- Help Center

What do B2B Customer Journeys Look Like in 2024?
We walk through how B2B businesses should approach constructing the ideal customer journey in 2024.
What is a B2B customer journey?
A B2B customer journey refers to all the interactions that take place between a business and a customer as the latter moves through the funnel. But in a B2B context, the customer in question is usually acting on behalf of their organization (e.g., a team of stakeholders looking to bring in a new email automation tool into their MarTech stack) .
As a result, B2B customer journeys are usually much longer than business-to-customer (B2C) interactions – sometimes culminating in months-long exchanges that require input from multiple decision-makers.
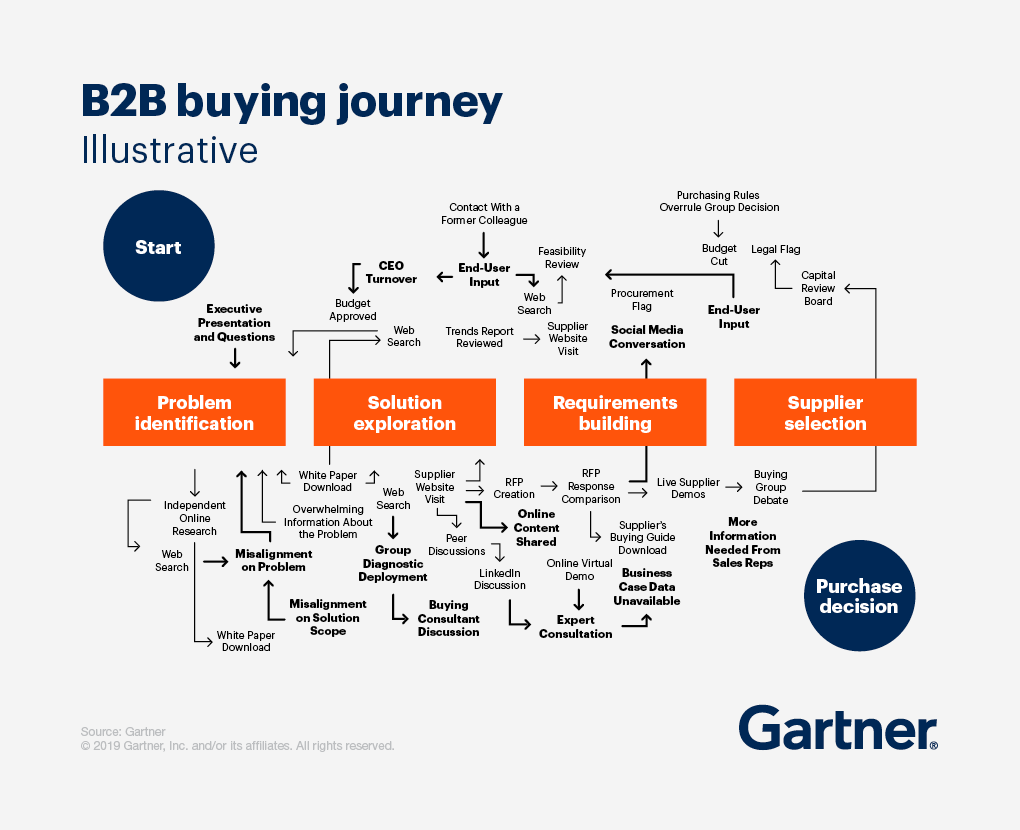
The 5 stages of the B2B customer journey
The customer journey describes all the interactions that take place between a customer and a business. It starts before a customer discovers your product and continues beyond the point of sale.
While they’re are key distinctions, both (B2B) and (B2C) customer journeys share the same five basic stages:
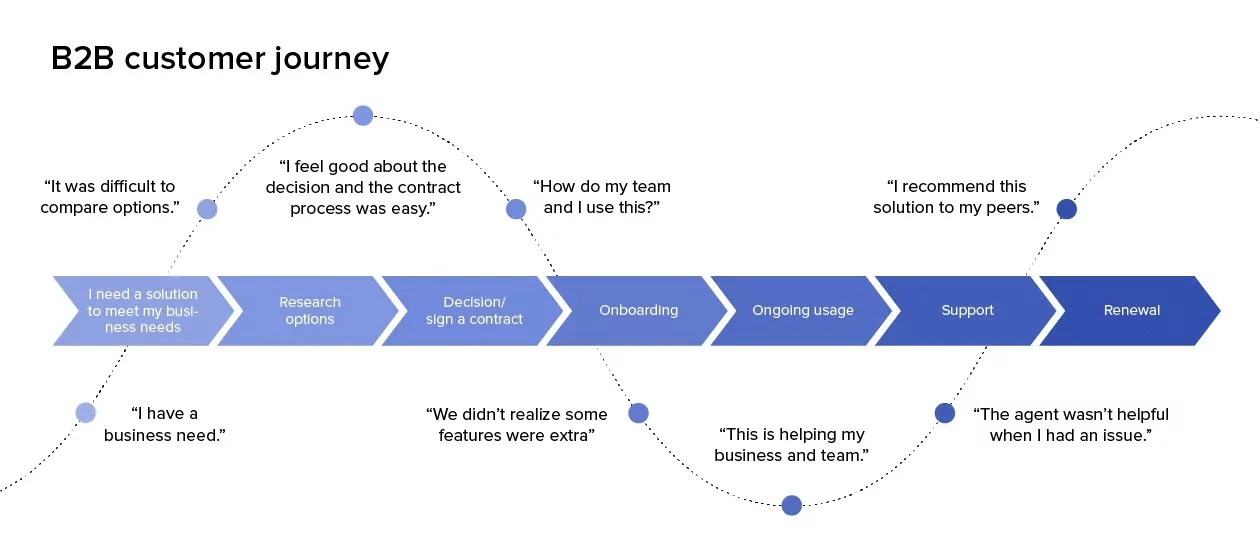
This is when a customer becomes aware of a specific pain point or need they have, and starts searching for a solution. From a business perspective, this is where having a sharp understanding of your audience and target personas comes into play. When driving brand awareness, you’ll often cater your messaging to speak to each individual and relevant persona. For instance, if you’re marketing a live chat tool, when advertising to a potential end user you’d likely showcase specific features and its ease of use. But when promoting it to someone in upper management, you may focus on the ROI their business stands to gain.
One way to capture your target audience’s attention is to run ads based on lookalike audiences – here’s how .
Consideration
The consideration stage is when a prospect discovers your product or service as a potential solution to their problem. This can look like: browsing relevant product pages on your site, requesting a demo, speaking with live chat bot – a sort of fact-finding mission to understand how your product stacks up to their expectations (and why it’s better than your competitors). As we said earlier, in a B2B setting this process can take a long time due to the multiple stakeholders involved in making a decision.
The conversion is the point when the customer makes a decision to commit to your brand, perhaps by signing up for an account or committing to a premium subscription (whatever your ultimate conversion goal happens to be).
Conversion is not the end of the road, though. Once a customer starts using your product or service, a new facet of the customer journey begins: one that’s concerned with helping them reach time-to-value as quickly as possible and preventing churn. This is where personalized onboarding flows can come into play, and when onboarding journey maps can be especially useful to have a solid idea of what milestones your customers should be hitting and when.
5 Tried-and-True Onboarding Campaigns + Templates
This step-by-step guide describes how to implement 5 user onboarding campaigns to drive long-term loyalty.
We use your information according to our Privacy Policy . You can update your preferences at any time.
You’re all set!
Thank you for downloading this content. We've also sent a copy to your inbox.
For example, at Twilio Segment we know that setting up a Source and Destination, and having data flow between these two points, is a crucial step for users to recognize product value. By analyzing the behavior of both retained and churned customers, we were able to pinpoint when, approximately, a customer should have completed this step – and proactively intervene if they seemed to be struggling.
You can learn more about how we used data to streamline onboarding here .
An overarching goal is to have your customers become staunch supporters of your product – not only so they remain customers, but so that they also become brand advocates.
Referrals are an incredibly powerful and cost-effective way to acquire new customers. And with the right data, you can pinpoint the most strategic time to ask customers to give a referral and even automate your referral program.
B2B vs. B2C customer journey mapping
Customer journey maps are “documents that visually illustrate customers’ processes, needs, and perceptions throughout their relationships with a company,” according to Forrester Research . They identify interactions and touchpoints at every stage of the customer lifecycle.
You create these maps to understand how customers view the experience of doing business with your company – meaning you take their perspective. That’s why Forrester also calls these documents “moment of truth” maps.
There are some differences between B2B and B2C journey mapping, however, mainly: the number of touchpoints, and the number of decision-makers and stakeholders involved.
Touchpoints
Customer journey touchpoints take place before, during, and after a sale. As B2B sales cycles tend to be longer than B2C ones, B2B customer journey maps have more touchpoints in the awareness and consideration stages.
Certain touchpoints are particularly important in B2B relationships – think reading case studies and customer testimonials, viewing product demos, comparing prices and product features, going through week 1 onboarding, and evaluating a plan upgrade.
Decision-makers
With B2B marketing, you have to convince multiple stakeholders of your product’s value since the end-user may not be the same person with the purchasing power. You need to understand these individual personas, and engage them on the channels they prefer .
By contrast, in B2C marketing, the consumer and end-user are usually one and the same person. (Family products tend to be an exception – for example, you’d market baby products to parents, not the babies themselves.)
How B2B customer journeys are evolving in 2024
B2B customer journeys are becoming more complex, as more business users now expect a customer experience similar to that of B2C brands. This demand is largely driven by millennials, who are now the primary B2B decision-makers, according to research by The B2B Institute and LinkedIn .
Being digital natives, millennials are used to cloud-based software and collaboration tools, and the experience of using these services has shaped their expectations of B2B products and solutions. For instance, they demand self-service sales transactions – choose a plan, pay for it, set up an account, and go. Gartner found that 44% of millennials don’t want to interact with a sales rep when it comes to making B2B purchases.
The report notes that millennials “are being met with a wave of new digital products, brand concepts, AI-powered plug-ins and productivity tools that are more akin to the consumer user experience of Uber and Airbnb than traditional business services.” To deliver similar experiences, B2B brands like Basecamp, Stripe, and Slack have mimicked popular lifestyle apps with their high-gloss marketing campaigns, aesthetics, and emphasis on UX.
The post-sale experience is changing, too. With the rise of “everything-as-a-service” models like SaaS, businesses need to convince customers to renew their subscriptions either monthly or annually. It’s now crucial to repeatedly engage customers at the service and loyalty stages through customer retention and engagement strategies.
3 challenges of B2B customer journey mapping
