
Do Cockroaches Travel Alone or in Groups?
Cockroaches are nocturnal, so you rarely see them during the day. While you may see a lone cockroach scuttling across the floor, they’re more likely lurking in large colonies somewhere dark and secluded where they’re safe from harm.
Cockroaches live in large colonies but travel around in small groups to forage food, water, and shelter. Doing so protects them from predators and other dangers. As soon as they find what they need, they release aggregation pheromones to let the rest of their colony know to join them. A group of cockroaches is called an intrusion. When they invade the home, they’re called an infestation.
A cockroach colony’s difficult to eradicate. They don’t all come out simultaneously, so you have more cockroaches inside your house than you expect. Calling in an extermination company is the best way to deal with the problem.
Are Cockroaches Social Insects?
Because cockroaches tend to emerge alone, it might surprise you to learn that cockroaches are social insects that prefer to live and travel in large groups. Doing so provides greater protection against predators and other dangers. As soon as they find an environment that provides them with what they need, they settle there as a colony.
To do this, The Chemistry of Pheromones and Other Sociochemicals describes how household roaches communicate through pheromones, which are a complex range of smells that transmit information and intent.
There are many different types used in roach communication, but aggregation pheromones gather them all into one place. This keeps the nest organized and tells cockroaches when to:
- Forage for food
- Move from one location to another
- Look for find shelter
The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that each cockroach group has its own aggregate pheromones, allowing them to communicate with members of their own colony. Scientists believe that pheromones comprise of:
- Skin . It’s thought that pheromones are made from waxy substances found on the surfaces of the cockroach’s skin.
- Poop . Other scientists believe that aggregate pheromones are found in roach poop in the form of nitrogen compounds.
- Fatty Acids . This is still up for debate, but these pheromones are made of fatty acids.
To release aggregate pheromones to talk to their colonies, cockroaches deposit their poop in various locations, alerting other cockroaches of where they are.
Similarly, foraging pheromones allow roaches to recommend food sources to each other. Once they find a suitable food source, they spread the word to the other cockroaches in the colony. This is why you’ll find multiple cockroaches feasting on the same food source.

Do Cockroaches Travel Alone?
Because cockroaches come out at night , it’s unlikely you’ve seen them moving around together. But cockroaches don’t like traveling alone. Instead, they live and travel in small family groups. Once they find a suitable place to settle, they build their colony by mating and multiplying, setting up small foraging groups.
Female cockroaches can produce as many as 30-40 cockroaches at a time, meaning their colony grows rapidly. Increasing their population has survival benefits, as it allows them to thrive as an entire group instead of being picked off by predators one by one.
However, every now and then, lone cockroaches enter houses to find shelter, also getting into them through wood, packaging, and furniture. These harmless loners rarely build colonies unless it’s a pregnant female.
Do American Cockroaches Travel in Packs?
American cockroaches live and travel in groups. Aggregate pheromones allow them to stay together and locate one another if they get separated.
When they’re in their groups, they explore their surroundings together and search for food as a foraging pack. It was previously thought that cockroaches forage individually, but this has been proven not to be true.
As soon as they find food and water, they send signals to the rest of the colony who’ve remained behind to come and join them. This method of communication and togetherness is crucial for their survival.
Unfortunately, this means if you see one American cockroach in your home, there’s likely to others hiding in a dark corner. Because they’re expert hiders, they’re hard to find.
Do German Cockroaches Travel in Packs?
German cockroaches live and travel in packs. Out of all cockroach species, they’re more likely to travel alone, but like all other species, they prefer to be in groups where there’s greater protection against dangers.
German cockroaches live in mixed-family aggregate groups of equal male and female numbers. 60% of the population are nymphs, and 40% are adults. They feed on the same food sources after getting the go-ahead from the foraging roaches.
How Many Cockroaches Live Together?
A cockroach nest can hold over 100 roaches at once. However, young colonies can contain only a handful of roaches. As mentioned, this number will quickly grow as the roaches breed and multiply.
Cockroaches won’t let the nest get too large. If the population grows too quickly and they have to compete for food, water, and shelter with one another, they’ll start to cannibalize the nymphs and weaker roaches in the colony to thin the numbers out. Cockroaches also reduce numbers to:
- Preserve the available food
- Consume energy during harsh conditions
- Replace lost nutrients
When starvation causes a colony to cannibalize , nymphs are usually the first to be eaten. That’s because, during the first through molts, they’re left with only a soft layer of skin.
Eventually, it’ll harden into a protective shell. Before this happens, adult cockroaches can penetrate their skin, tearing them apart.
Nymphs are also slow, meaning they can’t flee from larger, quicker cockroaches. Not only does this provide the surviving roaches with the nutrients they need, but culling nymphs make the population more manageable.

How Do Cockroaches Travel?
Cockroaches move through small holes, under doors, or up and down plugs and drains. They prefer gaps that are less than half an inch wide. They also travel by hitchhiking in cardboard boxes, furniture, suitcases, bags, and packaging materials. This is how lone cockroaches get into houses and buildings.
When they travel, they move along the edges of rooms, which allows them to remain undetected. However, because they usually surface when it’s dark, it’s hard to know whether they travel alone or in groups.
Both are true, especially if the colony’s small. In this case, lone cockroaches forage for food, while the rest remain out of harm’s way in a dark, quiet spot. Once the colony grows, they’ll form groups for protection and safety.
How Far Do Cockroaches Travel?
Cockroaches don’t travel far once they’ve invaded a building. Instead, they find a spot that suits them and make it their home, leaving it only to forage for food and water. If your house has an infestation upstairs and downstairs, you likely have two separate colonies in your home. That’s because the same family of cockroaches rarely split up and live apart.
Some cockroach species, including Asian, brown, and Smokybrown roaches, also fly, meaning it’s easy for them to get to difficult-to-reach places.
Cockroaches rarely live alone. If you only see one, there’s bound to be more lurking nearby . If you catch the infestation early enough, you may only have to deal with a small number of cockroaches. If the colony had time to multiply, you could be dealing with hundreds or even thousands of cockroaches.
Related Articles:

Understanding the difference between males and females can enable you to determine if you have a small or large infestation. Females may reproduce on their own (asexually) and increase the…

Cockroaches build nests in dark and humid/damp areas near sources of food and water. They'll live there unnoticed for weeks or months as they breed and multiply. You'll find nests…

Cockroaches are rumored to be invincible. They are certainly extremely resilient. Roaches can survive weeks without food or water, handle extreme temperatures, regrow limbs, and even live (temporarily) without a…

Cockroaches are known for eating anything, including each other. Cannibalism may be a disturbing trait to many, but loyalty to their species has never stopped a roach from picking its…

Jack Andersen
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Cockroaches: A Group Travel Itinerary
- Last updated Aug 18, 2024
- Difficulty Beginner
- Category Travel

Cockroaches are nocturnal insects that prefer to live in large groups, but they rarely appear in swarms. They are social insects that communicate through pheromones, a complex range of smells that transmit information and intent. They tend to emerge alone, but they don't like to travel alone. Cockroaches are resilient pests that exhibit odd behaviours and survival tactics, such as spending 75% of their time resting and being able to withstand temperatures as cold as 32 degrees Fahrenheit. They can also live for a week without their head.
What You'll Learn
Cockroaches are social insects that live in large colonies, they rarely travel alone, but in small family groups, they communicate through pheromones, they can survive for a month without food, they are most active at night.

Cockroaches are social insects that tend to live in groups. They emit pheromones that leave chemical odors in their feces and on their bodies. These pheromones serve as a means of communication for the insects. The odor of the pheromone causes the roaches to cluster together in a harborage area.
The gregarious German cockroach, for example, has an elaborate social structure involving common shelter, social dependence, information transfer, and kin recognition. The social biology of domiciliary cockroaches can be characterized by a common shelter, overlapping generations, non-closure of groups, equal reproductive potential of group members, an absence of task specialization, high levels of social dependence, central place foraging, social information transfer, kin recognition, and a meta-population structure.
Cockroaches have unusual reproduction methods. Females lay eggs in groups of 4-30 bundled together. It looks like one big egg, but is actually many small eggs encased together in what is called an ootheca. Some species retain their egg(s) and give birth to live nymphs. Cockroach eggs are bundled together in an ‘ootheca’. Once the egg hatches, the cockroach develops through several nymphal stages before moulting to the adult stage.
Cockroaches are considered pests because they can contaminate food and kitchen utensils with their frass (droppings), possibly spreading microbes and causing health problems. Some people may be allergic to cockroaches, and many people dislike their appearance. Large infestations can result in an unpleasant smell.
Exploring South America: What You Need to Know About Traveling with Hydrocodone Acetaminophen 5-325
You may want to see also
Cockroaches are nocturnal insects, so you're unlikely to see them during the day. While you may catch a glimpse of a lone cockroach scuttling across your floor, they are more likely to be hiding in large colonies in dark, secluded places, safe from harm.
Cockroaches are social insects that live in large colonies but travel in small family groups to find food, water, and shelter. This behaviour protects them from predators and other dangers. Once they have found what they need, they release aggregation pheromones to signal to the rest of their colony to join them. A group of cockroaches is called an intrusion, and when they invade a home, they are referred to as an infestation.
Cockroach colonies are challenging to eradicate because they don't all come out at once. This means that if you have cockroaches in your house, there are likely more than you think. Extermination companies are the best way to deal with a cockroach problem.
Cockroaches communicate through pheromones, a complex range of smells that transmit information and intent. Aggregation pheromones, in particular, are used to gather cockroaches in one place, keeping the nest organised and signalling when to move locations or find shelter. Each cockroach group has its own unique aggregation pheromones, allowing them to communicate only with members of their colony.
While cockroaches typically travel in small family groups, they live in much larger colonies. Female cockroaches can produce up to 30-40 cockroaches at a time, causing their colonies to grow rapidly. This rapid reproduction provides survival benefits, as a larger group is less likely to be picked off by predators one by one.
Macy's Day Parade: Slowest Show on Earth?
Cockroaches are social insects that usually live in groups. They are nocturnal, so you rarely see them during the day. While you may spot a lone cockroach, they are more likely to be hiding in a large colony somewhere dark and secluded.
Cockroaches communicate through pheromones, a complex range of smells that transmit information and intent. They can warn others of danger, suggest good food sources, encourage mating, and invite other cockroaches to shelter.
Cockroaches deposit their faeces in various locations, releasing aggregation pheromones to signal to their colony. This keeps the nest organised and unified, and tells cockroaches when to move location, where to find food and shelter, and when to invade a home. Aggregation pheromones also allow cockroaches to distinguish members of their own colony from other colonies. Each cockroach group has its own aggregation pheromones, which are sourced from the food they eat.
Foraging pheromones allow cockroaches to recommend food sources to each other. Once they find a suitable food source, they spread the word to the rest of the colony, which is why you often find multiple cockroaches feasting on the same food source.
Scientists believe that pheromones are made from waxy substances found on the surfaces of cockroaches' skin, or from nitrogen compounds found in their faeces. Another theory is that they are made of fatty acids.
Cockroaches also communicate through sounds, such as chirping, gentle songs, and hissing. However, this is more common in wild cockroaches than in household cockroaches.
How Can L1 Visa Holders Travel to Canada?
Cockroaches are nocturnal insects that live in large colonies but travel in small groups. They are social insects that prefer to be in groups, as this provides greater protection against predators.
While cockroaches need food and water to survive, they can go for extended periods without nourishment. Cockroaches can survive for up to a month without food, and only about a week without water. This ability to survive without food for long periods is due to their nature as cold-blooded animals. When food is scarce, cold-blooded animals like cockroaches can keep their body temperature low to preserve energy, allowing them to go for extended periods without eating.
In ideal conditions, with 36% to 40% humidity, all species of cockroaches can live for a month or more without food. Higher humidity levels, ranging from 50% to 100%, are more beneficial for cockroaches, indicating their strong dependence on water. In dry conditions, most cockroaches can only survive for about a week without water.
Female cockroaches tend to survive longer than males, and larger species fare better than smaller ones. The female German cockroach (Leucophaea maderae) can survive the longest without food or water, lasting up to 50 days.
Cockroaches are resilient and highly adaptable, making them challenging to eliminate. They can squeeze through tiny spaces, are nocturnal, and can withstand extreme temperatures, dehydration, and even radiation. They reproduce quickly and have developed resistance to many pesticides.
To effectively control a cockroach infestation, a multifaceted approach is necessary. This includes eliminating food and water sources, sealing cracks and crevices, and using targeted pest control products specifically designed for cockroaches.
Is it Possible to Travel Abroad with a U Visa: Exploring the Options
Cockroaches are nocturnal insects, so they are most active at night. This means you rarely see them during the day. They prefer to hide in dark, secluded areas, where they are safe from harm. They are often found in dark, warm, and moist areas inside houses, such as behind furniture and appliances, as well as under refrigerators and stoves. They can also be found in cupboards, cabinets, and crevices between floorboards and walls.
Cockroaches are driven by their basic needs, which are the same as those of any other animal. When they are awake, they seek food, water, and mates. They prefer to do this at night, when their biggest threat—humans—is less likely to be around. By being active at night, cockroaches can avoid being stepped on by humans, and they are less likely to have their food source removed.
Cockroaches are not scared of light, but they have evolved to associate light with humans, and humans with danger. So, when a light is turned on suddenly, they run away, not because they fear the light, but because they fear humans.
If you see a cockroach in your home during the day, it is likely that there are many more hiding. This is a sign of a potential infestation, and you may need to call a pest control expert.
Does Aya Healthcare Cover Travel Expenses for Employees?
Frequently asked questions.
Cockroaches are social insects that prefer to live and travel in groups. They rarely travel alone.
Cockroaches are nocturnal and prefer to live in dark, warm, and moist areas. They can be found in crevices between floorboards and walls, behind furniture and appliances, under refrigerators and stoves, and in cupboards or cabinets.
Cockroaches move through small holes, under doors, or up and down plugs and drains. They prefer gaps that are less than half an inch wide. They can also hitchhike in cardboard boxes, furniture, suitcases, bags, and packaging materials.
Cockroaches do not travel far once they have invaded a building. They find a suitable spot and make it their home, only leaving to forage for food and water.

- Majid Rana Author

- Alain Brady Author Reviewer
It is awesome. Thank you for your feedback!
We are sorry. Plesae let us know what went wrong?
We will update our content. Thank you for your feedback!
Leave a comment
Travel photos, related posts.

