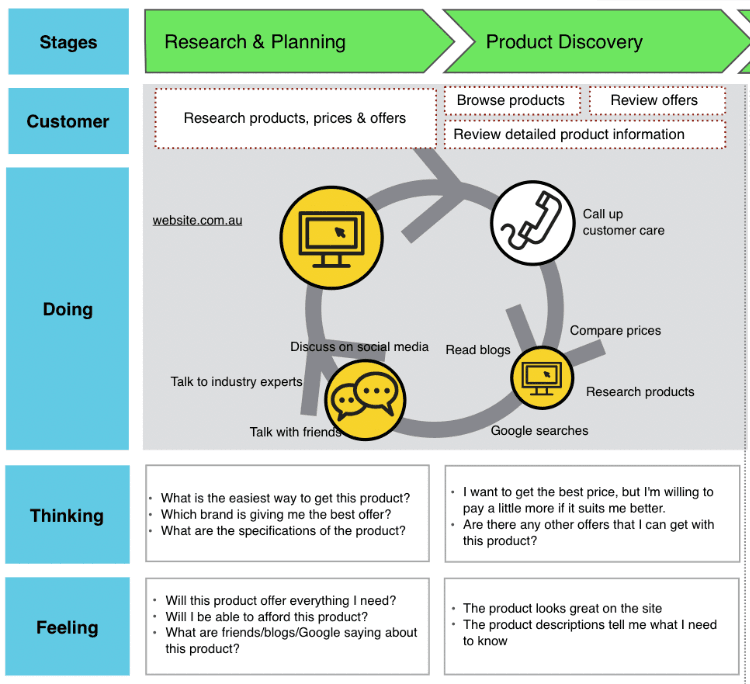
A map from MarketingMag.com.au revealing customer thoughts and feelings at each touchpoint
Some customer journey maps also integrate quantitative data into each step. By tracking key metrics—like your Net Promoter Score® (NPS®), customer satisfaction (CSAT) score, or customer effort score—you’ll get a data-informed view of the weak points in your journey.
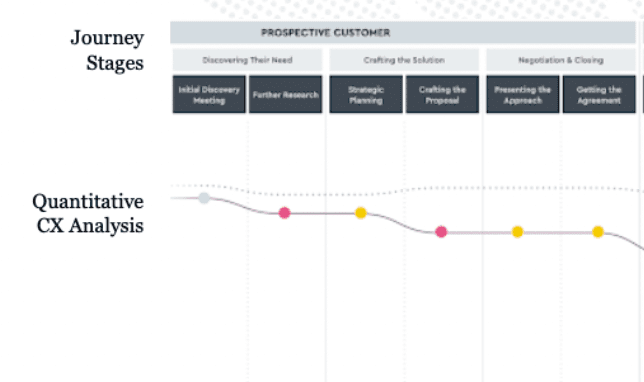
A customer journey map from Tallwave incorporating quantitative data
4 (very good) reasons to create customer journey maps
Sure, your company as a whole has a basic understanding of what customers do . But does every department have a consistent, detailed view of what they’re experiencing ?
Customer journey maps provide exactly that, bringing several key benefits with them:
1. Understand your customers’ motivations, drivers, and point points
In ecommerce, buying journeys are rarely simple. They usually entail a range of emotions, questions, and pains—ranging from “how quickly can I get this awesome dress?” to “am I really getting the best deal?” and “why is this so complicated?”
Customer journey maps give you an at-a-glance view of these vital insights, helping your entire company empathize with your audience.
2. Get your teams working together
Improving the customer’s journey, even at a single touchpoint, often requires multiple teams.
For example, imagine your new customers are confused about how to use your latest product. In this case, your customer service team could report their feedback to your content team. Your content team can then create educational product videos to provide helpful (and necessary) guidance.
Cross-team coordination like this is faster and easier when your company has a shared view of the customer’s experience.
3. Remove internal silos and clarify who owns what
Imagine a scenario where a customer buys a product and feels it doesn’t meet their expectations. When they contact your company, should customer support help them, or a technical product expert?
For growing companies, the lines of responsibility often get blurred. Customer journey maps help you determine which team is responsible for key actions and support at each step of the way.
4. Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
With a clear overview of the customer’s journey, your team can quickly home in on the touchpoints where something’s going wrong.
For example, you might realize many customers are landing on your product page, but few are completing purchases.
By mapping out the next steps they take and gathering data about their experiences, you discover that customers are dropping off at the shopping cart
A closer look at your behavior analytics data clearly shows visitors find the shopping cart UX confusing
With this knowledge, you can take action to simplify your customers’ shopping cart experience and track whether it helps you increase conversions .
What are the stages of the customer journey?
It’s important to remember that every customer’s journey starts before they land on your ecommerce site, and long after they make a purchase.
Most marketers consider the following stages when mapping out a customer journey:
❗️awareness.
Your customer’s journey starts when they become aware of a desire or challenge that your product addresses. This is where you can start appealing to them with content and marketing campaigns.
In the later stages of awareness, your customer educates themselves about the different products you have available.
💭 Consideration
In this stage, the customer considers whether your product is right for them. They may be trying to choose between several similar products or comparing your product with a competitor’s.
💡 Decision
Your customer has decided your product is right for them , but is weighing up final hurdles like price, delivery time, and payment options. To complete the purchase, they’ll also have to navigate your checkout process.
💰 Retention
After the sale, your customer’s evolving perception of your company will depend on delivery, support, and the product itself. If your customer has a positive experience, they may continue spending with you.
❤️ Advocacy
A remarkable experience may result in a customer becoming an advocate at the end of their journey. This could mean telling others about your company, discussing your products on social media, or positively reviewing your business on public platforms.
How to create a customer journey map for your ecommerce company
Every customer journey map is different—the data you include will be unique to your company. But if you’re an ecommerce business of any size, there are five steps you’ll need to take:
Define your goal
Are you trying to get more sales from visitors on mobile? Or more customers advocating for you? Or perhaps reduce the bounce rate on your checkout page?
By agreeing on a goal with your team, you can build your customer journey map with the right insights, metrics, and analyses in mind.
Gather relevant, accurate data
For your customer journey maps to be of maximum efficacy, you’ll want to gather a range of qualitative and quantitative data . The more data you have, the better—but the data you include in your map should always relate to your overall goal.
For example, let’s imagine that your goal is to increase sales. In this scenario, you could:
Learn how customers navigate your store across the shopping journey by conducting usability testing
Use surveys and interviews to understand what information customers need during the consideration phase
Gather behavior analytics data to uncover pain points and signs of frustration during the checkout process
Gauge overall satisfaction by tracking customer NPS across their entire pre-purchase journey
💡Pro tip: using Hotjar? Your job just got easier! With our Surveys and Feedback tools, you can ask visitors both closed and open-ended questions. For example, ask customers to rate your product page, then follow up by asking how you could improve it.
And when you’re gathering customer data, consider our new product for user-research automation, Hotjar Engage , which makes it easier than ever to interview customers and run seamless user testing.
5 types of user data you need to create a customer journey map
If you choose to create a customer journey map, you’re already engaging in data-driven marketing . Make your maps as useful as possible by taking relevant information from a wide range of sources.
1. Website journey data
Google Analytics (GA) is an essential part of your ecommerce website analysis toolkit. Its reports and dashboards give you a high-level overview of how people use and move through your site. What’s more, Google Analytics has a range of segmenting capabilities that let you gather data relating to your defined user personas.
For example:
The Behavior Flow report shows you the paths customers are taking through your site and where they drop off
The Conversion Path report shows you what platforms your customers are using at each stage of their journey
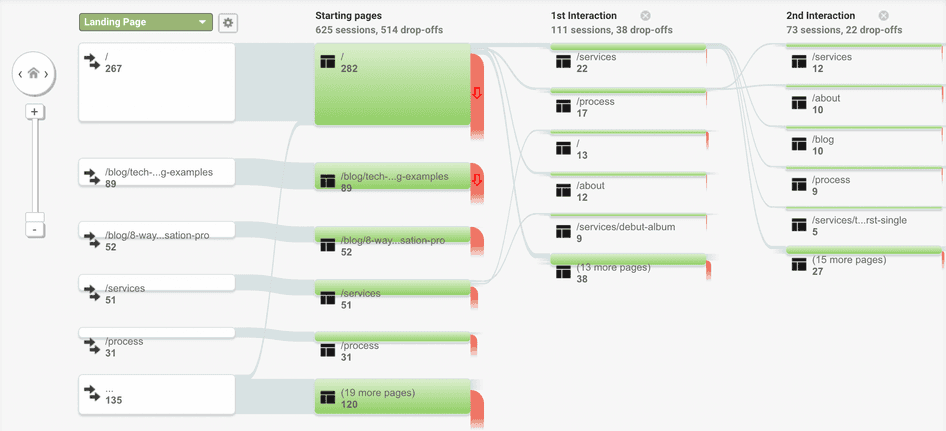
💡Pro tip: make your analysis easier by connecting GA to Hotjar with our Google Analytics integration . Then, leverage User Attributes to filter Hotjar data for specific audience segments you identified with Google Analytics.
2. Behavior analytics data
Now that you know what journeys your visitors take, you’ll want to see what they’re doing on each page. This is where behavior analytics tools, like Hotjar Heatmaps and Recordings , can help.
Scroll heatmaps show you where people stop scrolling on your product and support pages, showing you which parts of your page go unseen
Click heatmaps show you where people are clicking most, indicating how intuitive your UX design is and giving you ideas for improvements
Recordings let you rewatch individual journeys to find out how customers behave, where they get stuck, and what they do before clicking your call to action ( CTA )
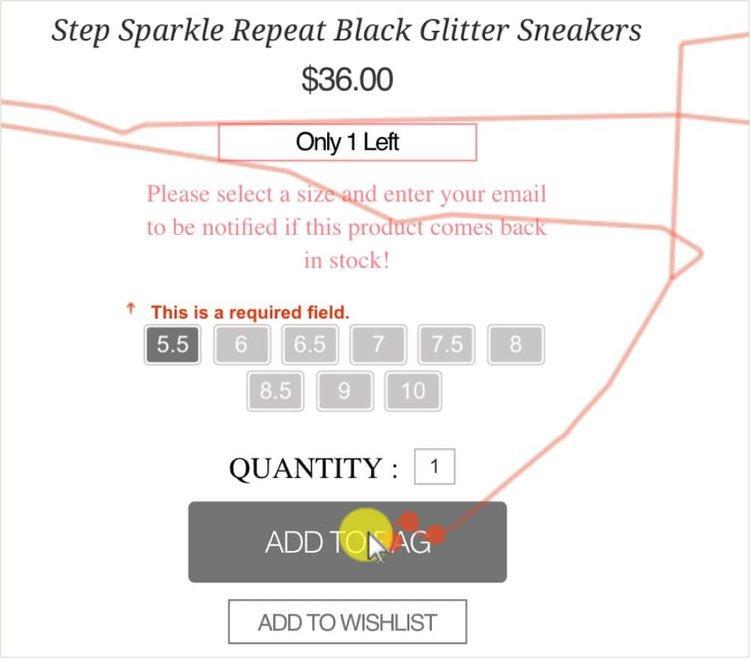
3. Email queries, chat logs, and customer support logs
Your company’s everyday conversations with customers are a gold mine of insights. They reveal what users commonly get frustrated with, what information they need, and how often specific problems occur.
Ideally, use a tool to categorize and log queries and support requests from your customers. You can then hold regular reviews with your sales and support teams to see how the trends fit into your customer journeys.
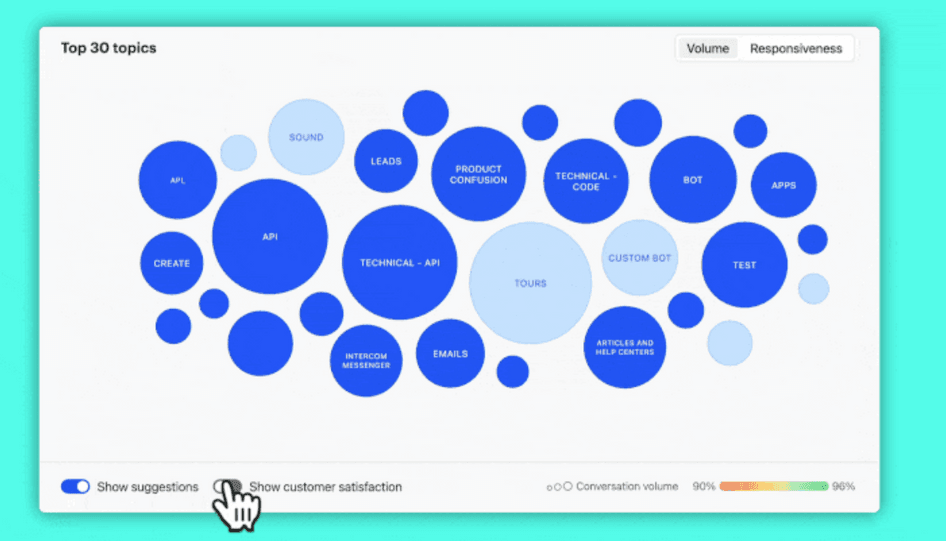
Customer support platform Intercom visualizes common conversation topics
4. On-site and email surveys
Asking your customers for feedback is an effective way to understand their experiences at different parts of their journey. In addition to getting subjective, descriptive feedback, surveys also give you quantitative data (like NPS scores) to support optimization efforts.
Following an interaction with customer support: email a survey that asks respondents to rate their customer satisfaction level. Include an open-ended question prompting customers to describe what you could do better.
Following a successful purchase: target shoppers with an on-site survey asking them to submit an NPS. Then, track how this score changes as you update and improve to your checkout process.
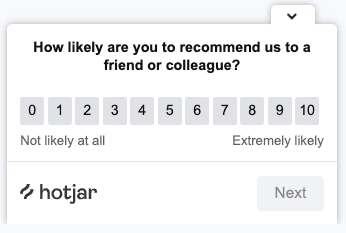
5. Customer interviews
Having one-on-one discussions with customers is a great way to dig further into their needs, motivations, and pain points. You might find it helps to offer customers an incentive to speak with you, but satisfied customers will often do so for free.
However, don’t focus solely on happy customers. Performing exit interviews with regular customers who change to another supplier can reveal a weak link in the customer journey.
❓Did you know? Hotjar recently added Engage , a user research tool, to our platform. Engage makes it easy to book, conduct, and analyze customer interviews, so you can find new insights more easily.
Create user personas for the customers you’re trying to serve
Depending on your goals, you might want to create multiple maps for different ‘types’ of customers. For example:
New customers + Existing customers
Actual customers + Ideal customers
B2B customers + B2C customers
Creating separate maps for your different customer types ensures more accurate, actionable maps. However, you’ll need a clear idea of who these customers are and how you can identify them. That’s why it’s a good idea to create a user persona for each distinct customer you’re trying to help.
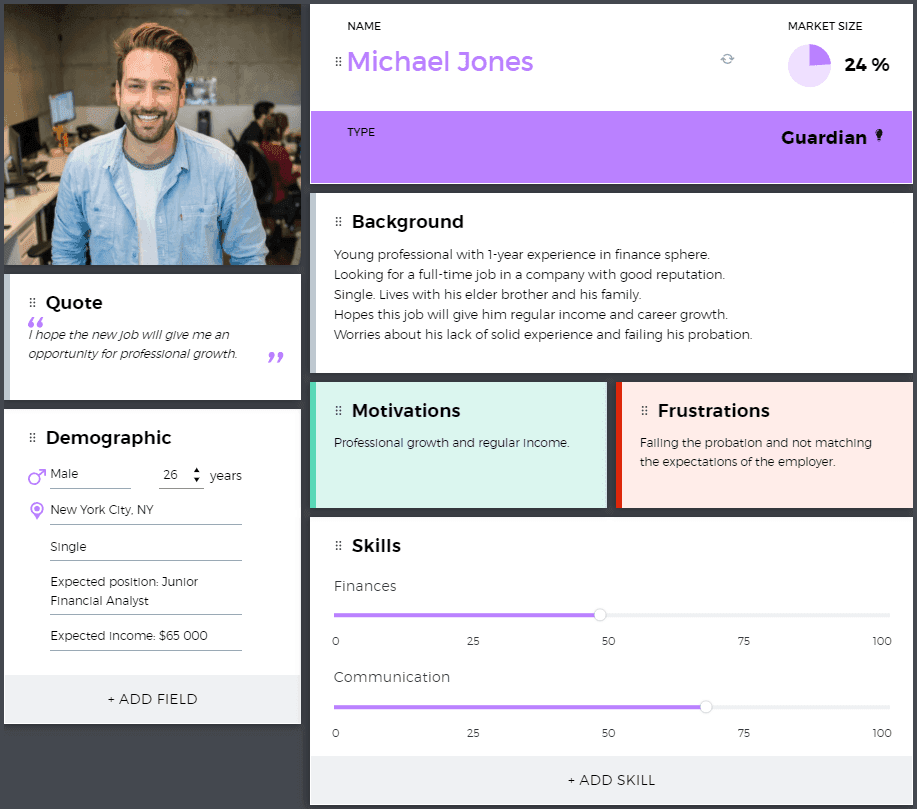
An example persona from UXPressia
💡Pro tip: with Hotjar User Attributes, you can cross-reference data from other platforms to get insights into specific user segments. For example, use Google Analytics to create a segment of new users who visit your site after clicking an ad, then watch Recordings of their journeys.
Why are user personas helpful in customer journey mapping?
Depending on your goals, you may be interested in different user personas: to improve sales of a specific product, you’d want to understand the needs and actions of customers who bought that product. To increase repeat purchases, on the other hand, you’d need to know how existing customers navigate your site and what they need from future purchases.
In both cases, you’d want to see how their journeys differ from other customers and visitors. Understand what they do on their journeys, and you’ll find ways to serve them better.
By analyzing the journeys of people who buy your flagship product, you learn that they often visit a competitor’s site to compare products. Using this insight, you add a table that compares your product with others, keeping visitors on your site and boosting sales in the process.
By analyzing the journeys of existing customers, you learn that they begin looking at related products in your range around three months after an initial purchase. Accordingly, you start sending automated emails around month three to grow sales while increasing customer delight .
Note: traditionally, marketers created user personas with demographic information like gender, sex, and age. Today, many marketers find it helpful to use the jobs to be done (JTBD) framework.
JTBD views user personas less in terms of qualities and more in terms of goals, motivations, and desired changes . Of course, this is perfect for customer journey mapping!
Unravel your customer referral paths
Your customers interact with your ecommerce business in various places, both online and offline. Understanding how these touchpoints fit together—and delivering a consistent experience across them—is the goal of omnichannel marketing.
In some cases, their journey will be a straight line:
The prospect enters ‘best winter jackets’ into a search engine
They immediately find your blog, click through to your store, and make a purchase
A week later, the customer receives their order and goes on social media to share their satisfaction with the product
However, in other scenarios, the journey will be more complex:
A prospect hears about your clothing brand from a friend
Weeks later, they see your brand on Instagram, visit your store, and sign up for your newsletter
The prospect then visits two other physical clothing stores to compare jackets
A day later, they receive an email from you offering a 10% discount on jackets they previously viewed—they return to your online store to make a purchase
The customer has a small issue with the order and calls your customer support line to resolve it
As a business, you might want to serve the second customer better so they can become an advocate, too. But to map out their journey accurately, you need to know where they came to you from—in other words, their referral path.
Combine data from your different tools to understand your customer referral paths
Building an accurate map of omnichannel journeys is challenging but not impossible. Ideally, you’ll look at data from two different tools.
Look for referral paths in Google Analytics. The Behavior Flow report tells you where website visitors are coming from (e.g. organic search or email).
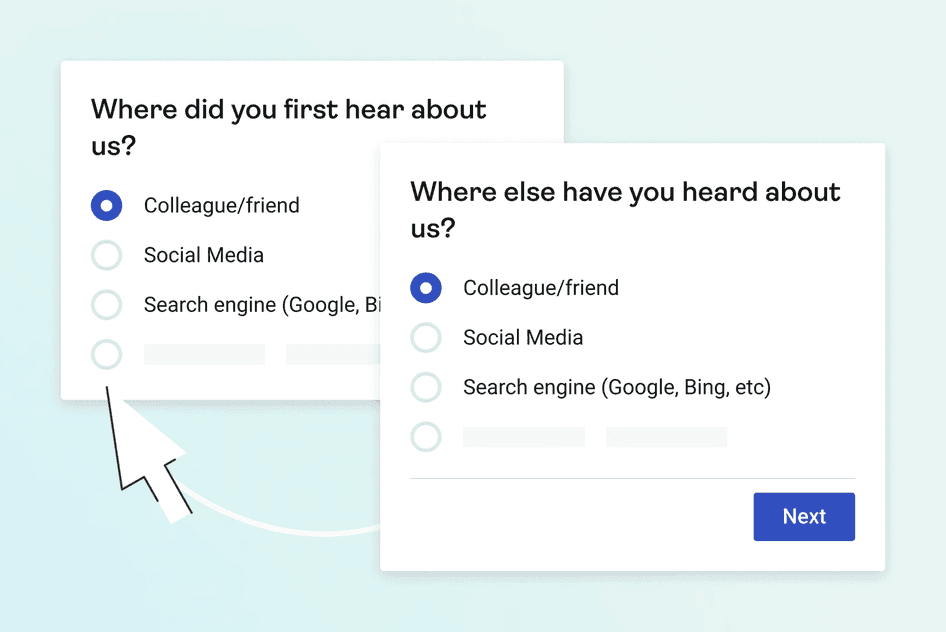
Use surveys to fill in the gaps. For example, when a customer signs up to your email newsletter, send a survey to ask how they discovered your brand.
Combining both these data points gives you a more complete customer journey map. And if you’re using Hotjar, our Segment integration helps you view survey responses for different audience segments by leveraging User Attributes.
Create (and update) your maps
Having gone through the previous four steps, you can build maps for each key customer persona. Your team is now in a great place to analyze and improve critical touchpoints along the customer journey.
But don’t forget that your business is always evolving, so your maps need to evolve with it.
Update journeys as they change. As you add new products, features, and marketing funnels, map out the new journeys your customers take.
Track and update key metrics. If you’re including quantitative data in your maps, like NPS or CSAT scores, track changes and update your maps every quarter.
Start mapping your ecommerce journeys today
The more complicated your customer journeys are, the more opportunities you have to delight—or disappoint—your audiences. Customer journey maps give your company a shared framework for improving their experiences across the entire conversion funnel .
But remember: your customer journey maps are only as good as the data you used to create them. By researching the what , how, and why of your customers’ behavior, you’ll build effective customer journey maps that drive real impact.
Solve your biggest conversion challenges
With tools like Recordings, Surveys, and Feedback, Hotjar helps understand why visitors don’t convert—and gives you the insights and information you need to make them.
Ecommerce customer journey map FAQs
Can customer journey maps help us improve our web design.
Customer journey maps help you zero in on parts of the customer journey that need the most attention: i.e. the points where customers are falling off or feeling dissatisfied with their experience.
You can then gather data around these conversion bottlenecks using behavior analytics platforms like Hotjar. If your research reveals a problem with web design , you can apply ecommerce CRO and web design principles to improve the page. Take a look at some recent web design examples to see how the best companies in the world are doing it.
How do early-stage ecommerce companies benefit from customer journey maps?
If your company is in an early stage of growth, you probably don’t have the resources to optimize your whole funnel. Customer journey maps help you identify the parts of your funnel to prioritize so you can use your resources efficiently.
You can then start gathering data and using ecommerce design metrics to inform future improvements.
Previous chapter
Shopping cart UX
Next chapter
How to Create a Customer Journey Map? Template, Examples
Appinio Research · 01.11.2023 · 32min read