Plotting out the B2B customer journey is a crucial step in empathizing with your prospects (and hopefully streamlining the path to conversion). However, B2B customer journey mapping is not without its challenges. As we mentioned above, these interactions can be complex, lengthy, and span numerous touchpoints. The point being: there is rarely a linear path between awareness, conversion, and retention when it comes to B2B customer journeys.
Below, we talk about these challenges (and how to overcome them) in more detail.
Identifying & prioritizing potential customer touchpoints
For a long time, marketers have turned to third-party cookies to help them with ad attribution and retargeting prospects. But in the past few years, data privacy regulations and browser-led changes on iOS, Safari, Firefox, and Chrome have been leading to one thing: the end of third-party cookies .
However, many companies haven’t completely broken up with third-party cookies yet – meaning they may be ill-equipped to understand the customer journey in its entirety if they don’t implement a new strategy.
So, what’s the way forward? In short, a prioritization of first-party data . This type of data, which businesses gather from direct interactions with their customers, is compliant and serves as a competitive differentiator (that is, no other business has access to those insights). But for first-party data to be effective, it has to be consolidated – or in other words, there shouldn’t be any blindspots between teams when it comes to customer interactions.
Integrating the customer experience across touchpoints
One goal of customer journey mapping is to create a consistent experience across channels and touchpoints. But as the number and variety of those touchpoints grow, integrating tools can be complicated.
For instance, different tools might use different naming conventions for data collection . You’d have to standardize these names if you want to unify data from multiple sources. To create this unified view, there are a couple steps you need to take:
Create a universal tracking plan for your business that clarifies the proper naming conventions for data, what’s being tracked (and why), and where that data originates from and ends up.
Ensure this data is consolidated into a central repository and that data is democratized across teams (e.g, marketing teams don’t need to depend on analysts or engineering to pull audience lists – they can do it themselves, in real time).
Preventing data silos & ensuring all teams can access customer data
The lack of integration between tools results in data silos and missed opportunities to engage customers. Let’s say sales has given a product demo to a specific prospect. If marketing doesn’t know that, they might email the prospect an invitation to try a demo. As a result, you waste the customer’s time (and your own), along with inviting their annoyance.
How Segment can supercharge your B2B customer journeys
What are the hallmarks of an effective B2B customer journey? As we’ve explored in this article, there are a few healthy indicators: an emphasis on first-party data, a democratization of data across teams, unified, real-time customer profiles .
With consumers gravitating to multi-channel interactions, it’s become imperative for businesses to fix any blindspots that may crop up in their strategy. Effective marketing and top-tier customer experiences are now built on data, and having a scalable infrastructure in place is fundamental.
Enter, the customer data platform. CDPs have emerged as a must for businesses, helping to collect, clean and consolidate data in real time and integrate every tool and app in their tech stack. Here’s how a CDP like Segment can supercharge B2B customer journeys.
Centralize & consolidate your data
Segment’s CDP can consolidate data from every customer touchpoint , ensure it’s cleaned and validated, and then send it to any downstream destination (like email, advertising, customer service, or product development software) for activation.
A common challenge for businesses is being able to consolidate and trust the data they collect to glean insights. Too often, data silos pop up due to disconnected tech stacks, resulting in blind spots across teams. This can wreak havoc on the customer experience and business operations.
Say a customer has an issue and tries to resolve it via live chat – providing details about their account, the problem at hand, and so forth. They end up being transferred to a phone call with a representative…and have to repeat everything they just went over. Not ideal.
With consolidated, trustworthy, and accurate data, businesses can have more precision in their customer interactions, creating a better overall experience that pays dividends when it comes to greater customer satisfaction and retention rates.
Create a single customer view
Identity resolution is the process of stitching together a customer’s behavior, from across channels, into a single, unified profile. This single view of the customer is essential for effectively engaging them – giving every team a 360-degree view of how they’ve been interacting with your business. It’s a crucial component of creating a cohesive customer journey, especially when these profiles are updated in real time .
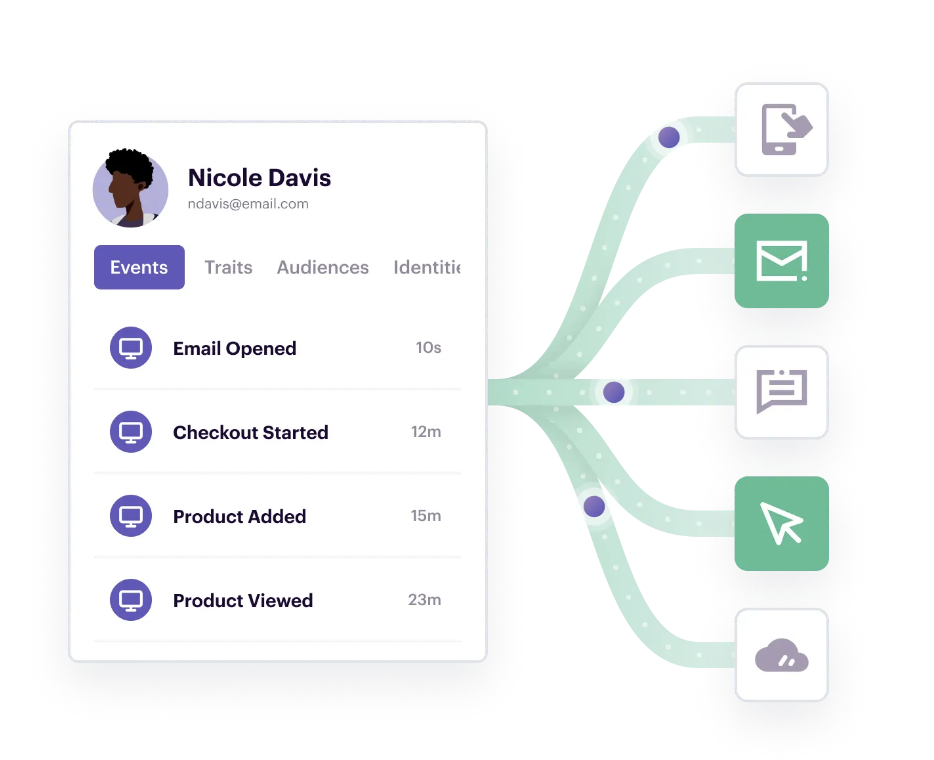
Personalize campaigns with real-time data
With this complete, overarching view of customer behavior, businesses can then leverage real-time data to personalize experiences at scale . For instance, with Segment Journeys , teams are able to orchestrate multi-step, and multi-channel campaigns based on a person’s actions in the moment .
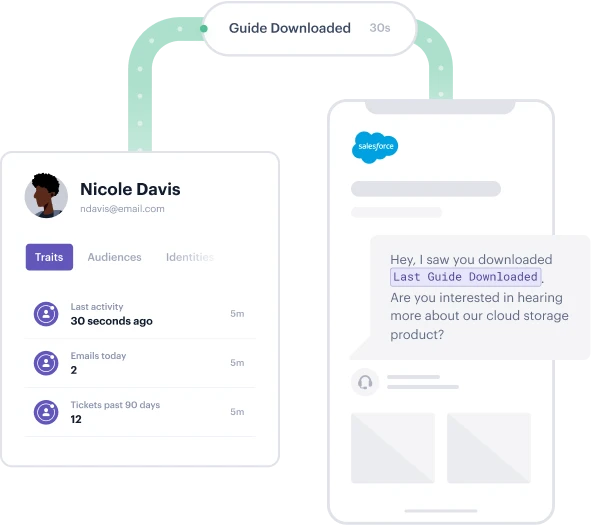
Interested in hearing more about how Segment can help you?
Connect with a Segment expert who can share more about what Segment can do for you.
For information about how Segment handles your personal data, please see our privacy policy .
Thank you, you’re all set!
We'll get back to you shortly. For now, you can create your workspace by clicking below.
Thank you for submitting your request for a demo! Answer 4 more questions to help us pinpoint exactly what your team needs to get started with Segment.
Frequently asked questions
What are the stages in the b2b customer journey.
B2B customers go through the Awareness, Consideration, Conversion, Service, and Advocacy stages.
What are the benefits of creating a B2B customer journey map?
A B2B customer journey map helps you visualize a customer’s interactions with your business from their point of view. It shows you the channels that customers prefer, the touchpoints that influence their conversion, and the experiences that tend to lead them to churn.
What are examples of customer touchpoints?
Seeing a social media ad, reading customer testimonials, conversing with a chatbot, and interacting with customer service are examples of customer touchpoints.
How are B2B and B2C journeys different?
B2B customer journeys tend to have longer sales cycles and more touchpoints in the awareness and consideration stages. Several people influence the purchase decision, and they may enter the journey at different points.
How can Twilio Segment help B2B companies construct customer journey maps?
Twilio Segment is a customer data platform (CDP) that unifies first-party data across multiple sources and creates customer profiles that are updated in real time. With visibility into omnichannel data, you can see when and how a customer interacts with your business before, during, and after a sale.