Your Perfect Guide to Shopping for Luggage for Airport Travel
- May 16, 2024

The Ultimate Guide to Traveling from Anchorage to American Samoa
- May 24, 2024

Travel Expo: What's the Deal?
- Sep 16, 2024

How to Travel to the Bahamas with a US Visa: Everything You Need to Know
- Mar 17, 2024

Your Guide to Paying for Your Travel Resorts of America Membership
- May 23, 2024

Exploring the Wandering Paths: Where Do Bucks Like to Travel?
- May 28, 2024

Do Cockroaches Come in Groups?
By Steve Martin

Cockroaches are one of the most common household pests, and for good reason. These insects are hardy, adaptable, and able to survive in a wide range of environments. They are also known for their ability to reproduce quickly, leading to infestations that can be difficult to control. One question that many people have about cockroaches is whether or not they come in groups, or if they are solitary creatures.
The answer to this question is that cockroaches do indeed come in groups, and are known to live in large colonies. Cockroaches are social insects, meaning that they live and work together in organized societies . In a cockroach colony, there is a clear hierarchy, with different roles and responsibilities assigned to different members of the group.
The leader of a cockroach colony is typically a female, who is responsible for laying eggs and overseeing the growth and development of the young. The other members of the colony are usually male, and their primary role is to protect the colony and gather food. Cockroaches are scavengers, and they will eat just about anything, including dead plants and animals, as well as human food and waste.
Cockroaches are also known for their ability to communicate with each other through a variety of means. They use pheromones to mark their territory and attract mates, and they can also make sounds and vibrations to alert other members of the colony to danger or the presence of food.
One of the reasons why cockroaches are such successful pests is their ability to reproduce quickly. Female cockroaches are capable of laying up to 50 eggs at a time, and they can do this multiple times throughout their lifecycle. The eggs are typically laid in hidden, protected areas, such as in cracks and crevices, or inside wall voids. When the eggs hatch, the young cockroaches, or nymphs, will stay close to the mother for the first few weeks of their lives, until they are old enough to fend for themselves.
Cockroaches are also able to survive for long periods of time without food or water, which makes them particularly difficult to eliminate. In fact, some species of cockroaches can go for several weeks without eating, and can survive for several months without water. This ability to withstand harsh conditions is one of the reasons why cockroaches have been around for so long, and why they are found in virtually every part of the world.
If you have a cockroach infestation in your home, it is important to take steps to eliminate them as soon as possible. Cockroaches can carry diseases and parasites, and they can contaminate food and surfaces with their droppings and secretions. There are several methods that can be used to control cockroach populations, including the use of traps, baits, and insecticides. It is often best to seek the assistance of a professional pest control company, as they have the knowledge and experience to effectively manage and eliminate cockroach infestations.
In conclusion, cockroaches do indeed come in groups, and they live and work together in organized colonies. These insects are known for their ability to reproduce quickly and withstand harsh conditions, which makes them difficult to control. If you have a cockroach infestation in your home, it is important to take steps to eliminate them as soon as possible, in order to protect your health and the integrity of your home.
- Recent Posts
- Do Cockroaches Bite Eyelids? Exploring Myths and Realities - December 31, 2023
- Country with the most cockroaches: unbelievable Findings - December 31, 2023
- How to Safely Remove a Cockroach from Your Laptop - December 31, 2023
Related posts:
- what does it mean to dream of cockroaches | interpretations
- do hamsters eat cockroaches? : Here’s What Experts Say
- Why Do Roaches Run Towards You? 10 Reasons
- do cockroaches have ears?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
When Do Cockroaches Come Out?

Cockroaches are primarily nocturnal and come out at night to forage for food and water. This article explains their nocturnal behavior and what it means for controlling infestations effectively.
- Cockroaches are primarily nocturnal and prefer dark, warm, and moist areas to hide during the day, becoming more active at night in search of food and water.
- The peak activity for cockroaches typically occurs in the warmer months, late spring through summer, due to ideal breeding conditions provided by higher temperatures and humidity levels.
- Cockroaches exhibit group behavior and communicate through pheromones, which can lead to increased sightings as they collectively respond to signals indicating food or danger.
- Environmental factors like temperature and humidity trigger cockroach activity, while human presence and activities, particularly related to food and waste, attract them.
- Cockroaches have adapted to urban environments, exploiting resources and habitats provided by human habitation, with regional variations affecting their activity patterns.
Table of Contents
Daily and Seasonal Activity Patterns of Cockroaches
Daily cycle: hiding spots and active periods.
Cockroaches are primarily nocturnal creatures that prefer to stay hidden during the day. They seek out dark, warm, and moist areas to rest and hide from potential threats. Common daytime hiding spots include cracks and crevices, behind refrigerators, under sinks, and within piles of clutter.
As night falls, cockroaches become more active as they emerge from their hiding places in search of food and water. This nightly activity is heavily influenced by the absence of light, as cockroaches are known to avoid illuminated areas. The cover of darkness provides them with a sense of security to explore and forage.

Seasonal Aspect: Roach Season and Peak Emergence
Cockroaches thrive in warm environments, which is why roach season typically coincides with the warmer months of the year. During this time, you may notice an increase in cockroach activity. The peak times for cockroach emergence are usually in the late spring through summer, as the higher temperatures and humidity levels provide ideal conditions for them to breed and seek out resources.
However, it’s important to note that while cockroaches are more visible during these warmer seasons, they can be active year-round, especially in human-inhabited environments where warmth and food are consistently available.
Group Behavior and Communication in Cockroaches
Do cockroaches live or travel in groups.
Cockroaches are known to exhibit group behavior, often seen when they infest an area. They may travel in groups, especially when a large food source is discovered. This behavior is part of their survival strategy, as moving in groups increases their chances of locating food and evading predators.
Communication Among Cockroaches
Cockroaches communicate through various means, including the release of pheromones. These chemical signals can indicate the presence of food, alert others to danger, or even attract mates. This form of communication is crucial for their survival and plays a significant role in their daily and seasonal activity patterns. When one cockroach finds a food source, its pheromones can lead others to the same spot, which is why you may suddenly see multiple cockroaches emerge in an area where only one was spotted before.
Environmental and Human Influences on Cockroach Emergence
Understanding what triggers cockroaches to come out is key to controlling and preventing infestations. Let’s explore the environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, as well as the impact of human presence and activity on cockroach emergence.
Triggers for Cockroach Activity
Environmental factors.
Cockroaches are highly influenced by their environment. They prefer warm temperatures and high humidity, which are conducive to their survival and reproduction. Sudden changes in the environment, like an increase in temperature or moisture, can trigger cockroaches to emerge from their hiding places as they seek out more comfortable conditions or new sources of food and water.
Human Presence and Activity
Human environments provide a buffet of resources for cockroaches, including food scraps, water leaks, and refuge in the form of clutter and garbage. Our daily activities, especially those related to food preparation and disposal, can inadvertently attract cockroaches. Even at night, when human activity typically decreases, cockroaches may come out to take advantage of the leftovers of the day.
Regional Variations in Cockroach Emergence
Cockroach activity can vary significantly based on regional conditions. Urban areas, with their higher density of buildings and waste, can offer more opportunities for cockroaches to thrive. Conversely, rural areas may experience less cockroach activity due to fewer resources and habitats suitable for these pests.
Geographic location also plays a role. In warmer climates, cockroaches can be active year-round, while in cooler regions, they may seek indoor warmth during colder months, leading to increased sightings in homes and businesses.
Human Environments and Urban Adaptations
Cockroaches have shown remarkable adaptability to urban environments. They have evolved to exploit the resources provided by human habitation. In cities, cockroaches can find ample food, water, and warmth, allowing them to remain active and reproduce throughout the year.
Our buildings provide cockroaches with numerous entry points and hiding spots. Gaps in walls, crevices around pipes, and even spaces beneath doors can serve as gateways for these pests. Once inside, they can easily navigate through wall voids and ductwork, spreading to different areas of a structure.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We're glad you found this post helpful.
Share it with your friends!
Our apologies if you found this post unhelpful.
Help us improve this post!
How can it be improved? Your feedback is important to us!
Disclaimer: The content of this post is intended for informational and educational purposes only and should not be seen as professional advice. Exercise caution and consult a professional as needed before acting upon any information provided. We do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or reliability of this information, products, services, or related graphics, and are not liable for any decisions made based on it. Use of this blog is at your own risk, and we disclaim responsibility for any losses or damages arising from its use.

Advertisement
How Cockroaches Work
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
Entomologists estimate that there are between 5 and 10 million species of insects on Earth . But if asked which insect they hate the most, many people would have no trouble choosing just one -- the cockroach.
There are plenty of reasons to dislike cockroaches. Their flattened bodies, leathery wings, skittering legs and long, waving antennae give some people the creeps. Because roaches eat garbage and waste, they can spread bacteria like Salmonella and Shigella from place to place. As they walk, they leave trails of fecal matter, which they use to find their way around. On top of being gross, these trails can cause stains and odors. The proteins in cockroach saliva and waste can also cause allergies and aggravate asthma.
People also hate roaches because they can be extremely difficult to get rid of. One reason is because of their natural behavior. They reproduce quickly and are hard to kill. Since they're nocturnal, many people don't notice their presence until there are so many that they've run out of places to hide. Roaches are particularly good at dodging and running from shoes, newspapers and other weapons, and several species have become resistant to insecticides.
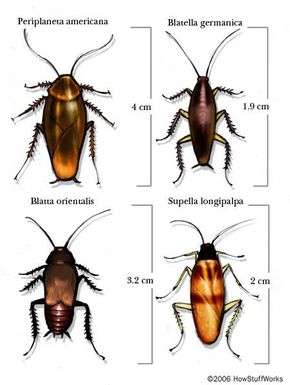
But of the 4,000 roach species that exist in the world, only a handful of them plague homes and businesses. These pest species include:
- Blatella germanica , the German cockroach
- Periplaneta americana , the American cockroach or palmetto bug
- Supella longipalpa , the brown-banded cockroach
- Blatta orientalis , the oriental cockroach
In fact, in many parts of the world, just one species -- the German cockroach -- is responsible for most infestations. Unfortunately, people take much of the blame for this worldwide prevalence. Most cockroach pests have spread across the planet by hitchhiking on boats, airplanes, trucks and even in moving boxes and grocery bags.
While Blatella germanica and a few others make nuisances of themselves, most species of cockroach generally mind their own business. Many cockroaches live in warm, tropical areas and feed on decaying wood and leaves. They help break down this organic debris; in the process, they add nutrients to the soil through their waste. They're also a food source for small reptiles and mammals. In other words, in spite of their bad reputation, cockroaches are an important part of many ecosystems.
Whether they're digesting wood pulp in a rainforest or hiding under a refrigerator, cockroaches are fascinating. They're primitive insects -- they existed millions of years before dinosaurs did and have evolved very little since then. In spite of their unchanging nature, they've survived when other species have not. For example, dinosaurs became extinct 65 million years ago, but cockroaches have thrived for 320 million years. We'll look at the physical features behind this uncanny survival next.
Cockroach Anatomy and Physiology
The cockroach life cycle and behavior, getting rid of roaches.
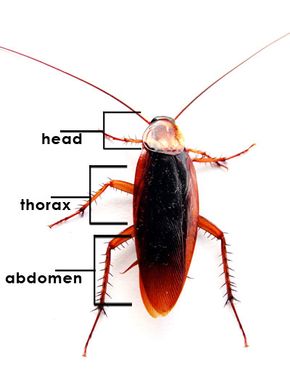
Most people can recognize cockroaches instantly. They're brown or black insects that are usually between half an inch and two inches long (12-50 millimeters), minus their long antennae. Their heads point downward, almost as if they're built for ramming. Males usually have wings, but females often don't. Those that do usually have vestigial wings -- small, undeveloped wings that often don't allow the roach to fly.
Although their reputation often sets them apart, roaches have a lot in common with other insects. Their bodies have three primary regions -- the head, the thorax and the abdomen. They have three pairs of jointed legs, one pair of antennae and a rigid exoskeleton . Roaches shed their exoskeleton, or molt , several times during their lives. After molting, most roaches are white and easily injured until a hormone called bursicon causes the exoskeleton to darken and harden. Sometimes, a roach can re-grow a lost limb when it molts and even put off molting to allow the new limb to grow.
Roaches' heads house their eyes , antennae and mouthparts. Contrary to popular perception, their heads also house their brains . However, much of their nervous system activity takes place in nerve ganglia located throughout their bodies. This is one of the reasons why a headless roach can live for more than a week. The other is that roaches don't breathe through a nose or mouth. Instead, they draw air through spiracles , or holes in their sides. Tubes called tracheae deliver oxygen from the spiracles to organs and tissues. When a headless roach finally dies, it dies of thirst.
Although not as distinctive as the eyes of dragonflies or houseflies, cockroaches' eyes are compound and are made of photoreceptor cells called ommatidia . A hard ring called the ocular sclerite surrounds the photoreceptors. Because of this compound structure, cockroaches see the world as a mosaic.
Movable antennae, also known as antennal flagella , allow roaches to feel and smell the world around them. Although the antennae look like threads, they're really made of lots of tiny, hair-covered segments. These segments are shorter and thicker near the roach's head, and they're longer and thinner near the tips.
Roaches' mouths, like those of other insects, are significantly different from mammals' mouths. However, many mouthparts serve the same function as parts of a mammal's mouth:
- The labrum and labium form lips.
- Two mandibles have cutting and grinding surfaces like teeth.
- Two maxillae manipulate the food while the roach chews.
A roach's thorax houses the attachments for three pairs of legs and, if the roach has them, two pairs of wings. Each of the three pairs of legs is named after the region of the thorax to which it attaches:
- The prothoracic legs are closest to the roach's head. These are the roach's shortest legs, and they act like brakes when the roach runs. A portion of the prothorax also covers the roach's head.
- The middle legs are the mesothoracic legs . They move back and forth to either speed the roach up or slow it down.
- The very long metathoracic legs are the roach's back legs, and they move the roach forward. Using its metathoracic legs, a roach can move about 50 body lengths in a second. A human moving that quickly would be running about 200 miles per hour. When a roach runs this quickly, it sometimes raises up and runs on its back legs only. The force of the air it encounters keeps it upright.
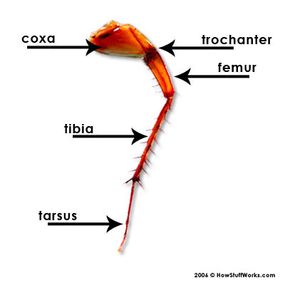
These three pairs of legs have substantially different lengths and functions, but they have the same parts and move the same way. The upper portion of the leg, called the coxa , attaches the leg to the thorax. The other parts of the leg approximate parts of a human leg:
- The trochanter acts like a knee and lets the roach bend its leg.
- The femur and tibia resemble thigh and shin bones.
- The segmented tarsus acts like an ankle and foot. The hook-like tarsus also helps roaches climb walls and walk upside down on ceilings.
Each leg moves up and down like a pogo stick and back and forth like a pendulum. The front and back legs on one side move at the same time as the middle leg on the other side. In this way, the roach can move over nearly any terrain.
When a roach is running as fast as it can, its legs move back and forth about 27 times per second. When it runs upside down on a ceiling, it takes longer steps in an attempt not to fall down. In fact, it takes significantly more energy for a roach to run upside down than to run up a vertical wall.
The Abdomen
Most insects have a segmented abdomen that contains most of their internal organs, and roaches are no exception. Inside a roach's abdomen, a tube-like heart moves blood to organs and tissues. Unlike human blood, a roach's blood doesn't use hemoglobin to carry oxygen, so it is colorless instead of red. The blood also doesn't travel through an extensive circulatory system. Although an aorta carries blood to specific organs, much of the blood travels through a network of spaces called a hemocoel . Roaches also store fat a little differently than people do. Instead of spreading it throughout most of their physical structure, they store it in one centralized location called the fat body .
A roach's digestive system is located in its abdomen, and much of it resembles a simplified version of a mammal's digestive system. However, a roach's digestive system has a few modifications that let it eat cellulose and other tough materials. One of these is a crop, which holds swallowed food until a toothy section of the digestive tract, called the proventriculus , can pulverize it. Sacs called the gastric cacea hold enzymes and microbes that continue to digest the food. This extra digestive help is particularly important if the roach eats cellulose or wood. Only after the material is thoroughly broken down can the roach's midgut absorb the food's nutrients.
Two segmented cerci lie on the exterior of the lower part of a roach's abdomen. These somewhat resemble antennae, and they can behave as sensory organs. A nerve inside the roach allows it to detect air movement around its cerci. This is one reason roaches can move out of the way very quickly if you try to catch or crush them.
Roaches' reproductive systems are also located in their abdomen. We'll look at this system and at the cockroach life cycle next.
Often, an antenna will continue to react to stimuli even after it has been removed from a roach. Scientists have taken advantage of this phenomenon to create theelectroantennogram -- an antenna attached to an oscilloscope. Researchers have used this device to study cockroach pheromones , or chemicals used to attract other roaches. These pheromones could be used to make more effective roach baits.
Cockroaches may seem indestructible, but they are food for a variety of other animals. Some species of wasp use cockroaches as incubators for their eggs. A female wasp will sting a roach or remove its antennae to disable it. Then, she will lay her eggs inside the roach, where they will grow until they hatch. In addition, another household pest, the common house centipede, eats cockroach nymphs.