Are your customers truly at the heart of your business strategy? Understanding their experiences and interactions is key to success. In this guide, we'll navigate the intricate landscape of customer journey mapping, equipping you with the tools and insights needed to create exceptional customer experiences. From deciphering customer touchpoints to harnessing the power of emotions, we'll dive deep into every aspect of crafting an effective customer journey map. Let's explore how to transform your customer relationships and elevate your brand.
What is a Customer Journey Map?
A customer journey map is a powerful tool used by businesses to gain a holistic understanding of their customers' experiences throughout their interactions with the brand. It is a visual representation that illustrates the entire journey, from the initial awareness stage to post-purchase engagement.
Components of a Customer Journey Map
- Stages: A typical customer journey is divided into stages, including awareness, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase phases. These stages represent the key milestones in a customer's interaction with your brand.
- Customer Actions: Within each stage, customer actions are documented. These actions can include visiting your website, researching products, making a purchase, seeking customer support, and providing feedback.
- Touchpoints: Customer touchpoints are the points of contact where interactions occur. These can be digital, such as website visits and social media interactions, or physical, like in-store visits and phone calls.
- Emotions and Pain Points: Effective journey maps also incorporate the emotional aspects of the customer experience. They highlight where customers may feel frustration, delight, confusion, or satisfaction.
- Moments of Truth: These are pivotal moments in the journey that significantly influence a customer's perception of your brand. Moments of truth can be positive, such as exceptional customer service, or negative, like unresolved issues.
Importance of Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping is more than just a visual representation; it is a strategic tool with significant business implications. Here's why it's essential:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: By understanding the customer journey, businesses can identify pain points and areas for improvement, leading to a smoother and more enjoyable experience for customers.
- Improved Customer Retention: Identifying moments of truth and addressing pain points can foster customer loyalty and increase retention rates.
- Higher Conversion Rates: A well-optimized customer journey can boost conversion rates at critical stages, such as during the consideration and purchase phases.
- Data-Driven Insights: Customer journey maps are grounded in data and feedback, providing actionable insights that guide decision-making and strategic planning.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: The process of creating a customer journey map encourages collaboration among different departments within a company, ensuring a unified focus on the customer.
- Competitive Advantage: A thorough understanding of the customer journey can differentiate your brand from competitors by delivering a superior and personalized experience.
In summary, customer journey mapping is a vital tool for businesses looking to deliver exceptional customer experiences, enhance brand loyalty, and remain competitive in today's market. It provides valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making and continuous improvement efforts.
How to Prepare for Customer Journey Mapping?
Once you've recognized the importance of customer journey mapping, it's time to prepare for the process ahead. Proper preparation lays the foundation for a successful journey mapping endeavor.
1. Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before diving into customer journey mapping, you must be clear about what you aim to achieve. Your goals and objectives should drive the entire process. Consider these questions:
- What specific insights do you hope to gain from the journey mapping process?
- Are you looking to improve specific touchpoints, reduce customer churn, or enhance the overall customer experience?
- How will you measure the success of your journey mapping efforts?
By defining your goals upfront, you can focus your efforts and ensure that the resulting map aligns with your business objectives.
2. Identify Your Target Audience
Understanding your audience is at the core of effective customer journey mapping. Your customers are unique, and their experiences may vary widely. To create a customer journey map that resonates, you must define your target audience . Consider factors such as:
- Demographics : Who are your typical customers in terms of age, gender, location, and income?
- Behavior: What actions do they take when interacting with your brand?
- Preferences: What are their communication preferences and channels of choice?
The more detailed your understanding of your audience, the more accurate and actionable your customer journey map will be.
3. Gather Relevant Data and Information
Data is the lifeblood of customer journey mapping. To create a comprehensive map, you need to gather as much relevant data as possible. Sources of data may include:
- Customer Surveys: Collect customer feedback to understand their pain points, preferences, and expectations.
- Customer Support Tickets: Analyze support tickets to identify common issues and areas for improvement.
- Website Analytics: Dive into website data to see how customers navigate and interact with your online presence.
- Sales Data: Examine sales data to gain insights into the customer buying process.
Effective data collection is essential for a successful customer journey mapping initiative, and Appinio can be your trusted ally in this endeavor. Appinio empowers you to gather valuable customer insights swiftly and efficiently. With access to a diverse pool of respondents, you can tailor your surveys to target specific audience segments, ensuring that you capture a comprehensive range of perspectives.
Harness the power of data-driven decision-making with Appinio, and transform your customer journey mapping into a dynamic and responsive strategy. Dive into the world of insights – book a demo today!
Book a Demo
The depth and quality of your data collection will significantly impact the accuracy of your customer journey map. Remember to maintain data privacy and security throughout this process.
4. Assemble Your Team
Customer journey mapping is not a solo venture. It requires a cross-functional team with diverse perspectives and expertise. Assemble a team that may include members from:
- Marketing: Marketers can provide insights into customer segmentation and messaging strategies.
- Sales: Sales teams can shed light on the buying process and customer interactions.
- Customer Support: Customer support representatives can share knowledge about common customer issues and pain points.
- Product Development : Product teams can contribute insights into product-related touchpoints and improvements.
Collaboration across these functions ensures a holistic view of the customer journey. Remember that each team member brings a unique perspective that can lead to valuable insights.
With your preparations complete, you're now ready to embark on the journey mapping process.
What is the Customer Journey?
Now that you've laid the groundwork for your customer journey mapping project, it's time to delve into the core concepts that will enable you to create a comprehensive and effective customer journey map.
Customer Touchpoints
Customer touchpoints are the various interactions and moments of contact that customers have with your brand throughout their journey. These touchpoints can occur across multiple channels, both online and offline.
To effectively map the customer journey, it's essential to identify and analyze these touchpoints:
- Website Visits: Consider how customers navigate your website, which pages they visit, and where they drop off.
- Social Media Engagement: Examine how customers interact with your brand on social media platforms and the sentiment of their interactions.
- Email Communication: Evaluate the effectiveness of your email campaigns and the responses they generate.
- In-Person Interactions: If you have physical locations or provide face-to-face services, assess the customer experience during in-person interactions.
By mapping customer touchpoints, you gain insights into the various channels customers use to engage with your brand. This insight is invaluable for improving the overall customer experience.
Customer Emotions and Pain Points
Understanding customer emotions and identifying pain points are central to creating a customer journey map that resonates with your audience. Emotions play a significant role in shaping the customer experience, so consider the following:
- Emotional Highs and Lows: At which touchpoints do customers experience high levels of satisfaction, delight, or frustration?
- Moments of Confusion: Identify areas where customers might feel lost or encounter difficulties.
- Customer Feedback: Analyze customer feedback, reviews, and surveys to uncover recurring emotional themes.
By acknowledging and addressing these emotional aspects of the journey, you can take steps to enhance the overall experience and create more positive interactions.
Customer Needs and Expectations
To create a customer journey map that genuinely aligns with your audience, you must pinpoint your customers' specific needs and expectations at each stage of their journey.
Consider the following questions:
- Desired Outcomes: What are customers trying to achieve at each stage of their journey?
- Expectations: What do customers expect from your brand at different touchpoints?
- Information Needs: What kind of information are customers seeking, and where do they expect to find it?
Understanding customer needs and expectations allows you to tailor your map to meet those requirements effectively. It also helps you identify opportunities for proactive engagement and value delivery.
As you move forward with customer journey mapping, keep these three fundamental elements in mind. They will serve as the building blocks for creating a detailed and actionable map that will help you enhance the overall customer experience.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
Now that you've gained a solid understanding of the customer journey and its key components, it's time to roll up your sleeves and start crafting your customer journey map. We will guide you through the critical steps involved in the creation process.
1. Select the Right Template or Format
Choosing the appropriate template or format for your customer journey map is the first crucial step. The choice depends on factors such as the complexity of your customer journey and the level of detail you wish to include. Common formats include:
- Visual Diagrams: These are graphical representations of the journey, often resembling flowcharts. They provide a visual overview of the customer's path.
- Spreadsheets: Spreadsheets can be used to create detailed, data-driven customer journey maps. They allow you to input specific metrics, timelines, and customer actions.
- Specialized Software: Various software tools are available specifically designed for customer journey mapping. These tools often come with pre-built templates and features for collaboration.
Consider your team's familiarity with the chosen format and ensure it aligns with your objectives. The chosen format should facilitate the clear communication of insights.
2. Map the Customer Stages
To create an effective customer journey map, you need to identify and define the stages your customers go through when interacting with your brand. These stages typically include:
- Awareness: The initial stage where customers become aware of your brand or product.
- Consideration: Customers evaluate your offerings, comparing them with alternatives.
- Purchase: The stage where customers make a buying decision and complete a transaction.
- Post-Purchase Experience: After the purchase, customers assess their experience with your product or service.
Understanding these stages helps you structure your map and align it with the customer's journey from discovery to satisfaction.
3. Document Customer Actions
At each stage of the customer journey, document the specific actions customers take.
- Visiting your website: Track the pages they view and interactions they make.
- Engaging on social media: Note the types of engagement, such as likes, comments, or shares.
- Making a purchase: Record the product or service bought and the transaction details.
- Providing feedback: Document instances where customers offer feedback, whether positive or negative.
By documenting these actions, you create a roadmap illustrating how customers engage with your brand throughout their journey.
4. Identify Key Touchpoints
Key touchpoints are the critical moments of interaction between your brand and the customer. These touchpoints significantly influence the customer's perception of your brand. Examples of critical touchpoints might include:
- Homepage visit: The first impression customers have of your website.
- Customer support interaction: How effectively and empathetically your support team handles inquiries.
- Checkout process: The ease and efficiency of the purchasing process.
- Product delivery or service fulfillment: The customer's experience after making a purchase.
Identifying these touchpoints allows you to prioritize them when making improvements to the customer journey.
5. Incorporate Customer Emotions and Pain Points
As mentioned earlier, emotions and pain points are integral to understanding the customer journey fully. When creating your map, consider:
- Emotional Impact: Include icons or indicators that represent the emotional highs and lows experienced by customers at different stages and touchpoints.
- Pain Points: Highlight areas where customers might feel frustration, confusion, or dissatisfaction.
By visualizing these emotional aspects, your map becomes more empathetic and actionable.
6. Highlight Key Moments of Truth
Moments of truth are pivotal points in the customer journey that significantly impact the overall experience. These moments can be both positive and negative. Examples of moments of truth include:
- Resolution of a customer issue: How effectively a problem is resolved can create a lasting impression.
- Personalized recommendations: Providing tailored suggestions can enhance the buying experience.
- Timely communication: Prompt responses to inquiries or order updates can boost customer satisfaction.
Identifying and emphasizing these key moments on your map helps ensure they are addressed and optimized.
With these steps, you're well on your way to creating a detailed and insightful customer journey map that will serve as a valuable tool for enhancing the customer experience.
Customer Journey Map Template
Creating a customer journey map begins with a well-structured template that serves as the foundation for your visualization. While every map should be customized to fit your specific business and industry , here's a basic template to get you started. You can adapt and expand upon it as needed.
1. Customer Persona
- Name: Give your customer persona a fictional name to humanize the journey.
- Demographics: Include details such as age, gender, location, and occupation.
- Goals: Outline the main objectives and needs of this persona in their interactions with your brand.
2. Stages of the Journey
- Awareness: Describe how the customer becomes aware of your brand or product.
- Consideration: Detail the process of the customer evaluating your offerings.
- Purchase: Explain the steps leading to a successful transaction.
- Post-Purchase: Highlight the experiences and interactions that occur after the purchase is made.
3. Customer Actions
- List the actions: Within each stage, enumerate the specific actions the customer takes. This could include visiting your website, subscribing to your newsletter, or contacting customer support.
- Timeline: Create a timeline for each action to show the sequence of interactions.
4. Touchpoints
- Identify touchpoints: For each action, identify where the interaction takes place. It could be your website, social media, email, phone, or in-person.
- Channels: Specify the channels used, such as website, mobile app, social platforms, or physical locations.
5. Emotions and Pain Points
- Emotions: Capture the emotional state of the customer at each touchpoint, whether it's frustration, delight, or satisfaction.
- Pain Points: Document areas where the customer might encounter difficulties or experience frustration.
6. Moments of Truth
- Highlight moments: Identify the pivotal moments that significantly impact the customer's perception of your brand, both positive and negative.
- Importance: Indicate the level of significance or influence each moment holds.
7. Opportunities for Improvement
- Actionable insights: Based on the journey map, list potential improvements and opportunities to enhance the customer experience.
- Responsible Parties: Assign responsibility for each improvement to relevant departments or team members.
8. Monitoring and Measurement
- Key Metrics: Define the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will help you measure the success of your journey map.
- Frequency: Specify how often you will revisit the map and update it based on new data and insights.
Remember that this template is a starting point. You can customize it to align with your specific industry, customer segments, and objectives. As you gather data, engage with customers, and analyze feedback, your customer journey map will evolve and become a dynamic tool for improving the overall customer experience.
How to Interpret the Customer Journey Map?
With your customer journey map in hand, it's time to roll up your sleeves and extract valuable insights. Let's explore how you can analyze and interpret your map effectively.
1. Identify Opportunities for Improvement
Your customer journey map is a treasure trove of insights waiting to be uncovered. Start by closely examining the map and identifying areas where improvements can be made. These opportunities might include:
- Pain Points: Pinpoint where customers encounter frustration, delays, or roadblocks. These are prime areas for improvement.
- Communication Gaps: Identify instances where customers may not receive clear or timely information.
- Missing Touchpoints: Check for stages in the journey where there might be gaps in engagement or opportunities to connect with customers.
By identifying these opportunities, you set the stage for enhancing the overall customer experience and increasing customer satisfaction.
2. Address Pain Points and Friction
Once you've identified pain points in the customer journey, it's essential to take action to address them. Consider implementing the following strategies:
- Streamlining Processes: Simplify and optimize processes to reduce friction and make interactions smoother.
- Improving Communication: Enhance communication channels to ensure customers receive timely and relevant information.
- Offering Solutions: Develop solutions that directly address the specific pain points identified in the map.
Addressing pain points and friction not only improves the customer experience but also contributes to customer loyalty and retention.