Retention Flow
Client Feedback
Multiple Websites

B2B Customer Journey: Stages, Map, and Examples.
12 mins read Aug 6, 2024

Ever wondered how to really understand your B2B customer? Well, that lies in something called a customer journey map. A roadmap guiding you through the whole process from the point of view of your customer. 🌟
This blog will break down what is B2B customer journey and B2B customer journey map and why it’s a game-changer for your business. We’ll look at how to create your very own map, from identifying the key touchpoints through to understanding how your customer feels and their motivations behind their actions at each stage.
You will learn:
- How to build a B2B customer journey?
- What is B2B customer journey mapping?
- How many stages of a B2B buyer journey are there?
Let’s get mapping! ❤️
Table of Content
- What is B2B Customer Journey
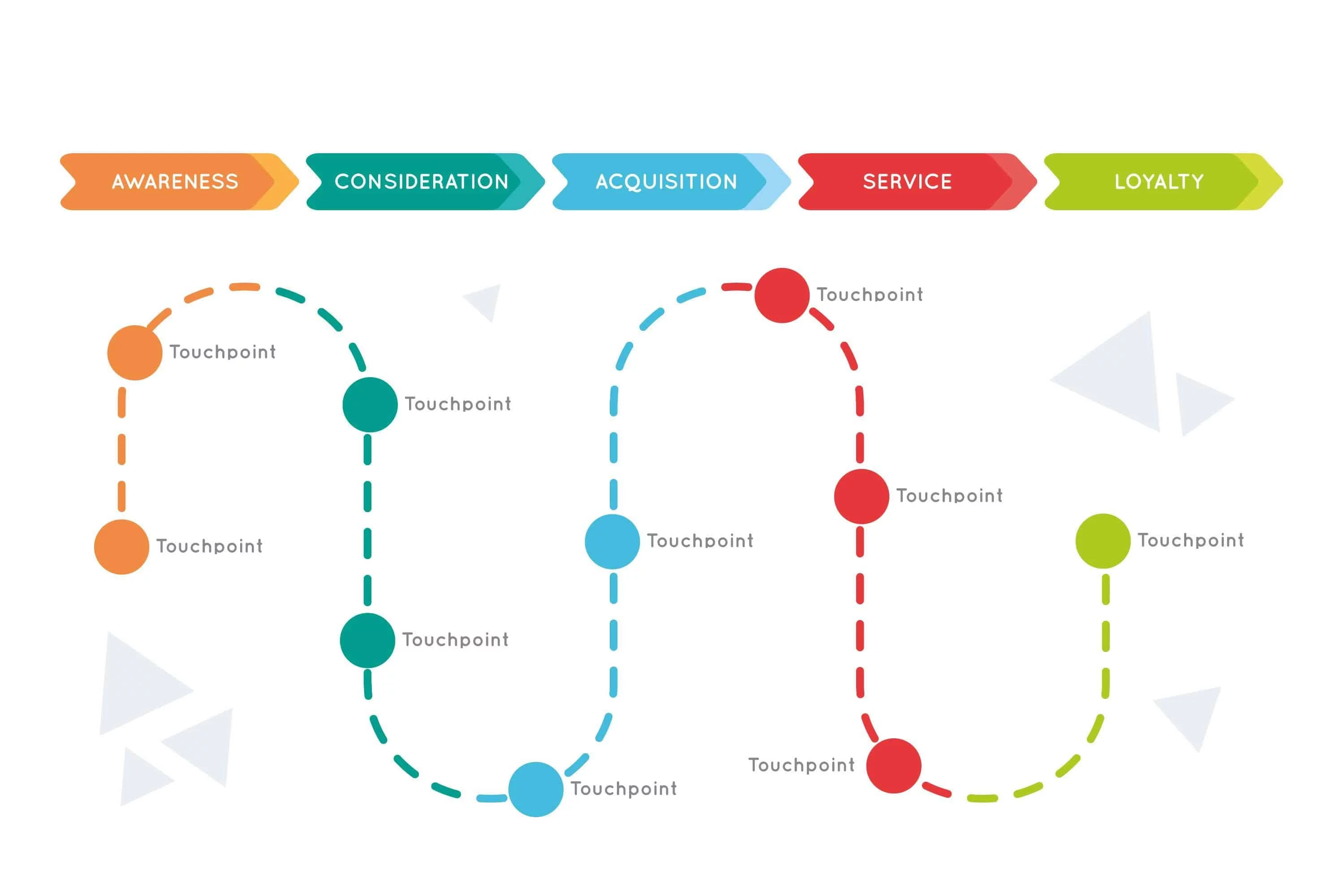
Stages of B2B Customer Journey
How to map the b2b customer journey, b2b customer journey touchpoints, examples of b2b customer journey maps, how to create a b2b customer journey map, how to optimize b2b digital customer journey, what is b2b customer journey.
B2B customer journey is the journey of customer from first learning about your brand till purchasing it. It includes all touchpoints, interactions, and experiences a business customer goes through with your company. This helps in understanding the journey so businesses can modify their customer retention strategies to suit the specific needs and preferences of their clients.
What is a B2B customer journey map?
It is a visual graphic of all the steps and engagements of the customer from first knowing about product to promoting it i.e. from awareness stage to advocacy stage.

It is the key to understanding customer touchpoints throughout the customer experience, and most importantly, opportunities to improve that experience.
B2B customer journey stages comprise of various steps. Let’s try to understand them individually.