As with many animals, cockroach reproduction relies on eggs from a female and sperm from a male. Usually, the female releases pheromones to attract a male, and in some species, males fight over available females. But exactly what happens after the male deposits his sperm into the female varies from species to species.
Most roaches are oviparous -- their young grow in eggs outside of the mother's body. In these species, the mother roach carries her eggs around in a sac called an ootheca , which is attached to her abdomen. The number of eggs in each ootheca varies from species to species. Many female roaches drop or hide their ootheca shortly before the eggs are ready to hatch. Others continue to carry the hatching eggs and care for their young after they are born. But regardless of how long the mother and her eggs stay together, the ootheca has to stay moist in order for the eggs to develop.
Other roaches are ovoviviparous . Rather than growing in an ootheca outside of the mother's body, the roaches grow in an ootheca inside the mother's body. In a few species, the eggs grow inside the mother's uterus without being surrounded by an ootheca. The developing roaches inside feed on the eggs' yolks, just as they would if the eggs were outside the body. One species is viviparous -- its young develop in fluid in the mother's uterus the way most mammals do. Ovoviviparous and viviparous species give birth to live young.

Whether mother roaches care for their young also varies from one species to another. Some mothers hide or bury their ootheca and never see their offspring. Others care for their offspring after birth, and scientists believe that some offspring have the ability to recognize their mothers. The number of young that one roach can bear also varies considerably. A German cockroach and her young can produce 300,000 more roaches in one year. An American cockroach and her young can produce a comparatively small 800 new roaches per year.
Newly hatched roaches, known as nymphs , are usually white. Shortly after birth, they turn brown, and their exoskeletons harden. They begin to resemble small, wingless adult roaches.
Nymphs molt several times as they become adults. The period between each molt is known as an instar . Each instar is progressively more like an adult cockroach. In some species, this process takes only a few weeks. In others, like the oriental cockroach, it takes between one and two years. The overall life span of cockroaches differs as well -- some live only a few months while others live for more than two years.
Cockroaches generally prefer warm, humid, dark areas. In the wild, they are most common in tropical parts of the world. They are omnivores, and many species will eat virtually anything, including paper, clothing and dead bugs. A few live exclusively on wood, much like termites do.
Although cockroaches are closely related to termites, they are not as social as termites are. Termite colonies have an organized social structure in which different members have different roles. Cockroaches do not have these types of roles, but they do tend to prefer living in groups. A study at the Free University of Brussels in Belgium revealed that groups of cockroaches make collective decisions about where to live. When one space was large enough for all of the cockroaches in the study, the cockroaches all stayed there. But when the large space was not available, the roaches divided themselves into equal groups to fit in the smallest number of other enclosures.
Another study suggests that cockroaches have a collective intelligence made up of the decisions of individual roaches. European scientists developed a robot called InsBot that was capable of mimicking cockroach behavior. The researchers applied cockroach pheromones to the robot so real roaches would accept it. By taking advantage of roaches' tendencies to follow each other, InsBot was able to influence the behavior of entire groups, including convincing roaches to leave the shade and move into lighted areas. Scientists theorize that similar robots could be used to herd animals or to control cockroach populations.
In addition to robotic intervention, there are several steps that people can take to reduce or eliminate cockroach populations. We'll look at these next.

Most pest control experts recommend two primary methods for controlling roaches. First, seal off any cracks or holes that roaches could use to get into your home. Roaches can fit into extremely small spaces, including cracks that are only 1/16 of an inch (1.5 millimeters) thick. For this reason, completely blocking all roach entrances can be very difficult. Determining which species of roach has entered your home can help you narrow down which parts of your home to focus on. The University of California has descriptions of the main pest species of cockroach and information on how to identify them.
Second, keep your home clean. Even spotless homes can become infested with roaches, but leaving food or garbage out in the open is likely to attract pests. Cover and seal all of your food, and wipe down counters and tables after eating. Sweep or mop your floor after cooking, and eat only in your dining area. Always wash dirty dishes promptly, since even tiny spots of food or grease can become food for roaches.
If these steps do not reduce the cockroach population in your home, the next step is to use traps to kill the roaches. Many experts suggest using traps before resorting to sprays or powders since you can look in the traps to see whether you've caught any roaches. If you haven't, you can move the traps to another location. This can help you figure out where the roaches are coming from and where to focus spray or powder treatments if they become necessary.
Many people prefer not to use poisons in their homes. However, experts caution that many natural devices for cockroach control, like ones that emit sound, do not really work. Fortunately, studies have shown that some natural substances can repel cockroaches:
- Nepetalactone, which is present in two forms in catnip
- Ceneole, also known as eucalyptol, which is present in bay leaves
- Osage orange oil, although scientists have not determined the exact active ingredient
Some infestations respond only to chemical deterrents or poisons. Your best bet may be to contact an exterminator who can determine exactly which species of cockroach is present and which chemicals to use to kill it. The University of California has more information about which chemicals are best to use on which species of cockroach.
Check out the links on the next page for lots more information on cockroaches, insects and related topics.
One common perception is that cockroaches will outlive humans, even in the event of a full-scale nuclear war. Opinions differ about whether this is the case. Some studies have shown that cockroaches, while hardier than humans, are more susceptible to radiation than other insects [source: ABC ]. However, others believe that since roaches' cells do not constantly divide the way people's cells do, they will be more likely to survive [source: Kunkel ]. Regardless of whether roaches could survive the initial blast, their need for warmth and moisture makes it unlikely that they could survive nuclear winter .
Lots More Informationf
Related articles.
- How Spiders Work
- How Cicadas Work
- How Venus Flytraps Work
- How Bats Work
- How Snakes Work
- How Termites Work
- How Fleas Work
- How Ticks Work
- How Chiggers Work
- How Mosquitoes Work
- Insect Quiz
More Great Links
- Animal Planet: Bug Week
- University of California at Berkley: PolyPEDAL
- Cyber Cockroach
- BlattaBase: The Cockroach Homepage
- Leurre: Artificial life Control in Mixed Societies
- Breene, Robert Gale. "Hissing Cockroaches: The Battletanks of the Cockroach World."http://www.anapsid.org/hissingroaches.html
- Burdick, Alan. "The Biomechanics of…Cockroaches." Discover. July 2004.http://www.discover.com/issues/jul-04/departments/biomechanics-of-cockroaches/?page=1
- Discover. "Inverted Insects." June 1996. http://www.discover.com/issues/jun-96/departments/invertedinsects795/
- Discovery: Yucky Roach World http://yucky.discovery.com/flash/roaches/index.html
- Elzinga, Richard J. Fundamentals of Entomology. Prentice-Hall. 1987.
- EPA: Indoor Environmental Asthma Triggers: Cockroaches and Pests.http://www.epa.gov/asthma/pests.html
- EPA: Roach Prevention Activity Web Site for Kids http://www.epa.gov/opp00001/kids/roaches/english/
- Guterman, Lila. "Trail of Dung Spells Disaster for Roaches." NewScientist. November 14, 1998. http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg16021601.900-trail-of-dung-spells-disaster-for-roaches.html
- Hadfield, Peter. “Robo Roach is Born." New Scientist. March 22, 1997. http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg15320744.100;jsessionid=GDLLELDFHHDB
- Harvard University. "American Cockroach Fact Sheet and Gallery." http://www.uos.harvard.edu/ehs/pes_american_cockroach.shtml
- Hecht, Joe. "Love it or Hate It." NewScientist. August 28, 1999. http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg16322013.900-love-it-or-hate-it.html
- Kruszelnicki, Carl. "Cockroaches and Radiation." Great Moments in Science. http://www.abc.net.au/science/k2/moments/s1567313.htm
- Kunkel, Joe. "Cockroach FAQ" http://www.bio.umass.edu/biology/kunkel/cockroach_faq.html
- Lowenstein, Frank and Sheryl Lechner. Bugs. Black Dog & Leventhal Publishers. 1999.
- Lyon, William F. "American Cockroach." Ohio State University. http://ohioline.osu.edu/hyg-fact/2000/2096.html
- Lyon, William F. "Brown Banded Cockroach." Ohio State University. http://ohioline.osu.edu/hyg-fact/2000/2098.html
- Lyon, William F. "Oriental Cockroach." Ohio State University. http://ohioline.osu.edu/hyg-fact/2000/2097.html
- National Institutes of Health. "Asthma Research at NIEHS." http://www.niehs.nih.gov/airborne/research/enviro/cockroach.htm
- NewScientist. "Nimble Pets." August 24, 2002. http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg17523573.500-nimble-pests.html
- Recer, Paul. "Cockroach Love: A Secret That Could Finally Kill Them."http://www.livescience.com/animalworld/ap_050217_cockroaches.html
- Rust, M.K. et al. "Cockroaches." University of California. http://www.ipm.ucdavis.edu/PMG/PESTNOTES/pn7467.html
- Scriven, Rory and Clifton E. Meloan. "Determining The Active Component In L,3,3-Trimethyl-2-Oxabicyclo [2,2,2] Octane (Cineole) That Repels The American Cockroach, Periplaneta Americana." 1984.
- Simonite, Tom. "Robo-roach Could Betray Real Cockroaches." New ScientistTech. May 2006. http://www.newscientisttech.com/channel/tech/dn9136-roboroach-could-betray-real-cockroaches.html
- Virginia Tech. Cyber Cockroach. http://www.ento.vt.edu/roach/
- Zimmer, Carl. "See How they Run." Discover. September 1994. http://www.discover.com/issues/sep-94/features/seehowtheyrun418/
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

- Use "Spacebar" or "Enter" to expand the My Account navigation menu.
- Use Down or Tab key to select next menu item.
- Use Up or Shift+Tab keys to select the previous item.
- Use Enter/Space key to visit the menu item.
- Use Esc key to leave the submenu.
- Use Left/Right arrow keys to allow users to navigate within the navigation links.
- Use Down arrow key to expand the submenu and up/down arrow keys to navigate within the submenu.
- Use Enter/Space key to select the menu/submenu items.
Fall Savings: Up to 30% Off - Shop Now »
Cockroaches (Roaches)
Shipping Zip Code:
- ‹ Roaches
- All About Roaches
*Also see our roach control page
All About the Different Types of Cockroaches, Cockroach Life Cycle, Cockroach Identification, and Cockroach Facts & More
What are roaches.
The name cockroach derives from the Spanish language cucaracha meaning cockroach. The transition of the word from Spanish to English came from the slang over time from “cuc-a-racha” to “cock-roach”. The scientific name derives from the Latin name for the insect.
- Doric Greek: βλ?ττα or blátta;
- Ionic & Attic Greek: βλ?ττη or blátt
- Blattodea- the cockroach order
There are 4,300 known species of cockroaches worldwide, and more are discovered all the time. Seventy of those species call North America their home. Out of all the species in the world, only around 30 to 35 are considered pests. The total number of roach species almost matches the number of mammal species, which are 5,400. Cockroaches today have related families and species still tied up in identification and yet to be discovered in the dense tropical regions around the world. They are the most successful ancient insect on the planet. These critters will eat anything and can survive absolutely anywhere other than the Polar Regions and above 2,000 meters in elevation. They are known to span and inhabit regions like the tropical rainforests, tropical forests, temperate forests, deserts, grasslands, and salt marshes. The cockroach order Blattodea is amongst some of the most talented and well adapted species of roaches. This family has the qualities of a super insect: some can live without water, can fly, are the fastest insect, are the most ancient, and can survive high levels of radiation and can survive by eating anything including their own vomit and each other.
- This means they eat their own feces!
- This means they eat their own vomit!
- This means they eat their own kind
- This means they love tight spaces and secure hiding places
- This means they have a distinct difference between male and female species.
- This means to produce eggs that hatch outside the body.
- Some roaches deposit the eggs and others carry the eggs along with them until they hatch.
- This is the structure within a cockroach that contains stored nutrients, uric acid, and endosymbiotic bacteria, each housed in a different cell type.
- The form in which an insecticide is applied: the most common formulations for roaches are sprays , dusts , and baits .
- Is the mechanism by which an insecticide, or roach killer , affects the insect in this case roaches.
- The cockroach fat body cell type that houses the endosymbiotic bacteria.
- The structure into which cockroaches deposit their eggs: also called an egg case.
- This is the shield-like plate covering the dorsum of the first thoracic segment in cockroaches.
Cockroach History
Where do roaches come from.
The cockroach, having been present on the planet amongst the first insects, currently has no proven origin. Scientist know that most roaches have come from the tropical regions all over the world and adapted to colder conditions - having over 300milion years to do so. The roach is suspected to have come onto the scene around 355 million years ago with the earliest roach-like fossil. They call this specimen a roachid, or the blattopteran. The fossil doesn’t exactly mimic todays roach with it being remarkably close to its cousin in evolution, the praying mantis, which does share features in this fossil.
The distribution of cockroaches is worldwide. They have evolved to live alongside humans and they do it well. The cockroach, like most insects, gained passports to any country through the aid of man. During the early centuries through trade routes, the Roach species became an invasive species on every continent humans inhabited. They are more prevalent in the tropical regions, but they can survive anywhere humans have established homes and food sources.
The Cockroach has been on the planet for approximately 250 to 300 million years. This dates back to as early as the Carboniferous times. Theories have speculated that the ancient ancestor of the cockroach predates the dinosaurs. During this insect order’s time on Earth, it has changed very little, keeping its features primitive or ancient like previous generations. It was said that the cockroach was amongst the first great expansion of the insect species.
The roaches appear to have achieved the optimum body form and other key features early in their evolution history. The theory is that the cockroach evolved the feature to fold their wings over their body to allow them the vital protect they needed. The traits gave the roach the ability to hide from predators and to escape various dangers to survive extinction where most insects were not successful.
Scientists also state that the development of the ootheca or egg sac carried by the female cockroach gave critical parental care and protection to sustain numerous generations allowing the species to survive countless millennia. Cockroaches have been clearly traced back to ancestral fossils that have remarkably almost the same morphology as current day roaches. Roaches have the innate ability to adapt to any situational condition that arises.
Another helpful adaptation is that cockroaches harbor a wide variety of symbionts in their gut as well as fat bodies. Scientific theories make the association that the microbes present have played a large role in the adaptation, evolution, and survival of cockroach species. The hindguts of most cockroaches, apart from one family of five species that have been examined, harbor a wide variety of microbes, including ciliates, amoebae, flagellates, and various prokaryotes. These microbial organisms all are believed to play a major role in digestion and the efficiency of the roach.
Why Do We Call Them Cockroaches?
The term “ blatta ” is derived from several branches of Greek languages for cockroach. Cockroaches are featured in literature and songs throughout history.
The Cockroach is featured in the "La Cucaracha" meaning "The Cockroach" that is a traditional Spanish folk-corrido or song that became popular in Mexico during the Mexican Revolution. The song is about the concern of a cockroach that has lost one of its six legs and is struggling to walk with the remaining five.
Cockroach Taxonomy
- Class Insecta - Insects
- Cryptocercidae: Most primitive ancient cockroaches
- Blaberidae: Blaberid cockroaches
- Blattellidae: Wood cockroaches
- Blattidae: Blattid cockroaches
- Polyphagidae: Sand cockroaches
Types of Roaches
There are many different types of roaches throughout the world, based on the regions they dwell in. Cockroaches can inhabit inside the home, outside the home, or both. If a roach prefers to dwell outside it is called a feral roach . The feral roaches still may end up inside the home but their survival is independent of humans. Next are the peridomestic roaches that can survive inside or outside the home. Then finally, the domestic roaches base their habitats of living inside homes only. These three regions allow you to further understand the cockroach and identify them.
In the Order Blattodea (Cockroaches)
- Blattellidae
- Polyphagidae
- Cryptoceridae
- Can range from 5-13 nymphal instars till they reach full maturity
- This just means the body is unspecialized or has not changed over time
Family Blaberidae
This family of cockroaches is the largest by size and species. Blaberidae cockroaches in some genera can be very large, like the Blaberus which is extremely large and reaches 80mm or longer. There are also over a dozen genera of Blaberid roaches with 2,000 species.
- Death’s Head Cockroach ( Blaberus cranifer )