3. Leverage Positive Touchpoints
Your customer journey map is not just about identifying issues—it's also about recognizing what's working well. Leverage the positive touchpoints to your advantage by:
- Replicating Success: Identify elements of these positive interactions that can be applied to other stages or touchpoints in the journey.
- Enhancing Personalization: Use insights from positive touchpoints to tailor your messaging and offerings to individual customer preferences.
- Fostering Engagement: Encourage more frequent and positive interactions by amplifying the aspects customers enjoy.
By amplifying positive touchpoints, you can create a consistently delightful customer journey that strengthens brand loyalty.
4. Align with Customer Needs and Expectations
Your customer journey map should be a reflection of your customer's needs and expectations. To ensure alignment, take the following steps:
- Regularly Review and Update: Keep your map current by revisiting it periodically to account for changes in customer behavior and market trends.
- Customer Feedback Integration: Continuously gather and incorporate customer feedback to adjust your map as necessary.
- Measure Performance: Use key performance indicators (KPIs) such as Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), and Conversion Rates to evaluate how well your map aligns with customer needs and expectations.
Alignment with customer needs and expectations is the cornerstone of a successful customer journey map. It ensures that your efforts are customer-centric and result in a more satisfying experience.
With your insights gained and improvements identified, it's time to move on to the next step: implementing changes based on the customer journey map.
How to Implement Changes Based on the Customer Journey Map?
After thoroughly analyzing and interpreting your customer journey map, it's time to put your insights into action. Implementing changes based on your map is critical to enhancing the customer experience and achieving your goals.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Collaborate across departments, including marketing, sales, customer support, and product development. Effective communication and teamwork are essential for successful implementation.
- Prioritize Actionable Insights: Not all insights from your map may be equally actionable or impactful. Prioritize changes that align with your objectives and have the potential to make the most significant difference in the customer journey.
- Develop an Action Plan: Create a detailed action plan that outlines the specific changes, responsibilities, timelines, and resources needed for implementation. This plan will serve as your roadmap for executing improvements.
- Test and Iterate: Before making broad changes, consider conducting pilot tests or small-scale implementations to assess their effectiveness. Continuously gather feedback and refine your approach based on results.
- Monitor and Measure Impact: Implement key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of your changes. Monitor metrics such as Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), Net Promoter Score ( NPS ), and Conversion Rates to gauge success.
- Feedback Loop: Maintain an open feedback loop with customers to gather their thoughts and reactions to the implemented changes. Customer feedback is invaluable for fine-tuning your efforts.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of all changes made based on your customer journey map. This documentation helps track progress and serves as a reference for future initiatives.
Examples of Effective Customer Journey Maps
To gain a deeper understanding of how customer journey mapping can be applied in real-world scenarios, let's explore some examples of companies that have successfully leveraged this strategy to enhance their customer experiences.
Example 1: Airbnb
Airbnb, the global vacation rental platform, excels at using customer journey mapping to create a seamless user experience. Their journey map spans from the moment a traveler starts searching for accommodation to the post-stay phase. Airbnb identified vital touchpoints, including website navigation, host communication, the booking process, and the stay itself.
How Airbnb Uses Journey Mapping:
- Personalization: Airbnb tailors its website content based on user preferences and search history, ensuring a personalized experience.
- Clear Communication: Hosts and guests can communicate through the platform, streamlining interactions and reducing friction.
- Post-Stay Engagement: After a stay, Airbnb encourages guests to leave reviews, fostering trust and transparency.
By mapping the entire journey and optimizing each touchpoint, Airbnb has become a customer-centric platform known for its user-friendly experience.
Example 2: Disney
Disney, a pioneer in the realm of customer experience, utilizes customer journey mapping extensively to create magical moments for visitors at their theme parks and resorts. Their journey map covers everything from planning a trip to the actual park experience and beyond.
How Disney Uses Journey Mapping:
- Pre-Visit Engagement: Disney engages customers even before they arrive by providing tools like the "My Disney Experience" app for planning and reservations.
- In-Park Experience: The company uses RFID technology for seamless entry, mobile food ordering, and interactive experiences within the park.
- Post-Visit Connection: Disney continues to engage with customers through personalized emails, offers, and surveys to gather feedback.
Disney's commitment to understanding and optimizing every stage of the customer journey contributes to its reputation as a world-class destination for families.
Example 3: Amazon
Amazon, the e-commerce giant , relies on customer journey mapping to enhance the online shopping experience. Their journey map encompasses the entire shopping process, from product discovery to delivery and customer support.
How Amazon Uses Journey Mapping:
- User-Friendly Interface: Amazon's website and mobile app are designed for ease of use, allowing customers to browse and purchase products effortlessly.
- Recommendation Engine: The company employs advanced algorithms to suggest products based on a customer's browsing and purchasing history.
- Efficient Fulfillment: Amazon's streamlined logistics and delivery services ensure prompt and reliable product deliveries.
Amazon's commitment to creating a frictionless shopping journey has made it a trusted and customer-centric e-commerce leader.
These examples showcase how diverse industries, from hospitality to entertainment and e-commerce, utilize customer journey mapping to create exceptional experiences. By examining their approaches, you can draw inspiration and adapt similar strategies to cater to your unique customer base and industry demands.
Remember, successful customer journey mapping is an ongoing process, so continue to refine and optimize based on customer feedback and evolving trends.
Continuous Customer Journey Optimization
Creating a customer journey map is not a one-and-done task; it's an ongoing process. To ensure your map remains relevant and effective in improving the customer experience, consider the following practices for continuous optimization:
- Regularly Update the Customer Journey Map: As your business evolves and customer preferences change, revisit and update your customer journey map accordingly. New touchpoints may emerge, and existing ones may evolve.
- Gather Customer Feedback and Data: Continue to collect feedback from your customers through surveys, reviews, and other channels. Use this data to refine your map and stay aligned with customer needs and expectations.
- Adapting to Changing Customer Behaviors and Trends: Keep a close eye on emerging trends, technologies, and shifts in customer behaviors. Be agile and ready to adjust your customer journey map to stay competitive and customer-focused.
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Analyze the customer journeys of your competitors to identify areas where you can differentiate and excel. Learn from both their successes and their mistakes.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Ensure your team members across various departments are well-trained and aware of the customer journey map. Encourage a customer-centric culture within your organization.
- Regularly Review and Revise Metrics: Assess the KPIs you use to measure the effectiveness of your customer journey map. Make sure they remain relevant and align with your evolving goals.
- Experiment and Innovate: Don't be afraid to experiment with new strategies, technologies, or approaches to enhance the customer journey. Innovation can lead to breakthrough improvements.
By continuously optimizing your customer journey map and staying attuned to your customers' evolving needs, you'll be better equipped to provide exceptional experiences that drive loyalty and business growth. Remember that customer journey optimization is an ongoing journey in itself.
Conclusion for Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey mapping is your compass to providing remarkable experiences for your customers. Following the steps outlined in this guide, you can now create effective maps, identify opportunities, and continuously optimize the journey. Remember, it's all about putting your customers first and making their interaction with your brand a journey they'll cherish. As you embark on your journey mapping endeavors, remember that the customer experience is ever-evolving. Stay agile, gather feedback, and adapt to changing customer behaviors and expectations. By doing so, you'll not only meet but exceed your customers' needs, fostering loyalty and driving your business toward long-term success.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map in Minutes?
Unlock the full potential of customer journey mapping with Appinio , the real-time market research platform that empowers businesses to harness real-time consumer insights for smarter, data-driven decisions. In just minutes, you can conduct your market research effortlessly, making it an integral part of your daily decision-making process.
- Instant Insights: Move from questions to actionable insights in a matter of minutes, ensuring you have the most up-to-date information to shape your customer journey map.
- User-Friendly: No need for a PhD in research – our intuitive platform is designed for anyone to use, making it accessible to every member of your team.
- Global Reach: With access to over 90 countries and the ability to define the right target group from 1200+ characteristics, Appinio enables you to reach your desired audience wherever they are.
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

17.04.2024 | 25min read
Quota Sampling: Definition, Types, Methods, Examples

15.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Market Share? Definition, Formula, Examples

11.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Data Analysis? Definition, Tools, Examples
How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map from Scratch

Creating a customer journey map can be a game-changer for your customer experience strategy. This is because online and offline buying has become increasingly complex
Think of the last time you purchased an item. Chances are you didn’t buy the first product you laid eyes on – you probably spent some time researching and interacting with companies, perhaps even on multiple devices.
And this is the way most consumers behave nowadays, for almost every product or service. According to a study led by Google, if we count all the possible research and interactions before and after a purchase, touchpoints may be anything from 20 (for candy) to 500 (for flights).

That’s why if you want to use an omnichannel approach effectively , and deliver excellent customer experience across all those touchpoints, you need to understand and map the customer journey.
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the customer journey — a view of all the interactions, touchpoints, and experiences that customers have with your brand up until purchase – and beyond.
Benefits of customer journey mapping
Companies that have built a customer journey map see a staggering 81 percent increase in customer satisfaction, based on a 2018 report. Other benefits include reduction in churn and complaints, and increase in Net Promoter Score .
Each one of the customer journey stages is an opportunity for you to stand out from your competitors by providing the right service at the right time. For example, if you know many customers check out your website before they make purchases, you’ll encourage them to buy from you if your site is easy to navigate with attractive UX.
What do you know about customer journey orchestration?
Find out how to individualize customer journeys and offer more personalized experiences.
6 steps to create a customer journey map
Each person will go through different steps in a different order. But, you don’t have to get every single detail correct. Focus on understanding the general pain points and feelings.
Here are six steps to do just that:
1. Get buy-in from stakeholders
Sync with other leaders in your company. For eighteen percent of companies, customer journey mapping is led by multiple stakeholders. And, when multiple stakeholders are involved, 92 percent of companies report positive or extremely positive impact of mapping. This means, the help of others might make your life easier and it’ll have a positive impact on your customer service goals .
So, make sure you collaborate with other departments. For example, you may need to talk about data: a CS leader might need the marketing department's help in understanding customer behavior on social media.
Also, getting buy-in from the very top is critical. The CEO, and generally the C-suite, may have deep insight into the customers. And, if they support the process, you can more easily get the resources you need to complete it (e.g. buying visualization software).
2. Buy stuff
Literally. Try buying one of your company’s products or services as if you were a consumer who’s only slightly familiar with your brand. Research online, click on ads, use the website product search, add products to your cart. Do this from mobile, desktop, and tablet.
While going through this exercise, note down the steps and touchpoints. Where did you go first and what did you do? Where would you go next if you were an actual customer? Here's a list with common touchpoints:
- Social media
- Content on the blog
- Physical shop
Also, note important points: what are the journey milestones? Which part of the process feels like a hassle? What’s missing that would make a customer’s journey easier?
3. Interview customers
If you want to get into customers’ minds, just ask them. About half of companies that map customer journeys use customer feedback solutions.
For example, you could prepare a short survey and offer a coupon or a small discount to those who complete it. You can use Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, or other survey tools. Questions could include:
- Where did you hear about our company?
- Please recall your first purchase with our company. How did you find the right product for you and what made you decide to buy it?
- What's the most frustrating experience you had while on our website?
- How have you interacted with our company via social media?
- Have you ever contacted our customer support? If so, what feedback can you give us?
Another (often better) way is to conduct customer interviews or collect their feedback directly. Your customer support team is invaluable here since they have access to customers on a regular basis. Invite frequent buyers and ask them to recall and describe the steps they took to buy your products.
4. Take advantage of data
Customer data is the most reliable way to inform your customer journey map. Check out your CRM or analytics tools to discover touchpoints and patterns.
Of course, make sure the data itself is reliable and complete. According to Treasure Data, 54 percent of companies say their biggest obstacle to leveraging data is “fragmented or siloed data.” If different systems hold data from different customer interactions, then it’s nearly impossible to have an accurate view of the customer journey.

To get rid of data silos, try customer service software which offers a unified customer view (UCV) . With a UCV, you can keep data from your interactions with customers, and their behaviors, demographics and information, in a single, easily accessible place. This way, you can map the customer journey more accurately – in fact, much of what you need is already displayed in the UCV.

5. Craft personas
This is a vital part of any customer experience strategy . You can create the customer journey map without paying attention to personas. But, if you do follow the persona road, you’ll have a greater opportunity to truly get into your customers’ minds and understand their wants and needs.
Based on the information you have collected, build personas of the types of customers usually interested in your business. These are the so-called “marketing” or “buyer personas” which are based on the purchasing habits, demographics, values, and goals of your customers.

For example, if you sell design software, your personas may be graphic designers, project managers, creative directors, architects, etc. Make the personas as detailed as possible based on the information you have. Then, you can build a customer journey map for each of the main personas you’re interested in.
6. Flesh out the journey
In order to map the customer journey, use a generic template as the backbone of the customer experience. This usually revolves around the following stages (which can be even more granular depending on a business’s needs):

This is just an example; you can choose a different system, like separating the consideration and research stages, merging decision and purchase, or adding stages like onboarding, after-sales customer relationship, online advocacy, and so on.
By using the information you’ve collected, start listing actions each persona might take. For example, according to research, 82 percent of smartphone users consult their phones on purchases they are about to make in-store. That means people on the consideration or research stages might start on mobile and end up at a physical store to purchase.
While you’re drawing the customer journey map, consider also the customers’ possible:
- Touchpoints. Where would they go from here?
- Feelings. What delights or frustrates them?
- Painpoints. What would they want improved?
Go into as much detail as you like. You know best how much information you need to visualize.
Customer journey map template
By following the steps above, you’ll build a customer journey map. Wondering what that looks like? Here’s a basic customer journey map example for one of the personas purchasing a laptop for business use:

When adding in visits to physical locations, switching from mobile to desktop, thoughts, and motivations of the customer, and so on, the customer journey can become very complicated. This diagram may be complex, but each point should be well-thought-out and easy to decipher.
For each pain point, find possible solutions and formulate a strategy to implement them.
Customer journey mapping tools
Creating the customer journey map takes time, so a dedicated visualization tool can make it faster. For example, you could evaluate tools like:
- Microsoft Visio
On to your (customer) journey
Mapping the customer journey takes time and effort. But, if anything is worthwhile, it is understanding your customers and what they want. Only then can you offer service that stands out and turn your customers into enthusiastic advocates of your brand .
Related Articles
Product Design Bundle and save
User Research New
Content Design
UX Design Fundamentals
Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
- UX training for teams
- Hire our alumni
- Student Stories
- State of UX Hiring Report 2024
- Our mission
- Advisory Council
Education for every phase of your UX career
Professional Diploma
Learn the full user experience (UX) process from research to interaction design to prototyping.
Combine the UX Diploma with the UI Certificate to pursue a career as a product designer.
Professional Certificates
Learn how to plan, execute, analyse and communicate user research effectively.
Master content design and UX writing principles, from tone and style to writing for interfaces.
Understand the fundamentals of UI elements and design systems, as well as the role of UI in UX.
Short Courses
Gain a solid foundation in the philosophy, principles and methods of user experience design.
Learn the essentials of software development so you can work more effectively with developers.
Give your team the skills, knowledge and mindset to create great digital products.
Join our hiring programme and access our list of certified professionals.
Learn about our mission to set the global standard in UX education.
Meet our leadership team with UX and education expertise.
Members of the council connect us to the wider UX industry.
Our team are available to answer any of your questions.
Fresh insights from experts, alumni and the wider design community.
Success stories from our course alumni building thriving careers.
Discover a wealth of UX expertise on our YouTube channel.
Latest industry insights. A practical guide to landing a job in UX.
How to design a customer journey map (A step-by-step guide)
A customer journey map is a visual representation of how a user interacts with your product. Learn how to create a customer journey map in this practical step-by-step guide.
The State of UX Hiring Report 2024
Learn how to start your UX career with hard facts and practical advice from those who have gone before you. In this report, we look at UX hiring trends in 2024 to help you break into the industry.
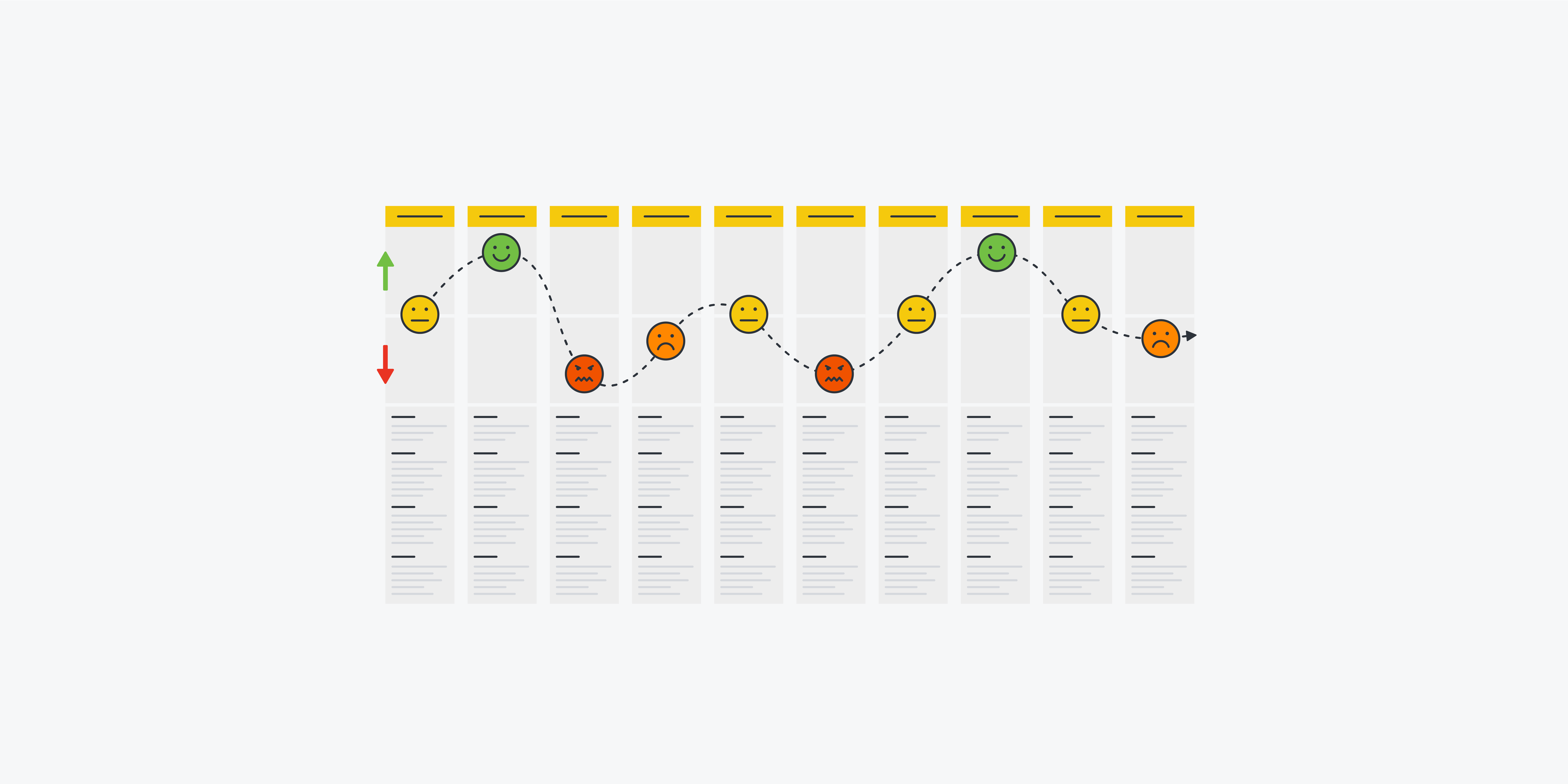
Successful UX design is rooted in empathy. The best designers are able to step into their users’ shoes and imagine what they think, feel, and experience as they interact with a product or service.
One of the most effective ways to foster user empathy and consider different perspectives is to create customer journey maps—otherwise known as customer journey maps.
If you’re new to journey mapping, look no further than this guide. We’ll explain:
- What is a customer journey map?
Why create customer journey maps?
When to create customer journey maps, what are the elements of a customer journey map, how to create a customer journey map (step-by-step).
If you want to skip straight to the how-to guide, just use the clickable menu to jump ahead. Otherwise, let’s begin with a definition.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UX]
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map (otherwise known as a user journey map) is a visual representation of how a user or customer interacts with your product. It maps out the steps they go through to complete a specific task or to achieve a particular goal—for example, purchasing a product from an e-commerce website or creating a profile on a dating app.
Where does their journey begin? What’s their first point of interaction with the product? What actions and steps do they take to reach their end goal? How do they feel at each stage?
You can answer all of those questions with a user journey map.
A user journey map template from Miro .
Creating customer journey maps helps to:
- Centre the end user and foster empathy. Creating a user/customer journey map requires you to step into the end user’s shoes and experience the product from their perspective. This reminds you to consider the user at all times and fosters empathy.
- Expose pain-points in the user experience. By viewing the product from the user’s perspective, you quickly become aware of pain-points or stumbling blocks within the user experience. Based on this insight, you can improve the product accordingly.
- Uncover design opportunities. User journey maps don’t just highlight pain-points; they can also inspire new ideas and opportunities. As you walk in your end user’s shoes, you might think “Ah! An [X] feature would be great here!”
- Get all key stakeholders aligned. User journey maps are both visual and concise, making them an effective communication tool. Anybody can look at a user journey map and instantly understand how the user interacts with the product. This helps to create a shared understanding of the user experience, building alignment among multiple stakeholders.
Ultimately, user journey maps are a great way to focus on the end user and understand how they experience your product. This helps you to create better user experiences that meet your users’ needs.
User journey maps can be useful at different stages of the product design process.
Perhaps you’ve got a fully-fledged product that you want to review and optimise, or completely redesign. You can create journey maps to visualise how your users currently interact with the product, helping you to identify pain-points and inform the next iteration of the product.
You can also create user journey maps at the ideation stage. Before developing new ideas, you might want to visualise them in action, mapping out potential user journeys to test their validity.
And, once you’ve created user journey maps, you can use them to guide you in the creation of wireframes and prototypes . Based on the steps mapped out in the user journey, you can see what touchpoints need to be included in the product and where.
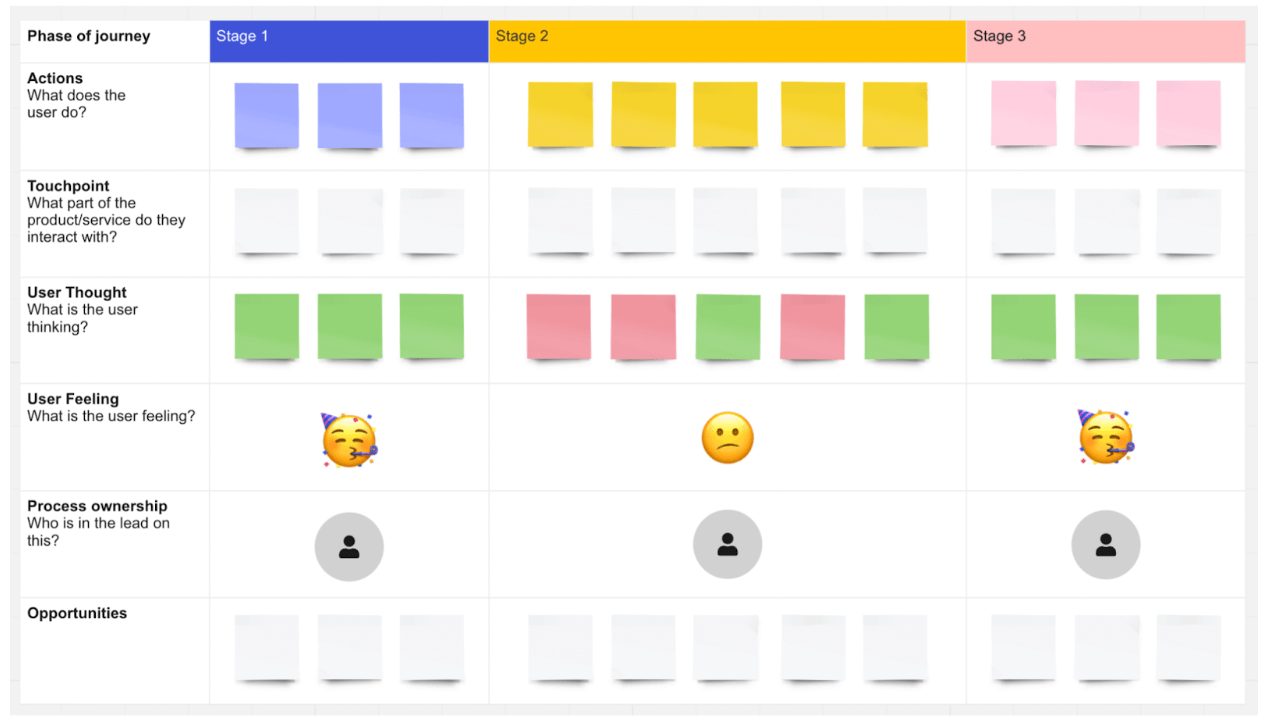
No two user journey maps are the same—you can adapt the structure and content of your maps to suit your needs. But, as a rule, user journey maps should include the following:
- A user persona. Each user journey map represents the perspective of just one user persona. Ideally, you’ll base your journey maps on UX personas that have been created using real user research data.
- A specific scenario. This describes the goal or task the journey map is conveying—in other words, the scenario in which the user finds themselves. For example, finding a language exchange partner on an app or returning a pair of shoes to an e-commerce company.
- User expectations. The goal of a user journey map is to see things from your end user’s perspective, so it’s useful to define what their expectations are as they complete the task you’re depicting.
- High-level stages or phases. You’ll divide the user journey into all the broad, high-level stages a user goes through. Imagine you’re creating a user journey map for the task of booking a hotel via your website. The stages in the user’s journey might be: Discover (the user discovers your website), Research (the user browses different hotel options), Compare (the user weighs up different options), Purchase (the user books a hotel).
- Touchpoints. Within each high-level phase, you’ll note down all the touchpoints the user comes across and interacts with. For example: the website homepage, a customer service agent, the checkout page.
- Actions. For each stage, you’ll also map out the individual actions the user takes. This includes things like applying filters, filling out user details, and submitting payment information.
- Thoughts. What is the user thinking at each stage? What questions do they have? For example: “I wonder if I can get a student discount” or “Why can’t I filter by location?”
- Emotions. How does the user feel at each stage? What emotions do they go through? This includes things like frustration, confusion, uncertainty, excitement, and joy.
- Pain-points. A brief note on any hurdles and points of friction the user encounters at each stage.
- Opportunities. Based on everything you’ve captured in your user journey map so far, what opportunities for improvement have you uncovered? How can you act upon your insights and who is responsible for leading those changes? The “opportunities” section turns your user journey map into something actionable.
Here’s how to create a user journey map in 6 steps:
- Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
- Define your persona and scenario
- Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions
- Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
- Identify opportunities
- Define action points and next steps
Let’s take a closer look.
[GET CERTIFIED IN UI DESIGN]
1. Choose a user journey map template (or create your own)
The easiest way to create a user journey map is to fill in a ready-made template. Tools like Miro , Lucidchart , and Canva all offer user/customer journey map templates that you can fill in directly or customise to make your own.
Here’s an example of a user journey map template from Canva:
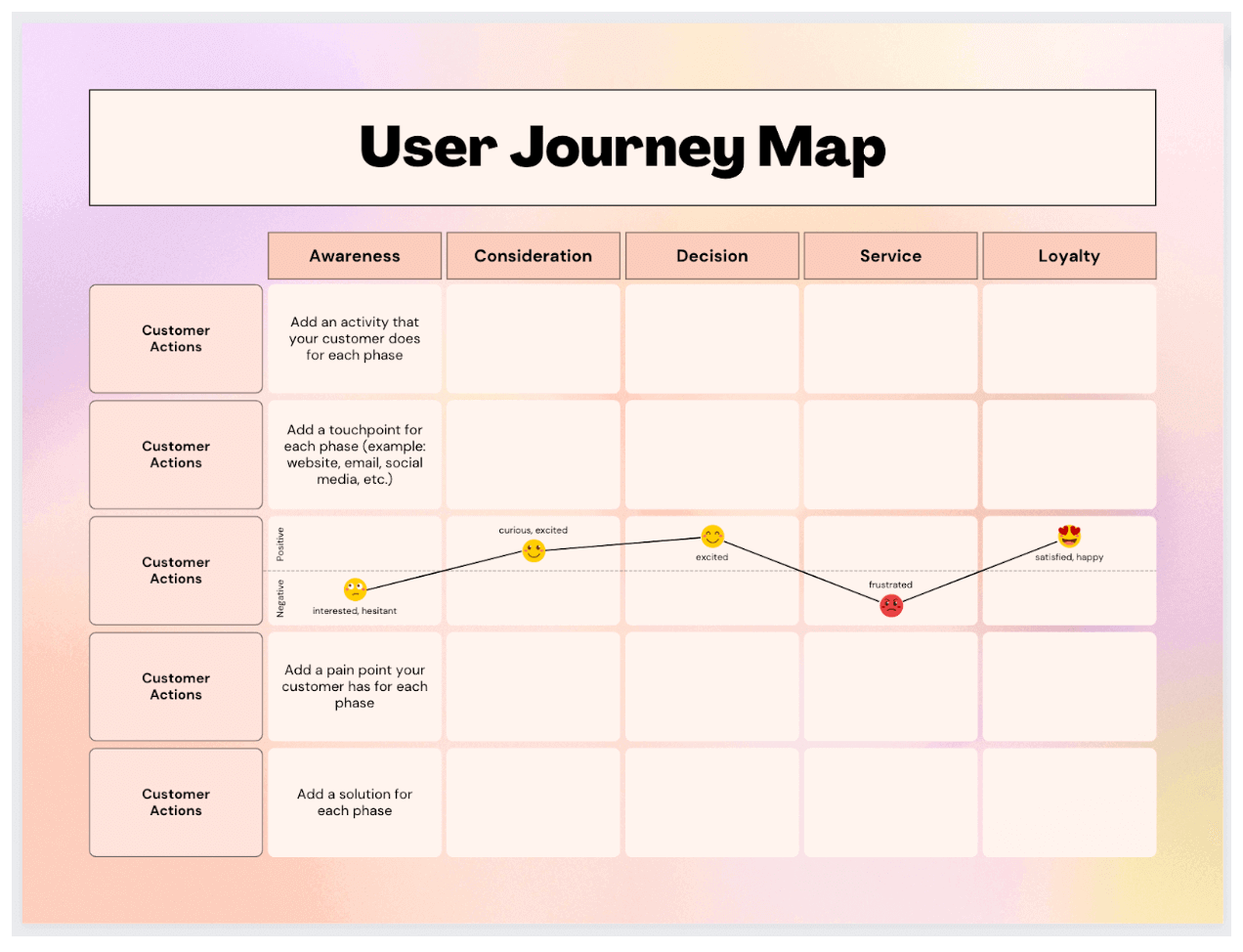
2. Define your persona and scenario
Each user journey map you create should represent a specific user journey from the perspective of a specific user persona. So: determine which UX persona will feature in your journey map, and what scenario they’re in. In other words, what goal or task are they trying to complete?
Add details of your persona and scenario at the top of your user journey map.
3. Outline key stages, actions, and touchpoints
Now it’s time to flesh out the user journey itself. First, consider the user scenario you’re conveying and think about how you can divide it into high-level phases.
Within each phase, identify the actions the user takes and the touchpoints they interact with.
Take, for example, the scenario of signing up for a dating app. You might divide the process into the following key phases: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Service, and Advocacy .
Within the Awareness phase, possible user actions might be: Hears about the dating app from friends, Sees an Instagram advert for the app, Looks for blog articles and reviews online.
4. Fill in the user’s thoughts, emotions, and pain-points
Next, step even further into your user’s shoes to imagine what they may be thinking and feeling at each stage, as well as what pain-points might get in their way.
To continue with our dating app example, the user’s thoughts during the Awareness phase might be: “ I’ve never used online dating before but maybe I should give this app a try…”
As they’re new to online dating, they may be feeling both interested and hesitant.
While looking for blog articles and reviews, the user struggles to find anything helpful or credible. This can be added to your user journey map under “pain-points”.
5. Identify opportunities
Now it’s time to turn your user pain-points into opportunities. In our dating app example, we identified that the user wanted to learn more about the app before signing up but couldn’t find any useful articles or reviews online.
How could you turn this into an opportunity? You might start to feature more dating app success stories on the company blog.
Frame your opportunities as action points and state who will be responsible for implementing them.
Here we’ve started to fill out the user journey map template for our dating app scenario:
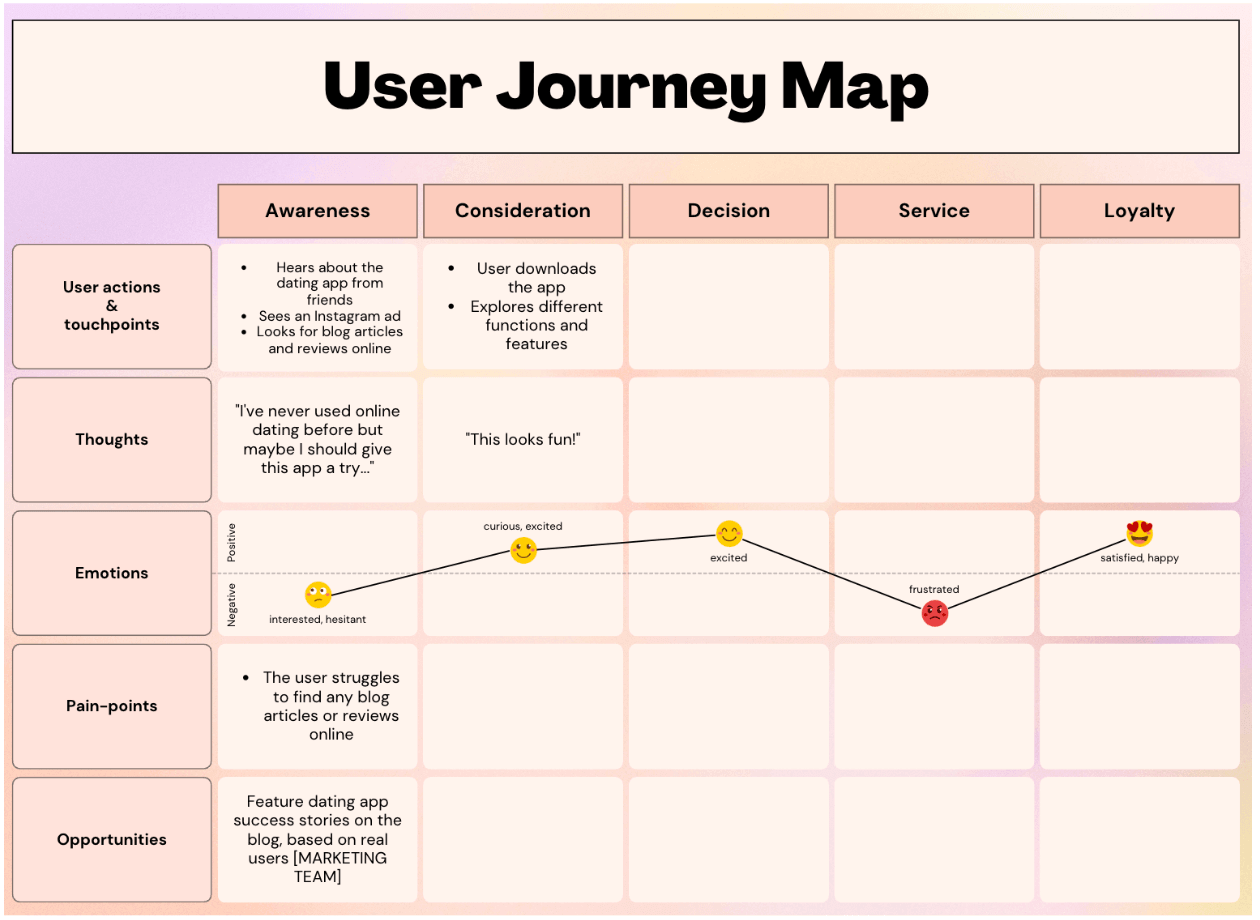
Repeat the process for each phase in the user journey until your map is complete.
6. Define action points and next steps
User journey maps are great for building empathy and getting you to see things from your user’s perspective. They’re also an excellent tool for communicating with stakeholders and creating a shared understanding around how different users experience your product.
Once your user journey map is complete, be sure to share it with all key stakeholders and talk them through the most relevant insights.
And, most importantly, turn those insights into clear action points. Which opportunities will you tap into and who will be involved? How will your user journey maps inform the evolution of your product? What are your next steps?
Customer journey maps in UX: the takeaway
That’s a wrap for user journey maps! With a user journey map template and our step-by-step guide, you can easily create your own maps and use them to inspire and inform your product design process.
For more how-to guides, check out:
- The Ultimate Guide to Storyboarding in UX
- How to Design Effective User Surveys for UX Research
- How to Conduct User Interviews
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the best UX insights and career advice direct to your inbox each month.
Thanks for subscribing to our newsletter
You'll now get the best career advice, industry insights and UX community content, direct to your inbox every month.
Upcoming courses
Professional diploma in ux design.
Learn the full UX process, from research to design to prototyping.
Professional Certificate in UI Design
Master key concepts and techniques of UI design.
Certificate in Software and Coding Fundamentals for UX
Collaborate effectively with software developers.
Certificate in UX Design Fundamentals
Get a comprehensive introduction to UX design.
Professional Certificate in Content Design
Learn the skills you need to start a career in content design.
Professional Certificate in User Research
Master the research skills that make UX professionals so valuable.
Upcoming course
Build your UX career with a globally-recognised, industry-approved certification. Get the mindset, the skills and the confidence of UX designers.
You may also like

The ultimate guide to mobile app design: Follow these UI principles & best practices
The best online survey tools to use in 2024

What is colour theory? A complete introductory guide
Build your UX career with a globally recognised, industry-approved qualification. Get the mindset, the confidence and the skills that make UX designers so valuable.
- Building Customer Experiences
- Scaling Your Store
- Conversion Optimization
- How to Sell Online
- Product News
How to Create an Ecommerce Customer Journey Map and Optimize for Sales
March 10, 2022

Elise Dopson

“I saw an ad for running shoes on Instagram, so I visited the store’s product page, read a review, and bought them.” — your (ideal) customer
As much as we’d like to think the steps someone takes to purchase from your store are always this simple, the reality is: they’re often far from it! Consumers switch between devices, channels, and platforms in the weeks leading up to a purchase.
And this information—their journey—can be crucial for you as you scale your brand.
A customer journey map shows the activities shoppers undergo prior to purchasing a product online (and can even extend to post-purchase activity). By understanding the pathway to purchase through your ecommerce site, you can better craft the right messaging to reach target customers , at the right time.
Below we’ll share how to create your own customer journey map, with tips on how to spot drop-off points and fix them.
The result? A positive customer experience that makes someone’s decision to purchase faster, easier, and friction-free.
This guide will cover:
What is a customer journey map?
The benefits of customer journey mapping, how to build a customer journey map.
A customer journey map is a visual representation of how people purchase products. You might see it called the “buyer journey” or “user journey map” as well.
In the case of ecommerce brands, a customer journey map shows:
- When a customer first became aware of a problem
- The options they considered when searching for a solution
- Why they decided to purchase your product
Take a look at this customer journey map example below by Nielsen Norman Group , which shows the touchpoints a customer has prior to buying a new car.
So-called “Emotional Eric” goes from seeing a TV commercial about a car company, through to downloading the mobile app, visiting a dealership, and driving away with a new vehicle. The map displays Eric’s thoughts, feelings, and considerations at each point in the journey, giving the dealership’s marketers greater insight into what Eric needs to see before converting.
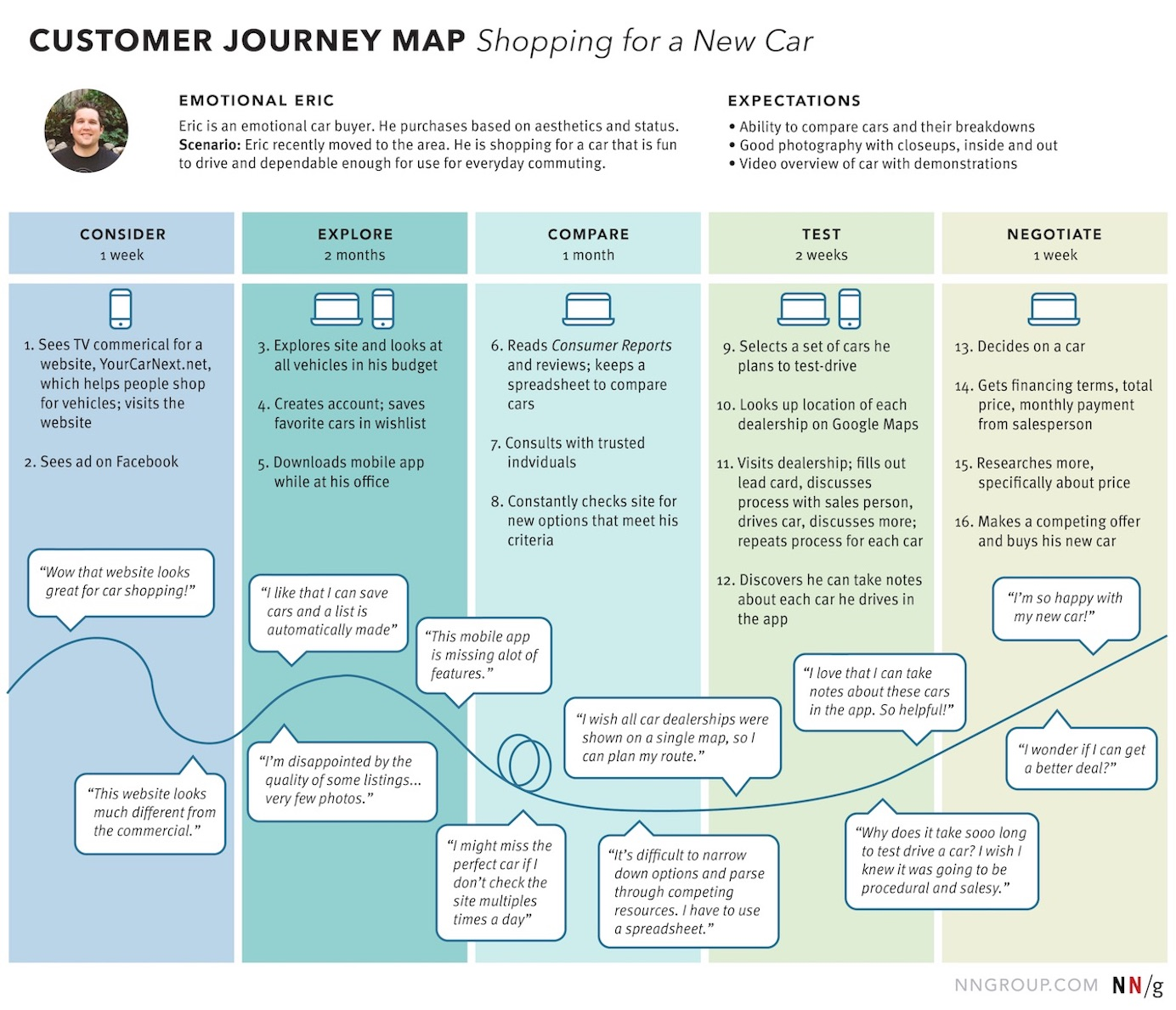
There are up to 24 million ecommerce websites in the world—many of which sell comparable products to those in your own inventory. Customers have more choices than ever. But what made existing customers—those who’ve given you their hard-earned cash—choose you?
Understanding the customer’s thoughts, feelings, and objections at each touchpoint gives you greater insight to improve your online store’s conversion rate.
Using the example of Emotional Eric, the dealership selling the car can use the customer journey map to:
- Personalize messaging . Purchase decisions depend largely on the content someone sees throughout their journey. Greater insight into thoughts, motivations, and customer pain points helps the dealership’s marketers produce materials that cater to Eric’s needs—from dedicated landing pages to social media posts.
- Understand channel performance. Your ecommerce brand may spend equal amounts of time on Instagram and Facebook. But a customer journey map could reveal TV commercials and Facebook advertising are the two channels that drive the most awareness with new customers. It makes sense to maximize ROI and double down on those channels instead.
- Prioritize user experience changes. If we come to learn Eric is disappointed by the quality of images in the mobile app, uploading new images can become a priority for the dealership. It’s a leak in their customer journey map that needs to be plugged to prevent other prospective customers from abandoning a purchase.