Awareness: Quite simple to understand that it the stage where customer get to know about your product. They can learn about your product through friend of friend, social media , your ads, Google etc. 70% of B2B buyers start their research with a generic search which means SEO and google is the main resource of Brand awareness.
Consideration: This is the second stage where customer will compare your product with the one they are using or with other competitors. The comparison can be based on pricing, features, quality, service, ease of use etc.
Decision: This is the stage where customer decides to subscribe to your product after a demo, free trial.
Retention: This stage comes when the customer wants to keep using your product and look for good customer support in case of issues.
Advocacy: This is the stage where customer reaches client loyalty which is they become your referrals and start promoting your product for free
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a B2B customer journey map:
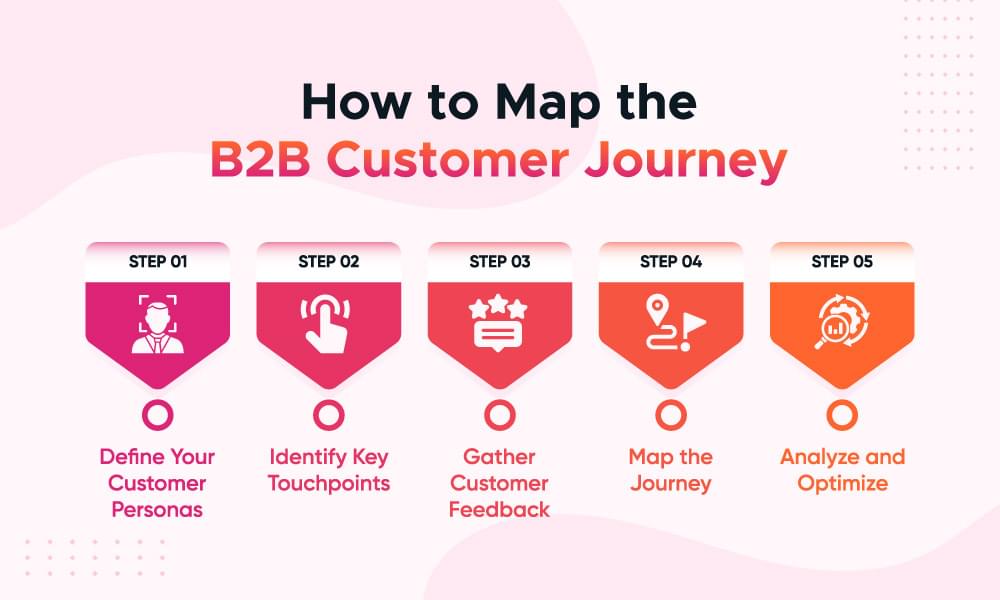
1. Define Your Customer Personas
Begin by describing the various categories of consumers that you serve. Customer personas should depict the different segments of your target market with information on their demands, challenges, and buying behavior. This is useful in the development of the journey map to specific target customer groups.
2. Identify Key Touchpoints
Some popular definitions of touchpoints are as follows: Touchpoints have been defined as those multiple points of contacts that customers have with the companies and/or the products within a definite time span. Such interactions may range from website visits, social media and emails, sales meetings, client contacting and support among others. In this case, mapping customer journey will assist in Identifying and rectifying all the points that are of significance to your business.
3. Gather Customer Feedback
This enables the company to determine which features are popular among its consumers and which aspects it needs to address. This is the process of getting feedback from the consumers because they are the ones who can give insights into the journey that they go through when interacting with a service provider. It can be done by utilizing questionnaires, interviews or by analyzing the customers’ feedbacks. You can use tools like Churnfree to gather customer feedback .
4. Map the Journey
Draw a map of a customer’s life cycle and mark the most significant milestones with reference to the case. If possible, utilize a B2B customer journey map template; otherwise, design it yourself by using flowcharts and diagrams. Make sure that according to the customer journey map all phases are described and shown properly.
5. Analyze and Optimize
After it is completed, review the journey map to realize areas of issues or opportunities in the process. Try to identify areas of potential customer dissatisfaction or certain elements that can slow down the latter down. It is essential to improve and optimize these contacts so that your customers have the best experience with your business.
It is crucial for organizations to comprehend the value that touchpoints contribute to the customer experience.

Website: Website is from where they purchase. Make sure it has all the information related to your product and is user-friendly.
Social Media: The next thing is your social media presence. Use LinkedIn, Facebook and Twitter to engage potential customers.
Email: The communication by e-mail is very effective in developing leads and keeping customers engaged.
Sales Meetings: A highly persuasive tactic is to get a one on one with a member of the sales team.
Customer Support: A good customer support helps in onboarding clients and maintain customer loyalty.
Product Demos and Trials: You could give to potential clients a chance to try your products, giving them an extra helping hand in the making of a decision.
To better understand how to create a B2B customer journey map, here are a few B2B customer journey map examples:
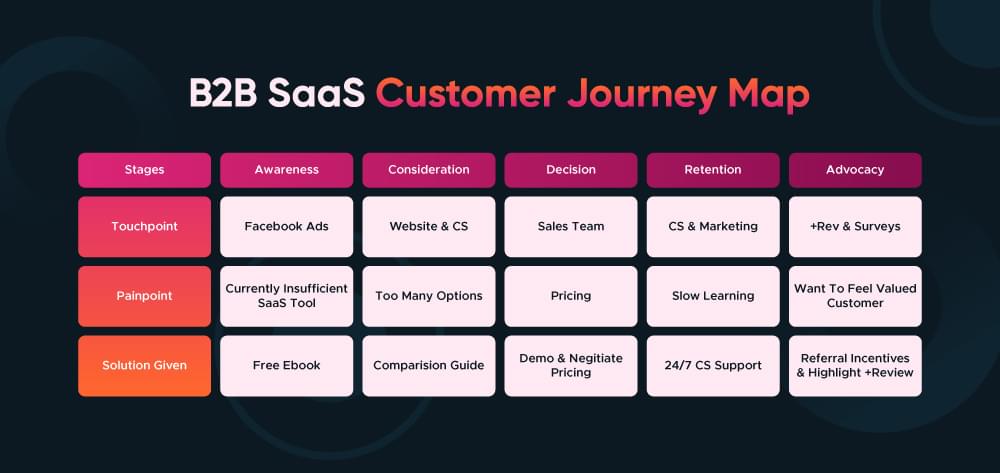
Example 1: B2B SaaS Customer Journey Map
- Awareness: The customer notice the SaaS product of their desire through Facebook ads and content marketing.
- Consideration: They visit the company’s website, go through cases and then initiate a demo through CS.
- Decision: Once the sales team has made a demo, and engaged in the discussions of the pricing strategies, the client signs up for the service.
- Retention: The customer is engaged to reduce churn saas by providing him on boarding support and ensuring that the product is meeting his/her needs.
- Advocacy: A happy customer spends time talking positively about the product, and recommends it to other companies.
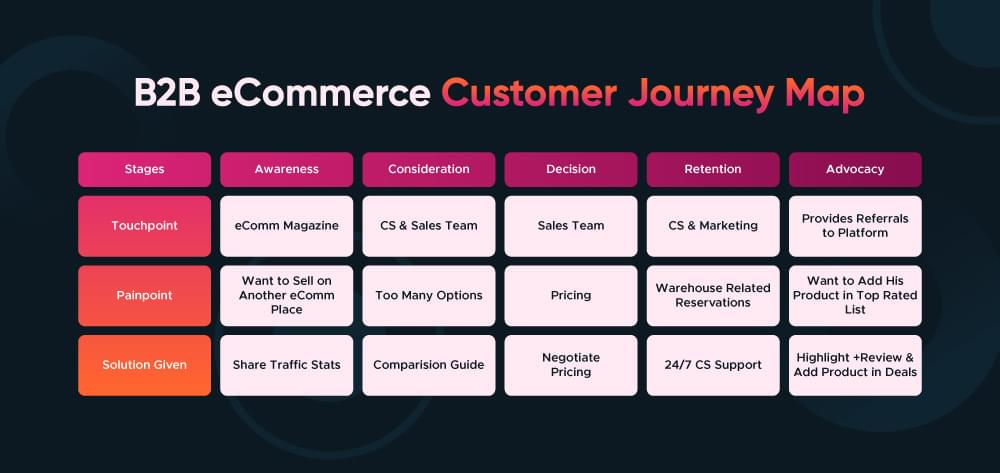
Example 2: B2B eCommerce Customer Journey map
Awareness: The customer acquires information about the specific eCommerce site through attending the trade shows and other publications.
Consideration: They go through the website, weigh the pros and cons and check out reviews.
Decision: After a series of meetings and negotiations, the customer signs a contract and starts using the platform.
Retention: Ongoing support and training sessions help the customer fully utilize the platform’s capabilities.
Advocacy: The customer is actively involved in case studies and is a source of referrals increasing the credibility of the platform.
An important typical question regarding customer journey mapping is “How to map customer journey B2B?” It may seem quite an exhausting task, however, it may prove to be quite manageable when streamlined properly.
Here are some tips:
Collaborate with Stakeholders:
This means to engage members of a team that are drawn from different departments including the marketing department, the sales department and the customer support department in order to have a broader view of the journey that customers undertake.
Use Data and Analytics:
Access information from CRM solutions, web traffic, customer surveys, and feedback to understand customers’ demands.
Focus on the Customer’s Perspective:
It’s important always to keep the customers’ perspective in mind when you are drawing the journey map.
Iterate and Improve:
When developing the customer journey map, it should be important that it is dynamic, changing with the business and customers’ needs. It should be revised periodically with new findings and experiences.
About 67% of the buyer’s journey is done online. Here are some strategies for optimizing the digital customer journey:
- Personalization: Market targeted information/content and promotions to make individual customers interested.
- Automation: Introduce the use of marketing automation to increase efficiency of the various tools in marketing.
- Content Marketing: According to research by FocusVision, B2B buyers consume an average of 13 pieces of content during their purchasing journey. Write high-quality, helpful articles, that provide solutions to potential and real problems of the target audience.
I hope this blog helped you understand and map your customer journey for your B2B business. I’m sharing some reads that you might be interested in.
📖 B2B SaaS churn rate benchmarks
📖 Average Churn rate of subscription services
📖 What is the most direct cause of customer loyalty
📖 Churn rate vs Retention Rate
📖 Gross vs Net retention
Why is the B2B customer journey important?
Understanding the B2B customer journey helps businesses modify their strategies to meet the specific needs of their clients and improve customer experience, leading to better customer engagement, satisfaction, and retention.
How do you map a B2B customer journey?
Mapping B2B customer journey involves defining buyer choices and preferences, outlining customer journey stages, identifying touchpoints, collecting customer data, analyzing pain points, and improve the journey.
What are the challenges in B2B customer journey mapping?
Some of the risks that need to be managed include decisions may be time-consuming; the sales cycle may be long; data may be isolated; the customer may have evolving needs; and lastly, measuring success may be a challenge.
How is the B2B customer journey evolving?
The B2B customer journey is developing with trends like digital transformation, personalization , customer-centric approaches, AI and automation, and omnichannel strategies. These trends are reshaping how businesses interact with their customers and meet their needs in this rapidly evolving 21st century.
How often should a B2B customer journey map be updated?
A B2B customer journey map should be updated at least once in 2-3 years. They should be updated as trends change and customer behaviors change. To know when you need to update your map, continuously monitor and collect feedback from customers.
Share this post
Boost your SaaS or eCommerce business growth. Create an account now.
Register for a free account now to start building your own retention flow. No binding contracts. Upgrade anytime!
Ask our dedicated support team if you have other questions!
Navigating the B2B Customer Journey: Definition, Stages, and Examples