- This pattern on the pronotum is referred to a “death patch” and inspires its name, “Death’s Head”
- The body is dark with brownish colored wings
- The size of this species varies from 40-60mm
- Biggest roach of the species is recorded at 80mm
- This species is the largest cockroach in North America
- The adults and larvae or young are active throughout the year in tropical and subtropical regions
- The distribution of this species spans from the southeastern United States down into Key West, and to the Caribbean, and into South America
- Cuban Cockroach ( Panchlora nivea )

- Cuban roaches are almost entirely translucent and pale green or pale blue-green
- Males have a slender tapering abdomen with a yellow colored underside
- Females are more broad at the abdomen region and darker than the males
- The size of this species varies from 12 to 20mm
- The Cuban roach species are noted as minor household pests, and prefer to spend the duration of their lives outdoors
- The adults and larvae or young are active throughout the year in the gulf coastal regions of North America
- The distribution of this species spans from Texas east to Florida, and south into central Mexico
- AKA: Hissing cockroach or hisser
- This is one of the biggest species of cockroach
- They range in size from 2 to 3 inches as adults
- The hissing cockroaches are native to the island of Madagascar
- They prefer to inhabit rotting logs and other leaf matter
- Commonly kept as a pet in large numbers
Family Blattellidae
This family is most commonly known as the wood cockroach or wood roach family. This family clings to the subtropical and tropical regions in the world. The Blattellids are known to be small outdoor roaches and wood roaches.
- German Cockroach ( Blattella germanica )
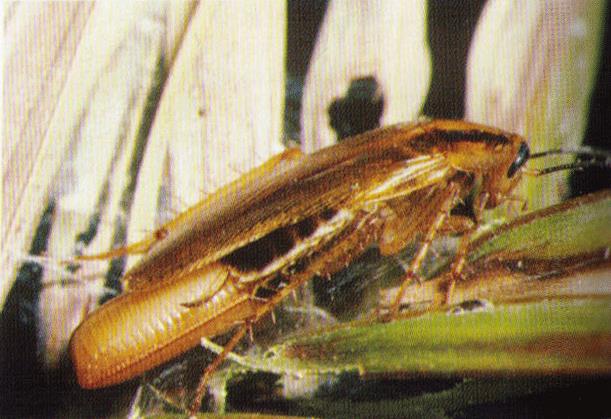

- The sizes of the species varies from 13 to 16mm
- Males are tan or a pale brown with two stripes or dark streaks down the pronotum
- The female is a darker variation of the male
- Both male and female German Roaches have wings
- This species’ distribution is found throughout the United States.
- They are active year round
- German Cockroaches typically invade houses, apartments, restaurants, other food preparation facilities, storage facilities in hotels, hospitals, and other institutions
- This species comes out at night to search for food and water
- If they are out during the day it indicates a severe infestation and German Roach control may be needed.
- Western Wood Cockroach ( Paroblatta americana )

- Males of the western wood roach are fully winged with a shiny pale brown color
- Females are dark brown and dark reddish brown mix and are wingless
- Sizes range from 8 to 15 mm
- These roaches prefer to live outdoors which means they are feral roaches
- They live in regions like grasslands, woodlands, and many other outdoor habitats
- There are 12 species of Paroblatta genus in the United States and Canada
- Male Western Wood Roaches are commonly drawn to spotlights and other lights around the perimeter of structures.
- To prevent them from enter the home after they are drawn in by the lights by understanding and controlling wood roaches .
- They are active mostly in the warmer months and spring through fall seasons
- The distribution of this species of wood cockroach is found in Oregon, California, Nevada, Arizona, and into parts of Baja California
Family Blattidae:
This family is known as the Blattid cockroaches. This is a diverse family with many genera and hundreds of species. The two genera Periplaneta and Blatta are the most widely distributed, whereas the rest of the genera are more regionally adapted. This family of roaches is known for being rather large and tend to prefer living outdoors. The species is commonly called Palmetto bugs.
- American Cockroach (Periplaneta americana)

- AKA: the Palmetto bug
- Size of this roach species ranges from 27mm to 40mm
- The distribution range of this species is from southern Canada throughout the United States and into Mexico
- This species is said to originate from Africa, transported on ships through travel and trade to become the cosmopolitan species they are today
- This species is active year round and love moist, warm locations
- Males are a polished red brown color with darker brown wings that are longer than its abdomen, have a pale head region or pronotum with two dark blotches on it
- The female has short wings that don’t extend beyond her abdomen
- The adults are somewhat weak fliers
- American cockroaches look to enter structures through sewage and plumbing systems
- American cockroaches are well known commercial pests of restaurants, supermarkets, bakeries, warehouse, shipyards, and other food industries
- Smoky Brown Cockroach (Periplaneta fuliginosa)
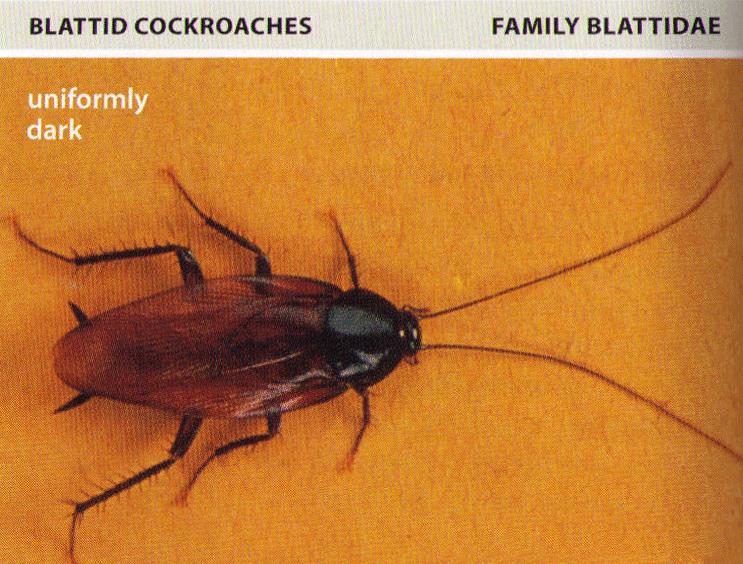

- This roach species is uniformly dark
- Both sexes of this species have wings that extend beyond the abdomen tip
- The size of this species ranges from 24mm to 33mm
- The Smoky Brown Cockroach is better known in history as the old world species and was a common house pest in the southeast.
- The Smoky Brown Roach is only second in abundance to the German Cockroach
- When outdoors they prefer to eat bird droppings and a wide variety of plant matter
- Smoky Brown cockroaches prefer to inhabit garages and outbuildings
- Large populations of this species can be found in large undisturbed wood piles
- The distribution range of this cockroach is from the Carolinas to Florida, then west to central Texas, and in isolated populations in the Midwest in heated buildings
- Oriental cockroach ( Blatta orientalis)

- AKA: Waterbugs
- The Oriental Roach species’ distribution range is from southern Canada and throughout the United States
- This species size ranges from 18 to 30 mm
- Oriental cockroaches are shiny and black - only the males have some dark reddish brown or blackish brown color and wings
- They are active year-round
- Oriental cockroaches prefer to live in a variety of places like basements, cellars, crawl spaces, behind radiators, under floor coverings, in hollow trees, and stumps
- When in clusters of dense populations, Oriental cockroaches give off a pungent odor
- This is a small species of cockroach which size ranges from about 10 to 14mm long
- The brown-banded cockroach has a dark tan to light brown overall body color
- The key identification characteristic is two light-colored bands across the wings and abdomen
- The bands can be hidden by the wings
- The male roach has longer wings that cover the abdomen and is more slender
- The female roach has shorter wings that do not cover the abdomen completely and is much wider than the male
- The range of the Brown-banded roach is found all over North America
Family Polyphagidae
This small family of roaches is commonly referred to as Sand Cockroaches . There are only a few described genera with around 100 to 150 species. The genera of the Arenivaga have evolved a system of absorbing moisture through the environment. Since most of this family is found in dry desert-like areas, this skill comes in handy.
- Desert Cockroaches (Arenviga spp.)

- In the polyphagidae family
- This species ranges from 15 to 24mm in size
- Males are pale with darker markings on wings
- Females have a brown or reddish color and are wingless with a distinctly visible body segmentation
- The sand cockroaches’ distribution, or range, is common to southern and southwest California
- Desert cockroaches are found in desert dunes, dry scrubby habitats, and other places beneath the ground
- Some desert roaches like to live in wood rat burrows
- Females are flightless and are found beneath stones or other objects
- Males of this species are fully winged and are frequently attracted to lights
- Because Desert Cockroaches live in dry conditions the roaches will absorb water vapor from the atmosphere through their mouthparts
Family Cryptoceridae
This is the most primitive or ancient family of cockroaches. This family has one genus and only 10 species or less. They are found in rotten logs in the United States, Korea, China, and Russia. They are reddish brown and both sexes are wingless as adults.
The controversial family Nicticolidae
This is one of the temporary genera that have an unknown placement for it amongst the roaches. The Nicticola genus does not contain endosymbiotic bacteria like the rest of its cousins. Many of this species has gone unidentified in this family so the current species count of roaches is much higher due to the undecided nature. The vast majority of cockroach species live in tropical regions of the world. These tropical regions are part of the world that has not been adequately assessed to establish the diversity of insect life.
Common Roach Species Comparison
Through extensive studies and research, the cockroach species have been shown to be extremely closely related to termites. The microbial symbionts in both roaches and termites are actually identical if not for the same purpose. Wood cockroaches are proven to have given rise to the termite family, and are at least the last connection in the lineage between the two forms of cockroach. The termites and wood cockroaches have modified symbionts to digest their wood that they consume. This inspired further research to knowing why. The roaches have obviously been on the planet longer than termite so they must have splintered off at some point countless millennia ago to become this modified roach family. The termite is actually an odd version of the cockroach that is one of the first insects to evolve on the earth!
This connection was made by the symbionts that are found in the gut of the two insects. They’re referred to as endomicrobia. The endomicrobia are classified as cytoplasmic symbiont protozoan in the guts of roaches and termites. Along with a host of bacteria and other flagellates that aid in digestion. Termites may look like white ants, but new genetic research confirms they are really a social kind of cockroach. The fact that normal cockroaches are primarily solitary animals and are compared with the termite’s complex society is an extreme thought. Researchers have also added that both species practice coprophagy, or eating feces. This fact could very well have led termites to evolve in the first place. Scientists had long known that cockroaches and termites were related to each other and to praying mantises. Some of the features they share include specialized cases that enclose their eggs, and perforations in the internal parts of their heads.
The termites over the years, decades, and millennia have been labeled with the name of the white ant. This term until recent years made sense being that the ants are in the social insect order. They live in colonies underground and have social rankings as well as queens. The major differences are the external anatomies and the choice to consume wood. Though there are some ant species that choose to call wood dwellings their home they do not actually ingest the wood. The ants merely reposition the wood or kick it out for the colony to grow within. Sometimes the ants will suck the moisture and oils out of the wood. Wood isn’t the ants’ primary source or choice of nourishment like the termite.
The termite has actually evolved to encase microbes and symbionts in the gut to aid in the digestion of wood. This is also a characteristic of all cockroach families with the exception of one family. In recent studies the push has been made to classify the cockroaches and termites into their own separate order. The research urges that the termites are not social pale ants, but actually social cockroaches.
They have moved the termites into the order Blattodea and the original order of Isoptera is now the infraorder under the cockroach order. The termites are actually stated as a cockroach family by entomologist Paul Eggleton from the natural history museum of London. Dr. Eggleton and his colleagues now conclude that the termites are a species of cockroach. The termite species has just evolved to mimic the social classes of the bees, ants, and wasp order.
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Subclass: Pterygota
- Infraclass: Neoptera
- Superorder: Dictyoptera
- Order: Blattodea
- Infraorder: Isoptera
General Cockroach Life Cycle
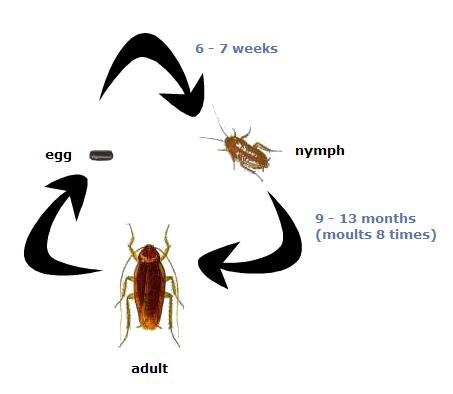
Image source: vtaide.com
The image above is a general life cycle of a cockroach.
Once the male and female roach reproduce or copulate the new generation begins brewing. The fertilized female now begins creating an egg capsule. The egg capsule created by the female cockroach is called an ootheca. This egg capsule grows as it fills up with up to sixty or more eggs. The egg swells and bulges out from the abdomen. Each species of roach deals with the ootheca differently. Some carry it until the young hatch, or drop the egg after carrying it for a time period, or finally just drop the ootheca once it is produced.
Once the young or nymph cockroach emerge, they then begin a 9-12 month nymph stage as they molt and grow to reach the adult stage. This phase of the life cycle can encompass as many as six nymph stages. The roach species have been known to in some cases in periods of improper diets to undergo over 10 to 15 nymph stages. The type of development the roaches undergo is called a hemimetabolus or paurometabolous metamorphosis. Hemimetabolus or paurometabolous means development by gradual metamorphosis in nymph stages that resemble small adults. After each molt, the cockroaches are white and the exoskeleton is soft and hardens short after a few hours.
General Cockroach Anatomy
External anatomy.
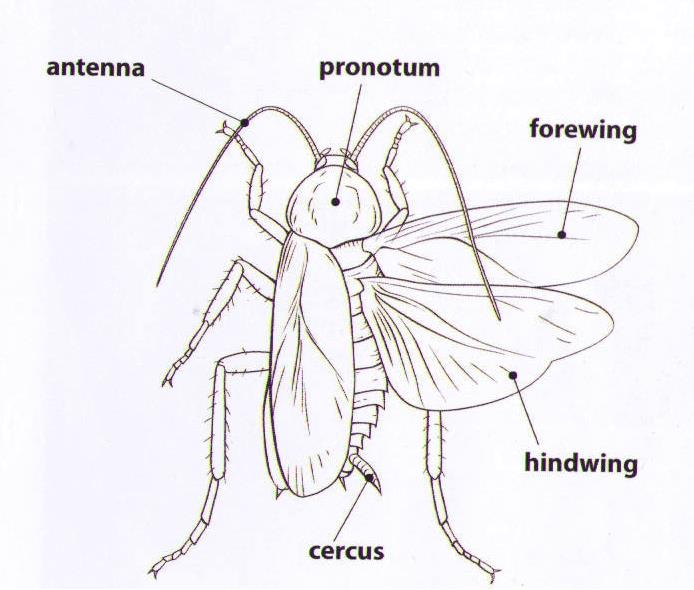
The current cockroach anatomy is split up into three main regions:
The external anatomy is made up of:
- an exoskeleton
Roaches have two forewings and two hind wings. The wings are called the left and right forewings and hind wings. The forewings are sometimes extended to cover the body of the roach. The six legs are named right foreleg, left foreleg, right mid-leg, left mid-leg, right hind-leg, and left hind-leg.
The exoskeleton has a region behind the head that is like a shield called the prothorex or pronotum. The legs are divided up into segments from the body out, coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, and ending at the tarsus.
Internal Anatomy
Internally, Cockroaches have a vast array of organs including:
- salivary gland
- lateral blood vessels
- dorsal blood vessel(heart)
- salivary reservoir
- coxal muscles
- metathoracic ganglion
- nerve center
- male and female reproductive organs
- ventral nerve cord
- dorsal tergites
- cercal nerve
- proventriculus
- enteric caeca
- ventriculus
- malpighian tubules
Cockroach Identification & Morphology
How to identify a cockroach:.
*See our step-by-step Roach Identification Guide for complete identification information.
- Count six legs
- Hard exoskeleton
- Thin transparent wings that lay and fold on the back
- Long flat body
- Two long antennae
- Reddish brown colored cockroaches are American or German roaches
- Dark Brown colored cockroaches are smokybrown or brown banded roaches
- Shiny black colored cockroaches are Oriental roaches
- 1-2 inches in length are the American, smoky brown, and Oriental cockroaches
- The smallest roach is on average a half of an inch and is the German cockroach
- German cockroaches also have two black racing stripes or to black parallel lines down the head and onto the wings
- Brown Banded roaches have tan bands around its abdomen in stripes
- These key features along with where you found the roach will help confirm the identification process
The cockroach has three body segments, six legs, and one pair of antennae. This is the common key morphology of all class Insecta lineages, or orders of insects. The exoskeleton is a hard protective covering and incases the internal organs. The exoskeleton is commonly divided into sclerites or plates. Roaches have unique mouthparts called the labrum, mandible, labium, and maxilla.
The differences between sexes is either clear to distinguish, or the species of roach is dimorphic. Dimorphism means that both sexes are exteriorly identical. In the dimorphic roach species both sexes possess wings and other similar features. Though several species of males have wings in the adult stage and the females remain wingless from the transition from nymph to adult. Then, in some cases, the wing lengths of species and body length sizes are different between sexes.