Not convinced on the power of journey mapping? High-performing teams are 1.6 times more likely to use customer journey management.
Though these personalization tactics aren’t just marketing checkboxes to tick. It’s a purchase motivator for the 65% of people who’d become a long-term customer of a store that provides a positive experience throughout the entire customer journey.
“Customer journey mapping heavily relies upon how the information is relayed to its target audience. The message should be clear and concise so that even a layperson has no trouble understanding the message.” — Albert Vaisman , founder of Soxy
When creating your own ecommerce customer journey map, you can focus on components of the journey (instead of taking on absolutely everything).
Though, as seen below, the highest performers are three times more likely to use customer journey orchestration, and two times more likely to analyze customer interactions over three or more channels over time. There’s a connection between how detailed you map your customer journey and the results you’ll reap!
This can guide your investment in the process.
#cta-visual-pb#<cta-title>Create a high-converting shopping experience that meets customers where they’re at<cta-title>Your perfect store is waiting for you to build it. Start building with Shogun today
Ready to uncover the steps a customer takes before purchasing your product? Here’s a step-by-step journey mapping process to create one for your ecommerce business.
1. Segment your audience
It’s impossible to lump all customers in one bucket. Different customers have different preferences, and use cases differ from product to product.
People who buy your toothpaste bundle won’t be solving the same problems as customers purchasing a teeth whitening kit.
“Some ecommerce brands don’t research enough, or the research they carry out is weak. You can’t start making a journey map through guessing.” — Ai Hiura , CMO and chief editor at FAVERIE
When building your customer journey map, don’t paint all customers with the same brush. Segment your audience by the traits they share, such as:
- Demographics. The beauty of ecommerce is selling products to anyone, anywhere. But scaling a global brand comes with its own challenges—like cultural differences. The shopping habits of European consumers differ from American consumers. You’ll want to consider segmenting out customers based on geographic location.
- Job to be done. The JTBD framework expresses the goal someone wants to achieve when purchasing a product. If you’re selling sneakers with your ecommerce website, for example, this can range from “look fashionable” to “support my feet when running.” You’ll want to identify your customer’s “jobs to be done” for various, finer segments of your audience.
- Product price. Customers purchasing expensive items have longer customer journeys than with cheaper items. The same applies to subscriptions. The higher the commitment, the longer the purchase journey. You can segment your audience by average order value ranges as you create your map.
2. Uncover common touchpoints
Once you’ve isolated your customer personas with segmentation, it’s time to conduct research.
Our goal at this point is to uncover the touchpoints a potential customer has prior to purchasing. Here’s how you can find them.
Collect customer data
There’s no better way to understand your customers than talking to them.
Aaron Masterson, founder of Local Furniture Outlet , says, “While it may be tempting to believe that we know more about our customers than we do, doing additional research that provides valuable data through interviews and analytics is the best way to approach building a customer journey map.
“Since customer journey maps are all about customers, it would be a mistake not to involve them when building one. Without putting customers at the center of focus, it is not possible to completely represent their experiences.”
Find the touchpoints previous customers had with your brand via order confirmation emails. Follow-up their purchase with an invite to complete a customer feedback survey —or, for more in-depth data, voice of the customer interviews.
Key questions to ask in these conversations include:
- What was happening in your life when you first decided you wanted to solve a problem?
- Did you consider any other options before purchasing this product? If so, why did you choose ours?
- What factors, if any, almost stopped you from purchasing this product?
You can use a market research repository like Userzoom or Aurelius to store all feedback—or a classic spreadsheet. Common themes will begin to appear over time, unveiling the touchpoints for your customer journey map.
#cta-paragraph-pb# Read more on creating buyer profiles: How—And Why—You Should Use Buyer Profiles and Quizzes for Your Store
Analyze your website activity and drop off points
While customer interviews are a great source of data, you’re not going to get the full picture of how people engage with your brand pre-purchase through interviews alone.
People forget about steps they’ve taken, thoughts they had, or content they engaged with. Customers also have a different point of view—even if they did take the same path to purchase.
Lift the lid on how potential customers engage with your website through:
- On-site surveys. Expand your data by surveying people in the middle of the customer journey—not just those who’ve completed it. Understand the frame of mind of a website visitor on your product page by asking, “What problem are you looking to solve?”
- Heatmaps. Software like Hotjar and Mouseflow shows “hot” parts of your website—places a visitor pays the most attention to. If you’re selling coolers through your online store, for example, you might find that people spend time reading whether items inside the box can withstand desert temperatures on a specific site page about this. That’s useful data for your customer journey map (maybe you can surface this info in your ads top-of-funnel, for example).
- Visitor recordings. Get granular with website activity by watching how people engage with your store. Pay close attention to the order in which they view different pages. Do they go from blog post to landing page to pricing page? Or the opposite direction?
- Google Analytics . Use the Shopping Behavior Analysis report to discover drop-off points or how many shoppers fall out of the customer journey. It becomes more clear where you need to focus your efforts (maybe you learn your new goal is to increase sessions with “add to cart” if drop off here is particularly noticeable, for example—or that you need to focus on cart abandonment).
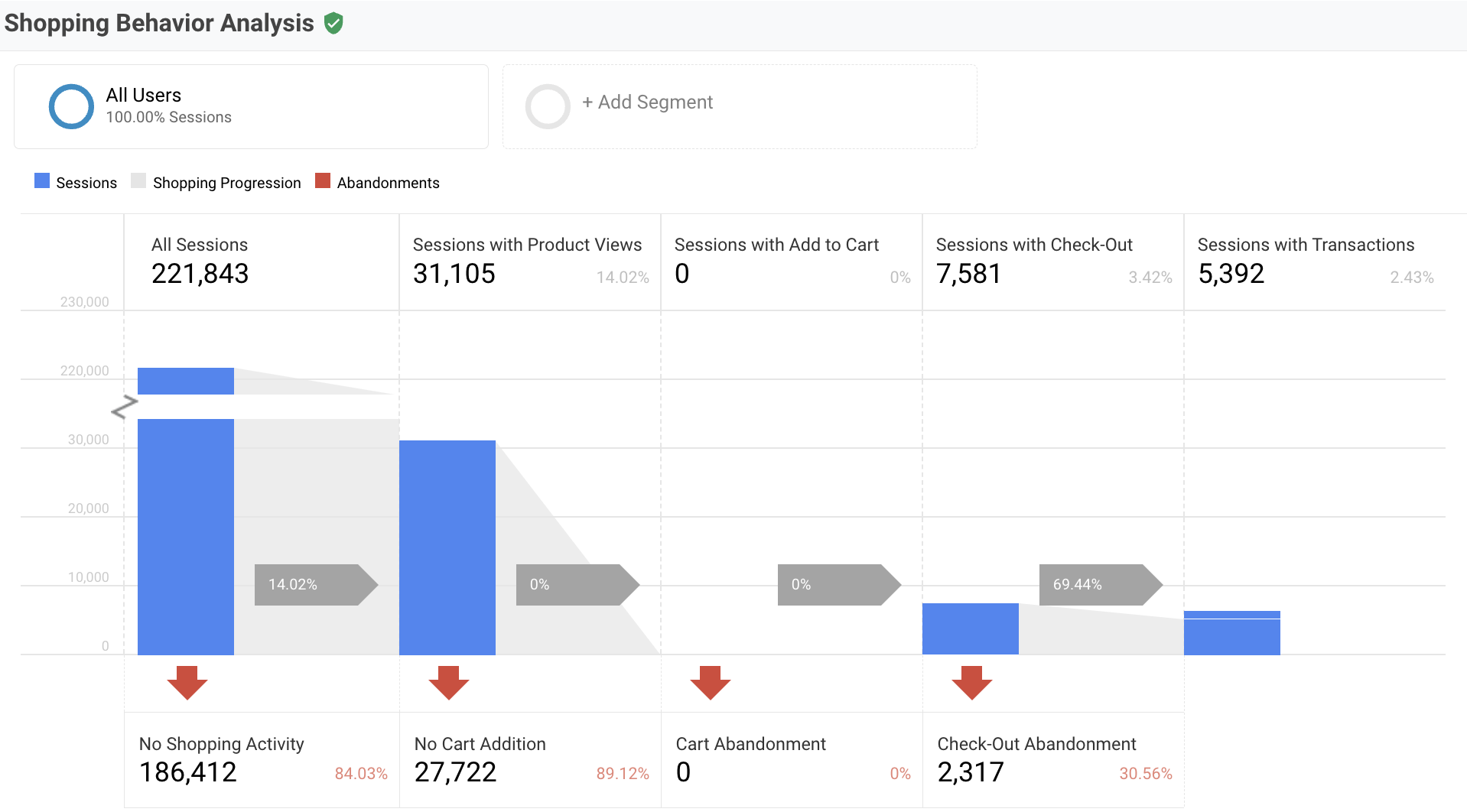
Albert Vaisman explains how they get their starting point mapped at Soxy: “I use direct traffic data when building a customer journey map. This measure provides me insight into how the target audience perceives my brand.
“I use direct traffic in my web analytics tool to observe the number of visitors who manually typed in my company’s URL. Then I compare this metric to other traffic sources. [I can also look at] my website’s bounce rate, optimizing accordingly.”
Mine your social media data
Social media is a hive of activity. Your ecommerce brand can listen in on conversations—even if your brand name isn’t explicitly mentioned—to understand the customer journey for products in your industry.
Adrienne Barnes, founder of Best Buyer Persona , is currently working with her client on this process. For shoe retailer Kuru Footwear , “We’re really trying to understand what was going on when a customer was encouraged to start looking for these shoes in particular.
“We’re trying to figure out when, in a buyer journey, do people go from being aware that they have a problem, to being solution or product aware?”
Using the orthopedic shoe example, Adrienne says the prospective customer is likely thinking, “I know that my feet hurt. I need something that’ll stop my feet from hurting. What are the things that I can do?” At this point, they start looking at shoes, insoles, surgery, or chiropractic care. You can see that on social media.”
“Delving into the social media data of the people who follow your brand can supply you with their age, gender, languages, and locations. You can also identify your audience’s interests, which can help you optimize your content strategy to address your target audience’s needs at every stage of the customer journey.” — Shaunak Amin , co-founder and CEO of SnackMagic
Collect team feedback
“A customer journey map is an organization-wide undertaking because the customer interacts with basically every part of a business,” says Stephen Light, CMO and co-owner of Nolah Mattress.
“Maps simply won’t be as effective as they could be without input from those actually delivering the customer’s experience.”
Merge the data you’ve got at this point from customers with your internal team feedback. Consult the following people to corroborate your existing data:
- Sales teams
- Stakeholders
- Customer support agents
- Social media managers
Chances are, they’ll have direct experience talking with your customers—valuable data you should add to your buyer journey map.
Validate your research
Not all data you collect throughout this process is 100% accurate.
“If you don’t talk to your customers and you’re not validating the things you see in your data, you could be putting the steps in the wrong place or making assumptions that aren’t true,” says Adrienne Barnes.
“We really put a microscope on the moment they decided to change or purchase a new product. That helps me identify: was it on social media? Was it within a Facebook group? An ad? I like to ask via interviews and verify via digital intelligence.”
As Adrienne says:
“People tell me, ‘I first heard about the product because I saw an ad on Instagram.’ I can go and look through analytics and internal data to see whether we’re actually doing that—including the conversions we’ve had and what [value props] we’re talking to within the ad.”
3. Organize customer touchpoints
At this point, you have more data than you know what to do with. It’s both a blessing and a curse.
Start making sense of your data by organizing touchpoints into different silos.
There’s no “best practice” for labelling these categories, though it makes sense to model your customer journey map on the marketing funnel.
Let’s put this into practice for building a customer journey map for an ecommerce business. For example, shoppers purchasing blue light-blocking glasses have the following touchpoints at each stage:
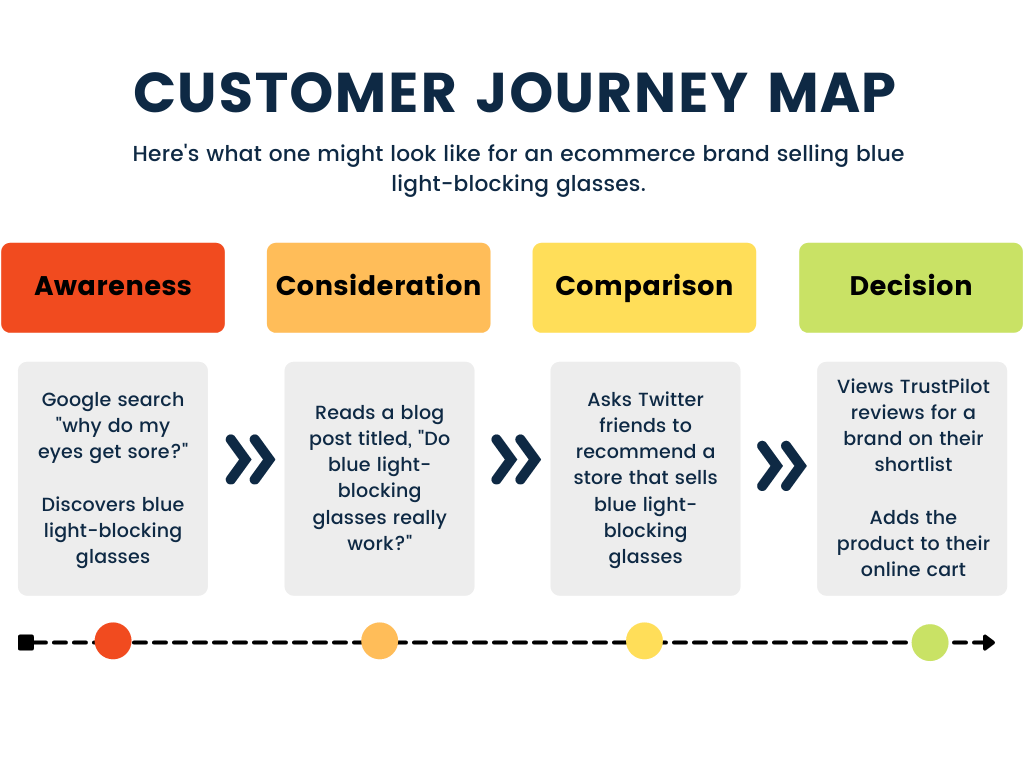
Next, you’ll add context around the thoughts and feelings the customer experiences at each stage in the buyer’s journey. This includes:
- Questions they’re asking
- Pain points they’re experiencing
- Actions they’re planning to take
Then, refine every interaction you have with your customer—including site content/copy, messaging, and your marketing strategy—to address each point at the right time . Each is an opportunity to personalize your approach and close the deal.
For example, if we learn that those shopping for blue light glasses need to see proof that they work (because they’ve tried solutions that don’t), you’re going to want to include this prominently across your ecommerce site:
- Endorsements from optometrists (social proof)
- References to scientific studies that prove the validity of blue-light glasses
- Case studies from previous customers whose eyes have stopped hurting because of the glasses
Consider as well that user-generated content could be a great way to address something like the consideration or comparison phases of the journey.
If we realize that in the consideration stage the customer wants to try on the glasses, maybe your eyewear brand needs to invest in a virtual try-on interaction on the site to help alleviate questions the customer has around the size of the glasses (something that’s difficult to judge online vs. in-store).
Warby Parker takes this approach with its mobile app . Shoppers can overlay eyewear onto a livestream of their face—much like a Snapchat filter—to see which suits them.
Finally, as customers reach the decision stage, they need one final vote of confidence before hitting “confirm order.”
If they’re struggling to overcome an expensive pair of blue light-blocking glasses, for example:
- Promote a free at-home trial or risk-free order
- Cross-sell lower priced items
- Show the shelf-life of your glasses (i.e. a $299 pair of your glasses every two years is cheaper than replacing $199 glasses yearly)
4. Identify points of friction
The goal of a customer journey map is to uncover the thoughts and feelings your target customer has prior to purchasing your product.
But not everyone will make it through the entire funnel. Customers fall out of the buying journey for several reasons—some of which are outside of your control; others you have the power to prevent.
Use the data collected earlier, including Google Analytics’ Shopping Behavior Analysis report, to uncover points at which customers stop engaging with your brand. This might be:
- When they switch devices
- When they exit your website
- When they read a specific piece of content
Once you isolate where customers are dropping off, you can make tweaks to your site and marketing materials to fix!
5. Improve your map’s conversion rate
Found the gaps in your customer journey? Next, plug the leaks and improve your conversion rate .
You’ll get customers from homepage to products, to purchase, and into post-purchase flows with as little friction as possible when you put yourself in the customer’s shoes.
For example, a consumer in the consideration stage falls out of the buying journey because they switched devices and couldn’t remember the name of the site they viewed. The potential fix might be a pop-up modal encouraging your website visitors to opt into SMS or email marketing (so the drop-off isn’t permanent!).
Similarly, you might find that customers fall out of the purchase journey because they haven’t found a solution to their problem. In this case, understand the customer’s perspective and:
- Run A/B tests on the site pages with the highest number of drop-offs to test your hypotheses of what needs to be added to this content to convert based on your new learnings.
- Cross-sell different items better positioned to the customer’s motivation you discovered with your customer journey map research
- Showcase social proof from customers suffering with the same issue your visitor has
Is your ecommerce website customer-centric?
As we’ve covered, in its simplest form, a customer journey map shows the touchpoints a shopper takes when purchasing items online, and you can even carry it into post-purchase.
Remember that while we can do our best to organize these touchpoints, your ecommerce customer journey map may never be entirely accurate—and that’s ok! As Adrienne Barnes says, “We like to think of a customer journey map as a linear process, but in reality, it’s pretty convoluted and messy.
“Have an awareness that the customer isn’t always going to follow your streamlined idea of a buyer journey. They have a whole life that purchasing your product is a minuscule piece of.”
Overall, work to uncover the touchpoints customers have for your ecommerce brand and craft the messaging your shoppers need. You’ll position your products in the right place, at the right time, to the right people—a winning formula for sales.
#cta-visual-fe#<cta-title>Create a high-converting shopping experience that meets customers where they’re at<cta-title>Your perfect store is waiting for you to build it. Start building with Shogun today