Companies that fail to meet their customers’ needs will drop out of the race faster than you can say B2B. So how can you avoid being one of them?
We’ll talk about how to navigate the B2B customer journey, discuss the various stages, and give you the tools to execute a customer-centric strategy.

Understanding the journey for a B2B customer will allow you to better position your business and its offerings and ultimately meet your customers where they are in that customer journey map. If you choose not to put these strategies in place, you’ll be losing resources, opportunities, and maybe even your customers.
Let’s first take a look at what exactly the B2B customer journey is.
Examining the B2B customer journey
The B2B SaaS customer journey is the path prospects or customers follow, going from a potential customer to an actual one. This path has many stages that are usually represented by a funnel.
The B2B SaaS customer journey outlines how prospects become customers.
It's often visualized as a funnel:
- Top of Funnel (TOFU) - Awareness: Prospects discover your brand.
- Middle of Funnel (MOFU) - Consideration: Prospects compare you to competitors.
- Bottom of Funnel (BOFU) - Decision: Prospects are ready to buy.
Unlike its B2C counterpart, the B2B customer journey is a much more complex purchase process involving multiple stakeholders, a much longer decision-making process, and transactions of much higher value.
When your marketing and sales are well-prepared, you can better anticipate and handle the customers’ needs which can lead to higher conversion rates and loyal customers.
Now, let’s unpack the customer journey stages:
First stage: Initial contact and awareness
The starting point of the B2B customer journey is about letting your prospective customers know you exist and getting that initial contact.
But you must set your brand and offering apart from your competitors. Why should they contact you if they can’t tell what it is that makes your product or service different?
→ Strategies for generating awareness
You’re already reading one of the ways brands generate awareness.You’ve arrived here at this blog post because you probably did a Google search and asked, “What is the B2B customer journey and its stages?”
- Content marketing & SEO: Blog posts optimized for search engines help people find your brand.
- Social media power: Repurpose content for social platforms to expand your reach.
- Targeted advertising: Reach your ideal audience through precise ad campaigns.
→ Identifying potential customer touch points
- Consistent analysis: Marketing teams constantly scan the B2B landscape for opportunities.
- Mapping and analysis: Track touch points like industry events, websites, social networks (like LinkedIn), and email campaigns to understand audience preferences.
→ Measuring awareness effectiveness
There’s no point in rolling out strategies and not analyzing whether they’re working.
- KPIs are key: Track metrics like brand visibility, website traffic, and social media engagement to gauge your success.
- Data-driven decisions: Use insights to refine your strategies for even better results.
The second stage of the funnel is where you really get to shine.
Second stage: Consideration and Interest
As we mentioned before, this part of the customer journey B2B funnel is where prospects are weighing the benefits and costs of your product or service.
Here is where you can really set yourself apart from the competition by demonstrating your value and building trust with potential customers.
→ Tools and techniques for nurturing interest
Equipping your box of tricks with the right tools and techniques is important when you’re trying to nurture the interest of your prospects down their journey in the funnel.
Customer relationship management (CRM) tools , highly-targeted messaging, and personalized content can all be implemented to maintain communication to make sure you’re staying top-of-mind.
→ Key metrics in the consideration stage
Here’s where you’ll want to evaluate lead quality. Sure, you could just throw any lead into the top of the funnel, but you want those high-quality leads to make sure the chance of conversion is higher.
You also want to monitor the lead-to-opportunity conversion rate as well as the time spent on pre-sales activities such as product demos. Here it’s going to be about efficiency and winning back time through process optimization.
→ Building relationships with prospects
The end goal, in the customer buying journey in B2B, should never just be the sale.
So many different things are happening to the prospect along their journey that if you ignore them, you may lose them to your competition.
Really understanding their needs, as well as transparent communication, go a long way to fostering great relationships .
Also, having consistent follow-up strategies is the key to sustaining these relationships way beyond just sales.
Do what you’re going to say you’ll do and personalize their experiences!
Now it’s time to get them to make that final decision.
Third stage: Decision and purchase
With the average SaaS sales cycle length of around 84 days, closing the deal will always be super satisfying.
But to get your prospect to the finish line, you have to concentrate on making the decision-making process easy by addressing concerns they may have.
Here’s where you’ll need to brush up on dealing with objections, too.
→ Influencing factors in B2B purchasing decisions
It’s not just pricing that can affect whether someone chooses your solution or not, but other things like the terms of the contract and if you offer stellar customer support will also come into play.
→ Role of content and demonstrations
Getting the right content to the right customer at the right time during the customer journey for B2B is crucial in helping guide their decision-making process.
Things like whitepapers, case studies, and product demonstrations can help the client see how your offering benefits them. It will give them a way to visualize how your tool or service could be implemented into their daily business.
→ Negotiation and closing strategies
1. Product expertise and pain point mapping
Sales reps must deeply understand the product and skillfully connect its features to the prospect's specific challenges.
2. Objection handling mastery
Reps must be prepared to address objections constructively and persuasively.
3. Effective negotiation
Salespeople should aim for mutually beneficial outcomes, demonstrating flexibility and a focus on the prospect's success.
4. Objection-handling techniques
Offering incentives like discounts, or demonstrating cost savings are valuable tools for overcoming objections.
But what now?
Post-purchase experience and customer retention
Along with marketing and sales, customer success teams make up the “trinity” of the customer decision journey for B2B.
Your organization must have strategies in place to ensure the customer is getting the most out of their experience with your product or service.
A successful customer onboarding program is vital to make that happen.
The importance of customer support and services
The first step is getting a prospect to sign up and become a customer. Now, your customer support team has to show they’re responsive to queries and provide tailored solutions to problems that might arise.
The aim here is to maintain high customer satisfaction and retention rates.
Feedback loop implementation
Not all customers are going to constantly write to you with questions or suggestions. In that case, you’ll need to reach out on a regular basis to collect customer feedback.
This isn’t just to hear what’s going well and what’s not but also to see if they have suggestions on improving your offering.
Making them part of your growth creates a feeling of “community” with your brand allowing them to align themselves with you in the long term.
Strategies for sustainable customer retention
→ Loyalty Programs - Reward long-term customers with perks like:
- Yearly discounts