Frequently Asked Questions About Cockroaches
Do cockroaches bite?
The cockroach can in fact bite humans. All cockroaches have mandibles and a nasty hunger that never ends, making the roach always in search of a food source. Though cockroach bites are rare most bites will occur in extreme cases of high populations or lack of food. In some cases, bites could occur while humans are falling asleep with food residue on clothing or on the face or skin which can draw the roaches in. They can feed on human flesh but the roach would much rather prefer the less luxurious dining style of leftover crumbs and scraps.
If a bite does occur this can be no joking matter. The bite can be almost unnoticeable but can result in a nasty infection or worse. The typical cockroach lifestyle of crawling through and living in the must filthy locations can allow the roaches to harbor a host of bacteria, parasites, viruses, and other microorganisms.
Do cockroaches fly?
Yes - cockroaches have wings that they use to fly. The adult roaches, and more commonly the male roaches, have wings to locate females. The wings allow the roach to travel more easily. Though not all roaches have wings and most of the roaches’ life is spent wingless until it is a mature adult. The nymphs are highly skilled jumpers, climbers, and sprinters. So no matter the stage of life the cockroach is an evasive creature.
What do cockroach droppings look like?
Cockroach droppings, depending on how fresh or not they are, are around one millimeter in diameter or smaller. The feces are also circular or spherical. The round droppings can vary in size depending on the life stage and size of the roach. The colors may vary as well from black, light brown, dark brown or brownish green. The color also depends on the diet of the roach.
What attracts cockroaches?
Research shows that cockroaches are drawn to one another. They pick up the pheromones given off by nearby roaches by the specialize antennae. The roach has over a hundred segments on each antenna that allow it to scene the presence of other roaches. Cockroaches do travel in packs once together. They unknowingly travel as a pack and prefer to be in groups. This factor allows them to protect one another and create new generations.
There are many factors that draw in and attract a host of different roach species. The feral roaches or wood roaches are oddly attracted to spotlights and can be uncontrollably attracted to homes. As a result the feral roaches are sometimes caught in the home.
Then in some cases the semi-domestic and domestic roaches are drawn to the primary source of clutter and food. The peridomestic and domestic roaches need to feed on the food humans eat, the waste, and trash of this food.
What do cockroaches do?
The cockroach loves to forage and eat at all hours. They also love to wonder around discovering new shelters, foods, and water sources. The number one concern of the cockroach is eating and finding water. The cockroaches’ kryptonite, so to speak, is its unavoidable urge to eat. They also love to be touched on all sides so they will hide in any crack and crevice they can fit in. The roaches also like to do most of their foraging in the night hours. They spend over 75 percent of the day resting or hiding.
Do cockroaches and asthma have a correlation?
Yes - cockroaches do cause asthma. The immune system works its best to try to prevent any foreign substance from entering into the body like bacteria and viruses. This response is to save us from a potentially dangerous illness or disease. The allergies come from the immune system overreacting once we inhale, swallow, or touch any foreign substances. These substances are called allergens. This response triggers the cells and body to attempt blocking these foreign particles resulting in the person having allergies.
The cockroach allergen is from the feces, saliva, and bodies of the roaches themselves in the vicinity of the allergy prone person. Over 80 to 90% of the urban homes have cockroaches, and from 900 to 300,000 insects. This overwhelming presence as a result is creating an increased chance of allergies becoming an issue and new ones becoming created.
Source: AAFA or the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America
Do cockroaches carry disease?
During the average cockroach adventure, they will find many dirty and filthy locations. This lifestyle makes the roach very dangerous. The cockroach can pick up or be introduced to a host of microbes such as bacteria and viruses. One of the cockroach diseases is called cockroach gastroenteritis. This is a bacterial infection the bacteria causes diarrhea and is a medicinal illness categorized by inflammation.
Do cockroaches come out at night?
Cockroaches are nocturnal in small populations. They prefer to hide their presence so to make scavenging missions safer. In larger populations the roaches can be seen during the day. This is usually one of the key signs of a high population, along with a musk or odor.
How far can cockroaches jump?
In recent research it has been recorded that the cockroach can jump over 48 times its body length! In measuring terms this is over 35 centimeters. This skill allows this roaches to jump all over the home at night unnoticed.
What is the average cockroach lifespan?
Cockroaches can live anywhere from six to 24 months depending on the area they inhabit. This fact can be arguable in domestic pet roaches that are in a controlled, safe environment and have constant nourishment resources. In fact, many people all over the world buy cockroaches and raise them as pets! This domestication of the species throws off the expected life span. The difference between a wild roaches’ life span and a domesticated roaches’ life span are very different but typically they both live at the longest two years or less.
Do cockroaches like beer?
Roaches do love beer. Why do you ask? Well they are drawn to the aroma of certain beer hops and brewing styles, along with the sugar in beer which is a natural give away. First you would want to take a jam jar or deep bowl with a rounded inside lip. Coat the inner lip with Vaseline. This is so the roaches won't be able to escape. The next step is to then put a slice of beer-soaked bread at the bottom. The cockroaches will be attracted by the smell of beer, but the Vaseline-coated lip will make it impossible for them to escape. You can then dispose of them however you see fit.
Could cockroaches survive an atomic bomb?
Cockroaches actually couldn’t survive the initial blast or explosion like any other organism. The cockroach is only able to withstand higher levels of radiation. The roach is recorded to be over 15 times more resistant to radiation than humans.
Where are cockroaches commonly found?
Roaches love dark, warm, dirty, and moist locations. They will thrive in these conditions and high populations congregate in these areas with these characteristics. This means that roaches are typically found in places like sewers, dirty homes, and abandon buildings. All of these places are dark, dirty, and full of clutter. Roaches also like to eat other animal feces so they can be drawn to all sources of pets and animals.
What do you call cockroaches that live outside or outdoors?
Outdoor roaches are called feral cockroaches . Feral roaches do not like being indoors, and often are by mistake. They have adapted to be outside so hints the term feral or wild. The wood roach species is a feral roach and has adapted to feed on the organic matter and wood to survive outdoors.
What are the natural predators of cockroaches?
There are a host of amphibians and reptiles that feed on the cockroach species. Small reptiles like geckos, lizards, iguanas, and young snakes. Then amphibians like frogs and toads. There are also a host of insects and arachnids. There are beetles, wasps, and most spiders hunt roaches. Roaches are also attacked by funguses that spread when a roache makes contact with one another.
Cockroach Facts
- Cockroaches today are remarkably identical in size, shape, and color. One of the oldest amber sealed roaches’ dates back to over 40 million years ago stuck inside the resin since the tertiary period/era.
- The world's smallest cockroach is only 3mm long and lives in ant colonies.
- The heaviest cockroach in the world is the huge Australian Rhinoceros Cockroach at 80mm in length and weighing in at one pound.
- The cockroach with the world’s largest wingspan, of up to 185mm is the Megaloblatta blaberoides .
- Cockroaches have over 150 articulated segments in its antennae.
- Cockroaches are attracted to the presence of other cockroaches. They naturally migrate with one another, and collectively decide to do things together.
- Cockroaches are the lab test specimens for all insecticides; scientists say if it can kill a roach, it can kill anything.
- Cockroaches are omnivores like humans and have evolved alongside us to survive in our environment.
- The American Cockroach actually originates from tropical parts of Africa.
- Cockroaches are extremely fast at reacting to the wind created by any external force. They can react within 50 milliseconds. This is due to the super quick connection between its thoracic ganglia, which are like a secondary brain, to react and position its body out of danger.
- The cockroach can run up to 50 times its body length on one second, which is equal to a human running 30km in on second.
- The cockroach can maintain peak velocity while clearing objects in its way.
- The cockroach has inspired today’s engineers to copy its body style for robots.
- The cockroach, in the science world, is a celebrity because of its sporty design and qualities that have made it the preferred test subject.
- Roaches can handle 15x more radiation and microwaves than humans.
- When food is scarce roaches will eat anything. They will eat feces and other roaches to survive.
- Cockroaches can lose their head and continue to live for two weeks.
Cockroach Facts for Kids
- Cockroaches are also called roaches
- Cockroaches have 3 pairs of legs. A pair means two legs, so roaches have a total of 6 legs!
- Roaches are lazy over 75% of the day. That is around 18 hours a day of being lazy!
- The cockroach is an animal. The cockroach families have been on the planet for over 300 million years!
- Cockroaches do not have bones! So the make up for it by having a hard exoskeleton or harden skin to protect then and hold them together.
- Roaches can run up to 3 miles per hour.
- There are over 5,000 species of cockroaches in the world.
- The cockroach has around 18 knees!
- Cockroaches can live for over a month without food, but only a week without water.
- When it is cold outside roaches like to cuddle and snuggle with one another.
- Cockroaches can hide in any crack as thin as a dime!
Best ways to make your home roach proof:
- Remove all the things they want such as food, water, and clutter.
- Store all food in storage containers, protecting all organic matter.
- Thoroughly clean the garbage area removing all organic matter.
- Remove all access to running water. Roaches seek out water when they first enter the home.
- Seal all potential entry ways, because roaches love to explore
Top three cockroaches that are considered pests in North America
- German cockroach
- American cockroach
- Oriental cockroach
Works Cited
“Amazing Roach Facts.” Discovery Kids. N.p., n.d. Web. 21 Nov. 2013.
Eiseman, Charley, Noah Charney, and John Carlson. Tracks & Sign of Insects & Other Invertebrates: Guide to North American Species. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole, 2010. Print.
Evans, Arthur V. National Wildlife Federation Field Guide to Insects and Spiders & Related Species of North America. New York: Sterling Pub., 2007. Print.
“Integrative and Comparative Biology.” Cockroaches: Ecology, Behavior, and Natural History. William J. Bell, Louis M. Roth, and Christine A. Nalepa. Oxford Journals and The Society for Integrative and Comparative Biology, 19 July 2008. Web. 21 Nov. 2013.
Resh, Vincent H., and Ring T. Cardé. Encyclopedia of Insects. Amsterdam: Academic, 2003. Print.
Can't find the product you are looking for? E-mail us and we'll get it for you!
We sell professional do it yourself pest control (diy), exterminator and extermination insecticide, pesticide, chemical and bug killer treatment products to spray, eliminate and exterminate pests.
Many of our products are not available in stores such as Home Depot, Walmart or Lowes.

Do Cockroaches Travel Alone Or in Groups?
Do cockroaches travel alone or in groups? This is a question that has long been debated by scientists and entomologists. Some believe that cockroaches are social creatures that live in colonies and travel in groups, while others believe that they are solitary creatures that prefer to travel alone. There is evidence to support both theories, but the truth may be somewhere in between. It is possible that cockroaches are social creatures when it comes to certain activities, such as mating and raising young, but they may also prefer to travel alone when foraging for food or shelter.
Do Cockroaches Travel Alone Or in Groups? We all know that cockroaches are one of the most hated insects out there. They’re dirty, they’re gross, and they seem to be able to survive just about anything. But one thing you may not know about cockroaches is whether or not they travel alone or in groups. The answer is: it depends. Some species of cockroach are known to travel in groups, while others are more solitary creatures. So if you’re wondering whether or not that lone cockroach you saw scurry across your floor was part of a larger group, there’s no easy answer. However, there are some general things you can keep in mind when it comes to cockroach behavior. For example, most roaches prefer dark, damp places to live – so if you see one roach, chances are there are plenty more hiding nearby. Additionally, roaches are attracted to food sources – so if you see one near your kitchen sink or garbage can, chances are there are more where that came from. In short, seeing a single cockroach isn’t necessarily cause for alarm – but it’s definitely something to keep an eye on. If you start seeing them regularly, it’s time to take action to get rid of them before they multiply and become an even bigger problem!
Scientists Explain Why You Can't Get Rid of Cockroaches
Can Roaches Travel from House to House
If you’re dealing with a roach infestation in your home, you may be wondering if these pests can travel from house to house. Unfortunately, the answer is yes – roaches are excellent climbers and can easily move between homes through cracks and crevices. Even if your home is clean and well-sealed, it’s possible for roaches to hitch a ride inside on luggage, furniture, or other household items. Once they’re inside, roaches can quickly multiply and become a serious problem. These pests are not only unsightly and unpleasant, but they can also carry diseases that pose a risk to human health. If you suspect that you have roaches in your home, it’s important to take action right away to get rid of them before they have a chance to spread. There are several effective methods for getting rid of roaches, including baits, traps, and insecticides. You may need to try out a few different techniques before you find one that works best for your particular situation. If you’re struggling to get rid of roaches on your own, don’t hesitate to reach out to a professional pest control company for help.
Do Cockroaches Travel in Clothes
If you’ve ever had the misfortune of dealing with cockroaches, you know that they can be persistent pests. And if you’re not careful, they can even hitch a ride on your clothes! That’s right, cockroaches can travel in clothes, and it’s actually not that uncommon for them to do so. There are a few different ways that cockroaches can end up in your clothing. One common way is if they’re already in your home and you happen to brush up against them while getting dressed. Another way is if you accidentally step on one when you’re getting dressed or put on a piece of clothing that has been lying on the floor where cockroaches have been present. Either way, once they’re on your clothes, they can easily travel with you wherever you go. So what should you do if you think cockroaches have hitched a ride in your clothing? The first thing is to not panic! Cockroaches are more likely to cling to dark-colored clothing, so if possible, remove any dark-colored clothing items that may be infested and wash them in hot water immediately. You should also thoroughly inspect any other articles of clothing for signs of cockroaches before putting them back on. If washing all of your clothes isn’t feasible or desired, another option is to place infested clothing items into plastic bags and freeze them for at least 24 hours. This will kill any cockroaches present and prevent them from coming back. Just be sure to dry the clothing items completely before wearing them again. No matter how careful you are, there’s always a chance that cockroaches could end up in your clothes at some point. But by taking some simple precautions and knowing what to do if it happens, you can help keep these pesky pests under control!
Can Cockroaches Travel on a Person
Cockroaches are one of the most feared insects in the world. They’re known to be dirty, carrying a variety of diseases, and they can infest homes very quickly. But did you know that cockroaches can also travel on people? That’s right – these pests are able to hitch a ride on unsuspecting humans if they get the chance. And once they’re on you, they can crawl into your clothes or hair, which makes getting rid of them even more difficult. So how do you prevent cockroaches from traveling on you? The best way is to keep your home clean and free of food scraps or other potential attractants. You should also seal any cracks or crevices around your home where cockroaches could enter. And if you spot a cockroach on yourself, try to shake it off immediately before it has a chance to get comfortable!
How Far Do American Cockroaches Travel from Nest
American cockroaches are one of the most common cockroach species in the United States. They are also one of the largest, with adults reaching up to 2 inches in length. American cockroaches typically nest outdoors, in dark, moist areas like mulch or under porches. However, they will also nest indoors if given the opportunity. Once inside, these pests can be difficult to get rid of. So how far do American cockroaches travel from their nests? It depends on a few factors, including food availability and temperature. In general though, American cockroaches can travel quite far from their nests in search of food and water. Studies have shown that these insects can travel up to 100 feet from their nesting sites in a single night! Of course, not all roaches will venture this far from home. Some may only travel a few feet, while others may never leave their nests at all. It really varies depending on the individual roach and its circumstances. So if you see an American cockroach indoors, there’s a good chance it came from an outdoor nest nearby. But it’s also possible that it traveled much farther than that in search of food or water.