Elise Dopson is a freelance writer for B2B commerce and martech companies. When she's not writing, you'll find her in the Peak Freelance community or on Twitter.
The latest ecomm tips sent to your inbox
Share this post, you might also like.
How to Add Related Products to your Shopify Store to Increase AOV
The Ultimate Google Optimize Alternative for Shopify
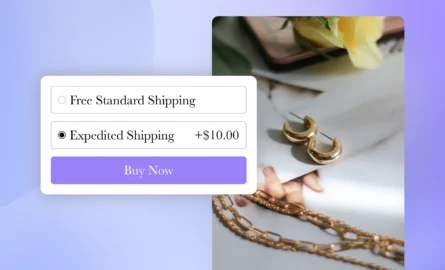
How To Set Shipping Rates by Location in Shopify
Advanced multi-store discounts.
[go_pricing id="pba-discounts"]
Cookie Settings is not available. Cookie Consent is disabled or is just disabled for your country.
- Jun 3, 2022
- 10 min read
The eCommerce customer journey and how to map it

Think about the last purchase you made.
How long did it take you to click ‘buy’? How many different sites, ads, emails, and stores did you check out before finally fetching your wallet?
Suffice to say that the typical buyer journey is anything but linear. Few shoppers convert right away, and every brand is challenged with adjusting their eCommerce marketing strategy to anticipate buyer movements both online and offline.
So, what can you do to stay ahead? Let’s talk more about what the eCommerce customer journey entails, and how to map your customer’s path to purchase when starting your business .
What is the eCommerce customer journey?
5 stages of the ecommerce customer journey, what factors affect the customer journey, customer journey mapping: why it’s a must, how to map the buyer journey for your business, example of a journey map.
Every so often, a buyer will take a relatively straight path to purchase. They'll search for a product, find your item, and within the same sitting, they'll complete the purchase.
But much more often, customers will be “pinballed” between various touchpoints. They’ll see between 6,000 to 10,000 ads in a day as they’re scrolling through their phones, checking their emails, or listening to Spotify. Then, once they decide to do some shopping, they’ll likely hop between Amazon, your site, and a competitor’s shop.
The eCommerce customer journey is the sum of all of these interactions (see our guide on what is eCommerce ). It begins with the moment a customer becomes aware of your brand to when he or she finally makes a purchase.
Some buyers will convert within mere days—while others may take several months or years. Tipping the scale towards the former outcome will require understanding the core stages and touchpoints of the customer journey and knowing how to make the best impact on your buyers.
Your customers’ overall journey can be broken down into five key stages.
01. Awareness
Your customer stumbles across your brand for the first time. Be it through an ad, social media, word of mouth, or SEO–they are now aware of your products. However, as noted earlier, many will not convert right away. Some may not even be looking to purchase anything at all.
At this stage, you’ll want to make sure you understand how people are finding your brand and who they are. Are they the buyer personas you expected to reach? How do demographics, acquisition source, and other factors affect what action your audience takes next?
While many visitors at this stage may just be “window browsing,” you’ve at least built some sort of brand recognition. Now it’s time to do something with it: retarget people, learn more about their interests, and guide them towards products that are most relevant to them.
02. Consideration
At this point, your buyer shows actual interest in your product. They’ve got their eyes on a particular product or set of products, and are deciding which one is worth buying.
Some may be trying to decide whether your item is a need versus a want. Others may be checking out product specs to make sure that your item is worth the price. Still others may be deal hunting or checking out options on competitive sites.
In any case, you’ll want to track which product pages people are spending the most time on, which products they’re comparing, and what other brands are on their radar. How can you convince them that your product is better? What can you do to build their confidence in your brand or incentivize a purchase?
03. Decision
Alas, your buyer makes a purchase on your site—assuming that the checkout process is easy and buyer friendly.
Your number one goal here is to make sure that the checkout process is seamless. Create a simple checkout flow, offer multiple (and secure) payment options, communicate your return policy, and provide all the information buyers need to feel supported by your brand.
Buyers should know when to expect their packages and any fees associated with their purchase. Don’t let any unwelcome surprises or lack of information lead to customers canceling their orders early.
04. Retention
Once a buyer makes their first purchase with your brand, they’ll ideally become a repeat customer . A positive customer experience—including excellent customer service, on-time delivery, and a multichannel marketing strategy—can work together to build customer loyalty .
Note that even though you’ve won the first sale, you’ll need to continuously earn a buyer’s patronage time and time again. Be consistent in your messaging. Engage buyers frequently. Offer incentives or employ strategies for upselling and cross-selling .
05. Advocacy
Happy customers have the potential to attract other happy customers. Buyers at this final leg of the customer journey are (hopefully) so happy with your product and/or service that they’re eager to spread the word to their friends and family.
Of course, this isn’t a passive activity. You’ll want to proactively nurture brand ambassadors by creating a customer loyalty program , hosting giveaways, showing appreciation, and taking other steps to inspire advocacy.
Your customers are a moving target. Between their unique preferences and backgrounds—plus their prior experiences with brands—there are tons of factors that shape the way they make their purchases.
As you track the various ways that customers interact with your brand, consider how trends like the ones below can make a big impact on the buyer journey.
Social and economic changes - e.g., the recent pandemic. These events tend to spur shifts in buying behaviors and expectations, as many types of businesses and buyers alike adapt to new realities. With each shift, consumers tend to get smarter and potentially pickier on what defines a good value and how to spend their money.
Convergence of online and offline shopping - Omnichannel retail isn’t just a concept anymore. Today, the lines between the offline and online worlds are increasingly blurred—with digital native brands like Warby Parker opening physical showrooms, and longtime retailers like T.J. Maxx investing more in online commerce. Curbside pickup, BOPIS, and in-store returns are just the beginning of what’s to come; brands should expect the customer journey to entail a greater mix of online and offline touchpoints, regardless of whether a customer originated online or not.
Corporate responsibility - Brands today are expected to do good. Inactivity or a difference in values could shape a customer’s engagement with your brand at any point of the buyer’s journey.
Choice paralysis - The proliferation of brands and products online have the ability to frustrate consumers. Make sure that your website is organized in such a way that customers know exactly where to find what they’re looking for. Make it easier for them to filter out noise and/or compare similar options. The last thing you want is for an overabundance of options—or poor site design—to deter your customers from buying. Learn more about combatting choice paralysis .
While customer journey mapping is an imperfect science, the benefits are undeniable.
In fact, 30% of surveyed retailers reported significant improvements in customer lifetime value and customer advocacy after investing in digital customer experience (CX). Roughly 23% reported an increase in average order size as well.
This exercise can help you to achieve multiple goal including:
Getting more clarity over how buyers interact with you - By carefully mapping your customer journey, you can gain a clear understanding of your buyers and their habits. A map helps you to see things from the buyer's perspective rather than your business’s perspective.
Improving customer retention rates - A map helps you to identify when and why prospective buyers are dropping. For example, an ill-worded message or one displayed in the wrong place at the wrong time could be all that’s causing buyers to regress in their journey. By making strategic changes and reducing friction in the customer experience, you can enjoy an easier time attracting and retaining buyers.
Sharpening your focus and organization - This exercise will force you to lay everything on the table–from all of your marketing campaigns to all the possible interactions a customer may have with your brand. From there, you can determine the health of each channel, who owns which touchpoint, and realistic goals for each event.
Increasing revenue - When you understand how buyers interact with your business in detail, you can more accurately cater your communications, offers, content, and promotions to influence sales. It’s all too easy to rely on assumptions or old habits when engaging customers. A journey map helps to shed light on biases and pain points that you may not have known were there before.
So how do you actually map the customer journey? Here are five steps to get you started.
Step 1. Describe your buyer personas
Before building a map, you must clearly define your target customer types. Are you looking to engage parents, young adults, or consumers with specific hobbies?
Your personas should include as much detail as possible. Make sure to base them around real data—not made-up, fake, or idealistic data. Talk to various stakeholders, interview your customers, consult social media, or perform user testing.
In other words, don't build a buyer profile based on what you think a customer should look like. Create your buyer personas using actual data you gathered from the places where they hang out and from talking directly to your target audience.
Step 2. Define the main character of your map
Now, you can decide which set of customers you’d like to analyze as part of the journey mapping process. The map will look different for each type of buyer you target, and trying to address all of them at once will only muddy the data.
To start, pick the most common persona (i.e., the most valuable or largest cohort). You’ll have an easier time collecting data this way, plus taking meaningful action from your journey map.
Step 3. Analyze on-site behaviors
As an initial step, check out the behaviors on your website and jot down the top pages that people enter your site from, where they exit or bounce, and which ones are the highest converting. Tools like Google Analytics and Wix Analytics can help to fill in these blanks.
To get more specific, make sure to filter your data according to criteria that’s most relevant to your buyer persona: geo, new versus returning users, and device (to name a few).
You may already start to see areas where people drop off and opportunities to optimize your site. You can additionally gain insight into what your buyer is more interested in buying based on where they linger on your site (though note that this could be heavily influenced by how accessible a page is from other areas of your site).
Step 4. List all other customer touchpoints
List out all the ways that your target buyer can interact with your company, both on and off your site. Include things like:
Social media
Review sites
Publications
Popup stores
Onsite banners
Physical stores
Marketplaces that you sell on
Help center
Loyalty program
Seasonal promotions
From here, you’ll want to list out all the possible actions someone could take from each channel. For instance, when someone interacts with a blog, he or she may subscribe to your newsletter, download a piece of content that you promote, click to another blog—or even request a demo. Alternatively, your visitor may bounce.
The purpose of this exercise is to audit all the CTAs you include on a single page, as well as links and other messaging that may influence a visitor’s behaviors. You’ll moreover want to look into whether reality aligns with expectations.
When you compare your list of expected behaviors with the data you gathered from Google Analytics, Wix Analytics, and other sources—do the results align? How can you better define the purpose of each channel, and match your goals with a visitor intent?
Step 5. Visualize the journey
Finally, you can document all of your findings into one easy-to-reference map. The scope of your journey map can vary depending on your goal. For instance, you could show the complete customer journey (as shown below) or hone in on just a part of it where you see the most room for improvement.
A map may cover everything from a buyer’s emotions, to their actions, to roles and responsibilities on your team at each stage. It can serve as both a tool for predicting buyer behaviors and keeping your team organized.
That said, there are several types of journey maps you can create:
Current state map - This shows how customers interact with your brand today. You could use it to compare behaviors between two different segments of buyers, or to uncover how customer emotions and behaviors vary depending on how they find your products (as an example).
Future state map - This illustrates the ideal journey that you want your customers to take. It helps your team rally around specific goals and identify critical points of a customer’s journey.
Day in the life map - This is similar to a current state map, except that it doesn’t start and end with a buyers’ interaction with your brand. It aims to understand all of their daily activities and lifestyles, with the goal of developing new, meaningful touchpoints.
Service blueprints - This takes a simplified version of one of the maps above, then adds in details about the various people, technologies, and processes that take place behind the scenes. The purpose is to audit and optimize how your team functions in the background to support the customer journey.
Let’s imagine that you own an online shop for pet supplies. You want to create a current state map in order to see how your core customers (new dog owners) are interacting with your brand. Your map may look something like this.
This helps your team keep track of the most effective campaigns, products, and channels. You’ll likely look to expand upon this map soon, as you get even more granular in your research or launch new campaigns.
There is no right or wrong way to create an eCommerce journey map. The framework outlined here is just meant to provide a good starting point. Once you have a baseline, you can continue to modify and rework your journey map to fit your unique business.
Remember that the customer journey is constantly evolving. Re-evaluate your eCommerce journey map once a quarter or at least once every six months. Aim to reduce friction in the customer journey and put assumptions to the test.

Allison Lee
Editor, Wix eCommerce
Allison is the editor for the Wix eCommerce blog, with several years of experience reporting on eCommerce news, strategies, and founder stories.
- Sell Online
Related Posts
What are flash sales? A step-by-step guide with examples
14 effective eCommerce marketing strategies for you to keep sales rolling in
4 strategies for abandoned cart recovery and how to reclaim those sales