- Access to exclusive features
→ Upselling & Cross-selling
- Identify if additional products or services can benefit your customer's business.
- Clearly demonstrate the added value they would receive.
→ Exceptional Support
- Emphasize your availability and responsiveness. This fosters trust and demonstrates your commitment to customer success.
The Result: These innovative strategies, combined with excellent support, will encourage customers to stay loyal for the long term.
The role of analytics in understanding the customer journey
Being able to take a look at your processes and strategies to make sure everything is going as it should is key to being successful and growing your business.
B2B organizations need to embrace analytics to smooth out the customer journey by identifying patterns, trends, and things that could be improved.
Key analytics tools and metrics
These tools provide data to inform strategic decisions and highlight customer pain points.
- Web Analytics: Google Analytics tracks website traffic, user behavior, and conversions.
- Marketing Automation Platforms (MAP): Tools like Hubspot Marketing Hub manage campaigns, automate tasks, and nurture leads.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Systems like Salesforce centralize customer data, interactions, and sales processes.
💡 Analytics are crucial. Without data-driven insights, you're operating without a clear direction.
Interpreting data for strategy improvement
The importance of data-driven insights cannot be overstated. Data is static, yes.
But how you interpret that data to improve your marketing or sales strategies dynamically, as well as product or service offerings, will ultimately determine your growth trajectory!
This is all great when everything is running smoothly, but what are some of the challenges or obstacles to your customers’ success during their journey?
6 Common customer challenges during their buyer’s journey
Your teams need to be able to put themselves in your prospects’ and customers’ shoes so they can effectively respond to their needs and provide a seamless experience. Identifying stumbling blocks that may lie in the path to your customer’s success is essential in creating a customer-centric business.
1. Lack of information
If your customer or prospect can’t find relevant product or service information to help them make informed decisions, you’ll most likely lose them. Make it easy to find relevant and comprehensive information about your offerings.
2. Too many choices
The modern market is flooded with products and services that are similar to each other. If you don’t find a way to differentiate your brand from your competition, you’ll make it overwhelming for customers to make a decision. Find gaps in your competitors’ strategy and exploit them by doing what they didn’t!
3. Lost in complex sales funnels
Is your website layout confusing or complicated to navigate? Or are they finding it hard to register for something? Worse still: they want to finalize a purchase but find the steps unintuitive and give up. Be sure to remember user experience across all your touchpoints to make sure you don’t lose potential customers at crucial decision-making points.
4. Inconsistent communication
If your branding and messaging are misaligned, this can negatively impact your potential and existing customers by confusing them and throwing them off-course on their journey with you. Be sure to create a seamless customer experience by making sure everything about your brand and messaging is aligned and consistent.
5. Bad customer service
We’ve all been there - struggling to get help on an automated customer service line or waiting days (or even weeks!) for an email response to an inquiry.
If your customer service team isn’t responsive, or it’s hard to get in touch with an actual human, your customers will feel neglected.
Have customer service that truly serves the customer by being available on multiple channels such as chat, email, and telephone.
Be sure to also have tools in place so your customer service team can deal with inquiries and issues in a timely manner and track the progress.
6. Lack of personalization
Today, your customers expect you to understand their specific needs. If you don’t offer personalized experiences and the customer feels they’re just a number to you, it will create a disconnect that will be difficult to resolve.
Be sure to use data-driven insights and other tools to see how you can create better personalization for your various customer segments along the entire journey.
When you have the right tool, ex. like emlen, you can really bring a level of personalization that will set you apart from your competitors.
How emlen’s insights can help optimize the customer journey
Understanding which content is relevant for your customer helps you to focus and streamline the customer journey.
This means your customers will only find and see what’s relevant to them, making their purchasing experience easy and as effortless as possible.
💡Here's how emlen can help:
→ Content relevance: Streamlining the customer journey
- Focus matters: Tailored content ensures customers find what they need, creating a smoother purchasing experience.
→ emlen's transformative approach
- Early integration: Introducing emlen Destinations early (e.g., after a successful call) provides seamless product exposure.
- Beyond product showcasing: emlen reveals who's visiting, highlighting genuine interest and aligning with your business goals.
→ Refined targeting and outreach
- Valuable insights: emlen's data fuels laser-focused marketing, replacing broad efforts.
- Engagement depth: Track content views, interests (case studies, videos), and repeat visitors for a detailed understanding of prospect behavior.
→ The goal: A resonant customer journey
- Tailored Approach: Use insights to personalize messaging and interactions.
- Customer-Centric Experience: Prioritize the prospect's needs and interests for maximum engagement.
Digital transformation and the B2B customer journey
Digital transformation has taken the B2B customer buying process and journey to another level by offering new channels for communication, ways to improve organizational performance and efficiency, and allowing businesses to enhance personalization for their customers.
→ Impact of digital channels
The rise of social media, email marketing, and webinars contributes strongly to the B2B online customer journey.
Before the arrival of these digital channels, organizations were limited in terms of customer touch points.
For example, the pandemic made it impossible for B2B companies to go to conferences or trade shows to meet with buyers.
That meant that businesses could still engage with their customers and not miss out because they used digital channels.
→ Using technology for a better customer experience
Artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics can help your organization by giving you personalized, relevant content and support to your customers. Things like tailored marketing materials, product recommendations, AI chatbots, and virtual assistants can drastically improve your customer’s experience with your brand.
Be there at every step of your B2B customers’ journey
When you can understand and then optimize the journey that your customers take with you, you’ll be one step ahead of your competitors.
Pay close attention to the customer data for customer journey maps and insights on how to continuously improve that journey and improve customer retention to stay ahead.
Don’t forget to:
- Map your B2B customer journey
- Use the right analytics and metrics tools
- Personalize their experience along all touch points
- Adopt technology to support your overall revenue and customer goals
The goal isn’t just to keep gaining new customers but to retain existing ones by converting them into repeat customers
If you’ve done your job right, brand advocates. So be sure to continue analyzing and improving along the way because the customer journey is always evolving!