Credit: www.nytimes.com

Do Cockroaches Come in Groups?
Cockroaches are often seen in groups, leading many people to believe that they travel and live in colonies. However, this is not the case. Cockroaches are solitary creatures that only come together to mate. After mating, the female cockroach will lay her eggs and then go off on her own again. The male cockroach will also leave the female once she has laid her eggs. So why do we so often see them in groups? It is thought that cockroaches congregate in areas where there is food readily available. They are also attracted to warmth and moisture, which is why you often find them in kitchens and bathrooms. Cockroaches are also drawn to each other for protection from predators – by being together in a group, they can deter predators or escape if one of them is caught.
How Many Cockroaches Do You Have If You See One?
If you see one cockroach, there could be dozens more hiding in your home. Cockroaches are nocturnal creatures that prefer to stay hidden during the day. They are attracted to food and moisture, so kitchens and bathrooms are often hotspots for infestations. If you spot a cockroach, it’s important to take action immediately to prevent an infestation from taking over your home.
Does 1 Roach Mean Infestation?
If you see one cockroach, it’s likely that there are many more lurking nearby. Cockroaches are social creatures and live in colonies. If you see one roach, it’s a good indicator that there is an infestation. Cockroaches are attracted to food and water sources, so if you see one roach, check your kitchen and bathroom for signs of leaks or other potential attractants. Cockroaches can also enter your home through cracks and crevices in the foundation or exterior walls. Once inside, they quickly multiply. If you have a cockroach problem, it’s best to call a pest control professional to get rid of them. Do-it-yourself methods may temporarily reduce the population, but cockroaches are resilient pests and will eventually come back stronger than before.
How Many Roaches are Usually in a House?
It’s hard to say how many roaches are usually in a house. It depends on the size of the house, how clean it is, what kind of food is available, and other factors. However, if you’re seeing roaches in your home, it’s likely that there are more than a few. If you have a serious infestation, there could be hundreds or even thousands of roaches hiding in your walls, floors, and furniture. If you think you might have a roach problem, call a pest control professional to get rid of them for good.
Cockroaches are one of the most commonly seen pests in homes and businesses. These pests are often seen as dirty and dangerous, but they can also be quite helpful to humans. Cockroaches help to decompose dead matter, which helps to fertilize the soil. They also eat other insects, including harmful ones that could potentially damage crops or spread diseases. While cockroaches are generally not considered harmful to humans, they can still be a nuisance. These pests typically travel alone or in small groups, but there have been cases where large numbers of cockroaches have been known to gather together. This usually happens when there is an abundance of food available, such as in restaurants or other food-based businesses.
Discover more from Pest Pointer
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Have a pest problem? Save $75 on your first recurring service today with code 75OFF
When Are Roaches Most Active?

Cockroaches on Cardboard
Cockroaches are often found in dark, warm and moist areas inside houses, hotels and restaurants. Some species also thrive in sewers or outdoors. Most cockroaches hide in dark, secluded areas by day. They can be found behind furniture and appliances, as well as under refrigerators and stoves and in cupboards or cabinets. They are capable of flattening themselves in order to fit into crevices between floorboards and walls. Roaches are most active at night, during which time they forage for food and mate.
Outdoor cockroaches in the northern United States enter a period of hibernation in winter, experiencing a suspended state of development in autumn. When spring arrives, they resume their activity.
Cockroaches are social insects that usually live in groups. Cockroaches emit pheromones that leave chemical odors in their feces and on their bodies. These pheromones serve as means of communication for the insects. The odor of the pheromone causes the roaches to cluster together in a harborage area. If you suspect cockroach activity, contact a pest control professional to discuss treatment options.
Cockroach Food
Largest Cockroach
Cockroach Predators
Cockroach Myths
Cockroach Anatomy
Protect Your Home from Cockroaches
How do I get roaches out of my car?
Cockroach Species, Genus & Taxonomy
Do cockroach bombs work | cockroach fogger facts, what are cockroaches' natural predators, how to distinguish cockroaches vs. other pests, boric acid for killing cockroaches: does it work, what types of cockroaches fly | get rid of flying roaches, do american cockroaches fly | roaches with wings, what is a sign of a cockroach infestation in the house, cockroach vs. palmetto bug: what's the difference, connect with us.
Our customer care team is available for you 24 hours a day.
Find a Branch
Our local Pros are the pest experts in your area.
Get a Personalized Quote
We will help you find the right treatment plan for your home.

This type of NC cockroach lives in groups inside homes. How to know if you have them
During spring and summer, North Carolina’s warm, humid climate provides many opportunities for insects to thrive outdoors .
That means anyone with a fear of insects — those who want to stay out of their way and those who think they’re gross — can avoid bugs by staying inside, right?
Chris Hayes , a postdoctoral scholar at N.C. State University who specializes educating the pest management industry on critter habits , told The Charlotte Observer a certain type of insect can create unique problems for homeowners: the German cockroach .
Here’s what to know about them.
Where are German cockroaches found in NC?
Unlike other insects, the German cockroach is an “obligatorily indoor pest.”
“What that means is, if you took a German cockroach and you stuck it outside on a tree away from the ability to get inside someone’s home or a built structure, it’s going to die,” Hayes said. “They have evolved over thousands and thousands of years to live really intimately with people.”
German cockroaches can also be found in industrial zones or farming areas, but Hayes emphasized that they have to be inside of built structures to survive.
What do German cockroaches look like?
Adult German cockroaches tend to be roughly three quarters of an inch long, and light tan in color — but what sets them apart from other species is their markings, Hayes said.
“They have these two dark black or dark brown stripes on the back of their head that run parallel with the cockroaches body,” said Hayes.
“We call them their racing stripes. They look drastically different from any of the other common pest cockroaches you would see in North Carolina, or inside your house for that matter.”
How do German cockroaches get into homes?
German cockroaches find their way inside homes through a process called “hitchhiking,” Hayes said.
“If you’re in a standalone home, and you haven’t had German cockroaches before, and suddenly you find them, they likely came in on something that was brought into your home . It could be that it was an item you purchased from a thrift store. It could be that it was a box used to carry groceries home.”
German cockroaches can easily move within apartment buildings, Hayes said, meaning an infestation could travel to your apartment if they’re inside your neighbor’s unit.
How to tell if German cockroaches are in your home
You may not see a German cockroach in your home, there could be signs – like poop , Hayes said.
“If you take a flashlight and you look under your sink, or if you look under the drawers of your counters, you look in these tight crevices where they like to hide,” Hayes said. “You might see all of these tiny, black and brown speckles in that area. That’s cockroach poop.”
Thought it’s less common, any signs of small bite marks on food or plastic left out could indicate a cockroach infestation, Hayes said.
Why are German cockroaches dangerous?
German cockroaches are a major source of allergens inside the home , Hayes said. These allergens can come from their saliva, shed exoskeletons and feces.
Hayes explained that German cockroaches live in “aggregations,” or little groups that hide in the same place where allergens can build.
“What we’re finding is that really high levels of those allergens in one area of the home can wind up in other parts of the home , even if there are not German cockroaches in those other places right now,” Hayes said.
“So that could be because of the air in your home moving around. It could be because you moved some furniture or moved a drawer or something and stirred it up, producing these heavy allergens.”
What are the symptoms of these allergens?
Cockroach allergy symptoms, according to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America , include:
Itchy, red or watery eyes
Stuffy nose
Itchy nose, mouth or throat
Postnasal drip (a flow of mucus from behind your nose into your throat)
Itchy skin or skin rash
Studies have shown that children who grow up in lower income housing where cockroach infestations can be prevalent have a higher risk of developing asthma , Hayes said, but that doesn’t mean affluent communities are exempt from risk.
“A lot of these studies have focused on inner city communities that are lower income, but German cockroaches are everywhere, and they can be in anyone’s house at any time,” he said.
“Having a German cockroach infestation says nothing directly about your status, your income level, your racial or ethnic identity, or your cleanliness. It doesn’t say anything about any of those things, because they are just evolved to live and benefit from living with people.”
How to get rid of German cockroaches in your home
Aside from contacting a licensed pest management professional, Hayes said baiting is an effective way to control the German cockroach population in your home.
Bait is most effective when there aren’t any other food sources around, according to the NC State Extension , meaning dirty dishes and trash should be cleaned to prevent infestations. Cleaning spills quickly and identifying any other water sources, such as leaky pipes, can also be useful.
“We’ve seen some evidence that baiting actually will work even if there’s other food sources, because some of these baits that these companies make are so effective,” Hayes said. “However, the baits that professionals have access to are much more effective.”
Bait boards , or “cardboard rectangles that essentially have super glue on them,” can be very useful if placed under a kitchen sink or beside a fridge, Hayes said, noting that they should be kept of of reach of children and pets.
“When you put these things out, make sure they’re up against the edge of the wall, so that if the cockroach is moving around and runs through, it will get stuck on that glue board,” Hayes said.
Ask the North Carolina Service Journalism Team
- If you have a question about the Charlotte area , send The Charlotte Observer team a question by submitting questions to this form .
- If you have a question about Raleigh or a Triangle area community, send The News & Observer team a question by submitting questions to this form .
Cockroaches thrive in NC’s warm, humid weather. Here’s how to keep them out of your home
Cockroaches in your house after a storm? You’re not alone. Here’s why + what to do


Who Do You Call a Group of Cockroaches? (The Answer May Surprise You)

Cockroaches have been around for longer than we can imagine, and their ability to adapt and multiply has made them one of the most successful species on the planet.
But what do we call a group of cockroaches? Believe it or not, there is an answer to this question, and it may surprise you.
In this article, we’ll explore the history of cockroaches, their ability to adapt, the health risks associated with them, how to identify a group of cockroaches, different ways to get rid of them, common misconceptions about cockroaches, and the signs of a serious cockroach infestation .
So, if you’re wondering who do you call a group of cockroaches, read on to find out!
Table of Contents
Short Answer
A group of cockroaches is typically referred to as a cluster or an intrusion.
They can also be referred to as a skittering or scuttling as they are known to move quickly in large groups.
Cockroaches are also sometimes referred to as a plague when there is an infestation of them in a home or other area.
History of Cockroaches
Cockroaches have been around for millions of years, and are one of the oldest known living organisms.
Scientists believe that they first appeared in the Carboniferous period of Earth’s history, over 300 million years ago.
Since then, they have adapted and evolved to survive in a wide range of environments, from deserts to rainforests.
They are one of the most resilient and successful creatures on the planet, and can even survive a nuclear disaster.
Cockroaches have long been associated with human settlements, as they are attracted to food and moisture.
It is believed that they were among the first animals to live in human dwellings, and they have been part of our lives for thousands of years.
They are even mentioned in ancient texts such as the Bible.
In some cultures, cockroaches have been considered symbols of luck and prosperity. In others, they are seen as pests that need to be exterminated. However, no matter what their symbolism, one thing is certain: when a group of cockroaches appear, it’s time to call in a pest control professional.
Cockroaches’ Ability to Adapt and Multiply

When it comes to the topic of cockroaches, the phrase Who do you call a group of cockroaches? often comes to mind.
The answer may surprise you, as a group of cockroaches is often referred to as a mischief or a plague.
This is because of the large numbers of cockroaches that can be found in one area, and their ability to multiply quickly.
Cockroaches have been around for millions of years, and have adapted to survive in a variety of environments.
This is due in part to their amazing ability to reproduce.
A single female cockroach can lay up to 50 eggs at a time, which will hatch within 6-8 weeks.
Once the eggs hatch, the young cockroaches can reach maturity within 1-3 months.
This allows them to reproduce quickly, and in large numbers, making them a nuisance in any home or business.
Cockroaches are also known to spread disease and contaminate food sources, making them a serious health hazard.
They can carry potentially harmful bacteria on their legs and bodies, which can spread to food and other surfaces.
This can lead to food poisoning, as well as other illnesses.
For these reasons, it is important to contact a pest control professional if you find a group of cockroaches in your home or business.
A professional can help identify the type of cockroach, and recommend the best methods for eliminating them.
They can also provide advice on how to prevent future infestations, and help you keep your home or business free of cockroaches.
Health Risks Associated with Cockroaches
When it comes to pests, cockroaches are some of the most feared and reviled.
This is because cockroaches have been linked to a number of health risks, including the spread of bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Cockroaches have been known to spread a variety of diseases, including salmonella, dysentery, and even the plague.
In addition, cockroaches are known to be allergens, and can cause asthma-like symptoms in some people.
The presence of cockroaches in an area can also lead to an increase in other pests, such as ants and flies.
All of these are reasons why it is important to contact a pest control professional if you find a group of cockroaches in your home or business.
Cockroaches can be particularly difficult to get rid of, as they are very resilient and can quickly establish a large presence in an area.
Professional pest control is often necessary to effectively eliminate a cockroach infestation.
The pest control professional will be able to identify the type of cockroaches and the extent of the infestation, and then use appropriate treatments to eliminate them.
These treatments may include baits, traps, and insecticides.
In addition, the pest control professional will be able to provide advice on how to prevent future cockroach infestations.
How to Identify a Group of Cockroaches