How to Create a Customer Journey Map That Connects
Nov 17, 2023 | Read time: 14 min.
Mike Rotella , Senior Marketing Specialist
- A customer journey map is a marketing tool that visually represents the journey customers take to reach a purchase decision, including the touchpoints and stages throughout that path.
- Customer journey maps help brands get the average consumer’s perspective to create a personalized research and buying experience.
- The customer journey mapping process takes stock of your assets and customer touchpoints, provides optimization opportunities, reveals gaps, and lets brands deliver value to consumers wherever they start their journey.
Contents Jump to
If you’re a marketer for a billion dollar retailer, you probably know your customers pretty well. No doubt you have dozens of buyer personas that describe when they wake up, their favorite foods, and where they shop. But, do you have a customer journey map?
Customer journey maps allow you to get a better understanding of the customer’s perspective so you can craft a more personalized shopping experience. The more you understand your customers, the better you can serve them and the more likely it is that they’ll come back again and again.
Read on and uncover the what, why, and how of customer journey mapping.
The traditional customer journey
At a high level, the customer journey is traditionally broken down into three stages:
- Awareness – The person is aware of a problem or opportunity, but they need more information so that they can fully understand the issue and specifically name it.
- Consideration – The person clearly understands the problem/opportunity. They are now thoroughly researching options so that they are aware of different methods for addressing the issue.
- Decision – The person is making a final decision as to which product/service to purchase.
The above describes the old customer journey, one that struggles to reflect the real customer lifecycle . It’s becoming outdated. With the advent of search intent-derived consumer insights and newer understandings of human behavior, updated models are required.
Today’s realistic customer journey:
- Acknowledges that journeys are non-linear, with consumers entering at many different points
- Divides consumers into two categories: the 95% researching, and the 5% who are ready to buy
- Better reflects consumer behavior and aligns with today’s customer needs
- Leverages touchpoints and assets to deliver substantial value at each step of the journey and before asking for a transaction
To get the most out of this article, we recommend checking out Rethinking the Buyer’s Journey for a full discussion on the real path consumers are taking.
What is a customer journey map?
MARKETING TERM DEFINITION Customer Journey Map A customer journey map is a visual guide illustrating the customer’s experience. It pinpoints key moments, showcasing customer needs and emotions, while also identifying brand touchpoints, gaps, and areas of friction.
Journey maps are like roadmaps for your customer personas. They go beyond demographic information and help marketing team members and stakeholders walk in your customer’s shoes. As a result, you’ll set more customer-focused business goals, and create a more seamless omnichannel experience.
Journey maps also give marketing teams a customer-centric visualization of how your target audience thinks. They encourage you to ask important market research questions like:
- What caused them to identify a frustration, problem, issue, need, or new goal or opportunity?
- What do they do when they realize this problem/opportunity?
- Where do they turn?
- What sources of information do they use?
- Where do they visit online?
- Whose advice do they seek?
- What frustrations do they encounter along the way?
- What are their questions at each step of the journey?
Think of all the different ways prospects experience your brand in real-time: email, social media, video, search engines, your website, TV, etc. The customer journey map helps you take stock of all these different customer touchpoints , optimize them, and fill important gaps.
Get Terakeet’s free customer journey map template below!
Customer Journey Map Template
Create better journey maps to reveal consumer needs.
Benefits of customer journey mapping
Creating a customer journey map is one of the most important visual tools brands can leverage to connect with their customers, truly understand their needs, treat them like real people, and ultimately, detect gaps and friction points that damage conversions.
Reveals audience insights
Customer journey mapping reveals how different types of customers move through your marketing funnel, which helps brands understand their customers’ needs in order to improve the user experience for each demographic. It also creates opportunities to optimize your marketing strategy across your buyer personas.
For example, millennials will interact with your company differently than baby boomers. C-Suite executives have different priorities than small business owners, and each will take different steps before arriving at the purchasing decision.
Journey mapping unlocks the many paths to a purchase that your audience travels on, and lets you optimize with deep audience insight in the driver’s seat.
Delivers value
When you understand the customer journey and have a map in place, brand marketers can zero in on each individual touchpoint or asset to ensure that each delivers a unique value to consumers. With each touchpoint optimized, brands establish a network ready to help consumers reach solutions and achieve customer satisfaction.
The value provided at each engagement gives consumers what they want, building the relationship way before they’re ready to buy. This helps boost the trust needed for transactions and puts the brand in the forefront of the consumer mind into the future.
Creates connections
All the effort of customer journey mapping pays off because it enables marketers to connect with consumers at all journey points. This eases friction points, and removes roadblocks that could lead to lost sales, increased churn, or a poor reputation. As a result, you’ll shorten the buying cycle, improve conversion rates, and increase customer retention.
Creating a great customer journey is the key to authentic connections. When you make authentic connections, the KPIs and metrics that indicate success necessarily move in the right direction.
How to create a customer journey map in 8 steps
This is how you can create a customer journey map (plus a few high-performance upgrades):
1. Set your goals
Before launching a journey mapping project, it’s important to have clear goals and objectives.
Determining your goals and measurement metrics will likely involve a cross-departmental team in order to understand the relevant needs of the project. What are you trying to improve? How will you measure it? What is your current conversion rate? Answering these questions can guide the process.
2. Define audience segments and buyer personas
First, define your audience segments based on the different types of customers that you serve. Then, create buyer personas within those segments.
If you sell consulting services, you may have one segment for healthcare clients, another for financial services, and yet another for technology. Or maybe you segment your audience by the number of employees or geography.
Perhaps you instead segment your audience by age group — an ecommerce fashion brand may target pre-teens, teens, and women separately. Or, if you’re a fashion brand like Athleta, you target by activity — yoga, running, hiking, cold weather training, tennis, golf, swimming, etc.
Once you segment your audience, build personas of your ideal customers in each segment. Here are some examples of buyer personas to get started.
Obviously, persona information will vary depending on whether you’re B2B or B2C and the price of your product/service. Some information you may want to include:
- Income / revenue
- Job to be done (JTBD)
- Pain points
- Products desired
- Features desired
The objective is to thoroughly understand your ideal customers. When you have clarity on what they want and what their struggles are, you can create a customer journey that resonates with them, guides them through the process, and moves them to take action.
3. Identify customer pain points with empathy maps
The next step in creating your customer journey map is to clearly identify customer pain points at each step of the journey.
In the initial awareness stage, what are they feeling? What frustrations are they experiencing? What is motivating them to start exploring solutions to their problem? Do they need a certain type of educational content?
During the consideration stage, what information do they need? What is keeping them from moving forward?
In the decision stage, what is hindering them from pulling the trigger? Do they have sufficient comparisons with alternatives? What are their fears, and how can you alleviate those fears? Have you provided them with sufficient social proof and assurances.
During the retention stage, gather Voice of the Customer feedback such as a net promoter score (NPS) from long-term customers.
Remember, the buying process is both factual and emotional. People’s decision making is based on a combination of concrete information and subjective emotions. To truly understand your customers, deploy an empathy map to address both types of potential roadblocks.
4. Use search intent data to deeply grasp customer desire
“How do I find out what questions and searches potential customers are performing?” you might ask.
The answer: search intent data from what we call the world’s most honest focus group — Google.
The searches of millions of users are available to marketers to really understand consumers, their motivations, and how to help them solve their biggest pain points.
Consumers who need to find solutions go to Google and seek out exactly what they want. Search-derived consumer insight answers the what and lets brands prepare a journey that aligns.
Brands that strategically leverage this revealing, honest customer data can use it at every point across the customer journey map to deliver what people want. Then tools like the MACH-6 can be used to provide structure to customer journey touchpoints through your network of assets (more on that in step 6). This builds authentic connections and ensures your map actually reflects reality.
Boosting customer engagement
At each step of the customer journey, you need to have specific, effective ways to engage with your audience. You need to be able to speak to relevant pain points, thoroughly answer questions, and help prospects take the next step in the buying journey.
There are dozens of ways to engage your audience. You need to choose the ones that will best serve your potential customers in contextually relevant ways through their journey. At each step in the customer journey map, determine what the potential customer wants or needs most and how you can provide that for them.
It’s about creating the best possible customer interaction by delivering on customer expectations. Search intent data makes this achievable.
5. List the customer touchpoints
What are customer touchpoints ? They’re all the different ways a prospective customer interacts with your brand during their journey. This includes, but isn’t limited to:
- Your website
- Third-party websites
- Social media
- Search engines
- Review sites
- Influencers
- Product demos
- Sales team interactions
- Customer support/customer success interactions
Include each touchpoint in your customer journey map. Seeing the different touchpoints gives you insight into the different steps customers take before finally making a buying decision.
By understanding their state of mind at each step in the customer journey, you can uncover psychological triggers that can help them feel more confident in taking the next steps. You can then optimize each brand touchpoint, or even reduce the number of touchpoints required.
Audience actions
When identifying touchpoints, focus primarily on ones where people take action. Whether they click on a Google search result, interact on social media, or respond to an email, look for all the different ways your audience takes action.
Once you have a list of actions, determine the underlying motivations and reasons at each step in the journey. Then, look for ways to reduce the number of actions a person must take along their customer journey to increase conversion rates.
Questions throughout the customer journey
It’s also important to identify the questions potential customers ask at each touchpoint in your customer journey map. Confusion, jargon, and uncertainty can hinder prospects from moving forward in the buying journey.
Document the actual questions running through the minds of your prospective customers at each step of the journey. Do this, and you’ll likely be ahead of many of your competitors.
If you don’t know the questions they are asking, start interviewing them and conduct surveys. You can also get insight from live chat sessions, your salespeople, and support teams. Even better, use search intent data — see step 5.
The more questions you can answer at each touchpoint, the less friction potential customers will feel and the more likely it is that they’ll move on to the next phase of the journey.
6. Organize your touchpoints by degree of control
The MACH-6 , an asset organization tool, can help you arrange your touchpoints across the customer journey in a more strategic manner. Instead of a big list of brand-owned and unowned properties, the MACH-6 arranges touchpoints based on degree of brand control.
You start with your owned assets , those you fully control, move into those you manage, then focus on those you merely influence.
Using this framework, you can assess all the assets you have, where they land on the MACH-6, and determine what linkages are missing, need development, or require optimization.
7. Re-assess your current state customer journey and develop your future state
Next, determine how your current journey looks. This will help find gaps, friction points, and alignment opportunities.
Start with an audit of your current traffic sources and referral channels. This data is available in analytics platforms. Where are your consumers coming from? Social? Organic search? It’s likely a mix of many sources.
Assess the existing touchpoints that support the journey your audience is on. Take inventory of everything you have — corporate site, blogs, social media accounts, and more — and map it out.
When you know what your asset landscape looks like, you reveal the areas that miss the mark, and the assets that need refinement—more on that next.
8. Finalize your customer journey map
Next, create a final blueprint for your customer journey map. Based on the above you now understand your consumer and what they want, you know how to solve their pain points, and most important, you know where you’ll deliver solutions across the customer journey.
Use all of that for your mapping process and you’ll create a strategic customer journey map that reflects how real consumers behave in the modern digital marketplace.
Customer journey map example
For example, let’s look at Ember , which sells temperature-controlled coffee mugs. What does their customer journey look like and how should they engage their audience?
- A potential customer realizes how often they have to reheat their coffee because it gets cold.
- They become frustrated and Google terms like “coffee warmer” or “how to keep coffee hot”.
- They find lists of hacks to keep their coffee warm, including cup sleeves, scarves, lids, and metal coffee beans. However, there are few mentions of Ember or temperature-controlled mugs.
- They don’t find Ember in the first two pages of Google organic results.
- Ember is included in the product ads in the search results. But banner blindness causes most people to scroll past the ads.
- Ember could use interactive assessments to discover when users search for hot coffee (e.g., the weekend at home, during the workday while at the office).
- Where Ember does better is in the middle of the content marketing funnel . After coffee lovers discover Ember, they check out the brand.
- This is where Ember’s videos make a difference. Ember’s videos cover everything from product introductions to recipes to the brand’s focus on “putting time back”. Some videos have thousands of views, while others have millions.
- While on the Ember website, the brand shares its purpose, commitment to exceptional design, and its technology. On the product pages themselves, they seal the deal with video, customer reviews, product details, a CTA for the help center, and a FAQ.
How to get the most out of your customer journey map
Anyone can create a customer journey map but there are a few ways to ensure your map actually works, and actually represents reality. Here’s how:
Achieve audience alignment with search intent – a reminder
Customer journey maps are only as effective as the data you use to build them. If you misunderstand what people want and fumble that moment of value delivery it erodes audience alignment. Each time you serve something the consumer does not want, is not asking for, or is not ready for, this erosion strengthens. With the wrong approach, it’s easy to produce a misaligned map.
For this reason — we want to reiterate — search intent data is the key to truly understanding real people and helping them in real ways. That’s what alignment looks like.
Create a consistent, superior customer experience
A major goal of creating a customer journey map is to ensure that you provide a superior digital customer experience (DCX) from start to finish. Set this as a central goal from the jump, along with your business goals.
A user journey map clarifies each step a customer takes so you can make them as pleasing and painless as possible. Outstanding experiences leads to more customers, orders, and revenue.
Need proof? Look no further than Amazon.
Known for their obsessive focus on the customer’s experience, they’ve spent billions to make online purchasing as easy as possible. One-click ordering, free two-day shipping, ultra-personalized recommendations — the list goes on and on. The result of creating such a fantastic experience is millions of customers and hundreds of billions in revenue.
Focus on authentic consumer connections and the rest will follow
Obviously, brands want to create a customer journey that results in leads and transactions. And while this may define the ultimate success of your efforts, reaching that goal requires a focus elsewhere; a focus on building authentic consumer connections.
From start to finish, brands that build customer journey maps around a reception marketing paradigm and customer-centricity achieve bigger wins when it’s time to buy. So rather than building some linear, basic map aimed at making sales, create one to make connections with consumers by providing upfront and consistent value.
The evolution of customer journey maps
Customer journey maps are still a vital tool in the modern marketer’s arsenal, but as we’ve noted above, things have changed and continue to evolve.
The biggest learning over the past several years is that traditional marketing models have simply not kept pace with the consumer. Nor have interruptive techniques. And, as discussed, even the way customer journeys look has changed, making it more difficult than ever to build authentic connections .
With this in mind, by augmenting the standard customer journey map with a few new elements — owned assets, search intent, and the MACH-6 — they become more effective in the context of today’s consumers.
This approach builds your strategy on a strong owned asset optimization (OAO) foundation, one in which:
- You really understand your consumer and their needs
- You have a sophisticated touchpoint network to deliver solutions
- You are prepared to deliver value when audiences actually want it
We recommend reading the following article to see how these three elements create a marketing paradigm shift, and how your brand can capitalize on it:

Owned Asset Optimization (OAO) | The Foundational Guide
Read next....
Responding to RSV: How Pharma Brands Can Help 131 Million People
Mar 29, 2024

Terakeet Appoints Industry Veteran and Fortune 50 Adviser David Minifie as Chief Marketing Officer
Mar 14, 2024

Learn how consumer insights can drive consumer connection
CMO-level insights, digital trends, and thought leadership sent to your inbox.
Unlock instant access to 25+ digital marketing resources and the OAO 101 introductory email course to kick start your strategy.
Terakeet uses cookies to enhance your experience and analyze traffic. By clicking accept you agree to our use of cookies.
- Woopra Logo
- Platform Customers Pricing Resources Company
- Log in Start For Free
- Automations
- Integrations
- Documentation
Unraveling the Retail Customer Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Mapping

Customer journeys are the lifeblood of retail. Understanding the unique steps customers take from discovery to purchase is crucial.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of retail customer journey mapping and its significance in today's rapidly evolving marketplace.
Let's embark on this enlightening voyage.
What Is A Retail Customer Journey Map?
A retail customer journey map is a visual story of your customers' interactions with your brand. It's a depiction of the path customers take from initial contact through to a long-term relationship.
It's a vital tool for understanding customer experience. By capturing all touchpoints and phases in the buying process, it enables businesses to identify opportunities and pain points.
The journey begins when a customer first becomes aware of your brand. This could be through advertising, word of mouth, or a search engine result.
The journey then continues as they gather information, make a decision to buy, and finally make a purchase.
After the purchase, the journey doesn't stop. How does the customer feel after buying? What's their experience with your after-sales service ? These questions form the final parts of the journey map.
By mapping the retail customer journey, brands can empathize better with their customers. It highlights where the customer's experience is smooth and where it's not.
This insight drives improvements in the overall shopping experience.
So, a retail customer journey map is more than a diagram. It's a catalyst for creating a better, more customer-centric business.
5 Phases Of The In-Store Customer Journey
Customers navigate various stages when interacting with a retail store.
Understanding these distinct phases is key to improving their shopping experience.
Let's delve into the five crucial stages of the in-store customer journey: Pre-visit, Entrance, Exploration, Purchase, and Post-Purchase.
Pre-visit Phase
The Pre-visit phase marks the beginning of the customer journey. It's when customers become aware of your brand and what it offers.
This could occur through online research, advertisements, or word-of-mouth recommendations.
During this phase, potential customers form their initial impressions of your brand.
They might visit your website or social media pages, read online reviews, or browse through your online catalog.
In essence, they're gathering information to decide whether your store meets their needs. This phase sets the tone for the customer's future interactions with your brand.
Ensuring a positive pre-visit experience is key to attracting potential customers to your physical store.
Also Read: Customer Journey Optimization
Entrance Phase
The Entrance phase begins when customers step into your physical store.
First impressions matter immensely, and this stage sets the tone for the entire shopping experience.
Here, customers form opinions about your store's ambiance, cleanliness, layout, and staff availability.
Factors like lighting, music, and in-store marketing materials can influence their overall perception.
Customers also start to gauge the level of customer service. They notice if staff members are welcoming and ready to assist.
They may also look for clear signage to guide their shopping journey.
The goal during the Entrance phase is to create a positive, inviting atmosphere. It's about making customers feel comfortable and eager to explore what you have to offer.
Exploration Phase
The Exploration phase is the heart of the in-store shopping experience . This is where customers dive into your product offerings and evaluate their options.
During this phase, customers browse through your store, interact with products, and compare different items.
The organization of your merchandise, the quality of the product displays, and the ease of finding desired items all play crucial roles.
In-store staff can greatly influence this stage. Their product knowledge, helpfulness, and ability to cater to customer needs can enhance the shopping experience.
The goal here is to provide a seamless and enjoyable exploration experience.
When customers feel well-served and find what they're looking for easily, they're more likely to make a purchase.
Also Read: Customer Journey Metrics
Purchase Phase
The Purchase phase is the pivotal moment when a customer decides to buy.
This stage revolves around the checkout process and the final steps that lead to a successful transaction.
Here, customers evaluate their chosen products one last time before making the final decision. They consider factors like price, quality, and perceived value.
The ease of the checkout process also plays a significant role.
At this point, friendly and efficient customer service can make a substantial difference.
Quick checkout lines, multiple payment options, and proactive assistance can help seal the deal.
The goal in the Purchase phase is to make the transaction as smooth as possible. Any hiccups at this stage could deter a customer from completing their purchase.
Post-Purchase Phase
The Post-Purchase phase happens after customers have made their purchase and left your store.
It's about fostering a long-term relationship with them, ensuring they're satisfied, and encouraging them to return.
This phase includes elements like customer service support, return or exchange policies, and feedback collection.
Your engagement with the customer during this time can greatly affect their overall perception of your brand.
Remember, a positive post-purchase experience can turn one-time shoppers into loyal customers.
It can also lead to positive word-of-mouth marketing, boosting your brand's reputation.
The goal here is to leave a lasting impression, ensuring that the customer feels valued and appreciated.
It's about turning a single transaction into an ongoing relationship.
How To Build A Retail Customer Journey Map
Creating a retail customer journey map is a strategic process. It involves data collection, identifying touchpoints, and ongoing revisions.
In the following section, we'll guide you through a step-by-step process to create your own customer journey map, helping you to better understand and enhance your customer's experience.
Also Read: Customer Analytics
Creating a retail customer journey map begins with setting a clear goal.
Your goal could be improving customer service, reducing churn rate, increasing customer loyalty, or optimizing in-store experiences.
Decide what part of the customer journey you want to focus on. Are you interested in the entire journey, or do you want to concentrate on specific touchpoints or stages?
You could also tailor the map to a particular customer persona or demographic group.
This initial goal-setting step provides direction for your journey mapping project. It guides the kind of data you'll collect and the insights you're hoping to gain.
A clear goal ensures your map is focused and relevant. It steers the development of strategies to improve your customer's experience in line with your business objectives.
Remember, a well-defined goal is the foundation of a successful customer journey map.
Keep Tracking & Analytics Tools Ready
With your goal set, the next step is to prepare your tracking and analytics tools.
These are vital for gathering data about your customers and their interactions with your brand.
Your tracking tools could include a website analytics tool like Google Analytics, which provides insights into how customers interact with your online platforms.
Heat mapping tools can also be beneficial for understanding on-page customer behavior.
In-store, consider using tools like customer feedback surveys, mystery shopping, and point-of-sale data analysis.
Technologies like Wi-Fi analytics or people counting cameras can also provide data about in-store customer behavior.
These tools help you gather quantitative data, such as how many people visited your store or website, what they purchased, and how much time they spent.
Having your tracking and analytics tools ready ensures you have reliable data to build your customer journey map.
Collect Data
Once your tools are set up, it's time to collect data. Your goal here is to gather as much information as possible about your customers and their shopping behavior.
Start by gathering demographic data. Who are your customers? What are their ages, genders, locations, and income levels?
This information can help you understand who you're serving and what they might expect from your brand.
Next, collect behavioral data. What are customers buying? When are they visiting your store or website? How much time are they spending? This can reveal patterns in shopping behavior.
Don't forget about attitudinal data. How do customers feel about your brand?
You can gather this information through surveys, feedback forms, or social media sentiment analysis.
The more comprehensive your data collection, the more detailed and accurate your customer journey map will be.
Understanding your customer's behaviors, attitudes, and demographics is key to crafting an effective map.
Identify All The Possible Touchpoints
After collecting data, the next step is to identify all the possible touchpoints.
Touchpoints are the various ways customers interact with your brand, from initial discovery to post-purchase.
These might include your website, social media platforms, email newsletters, in-store interactions, customer service, and even word-of-mouth referrals.
Remember to consider both online and offline touchpoints.
Examine each touchpoint from your customer's perspective. What are they experiencing at each stage? Are there any obstacles or frustrations they encounter? What moments delight them?
Mapping out these touchpoints gives you a comprehensive view of your customer's journey.
It highlights areas where you're providing excellent service and where you might be falling short.
Identifying all possible touchpoints is crucial to building an accurate customer journey map.
It's the step that brings your map to life, illuminating the path your customers follow when interacting with your brand.
Plan The Journey Map
With your data and touchpoints identified, it's time to plan your journey map.
This visual representation of your customer's experience will help you see their path through their eyes.
Start by plotting out the stages of the customer journey we discussed earlier: pre-visit, entrance, exploration, purchase, and post-purchase.
Then, populate each stage with the relevant touchpoints.
Use the data you collected to depict what happens at each touchpoint. Highlight areas of customer friction and delight. Include customer thoughts, feelings, and expectations.
Your map could be a simple flowchart, a storyboard, or an intricate infographic. Choose a format that suits your needs and preferences.
Remember, the purpose is to facilitate understanding of your customer's experience.
Creating a journey map is like piecing together a puzzle. Each touchpoint, each piece of data, adds to the overall picture of your customer's journey with your brand.
Take Feedback & Revise The Map
Once your customer journey map is drafted, it's essential to seek feedback and be ready for revisions.
Your map should be a living document, continually updated as you gain new insights and as your customers' behaviors evolve.
Share the map with your team, especially those who interact directly with customers. Their frontline experience can offer valuable insights.
Are there touchpoints they feel have been overlooked? Do they have suggestions for improving customer experiences at specific stages?
Next, seek feedback from your customers. Use surveys or interviews to understand if your map aligns with their actual experiences.
They are the ultimate source of truth about the customer journey.
Finally, use the feedback to revise your map. Make necessary adjustments to reflect the most accurate customer journey.
Remember, creating a customer journey map is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Regular revisions ensure your map stays relevant and valuable.
The Best Examples Of Retail Customer Journey Maps
Zara's customer journey starts with creating a buzz around its fast-fashion model.
Through social media platforms and window displays, Zara attracts customers with their fresh, trendsetting styles.
Once in-store, customers are greeted by well-organized, frequently updated merchandise that encourages exploration.
The purchase phase is expedited by helpful staff, clear price tags, and multiple payment options.
After purchase, Zara keeps customers engaged through email newsletters, featuring new collections and fashion tips.
The seamless integration of online and offline channels enhances Zara's customer journey.
2. Starbucks
The Starbucks journey begins with its strong brand presence and enticing aroma. The entrance phase is about welcoming customers into a comfortable, cozy space.
During the exploration phase, customers choose from a wide range of beverages and food items, with staff readily available to assist.
The purchase phase includes an easy, efficient payment process and the Starbucks rewards program.
Post-purchase, Starbucks engages customers through the mobile app, offering personalized deals and rewards for loyal customers.
IKEA's journey starts with its catalog and website showcasing stylish, affordable furniture.
In-store, customers enter a well-planned route displaying various room setups, sparking inspiration.
During the exploration phase, customers interact with the products in home-like settings.
At the purchase phase, customers are guided to the warehouse to pick up flat-packed products, with staff available for assistance.
Post-purchase, IKEA provides detailed assembly instructions and customer service for any issues, reinforcing IKEA’s commitment to customer satisfaction.
Understanding the retail customer journey is paramount in today's competitive marketplace.
By mapping this journey, brands can uncover key insights to improve customer experiences and drive loyalty.
It's an ongoing process that requires continuous tracking, analysis, and improvement. Start your journey mapping today and unlock a new level of customer-centric success.
Full insight into the customer journey. No SQL required.
Get started with Woopra for free to see who your customers are, what they do and what keeps them coming back.
Related Articles
The beginner’s guide to behavioral targeting to increase conversions.