Marc is co-founder of emlen and responsible for the go-to-market strategy and execution that convinces today's modern B2B buyer.
Subscribe to our blog!
Articles like this.

19 Examples of B2B Sales Enablement Content to Support Your Sales Team

The Ultimate Guide to Signal-Based Selling in B2B

The emlen Guide to Aligning your B2B Buying Center

B2B Customer Journey: Mapping, Strategies, and Benefits

Are you lost in the maze of your B2B customer journey? This guide will map it out for you.
The B2B customer journey highlights the touchpoints of one business (the vendor) with another (the customer). One of the key focuses of mapping this journey is to provide a better experience to customers from research to post-purchase.
Mapping the B2B journey helps your business better understand the customer’s path during their decision-making process.
This guide brings everything related to the B2B customer journey, its stages, and the need for customer journey mapping.
Table of Contents
What is a b2b customer journey, b2b customer journey stages, why conduct customer journey mapping, b2b vs b2c customer journey, how to create a b2b customer journey map.
The B2B customer journey refers to all the interactions a business goes through when considering and ultimately purchasing a product or service from another business.
It’s essentially the path a company takes from becoming aware of a need to becoming a customer.
1. Awareness
The awareness stage marks the beginning of a B2B customer journey. Here, potential customers first recognize a problem or need within their business. This could be triggered by anything from operational inefficiencies to a lack of specific resources.
Providing valuable educational content is key to grabbing their attention at this stage. This content should address their specific problems and demonstrate your expertise in the area.
2. Consideration
At this stage, the potential customer is interested and actively researching solutions to their problem. They compare vendors and evaluate options based on features, benefits, and cost.
At this stage, you can nurture their growing interest by providing valuable resources to help them make better decisions. Offer product demos or trials to showcase your product’s capabilities in action.
3. Decision
This is the critical stage where the potential customer makes a final decision. They might request demos and proposals or negotiate pricing before committing.
You can address any remaining concerns and show the value you can deliver. Offer product demos or trials to showcase your product’s capabilities. Provide clear and transparent pricing information. Be responsive and address any questions or concerns promptly.
4. Implementation
Once the customer decides to move forward, this stage involves finalizing the purchase agreement and implementing the solution.
Ensure a smooth onboarding process and provide excellent customer service. Offer clear documentation and training materials. Be available to answer questions and address any initial challenges.
5. Retention and Advocacy
The journey doesn’t end with the purchase. Your goal is to retain the customers, build long-term loyalty, and turn them into advocates for your brand.
Provide ongoing support and ensure customer satisfaction. Offer additional resources and training opportunities. Gather feedback and continuously improve your product or service.
Customer journey mapping is a way to visualize customers’ experiences, processes, and needs while they are interacting with your business. This will allow you to overcome their obstacles and make the process efficient and seamless.
By mapping this journey, you gain valuable insights that can be used for:
Better Insight into Customers
Mapping the customer’s journey gives you insight into what they need, what motivates them, and their pain points. This helps your company realize its challenges as well as the decision-making process and prioritization, resulting in improved customer experience.
Personalized Approach
A customer journey map created with deliberation provides adequate personalized experiences to your customers, thereby developing stronger relationships and significantly increasing customer satisfaction.
Reference for Your Team
The essence of customer journey mapping is to serve as a point of reference for different teams in your organization. Marketing, sales, customer service, and product development departments become more closely aligned and collaborative to ensure a consistent and integrated customer experience across all touchpoints.
Both B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-consumer) customer journeys include the entire customer interaction with a business, from discovering a product to making a purchase.
The main goal of both journeys is to provide an elevated customer experience. However, there are quite a few differences between the two.
Creating a B2B customer journey map helps your business understand the interactions with customers throughout their purchasing process and identify any problems they face.
Here are the steps involved in creating a B2B customer journey map:
1. Define Your Buyer Personas
Buyer personas are hypothetical representations of your customers.
You create different customer personas based on decision-making units and different buyer types within your target market segment (e.g., company size, industry).
This will help you know about the customers better and identify target customers.
2. Identify Key Touchpoints
The second step involves mapping out all customer interactions with your brand throughout their journey.
You can identify all possible points of contact, including online interactions (website visits, social media), offline interactions (industry events, sales calls), and customer support interactions.
3. Analyze Customer’s Current Experience
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system can become a valuable tool for understanding how customers experience your brand.
It allows you to gather customer feedback from various sources, including surveys, interviews, and even built-in analytics.
You can transform this information into a clear picture by employing data visualization tools. These tools help you uncover trends and patterns hidden within customer behavior.
4. Highlight Areas of Improvement
You can pinpoint areas where customers struggle by mapping the customer journey and gathering feedback. This allows you to identify and address their dissatisfaction, leading to targeted improvements.
Here, you focus on solutions: providing clear and concise product information through accessible channels like user guides and interactive tutorials. Additionally, ensuring readily available customer support empowers customers to get the help they need when they need it.
5. Implement Changes
The next step is to make strategic adjustments to optimize the customer journey. It is essential to develop an action plan to address the gaps and opportunities identified with the help of your customers’ feedback and implement the changes in a phased manner.
Train your team with each new upcoming process or tool to make the implementation successful. Consider tools like marketing automation platforms to streamline communication and personalize B2B interactions.
6. Monitor and Iterate
Continuous improvement depends on constantly assessing change’s effect while making necessary adjustments. Regular customer feedback and journey analysis identify new opportunities for improvement by creating metrics and KPIs to measure.
As your business and customers evolve, iterating on your customer journey map ensures that your strategies remain effective and relevant.
To Sum It Up
The B2B customer journey is a complex but vital component of any business strategy. By mapping and understanding the customer’s journey, your company provides superior customer experiences. This increases customer loyalty and growth.
The goal of B2B customer journeys is not just to make a sale but also to build a lasting relationship with customers.

Related Post

The Essential Guide to Measuring Customer Satisfaction
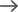
7 Best Practices to Enhance B2B Customer Experience

7 Best Practices to Ace B2C Customer Experience
Copyright © gocustomerexperience.com . All Rights Reserved.

- Best Practice
- ReachStream Tips
- What’s New?
- Help Center

Get 100 Views, 25 Credits & Free Monthly Recharge
- Best Practice | Marketing
B2B Customer Journey in Sales and Marketing (2024)
- June 28, 2024

- Defining the B2B Customer Journey Map
- What Are the Stages of the Customer Journey Map ?
B2B Customer Journey Touchpoints
- Why Should You Look Into B2B Customer Journey
B2B Customer Journey Map Example
Final thoughts.
By 2025, 80% of B2B sales interaction is expected to occur digitally.
Where does that leave the industry? According to a report by Gartner, the industry has been shifting towards a buyer-centric, digital model. In other words, like B2C, the customer and their experience are starting to take the front seat. This leaves us with one question: What can B2B companies do to stay ahead ?
The answer? B2B customer journey mapping.
Defining B2B Customer Journey Map
So far, the idea of mapping a customer’s journey and refining their experience has been common in B2C. However, with the increasing need for digital presence and changing B2B buyer behaviors, businesses selling to businesses also have to adopt a customer-centric approach.
But what is the customer journey? Simply put, it is a map of how and when a customer interacts with the company. Businesses use this to understand and analyze the different touchpoints they can access. You can use this map to determine how a customer interacts with your company before, during, and after buying from you.
What Are the Stages of the Customer Journey Map?
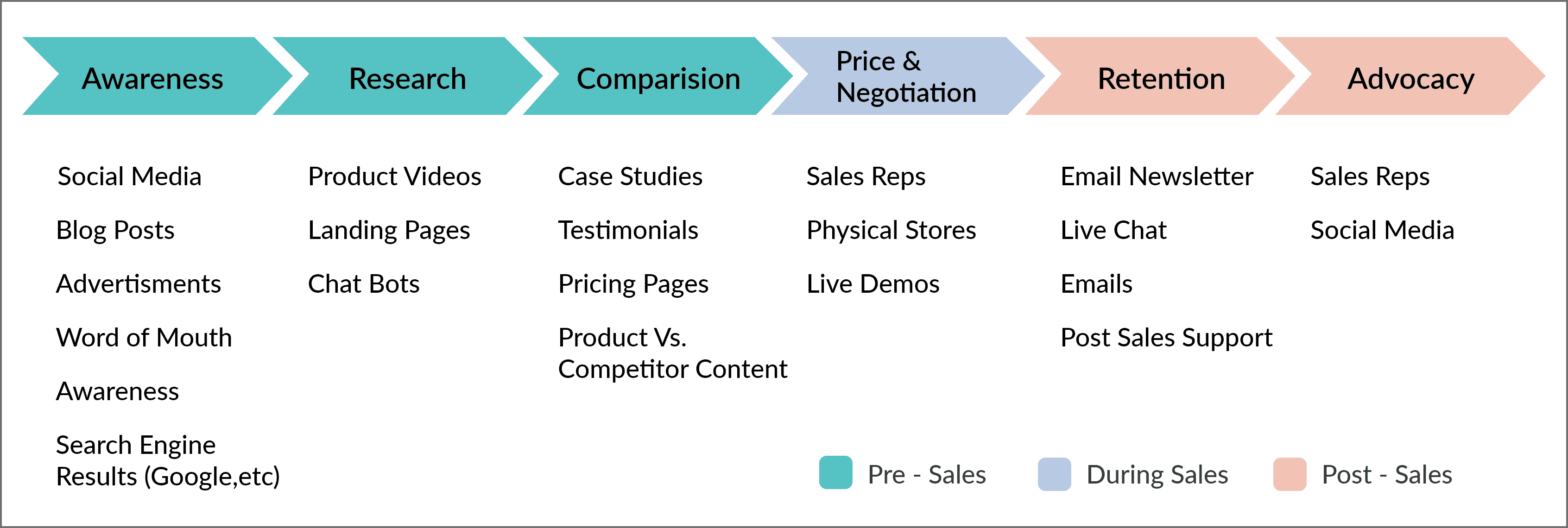
The pre-, during, and post-sales stages can be further divided into multiple steps: awareness, research, comparison, pricing and negotiation, retention, and advocacy .
The awareness stage is when the ICP hears about your brand for the first time. This can be through word of mouth, targeted ads, social media feeds, Google searches, or maybe even cold outreach.
The research stage is when the prospect is looking for information about you and your solutions and considering your product as a potential solution. You can provide accurate information about your products and features through product videos, demos, etc.
Comparison:
A buyer will never look up a product and buy it. Often, the B2B buying process involves shortlisting products and comparing them for a clear, logical choice. The comparison stage is high-risk—your customers can easily fall off the map. Provide and highlight your unique selling point, use case studies, and make your product stand out against the competitors to help your prospects move to the next stage.
Pricing & Negotiation:
During the sales stage, keep your pricing clear and your sales team on point. This is the part where the final decision is made. Build on your USP, create a positive relationship, and use other sales tactics to win the deal.
While the buyer journey ends at buying the product (as the name suggests), the customer journey involves post-sales as well. Retaining clients and reducing churn can increase ROI. Foster trust, look for feedback and reward customer loyalty.
At this point, your client will do your marketer’s job. Customers with high satisfaction and loyalty will recommend your products to others, advocating for your business. Offer referral bonuses and special deals, and look for testimonials or case studies.
The exact stages of your customer journey map may differ. For example, the SaaS customer journey map may include a whole new step called On-boarding. However , you can use these stages as the starting point for research on B2B customer journeys.
How you approach touchpoints can make or break your ROI. Touchpoints are the exact places where your customers come in contact with you. This can look like filling in a form on your website, reading your LinkedIn post, or contacting your sales rep.
Understanding which touchpoint is used at what stage will allow you to personalize the experience. The better the experience, the better the chances of retention and advocacy.