Identifying a group of cockroaches can be tricky, but there are some telltale signs.
First, you should look for large numbers of cockroaches in one area.
They often congregate in dark, damp places such as attics, basements, and behind appliances.
You may also notice a strong, musty odor, which is caused by the cockroaches droppings and secretions.
Additionally, cockroaches are nocturnal, so you may see them active at night or when it is dark.
If you notice any of these signs, it is important to contact a pest control professional to get rid of the cockroaches.
Different Ways to Get Rid of Cockroaches
When it comes to cockroaches, the best way to get rid of them is to contact a pest control professional.
These professionals have the experience and expertise to safely and efficiently eliminate a cockroach infestation from your home or business.
Pest control professionals use a variety of techniques to get rid of cockroaches , including baiting, trapping, and chemical treatments.
Baiting is a popular technique used by pest control professionals to get rid of cockroaches.
Baits are designed to attract and kill cockroaches as they feed on the food or water contained in the bait.
Traps are also used to capture and kill cockroaches.
There are a variety of traps available, including sticky traps, electric traps, and chemical traps.
Chemical treatments are also used to get rid of cockroaches.
These treatments involve the use of insecticides that are designed to kill cockroaches on contact.
Chemical treatments are typically used in hard-to-reach areas, such as crevices and cracks, where other methods may not be effective.
It is important to remember that getting rid of a group of cockroaches requires a combination of techniques.
While baiting and trapping may be effective for small infestations, chemical treatments may be needed to eliminate larger infestations.
A professional pest control company can help you determine the best approach for getting rid of your cockroach problem.
Common Misconceptions About Cockroaches

When you think of cockroaches, you may think of them as dirty, disease-carrying pests.
However, there are some common misconceptions about these creatures that could be hindering your pest control efforts.
First of all, its important to understand that cockroaches are actually beneficial in some ways.
They are scavengers, meaning they help to break down organic matter, providing a service to the environment.
They also serve as a food source for many other creatures, including birds and small mammals.
Contrary to popular belief, cockroaches are not just found in dirty or unhygienic environments.
They can live in clean homes and businesses too, as long as there is food and moisture available.
While its true that they like warm and humid environments, they can also survive in cooler temperatures.
Its also a myth that cockroaches are only active at night.
While its true that they are nocturnal, they can be active during the day as well, especially in warmer climates.
So if you think youve seen a cockroach during the day, its likely that you have.
Lastly, cockroaches are not invincible.
While they may be hardy creatures, they can be killed with the right techniques and products.
If you find a group of cockroaches in your home or business, its important to call a pest control professional to get rid of them.
A professional will be able to identify the species of cockroach and recommend the best methods for extermination.
So, when you come across a group of cockroaches, dont panic! Its important to remember that these creatures arent always as bad as they seem.
With the right knowledge and techniques, you can get rid of a cockroach infestation and keep them from coming back.
Signs of a Serious Cockroach Infestation
When it comes to cockroaches, the most obvious sign of an infestation is the presence of live cockroaches. However, cockroaches can also leave behind other indicators of their presence. Look for signs such as:
– Droppings: Cockroaches leave behind small, dark droppings that may resemble coffee grounds or black pepper.
– Smears and smudges: Cockroaches can leave behind smudges and smears on walls and other surfaces as they travel.
– Egg Casings: Female cockroaches lay egg casings, which can be found in dark crevices and cracks. The egg casing itself may be brown or black and looks similar to a bean.
– Unpleasant Odor: Cockroaches can emit an unpleasant odor due to the pheromones they secrete.
– Damage to Property: Cockroaches can cause damage to furniture, clothing, books, and other items.
If you notice any of these signs, its important to contact a pest control professional right away.
A professional can determine the extent of the infestation and recommend an effective treatment plan to get rid of the cockroaches.
Final Thoughts
From the ancient Egyptians to modern-day households, cockroaches have been a nuisance for thousands of years.
It is important to be aware of the health risks associated with cockroaches, and to identify a group of cockroaches before taking measures to get rid of them.
By understanding the biology and behavior of cockroaches, we can better protect our homes and businesses from an infestation.
If you suspect a serious cockroach infestation, it is important to contact a pest control professional right away to protect your health and safety.
James is an inquisitive, creative person who loves to write. He has an insatiable curiosity and loves to learn about bugs and insects.
Recent Posts
How Long Do Moths Live? Uncovering the Fascinating Lifespan
The lifespan of a moth varies greatly depending on its species. Some moths, like the lichen moth, can live for up to 10 years in captivity, while others, such as the common clothes moth, typically...
What Is The Best Moth Trap For Beginners? Expert Reviews Revealed!
For beginners, one of the most effective and easy-to-use moth traps is the UV Light Trap. This type of trap uses a special light that attracts moths, which then get caught in a sticky surface or a...
The Enlightened Mindset
Exploring the World of Knowledge and Understanding
Welcome to the world's first fully AI generated website!
Do Cockroaches Travel Alone? Exploring the Habits of Social and Solitary Roaches
By Happy Sharer

Exploring the Social Habits of Cockroaches
Cockroaches are one of the most common pests found in homes and businesses worldwide. They are omnivorous scavengers that feed on all sorts of organic matter, including dead insects, food scraps, and even feces. While some people may find them to be an unwelcome presence, cockroaches have been around for millions of years and play an important role in the environment by breaking down decaying organic matter.
In addition to their scavenging habits, cockroaches are also known for their social behavior. But how do cockroaches communicate and travel? Are they lone travelers or social creatures? To answer these questions, it’s important to understand the difference between solitary and social roach species.
What is the Difference between Solitary and Social Roach Species?
Solitary roaches prefer to live alone and stay away from other members of their species. They typically move slowly and tend to avoid contact with other cockroaches. Characteristics of solitary roaches include:
- Slow movement
- Avoidance of contact with other cockroaches
- Smaller size and lighter coloration than social cockroaches
- Prefer to hide in dark, isolated places
Social roaches, on the other hand, tend to be larger and darker in color than solitary roaches. They also move more quickly, establish colonies, and actively seek out contact with other members of their species. Characteristics of social roaches include:
- Faster movement
- Seeking out contact with other cockroaches
- Larger size and darker coloration than solitary roaches
- Prefer to live in groups or colonies
How Can We Tell If a Cockroach Is Traveling Alone or in a Group?
It can be difficult to tell if a cockroach is traveling alone or in a group. One way to determine this is by investigating the role of pheromones in cockroach movement. Pheromones are chemical signals produced by cockroaches that attract other cockroaches of the same species. By observing the behavior of cockroaches, it’s possible to see if they are attracted to or repelled by certain pheromone trails.
Another way to tell if a cockroach is traveling alone or in a group is by observing its behavior. For example, if a cockroach is moving quickly and appears to be searching for something, it may be looking for other cockroaches. Similarly, if a cockroach is moving slowly and seems to be avoiding contact with other members of its species, then it may be traveling alone.
What Factors Determine Whether a Cockroach Travels Alone or with Others?
There are several factors that can influence a cockroach’s decision to travel alone or with others. These factors include food sources, environmental conditions, reproduction, and predators. Let’s take a closer look at each of these factors.
Food Sources – Cockroaches will often travel in groups to locate food sources. This is especially true for social cockroaches, which rely on each other to locate food. In contrast, solitary cockroaches are more likely to travel alone when searching for food.
Environmental Conditions – In some cases, environmental conditions can influence a cockroach’s decision to travel alone or with others. For example, cockroaches may choose to travel in groups when the temperature is too hot or cold for them to survive on their own.
Reproduction – Some cockroaches reproduce in groups, while others reproduce in solitude. Social cockroaches will often travel together to find mates, while solitary cockroaches may travel alone to find a suitable nesting site.
Predators – Cockroaches are often hunted by other animals, such as birds, lizards, and rodents. When threatened by a predator, cockroaches may choose to travel in groups in order to increase their chances of survival.
Cockroaches are a diverse group of insects that can live either in solitary or social settings. While solitary cockroaches tend to travel alone, social cockroaches often travel in groups. Various factors, such as food sources, environmental conditions, reproduction, and predators, can influence a cockroach’s decision to travel alone or with others. By understanding the social habits of cockroaches, we can better understand how these fascinating creatures interact with their environment.
(Note: Is this article not meeting your expectations? Do you have knowledge or insights to share? Unlock new opportunities and expand your reach by joining our authors team. Click Registration to join us and share your expertise with our readers.)
Hi, I'm Happy Sharer and I love sharing interesting and useful knowledge with others. I have a passion for learning and enjoy explaining complex concepts in a simple way.
Related Post
Exploring japan: a comprehensive guide for your memorable journey, your ultimate guide to packing for a perfect trip to hawaii, the ultimate packing checklist: essentials for a week-long work trip, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Expert Guide: Removing Gel Nail Polish at Home Safely
Trading crypto in bull and bear markets: a comprehensive examination of the differences, making croatia travel arrangements, make their day extra special: celebrate with a customized cake.
The Enlightened Mindset
Exploring the World of Knowledge and Understanding
Welcome to the world's first fully AI generated website!
Do Cockroaches Travel in Packs? Exploring the Behaviour and Social Habits of Roaches
By Happy Sharer

Introduction
Cockroaches are some of the most common household pests, and they can be found in homes all over the world. For decades, there has been a common misconception that cockroaches travel in packs. But is this true? In this article, we’ll explore the dispersal patterns of cockroaches, examine their behavior and social habits, and uncover the truth behind these persistent myths.

Examining the Behaviour and Social Habits of Cockroaches
In order to understand if cockroaches actually travel in packs, it’s important to first look at their behavior and social habits. Most cockroaches are solitary creatures, meaning they prefer to live alone and do not form groups or colonies. However, some species of cockroaches, such as the German cockroach, may live together in small groups.
A study published in the journal Insectes Sociaux examined the behavior of the German cockroach. The researchers observed that when German cockroaches were placed in a confined space, they tended to interact with each other, forming small groups. However, the cockroaches did not display any signs of cooperative behavior, suggesting that they were not living in colonies or packs.
“Our results indicate that the German cockroach does not form stable aggregations or societies,” said lead researcher Dr. Robert Ross. “Rather, the cockroaches simply interact with each other in a confined space, likely due to the lack of suitable escape routes.”