How to get Started with Analytics
From emails to customers — woopra campaign tracking, 5 actionable methods to engage mobile customers, explore topics.
© Woopra, Inc. 600 California St 11th Floor San Francisco, CA 94108
- Request a demo
- Product Analytics
- Customer Analytics
- Customer Journey Analytics
- Google Analytics F.A.Q.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of service

Online Shopping Customer Journey Map
Create a modern customer journey and much more by modifying this online shopping customer journey map template.
- Design style vintage
- Colors light
- Size Letter (11 x 8.5 in)
- File type PNG, PDF, PowerPoint
- Plan premium
Explore more
Online Shopping Customer Journey Map Template
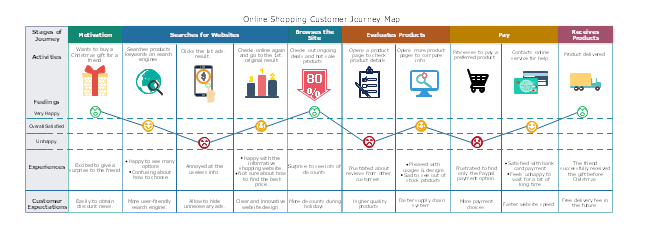
Download Template:
Get EdrawMax Now!
Share Template:
- Process Flowchart
- Cross-Functional Flowchart
- Data Flow Diagram
- IDEF Diagram
- Basic Org Chart
- Photo Org Chart
- Creative Org Chart
- Family Tree
- Rack Diagram
- Network Topology
- CCTV Network
- AWS Diagram
- Azure Diagram
- GCP Diagram
- Cisco Network
- Active Directory
- Neural Network
- Column Chart
- Doughnut Chart
- Spider Chart
- Scatter Plot
- Bubble Chart
- Gauges Chart
- Comparison Chart
- Seating Plan
- Office Layout
- Garden Design
- Wiring Plan
- Security and Access Plan
- Fire Escape Plan
- Reflected Ceiling Plan
- Plumbing and Piping Plan
- Arrow Diagram
- List Diagram
- Pyramid Chart
- Venn Diagram
- Circular Diagram
- 2D Block Diagram
- 3D Block Diagram
- SWOT Matrix
- Brainstorming
- Marketing Diagram
- Fishbone Diagram
- Value Stream Map
- Enterprise Architecture
- Concept Map
- Bubble Diagram
- Strategy and Analysis
- Main Idea and Details
- Sequence Chart
- Compare and Contrast
- Vocabulary Study
- Grid and Matrix
- Fact and Opinion
- K-12 Education
- Process Flow Diagram
- Electrical Diagram
- Circuit and Logic
- Schematic Diagram
- Laboratory Equipment
- Human Anatomy
- Mathematics
- Gantt Chart
- Project Timeline
- Quotation Form
- Report Form
- UML Diagram
- Database Diagram
- Directional Map
- More Templates
- Case studies
- Expert advice
Retail food customer journey: A taste of experience excellence
Have you ever wondered why customers choose one retail store over another? What makes them leave and never come back? Is it an unsuitable location, a bad name, high prices, or a small assortment? Is it a customer service assistant who wasn’t helpful enough or even rude? Or is it something else?
Well, all of these (and even more) is the answer. That’s why forward-looking brands started putting themselves in customers’ shoes long ago to discover what drives their clients. And the smartest ones found a way to go even further by getting into buyers’ heads, reading their thoughts, and identifying their needs and wants at every stage of the journey.
Have you guessed already that we’re talking about buyer personas and customer journey maps? Creating personas is a valuable initial step in grasping your customers' true needs and their experiences with your business. Once you have personas, you can proceed to develop retail customer journey maps for them.
- 1.1 What can you do as a part of your research?
- 2.1 Stage 1: Research
- 2.2 Stage 2: Decision
- 2.3 Stage 3: Getting to the supermarket
- 2.4 Stage 4: Arrival
- 2.5 Stage 5: Pre-entry
- 2.6 Stage 6: At the supermarket
- 2.7 Stage 7: Purchase
- 2.8 Stage 8: Leaving
- 2.9 Stage 9: Bonus program
- 2.10 Stage 10: Coming back
- 3.1 Sustainable lines
- 4 Summing up
Defining your personas
To correctly define your personas , you need to start with the research step (e.g., collect feedback from your customers and customer-facing staff), then segment the data into customer groups and turn them into personas.
What can you do as a part of your research?
- Conduct surveys to gather data on the age, gender, location, income, and occupation of your customers. For instance, use online forms or in-store questionnaires to collect this information.
- Observe customer behavior in your store. Note what people purchase, how often they visit, and which sections of your store they frequent.
- Examine customer purchase history using your point-of-sale system to understand their buying patterns and preferences. This data can reveal what products are most popular.
- Create feedback forms or comment cards in your store, and encourage customers to share their opinions and suggestions. Analyze the feedback for common themes.
- Monitor online reviews and social media mentions related to your store. Pay attention to what customers say about their experiences and what they like or dislike.
- If you have an online presence, use website analytics tools to track user behavior. Analyze data on page views, click-through rates, and time spent on different sections of your website, and other data.
- Conduct one-on-one or group interviews with customers to gain deeper insights into their motivations, challenges, and preferences. Ask open-ended questions to encourage detailed responses.
- If you have a loyalty program, use the data collected to understand customer loyalty and their purchase habits. Loyalty programs can reveal who your most dedicated customers are.
- Utilize third-party market research and consumer behavior data to complement your in-house research. This can provide a broader perspective on your audience, as the same people often buy from many companies in the market. That’s why you can even study the customer personas of your competitors, as this can provide insights into what similar customers might expect from your retail food store.
Once done, choose the persona(s) you will build a map for. The choice depends on your priorities. This can be the most profitable persona, or the one who visits your store more often than others, or the one who stops coming to the shop after a couple of visits. Each will have an individual journey and unique challenges.
Building a customer journey map for a food retail
First of all, you need to define the journey stages of a persona you decided to build a map for. Remember, a customer's journey doesn't start when they step into the store; it begins way before that when they realize they need something. So, if you want to understand the whole journey, don't forget that early part.
For this article, we built an end-to-end customer journey for a food retail store. Read on to get an idea of what your own map might look like.
Stage 1: Research

Your persona understands their need in a couple of ways. It could be that their home is running low on food supplies, and they realize it's time to restock the pantry and refrigerator. Alternatively, they might have a special event, like a gala dinner, on the horizon, and they recognize the need to purchase specific ingredients to prepare for the occasion. Or maybe the persona has rented a flat from a real estate agency and moved to it.
Our persona’s name is Olivia. She recently moved to a new area and, of course, her refrigerator is empty, but she is not yet familiar with the new location. What is Olivia doing? Asks for advice from neighbors.
Notice how the grocery shopping experience of other customers affects Olivia’s journey.
So, what do you need to reflect on at this stage of your persona's journey? The process: how they realize their need, how they fulfill it, through what channels, what emotions they experience, what expectations they have, how they interact with your business.
After writing down all that in the sections of your map, identify the challenges your persona is facing at this stage (if there are any) and do the same at other stages. Even if at some stages you won’t find things to improve, you may identify your business’s strengths, enhance those, and use them to your advantage.
The same sections should be filled out for all the further stages of your persona’s journey.
Stage 2: Decision

After receiving the necessary information, your persona faces a choice since there is always more than one store nearby. What can work against you? What, on the contrary, will make you stand out from other options?
For example, Olivia chooses a supermarket, although it’s located further away than the local store. Why? Because she needs a rare product that can’t be found in small stores.
Always notice what drives the persona to choose in your favor, as these are your strengths, which you can emphasize in advertising materials. Likewise, address consumers’ concerns, as these are opportunities for growth and improvement.
Stage 3: Getting to the supermarket

It's time for the persona to get to your store. How easy is it to find the right way? Are there any billboard advertisements on the road pointing the way to the store? How can the persona get to you: by private transport, bus, taxi or on foot?
In our case, Olivia is driving her own car, so her key problem is (or isn’t?) navigation. She turns in the wrong direction a few times, so her grocery store experience spoils, although she hasn’t even crossed the threshold of the supermarket.
Stage 4: Arrival
So, your persona arrives at the store. What's there for them? Underground parking? Endless chaos and searching for a parking space? Lack of parking? Paid parking?
Olivia is lucky — the supermarket has a parking lot. But finding a parking place is not that easy. It’s vital to understand the approximate flow of customers in your store. Is your parking large enough to accommodate all visitors' cars?
If a buyer is looking for a parking place for too long, they enter the store in a bad mood, and this definitely affects their grocery shopping experience, as well as the desire to return.
Stage 5: Pre-entry

It would seem that nothing can happen on a short stage of a customer's journey from a car, bus stop, or traffic light to the store door? Many will not even include this stage in the map. Too bad. Have you ever thought about the fact that there is a whole minefield of other cars between the customer's car and the entrance?
For example, Olivia is nearly hit by a car on her way to the store. You should probably make a pedestrian crossing or even install a traffic light if the parking lot is too large.
Stage 6: At the supermarket

Finally, your persona is inside the store. What do they see? Is it easy for them to navigate? Even in the already familiar supermarkets, there are rearrangements, and buyers, only remembering where their favorite products are, have to look for them. Again. Are there staff members your persona can turn to for help? Are there enough shopping carts? Or small baskets for those who need to buy just a few items?
Olivia is having trouble finding a product. Store employees are unable to help her find it. The sections of the store have no signs. How can a visitor help themselves? For example, you could install a display or a couple of them with an electronic map of the supermarket. It will be convenient to quickly edit it, unlike a printed map.
Stage 7: Purchase

The moment of purchase. Sometimes shopping is very enjoyable, but the primary headache awaits at the checkout. Are there enough checkouts in your supermarket? Are you increasing the number of cashiers during peak hours? Does the store have self-checkouts? At this stage, another problem may arise, the payment process. Do you accept all credit cards? Can a customer use a discount coupon?
Olivia, approaching the cash register, realizes that she will have to stand in a huge queue. She notices information about the discount program but cannot find out the details until her turn comes up. On the one hand, that's good, as you managed to draw the buyer’s attention to a beneficial part of your service. Adding a QR code, via which the customer can immediately register in the program, will help to while away the time in the queue and the future discount will compensate for the waiting time.
Stage 8: Leaving

Well, the buyer paid for their groceries, and now they somehow need to leave the store and either bring the purchase to the car or even at home. Consider if you have staff to help them carry the bags to a vehicle or if you have special carts. How strong are the bags in which you pack the purchases? Can they tear up while the customer walks home? It would be a good idea to provide a paid service of transferring a buyer to their house, highlighting your store among similar ones. This service can be free for people with huge bills. Although Olivia arrived in her car, she still needs to put her purchase in the trunk, and the bags were quite heavy. There are no assistants among the staff, and she has heard that the carts couldn’t be taken out of the store. Olivia may turn to other buyers for help, but her grocery store experience with you will be spoiled.
Stage 9: Bonus program

Let's say you have a bonus program or some other loyalty system . The buyer finds out about it and tries to register. What could go wrong? Everything. The application may not launch, it may contain bugs, and the loyalty system itself may be too complex, so the buyer decides to give up.
Olivia finds more detailed information about your bonus program on the Internet, and wants to install the application, but it is not compatible with her device. She doesn’t plan to change her smartphone in the near future, but she also wants to get a discount.
How can you help? Offer customers to register their personal accounts not only in the application but also on the website. Accrue bonuses by the buyer's phone number or issue plastic cards as an e-card replacement. This way, you will cover the maximum number of your customers, including not very tech-savvy people, or children who were sent to the store by their parents, and so on.
Stage 10: Coming back

This stage is no less significant than all the previous ones since the buyer can always change their mind and not return. Will the persona want to return to your store?
Everything that we talked about above influences their decision. But additional factors may appear. For example, the persona enjoyed their grocery store experience, but in a conversation with friends it turned out that they were less fortunate in your service. Someone else’s problem may affect this persona’s opinion. Or pretty ripe apples from your store turn out to be not so pretty on the inside. Or maybe your work schedule will not fit into the rhythm of the buyer’s life.
Olivia decides to return. After all, where else would she buy quinoa? She already finds it easier to navigate the supermarket, but the long queue at the checkout is still annoying. Olivia came during the hours when the bulk of people were at work, but this did not affect the queues in any way.
How many chances will Olivia give your store? How soon will she know that there is another large supermarket nearby? Are you sure she won’t become their client?
Analyzing a customer journey map for a food retail
Once the map is ready, use it to understand what needs to be improved to encourage your customers to choose and stay with you. Put this information into action, and it won’t take long to see the result.
Sustainable lines
If you want to go beyond the usual customer journey map and pay special attention to some aspects that matter to your case, feel free to add custom sections. In this template, we introduced sustainability-related lines and considered how a retail business interacts not only with the buyers but also with the environment.

You might have little to no experience with customer journey mapping, but it’s not as difficult as it seems. Check out our updated Retail food customer journey map template to learn what a customer persona and a customer journey map for your store might look like.
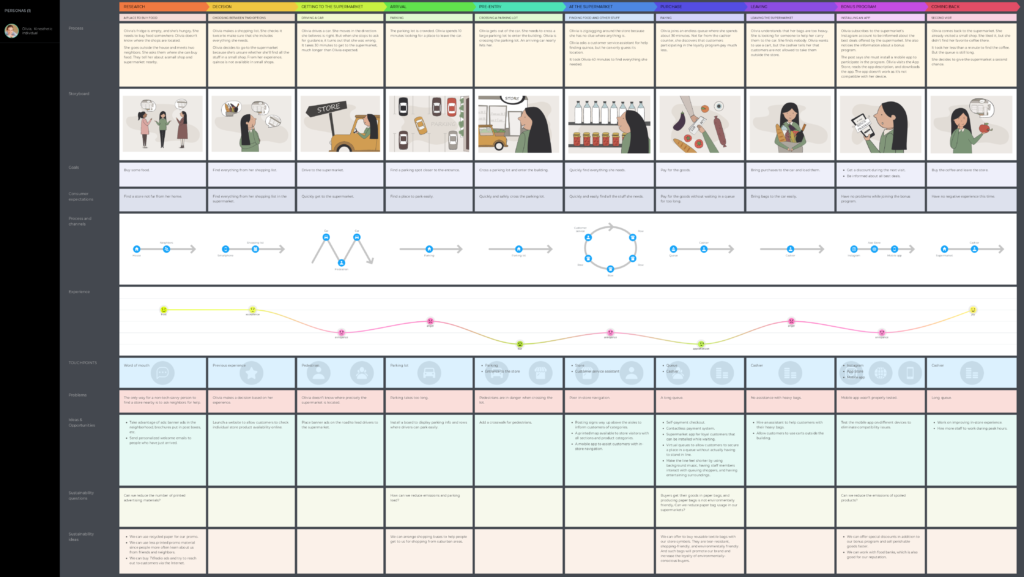
You can easily turn this CJM template into your map if you want by using our CJM tool . And it’s absolutely free.
OPEN THE TEMPLATE
Rate this post

We’re thinking about building a food and beverage customer journey, so this article was useful. Especially the dramatic episode of Olivia nearly getting hit by a car. A bit over the top, but a good reminder that no interaction or opportunity in the customer experience is too small.
Great template. I think there’s a common misconception that the only companies that should be building journeys are digital-only. It’s nice to see an example for a grocery shopping customer journey that’s almost exclusively offline.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
6. Make the customer journey map accessible to cross-functional teams. Customer journey maps aren't very valuable in a silo. However, creating a journey map is convenient for cross-functional teams to provide feedback. Afterward, make a copy of the map accessible to each team so they always keep the customer in mind.
The ecommerce customer journey is the complete end-to-end experience of a customer from the initial interaction with a brand's online store to the final purchase. This includes browsing, product selection, checkout, and post-purchase support. Understanding and optimizing the ecommerce customer journey helps businesses enhance engagement and ...
Creating a customer journey map as a team helps bring new perspectives to the table. It's also easier to align with a shared vision of what customers go through and what needs to be improved on. When solutions are formed and planned, it's then easier to assign responsibilities for each touchpoint and channel.
Customer journey maps help you determine which team is responsible for key actions and support at each step of the way. 4. Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers. With a clear overview of the customer's journey, your team can quickly home in on the touchpoints where something's going wrong.
Pricing starts at $29/month per user. Touchpoint - Touchpoint is an intuitive web-based app for creating customer journey maps and analyzing customer behavior. It is built with collaboration in mind and is ideal for those retailers looking for a straightforward and scalable solution. Pricing is available on request.
Touchpoints: meeting a courier, signing delivery documentation. Here is what the backbone of the e-commerce customer journey map will look like. See a full-size image. In the same way, you can divide the purchasing process into "Review cart", "Checkout", "Payment", and other stages and analyze them in your map.
3. Gather Relevant Data and Information. Data is the lifeblood of customer journey mapping. To create a comprehensive map, you need to gather as much relevant data as possible. Sources of data may include: Customer Surveys: Collect customer feedback to understand their pain points, preferences, and expectations.
Then, arrange each touchpoint sequentially so you can see the big picture. 4. Design a Visual Representation of the Customer Journey. After defining business goals, identifying key stages in the customer journey, and defining customer touchpoints, it's time to actually create your customer journey map.
1. Get buy-in from stakeholders. Sync with other leaders in your company. For eighteen percent of companies, customer journey mapping is led by multiple stakeholders. And, when multiple stakeholders are involved, 92 percent of companies report positive or extremely positive impact of mapping.
Here's how to create a user journey map in 6 steps: Choose a user journey map template (or create your own) Define your persona and scenario. Outline key stages, touchpoints, and actions. Fill in the user's thoughts, emotions, and pain-points. Identify opportunities.
5. Map the Journey. You need to map the customer journey using a visual tool or template that shows the stages of the journey, the touchpoints at each stage, and the customer insights for each touchpoint. You can use different colors, icons, shapes, or graphs to illustrate the customer journey map and make it easy to understand.
A customer journey map is a visual representation of how people purchase products. You might see it called the "buyer journey" or "user journey map" as well. In the case of ecommerce brands, a customer journey map shows: When a customer first became aware of a problem; The options they considered when searching for a solution
5 stages of the eCommerce customer journey. Your customers' overall journey can be broken down into five key stages. 01. Awareness. Your customer stumbles across your brand for the first time. Be it through an ad, social media, word of mouth, or SEO-they are now aware of your products.
A customer journey map helps you gain a better understanding of your customers so you can spot and avoid potential concerns, make better business decisions and improve customer retention. The map ...
At each step in the customer journey map, determine what the potential customer wants or needs most and how you can provide that for them. It's about creating the best possible customer interaction by delivering on customer expectations. Search intent data makes this achievable. 5. List the customer touchpoints.
Step Seven: Map Out The Discovery Phase Of Your Customer Journey Map. Now that you have your audience persona and your customer data you can begin to develop your customer journey map. The first phase is centered around discovery. This phase of your map should include: The reason they are searching for a product.
Customers navigate various stages when interacting with a retail store. Understanding these distinct phases is key to improving their shopping experience. Let's delve into the five crucial stages of the in-store customer journey: Pre-visit, Entrance, Exploration, Purchase, and Post-Purchase.
Here are a few key steps for creating a customer journey map: Clearly state your objectives. Profile your customer persona. Perform research. Identify customer touchpoints. Experience the customer journey map for yourself. Make changes and resolve. 1. Clearly state your objectives Be sure to set a few goals when designing your customer journey map.
Be sure to check the e-сommerce customer journey maps to better understand how online shopping differs from in-store experience and what you can do to encourage your clients to come back again and again. Free ready-to-go customer journey map and personas templates for e-commerce, retail, shopping malls, supermarkets, grocery stores.
Colors light. Size Letter (11 x 8.5 in) File type PNG, PDF, PowerPoint. Plan premium. Design a contemporary buyer journey and other mind maps with this Online Shopping Customer Journey Map Template. Change the icons, use a subtle font, and apply a modern color palette. Browse Venngage for more customizable customer journey templates.
The online shopping customer journey map template illustrates the general process of user experience in ordering online. It offers customers an efficient way to engage with their brands. It offers customers an efficient way to engage with their brands.
Check out our updated Retail food customer journey map template to learn what a customer persona and a customer journey map for your store might look like. You can easily turn this CJM template into your map if you want by using our CJM tool. And it's absolutely free. OPEN THE TEMPLATE. Rate this post.