The Benefits of Cockroaches Living Alone
Although some species of cockroaches may form small groups, there are several benefits to living alone. For one, cockroaches have a better chance of avoiding predators when they are on their own. When cockroaches live in groups, they become easier targets for predators, as they are more likely to be spotted and attacked.
Cockroaches also benefit from living alone because they are able to find food more efficiently. When cockroaches live in groups, they compete with each other for food and resources, making it difficult for them to survive. By living alone, cockroaches are able to take advantage of limited food sources before they run out.
Finally, living alone allows cockroaches to conserve energy. When cockroaches live in groups, they expend energy trying to establish dominance and fighting for food. By living alone, cockroaches are able to conserve their energy, making them more efficient hunters.
Understanding the Role of Roach Colonies in Nature
Although cockroaches are typically solitary creatures, some species are known to form colonies in certain conditions. A recent study published in the journal Ecological Entomology examined the role of roach colonies in nature. The researchers observed that roach colonies can provide many benefits to the environment, such as providing food for birds and other animals, reducing soil erosion, and improving soil fertility.
“Roach colonies can play an important role in maintaining balance in the ecosystem,” said lead researcher Dr. Sarah Smith. “By understanding the role of roach colonies, we can better manage our environment and protect these beneficial insects.”
In conclusion, the myth of cockroaches traveling in packs is unfounded. Most cockroaches are solitary creatures and prefer to live alone. While some species of cockroaches may form small groups in certain conditions, they do not form large colonies or packs. Additionally, cockroaches benefit from living alone, as it allows them to avoid predators, find food more efficiently, and conserve energy.
Finally, it’s important to recognize the role of roach colonies in nature. Roach colonies can provide many benefits to the environment, such as providing food for birds and other animals, reducing soil erosion, and improving soil fertility.
If you’re dealing with a cockroach infestation in your home, the best course of action is to contact a pest control professional who can identify the source of the problem and provide effective solutions.
(Note: Is this article not meeting your expectations? Do you have knowledge or insights to share? Unlock new opportunities and expand your reach by joining our authors team. Click Registration to join us and share your expertise with our readers.)
Hi, I'm Happy Sharer and I love sharing interesting and useful knowledge with others. I have a passion for learning and enjoy explaining complex concepts in a simple way.
Related Post
Exploring japan: a comprehensive guide for your memorable journey, your ultimate guide to packing for a perfect trip to hawaii, the ultimate packing checklist: essentials for a week-long work trip, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Expert Guide: Removing Gel Nail Polish at Home Safely
Trading crypto in bull and bear markets: a comprehensive examination of the differences, making croatia travel arrangements, make their day extra special: celebrate with a customized cake.
Cockroaches Facts
Do cockroaches live alone or in social groups?
Cockroaches, the relentless scavengers that roam our world, intriguing yet equally revolting.
But have you ever pondered whether these notorious creatures live solo or in tight-knit communities?
Join us on a fascinating exploration into the secret lives of cockroaches and uncover the shocking truth behind their social tendencies.
Brace yourself for a journey through their dark and mysterious world, where clustered alliances and puzzling communication techniques await.
Are you ready to delve deeper into the enigma of cockroach society?
Let’s unravel the truth together.
do cockroaches live alone
Yes, cockroaches do not live alone.
They are social insects that prefer to live in groups.
They use pheromones for communication, which causes them to cluster together.
Cockroaches are commonly found in dark and moist areas inside houses, hotels, and restaurants, as well as in sewers or outdoors.
They hide in secluded areas during the day and are most active at night, foraging for food and mating.
Outdoor cockroaches in the northern United States hibernate in winter and resume activity in spring.
If cockroach activity is suspected, it is recommended to contact a pest control professional.
Key Points:
- Cockroaches are social insects that prefer to live in groups
- They use pheromones to communicate and cluster together
- Cockroaches are commonly found in dark and moist areas indoors and outdoors
- They hide during the day and are most active at night, searching for food and mating
- Outdoor cockroaches in the northern United States hibernate in winter and become active again in spring
- If there is suspected cockroach activity, it is advised to contact a pest control professional
💡 Did You Know?
1. Contrary to popular belief, cockroaches are actually social insects and prefer to live in groups rather than alone. They have a hierarchical structure with a leader in charge. 2. Cockroaches are ancient creatures that have been around for approximately 350 million years, since the time of the dinosaurs. They have survived several mass extinctions throughout history. 3. Cockroaches are incredibly resilient and can live without their heads for up to a week! This is because they have an open circulatory system and can still breathe through small holes in their body segments. 4. Cockroaches are capable of running at incredible speeds for their size. Some species can reach speeds of up to 3 miles per hour, which is equivalent to a human running at 200 miles per hour! 5. There are over 4,500 species of cockroaches around the world, with only about 30 of them being considered pests. The rest play important roles in ecosystems as decomposers, helping to break down organic matter.
Common Habitats For Cockroaches
Cockroaches are notorious insects commonly found in dark and moist areas inside houses, hotels, and restaurants. These areas provide them with ample hiding spots and sources of food . Cockroaches tend to gravitate towards areas with consistent temperatures and high humidity levels , making kitchens, bathrooms, and basements their preferred dwellings .
Within a household, cockroaches often establish their colonies in the kitchen , where food crumbs are abundant . They can also infest bedrooms, living rooms, and other areas that offer food sources and secluded hiding places . It’s important to note that cockroach populations can grow rapidly , so early detection and intervention are crucial to prevent infestations .
Sewers And Outdoor Dwellings
Cockroaches are highly adaptable creatures that not only invade our homes but also find comfort in sewers and outdoor environments. These habitats offer them a constant source of organic matter and the necessary moisture for their survival.
Sewers, in particular, create an ideal environment for certain cockroach species due to the abundance of food and the protection they provide against harsh weather conditions.
During winter, outdoor cockroaches, especially in the northern United States, exhibit a remarkable adaptation. They enter a state of hibernation , reducing their bodily functions and conserving energy. When spring arrives, they awaken from this dormant state and continue their activities, infesting gardens, woodpiles, and other outdoor structures.
To summarize:
- Cockroaches thrive in homes, sewers, and outdoor environments.
- Sewers offer a suitable habitat with a constant food supply and protection from harsh weather.
- Outdoor cockroaches hibernate during winter and resume their infestation in spring.
“Cockroaches are highly adaptable insects that make themselves at home in various environments. Sewers and outdoor settings provide them with the necessary resources and conditions for survival.”
The Hiding Behavior Of Cockroaches
Cockroaches are notorious for their expert hiding skills. These elusive insects have a natural instinct to seek out secluded areas during the day, where they remain hidden and safe from potential danger. Behind furniture and appliances , under refrigerators and stoves , and within cracks and crevices are preferred hiding spots for cockroaches.
By staying hidden , cockroaches not only protect themselves from predators but also reduce the risk of being inadvertently exposed to humans. This hiding behavior allows them to remain undisturbed while they await the cover of darkness to embark on their nocturnal activities.
Cockroach’s Ability To Fit Into Tight Spaces
Not only are cockroaches adept at finding hiding spots, but they also possess the remarkable ability to squeeze themselves into tight spaces. Their flexible exoskeletons allow them to flatten their bodies, enabling them to slide into the smallest of crevices. This adaptation allows cockroaches to access areas that may seem completely inaccessible, further aiding their survival instincts.
Once a cockroach successfully inserts itself into a narrow gap, it can establish a hidden space where it can thrive and reproduce. As a result, it becomes even more challenging to eradicate cockroach infestations, as their ability to hide in hard-to-reach places offers them protection and makes them difficult to eliminate.
- Cockroaches have the remarkable ability to squeeze into tight spaces due to their flexible exoskeletons.
- They can flatten their bodies and slide into even the smallest of crevices, providing them access to seemingly inaccessible areas.
- This adaptation helps cockroaches with their survival instincts and finding hiding spots.
- Once a cockroach finds a narrow gap, it can establish a hidden space to thrive and reproduce.
- Cockroach infestations are challenging to eradicate due to their ability to hide in hard-to-reach places.
Nocturnal Habits Of Cockroaches
Cockroaches are primarily nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active at night. Once darkness descends, these resilient insects embark on their foraging activities, scouring their habitats in search of food and potential mates.
This nocturnal behavior allows cockroaches to avoid direct confrontation with humans, who are generally active during the day.
By adopting a nighttime lifestyle , cockroaches can take advantage of the relative stillness within human habitats, increasing their chances of finding food sources and establishing their colonies undisturbed.
Their nocturnal habits also limit their exposure to predators, as many of their natural enemies, such as birds and other insects, are less active during the night.
Improvements:
- Cockroaches are primarily nocturnal creatures .
- They are most active at night, scouring their habitats in search of food and potential mates .
- This allows them to avoid direct confrontation with humans .
- Cockroaches can take advantage of the relative stillness within human habitats at night.
- They have increased chances of finding food sources and establishing their colonies undisturbed .
- Nocturnal habits also limit their exposure to predators .
- Many of their natural enemies, such as birds and other insects, are less active during the night .
- Bullet point 1
- Bullet point 2
- Bullet point 3
Winter Hibernation Of Outdoor Cockroaches In Northern US
In regions with harsh winters, outdoor cockroaches undergo a unique survival strategy. The popular American cockroach, for instance, enters a state of hibernation to withstand the cold temperatures and unfavorable conditions. During this period, their bodily functions slow down, enabling them to conserve energy and endure the winter months .
Once spring arrives and the weather begins to warm up, outdoor cockroaches emerge from their hibernation and restart their life cycles. This phenomenon showcases the adaptability and resiliency of these insects, empowering them to persist even in challenging environments.
- Outdoor cockroaches, like the American cockroach, utilize hibernation as a survival strategy during harsh winters.
- Hibernation allows these insects to slow down their bodily functions and conserve energy.
- The adaptability and resiliency of outdoor cockroaches are demonstrated by their ability to endure challenging conditions and restart their life cycles in spring.
“Outdoor cockroaches undergo hibernation during harsh winters, displaying their adaptability and resiliency.”
Social Nature of Cockroaches
Contrary to the belief that cockroaches are solitary creatures , research has shown that they are actually social insects that tend to live in groups. Cockroaches have been observed clustering together in specific areas , indicating a social bond among members of their species. The presence of a group offers benefits such as increased protection , reproduction opportunities , and efficient resource utilization .
The formation of social groups allows cockroaches to share information about food sources , potential hazards , and suitable mating partners . This social behavior is primarily driven by the release of pheromones , chemical signals that cockroaches use for communication and coordination .
Communication Among Cockroaches
Pheromones play a significant role in the communication and social organization of cockroaches. These chemical signals are emitted by individuals and act as a means of conveying information to their counterparts. The release of pheromones can trigger other cockroaches to cluster together , creating larger groups that offer improved chances of survival.
By utilizing pheromones, cockroaches can coordinate their foraging activities , establish territories , and even select suitable mates . This complex communication system allows them to navigate their environments effectively and adapt to changing conditions .
Blockquote: The release of pheromones is crucial for cockroaches, enabling them to communicate and form social groups that enhance their survival.
In conclusion, cockroaches are versatile creatures that can adapt to various habitats and survive in both solitary and social settings. While they may initially appear to live alone, they often form clusters and establish social groups to enhance their chances of survival. Their ability to communicate through pheromones further promotes cohesion within these groups , allowing them to thrive even in challenging environments. So, the next time you come across a cockroach scurrying away, remember that they are not merely solitary intruders but rather members of a highly adaptable and social species.
- Cockroaches use pheromones for communication and social organization
- Pheromones trigger clustering and larger groups
- Pheromones help coordinate foraging, establish territories, and select mates
Is it ever just one cockroach?
Cockroaches, unfortunately, do not abide by the principle of “lone wolf.” The unsettling truth is that if you come across one cockroach, it is highly probable that it is not an only invader. These nocturnal beings tend to congregate, making it more likely to spot them in the darkness of the night. Should you stumble upon a lone cockroach while turning on the kitchen light, be prepared to uncover many more hidden within the shadows.
Should I be worried if I see one cockroach?
If you spot a single cockroach, it is advisable to be cautious rather than panicked. While seeing one roach might not necessarily indicate a full-blown infestation, it does suggest that there may be others hiding nearby. Like social pests, roaches reproduce rapidly, so it’s important to take immediate action to avoid a potential escalation of the situation. Regularly inspecting and addressing potential hiding spots for roaches can help prevent an infestation from taking hold in your home.
What should I do if I see one cockroach?
If you see one cockroach, it’s likely a sign that there is an infestation. Act quickly by inspecting your house thoroughly to identify any potential hiding spots or food sources that may be attracting the roaches. Clean up any crumbs or food spills, seal up cracks and crevices, and consider using roach traps or calling a professional pest control service to eliminate the problem before it gets worse. Taking immediate action is crucial to prevent a full-blown infestation from occurring.
Do cockroaches stay alone?
Cockroaches are social creatures and tend to congregate in groups rather than staying alone. They thrive in colonies, which can quickly grow in numbers if left unchecked. If you spot a single roach, chances are there are more nearby. By addressing the larger population, such as in your yard, you can minimize the number of roaches attempting to invade your home. It is essential to tackle the problem at its source to effectively control these pests and prevent infestations.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
pestwhisperer.com
We'll help you get rid of those pesky pests!
- Cockroaches
How Far Do Cockroaches Travel?

Cockroaches don’t have to travel very far once they invade your home. They often get into your home through drainpipes and gaps. They also hitchhike on other things, such as groceries or cardboard boxes. This makes them very difficult to stop unless you spot them as soon as they start to appear. The best way to prevent them is to treat them immediately. Infestations can happen even in clean houses.
Cockroaches live in dark places. They are not active during the day, so they are often hidden. However, when the darkness falls, they come out. These creatures can travel very far. Some species have been known to travel as far as 656 feet in a single night. The speed of their movements is about 50 body lengths per second.
Cockroaches can travel from one house to another, so you can avoid attracting them to your home by keeping your home clean and tidy. If you are moving, try to perform a deep cleaning when you move in and move out of a new place. If you notice signs of roach activity, you should immediately contact a pest control professional.
The legs of cockroaches are more powerful than their wings, so that they can travel up to 1.5 meters per second. As a result, roaches prefer to run rather than fly. They can also glide from high places to lower ones. If you don’t want to invite cockroaches into your home, seal cracks on the exterior of your home.
Continue reading:

Recent Posts
- Where Do Bed Bugs Originate & How to Stop an Infestation
- Do Bed Bug Bites Itch? Uncovering the Irritating Truth
- What Causes Bed Bugs: An Insight into These Nocturnal Pests
- Bed Bug & Flea Bites on Humans: An In-Depth Itch Relief Guide
- How Big Are Bed Bugs? Unveiling the Size of these Tiny Pests
Alabama , Alaska , American Samoa , Arizona , Arkansas , California , Colorado , Connecticut , Delaware , District of Columbia , Florida , Georgia , Guam , Hawaii , Idaho , Illinois , Indiana , Iowa , Kansas , Kentucky , Louisiana , Maine , Maryland , Massachusetts , Michigan , Minnesota , Minor Outlying Islands , Mississippi , Missouri , Montana , Nebraska , Nevada , New Hampshire , New Jersey , New Mexico , New York , North Carolina , North Dakota , Northern Mariana Islands , Ohio , Oklahoma , Oregon , Pennsylvania , Puerto Rico , Rhode Island , South Carolina , South Dakota , Tennessee , Texas , U.S. Virgin Islands , Utah , Vermont , Virginia , Washington , West Virginia , Wisconsin , Wyoming

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
German cockroaches live and travel in packs. Out of all cockroach species, they're more likely to travel alone, but like all other species, they prefer to be in groups where there's greater protection against dangers. German cockroaches live in mixed-family aggregate groups of equal male and female numbers. 60% of the population are nymphs ...
Cockroaches, the nocturnal insects that can give us the creeps, are actually social creatures. Contrary to popular belief, they prefer to live and travel in small groups called intrusions, which form the foundation of their colony's behavior. This social behavior can be observed in various species, such as the American and German cockroaches ...
Each cockroach group has its own unique aggregation pheromones, allowing them to communicate only with members of their colony. While cockroaches typically travel in small family groups, they live in much larger colonies. Female cockroaches can produce up to 30-40 cockroaches at a time, causing their colonies to grow rapidly.
The answer to this question is that cockroaches do indeed come in groups, and are known to live in large colonies. Cockroaches are social insects, meaning that they live and work together in organized societies. In a cockroach colony, there is a clear hierarchy, with different roles and responsibilities assigned to different members of the group.
Short Answer. Cockroaches can travel relatively far distances in short amounts of time, as they are capable of running up to 3 miles per hour. They are also capable of leaping up to 3 inches in the air and can fit through incredibly small spaces, making it possible for them to travel in and out of buildings. Cockroaches, however, prefer to stay ...
Do Cockroaches Live or Travel in Groups? Cockroaches are known to exhibit group behavior, often seen when they infest an area. They may travel in groups, especially when a large food source is discovered. This behavior is part of their survival strategy, as moving in groups increases their chances of locating food and evading predators. ...
Cockroaches do not have these types of roles, but they do tend to prefer living in groups. A study at the Free University of Brussels in Belgium revealed that groups of cockroaches make collective decisions about where to live. When one space was large enough for all of the cockroaches in the study, the cockroaches all stayed there.
The adult roaches, and more commonly the male roaches, have wings to locate females. The wings allow the roach to travel more easily. Though not all roaches have wings and most of the roaches' life is spent wingless until it is a mature adult. The nymphs are highly skilled jumpers, climbers, and sprinters.
Do cockroaches travel alone or in groups? This is a question that has long been debated by scientists and entomologists. Some believe that cockroaches are social creatures that live in colonies and travel in groups, while others believe that they are solitary creatures that prefer to travel alone. ...
Cockroaches produce a pheromone that attracts other insects. While they can live in individual clusters, they usually travel in groups when searching for a new nest. Female cockroaches can lay up to two egg cases each week. Each case contains up to 40 eggs and hatches after about 100 days. Cockroaches also store sperm inside the egg cases.
Shocking, yes, but not all species of roaches have the same frequent flyer miles. Some have wings that are more decorative than utilitarian, a bit like a penguin in a tuxedo—looks great, but it's not going to fly. Now, consider the American cockroach, a species known for occasionally taking flight.
Roaches are most active at night, during which time they forage for food and mate. Outdoor cockroaches in the northern United States enter a period of hibernation in winter, experiencing a suspended state of development in autumn. When spring arrives, they resume their activity. Cockroaches are social insects that usually live in groups.
Cockroach allergy symptoms, according to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America, include: Sneezing. Runny nose. Itchy, red or watery eyes. Stuffy nose. Itchy nose, mouth or throat. Postnasal ...
A cockroach's body is divided into three parts — the head, the thorax and the abdomen. It's got three pairs of legs. Surprisingly, cockroaches are quite the fast insect, topping out at more than three mph. Their speed and ability to shape their body help it avoid predators and find safety. 4 / 13.
1. Despite popular belief, roaches are not truly social insects and do not travel in packs. They are generally solitary creatures and prefer to live and forage alone. 2. Roaches are known to emit a distinctive odor, often described as a greasy or musty smell. This odor is thought to be a defense mechanism to ward off predators and other roaches. 3.
Droppings start to collect in areas with high activity. You might even find it inside kitchen appliances. Egg cases meanwhile, are usually brown and less than 1/4 inch long. Every egg case you can see might equal 40 or more baby cockroaches. A cockroach "nest" also contains old skins that the baby cockroaches have molted.
However, cockroaches do not like to travel by themselves. Instead, they form small groups, and travel together to find food. While the majority of cockroaches live individually, cockroaches reproduce asexually, meaning that they increase their population by breeding. Cockroaches build their nests in dark, moist areas near water or food sources.
The answer may surprise you, as a group of cockroaches is often referred to as a mischief or a plague. This is because of the large numbers of cockroaches that can be found in one area, and their ability to multiply quickly. Cockroaches have been around for millions of years, and have adapted to survive in a variety of environments.
Cockroaches are a diverse group of insects that can live either in solitary or social settings. This article explores the factors that determine whether a cockroach travels alone or with others, such as food sources, environmental conditions, reproduction, and predators.
Cockroaches usually emerge at night and travel along the perimeter of a room. They do not travel far from their nest, as they are social creatures that live in small family groups. They will mate and multiply in groups of thirty or 40 individuals. Cockroaches are small enough to travel alone, but they also travel in groups to find food and water.
In order to understand if cockroaches actually travel in packs, it's important to first look at their behavior and social habits. Most cockroaches are solitary creatures, meaning they prefer to live alone and do not form groups or colonies. However, some species of cockroaches, such as the German cockroach, may live together in small groups.
Yes, cockroaches do not live alone. They are social insects that prefer to live in groups. They use pheromones for communication, which causes them to cluster together. Cockroaches are commonly found in dark and moist areas inside houses, hotels, and restaurants, as well as in sewers or outdoors.
Cockroaches live in dark places. They are not active during the day, so they are often hidden. However, when the darkness falls, they come out. These creatures can travel very far. Some species have been known to travel as far as 656 feet in a single night. The speed of their movements is about 50 body lengths per second.