Why Should You Look Into B2B Customer Journey?
The B2C industry has already embraced conducting customer journey mapping and has seen incredible results. The argument that B2B is not customer-centric is no longer valid. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for personalized experiences that cater to their needs. They have also moved to the digital space.
In other words, they make most of their decisions based on the business’s online presence and content. The more the buyers move into the digital space, the more complex their buying behaviors become. Understanding the already complex B2B relationships in the context of digitalization and buyer-centric space needs careful analysis.
According to Gartner , 80% of firms expect to compete based on customer experience. The B2B customer journey is slowly becoming important in the industry.
Here is an example of a map of the B2B customer journey. Keep in mind that this is a general map and should be customized for your niche.
While the B2B industry is moving towards a more digital approach, 82% of buyers still accept meetings from SDRs who reach out to them first.
Combine traditional B2B sales tactics with content marketing for the best results. You can use ReachStream to continue traditional B2B sales and generate targeted leads. And leverage other digital marketing strategies with CRMs, Google Analytics, etc.
Sign Up today for 25 free credits every month.
Boost your sales pipeline with our powerful list builder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 6 stages of the customer journey.
The six stages of the customer journey are Awareness, Research, Comparison, Pricing & Negotiation, Retention, and Advocacy.
What is the B2B customer journey?
It visualizes the path that a B2B buyer takes to search, consider, buy, renew, and maybe even advocate. while there are different ways of looking at this journey, the most common involves the six stages mentioned above.
How does understanding the B2B customer journey improve sales?
Understanding the journey an average B2B buyer takes can help determine high-risk areas and other parts that require fine-tuning. Since relationships are central to the B2B buying process, having a smooth sales cycle will help with customer retention and reduce churn.
How is B2B customer journey different from B2C?
B2B journeys involve a complex decision-making process. while B2C journeys don’t necessarily include a salesperson, B2B journeys almost always include demo meetings, negotiations, and other processes that involve multiple decision-makers and a sales team.
Don't forget to share this post!
Check out our other blogs!

Buy Leads: The Complete Guide on Buying Business Leads

AI for Sales: 5 Best AI Tools for Free Cold Calling Scripts
Cold Calling Metrics: Effective Templates for Cold Calling KPIs

Ultimate Guide to Building a Targeted Cold Call List

Nurture Your Knowledge Tree
Enrich your acumen with the latest research, think-pieces, expert insights, and more.

- [email protected]
- +1(669)-544-2861
- Become a Data Partner
- Reach API Document
- Company and Contact Data
- Marketing Data
- Technology Insights

By clicking Subscribe,you agree to ReachStream’s Privacy Policy and consent to receiving newsletters.
- Gamification Engine Grow engagement with powerful gamification features
- Enterprise Ready Security, scalability, reliability and integration
- Financial Services
- Professional Services
- Travel & Hospitality
- Telecommunications
- Manufacturing
- Media & Entertainment
- Learning & Training
- Call Center Engagement
- Sales Motivation
- Channel Motivation
- Performance Management
- Development Teams
- Customer Loyalty
- Employee Onboarding
- Remote Work
- Community Engagement
- Product Managers
- Engineering
- Blog Catch-up with product, industry and company updates
- Infographics Collection of infographics with gamification insights
- Gamification Guide Step-by-step guide to learn in-depth about gamification
- Support Customer success and support at your service

Mapping the B2B Customer Journey: Key Stages and Touchpoints
The B2B customer journey serves as a compass for businesses navigating the complex realm of buyer interactions and decision-making. Understanding the intricacies of this journey is crucial for organisations looking to build lasting partnerships and drive exceptional business outcomes.
A customer journey map helps B2B operators re-imagine their customer journey and deliver more personalised experiences. It presents a great opportunity to reinforce brand awareness and drive customer satisfaction.
This article explores B2B customer journey mapping, unravelling its key stages and touchpoints that pave the way to fruitful business relationships.
Table of Contents
How B2B and B2C customer journeys are different
What makes an effective b2b customer journey map, why you need a b2b customer journey map, #1. awareness, #2. consideration, #3. decision-making, #4. implementation, #5. support and relationship management, #6. renewal and expansion, awareness stage, consideration stage, decision-making stage, implementation stage, support and relationship management stage, renewal and expansion stage, define buyer personas, conduct customer interviews, analyse data and metrics, collaborate with sales and customer service teams, conduct journey mapping workshops, analyse competitor journeys, machine learning in finance: 12 essential applications, how to create interactive compliance training for bank employees, how fintech apps are using gamification to increase user engagement, top gamification companies for employee & customer engagement, what is the b2b customer journey.
The B2B customer journey refers to the process that business-to-business (B2B) customers go through, from problem identification to post-purchase.
The process encompasses the entire lifecycle of a B2B buyer’s interactions with a company or brand. This includes their research, evaluation, purchase, ongoing relationship with the business and experiences along the way.
Consider a small business needing a scalable CRM (customer relationship management) solution, for example. There are many steps that it goes through before committing to a purchase. Even after the purchase, there are still post-purchase steps to cover, such as setting up the CRM system and providing after-sales services. That’s all part of the customer journey.
The B2B customer journey is characterised by multiple touchpoints across various channels. It is influenced by several factors, including industry-specific needs, organisational dynamics, and the involvement of decision-makers. Ultimately, the lasting impression of this journey is what defines the overall customer experience
Businesses and individual consumers approach the buying process quite differently. Understanding these differences is crucial for companies to tailor their strategies effectively to meet their customers’ unique expectations.
Some key aspects in which B2B and B2C (business to customer) journeys differ include:
- Target audience — As a B2B operator, you rarely buy or sell to one person. More likely, you’ll transact with businesses, organisations, or a diverse group of individuals composed of stakeholders, senior management, and end-users
- Complexity — B2B customer journeys tend to be more complex and involve longer sales cycles compared to B2C journeys. For example, B2B purchases typically involve higher stakes and larger investments, so there are often multiple decision-makers and longer negotiation processes.
- Decision-making factors — B2B customer journeys prioritise factors such as ROI, efficiency, scalability, and alignment with organisational goals. On the other hand, B2C journeys are frequently influenced by emotions, lifestyle preferences, and individual satisfaction.
- Relationship duration — B2B customer journeys typically involve longer-term relationships compared to B2C. This often necessitates continued engagement and support beyond the initial purchase. With B2B transactions, you look at ongoing partnerships, term contracts, or retainer arrangements.
- Personalisation approach — B2B journeys often emphasise customisation to meet the specific requirements of the purchasing organisation or target market segment. B2C customer journeys, on the other hand, may prioritise personalisation based on individualised experiences.
- Communication channels — B2B customer journeys typically involve multiple touchpoints across various channels, including direct sales interactions, professional networks, and industry-specific publications. B2C customer journeys rely heavily on digital channels such as websites, social media platforms, and online marketplaces.
What is the B2B customer journey map?
Simply put, the B2B customer journey map is a framework for capturing the customer experience. This visual representation illustrates customers’ pain points and their internal perception of the company throughout the business relationship.
Source: apizee.com
These insights help the business identify areas to optimise to design and deliver more positive customer experiences.
Mapping the B2B customer journey requires a business to step into the customer’s shoes to see how its processes impact its purchase decisions.
The customer journey map is a blueprint for the journey the customer takes. This means it should be comprehensive enough to cover all the important touchpoints — from initial awareness to post-sale.
Depending on the type of business relationship, customer journey maps should also cover the cessation of the relationship with the company. How a business handles this stage can be crucial to minimising churn and encouraging future relationships.
Generally speaking, effective customer journey maps should include the following:
- A detailed flowchart of the customer journey showing the various interactions between the customer and the company
- Clearly outlined customer pain points or issues that may get in the way of a positive customer experience
- Identified areas where the company can take action to improve overall customer satisfaction
- Details about what departments or people are responsible for moving the customer relationship forward at each touchpoint
- Well-defined linkages between touchpoints
- The company’s performance at each touchpoint
Mapping the B2B customer journey gives businesses a powerful way to understand and cater to their customers effectively.
Here are the key reasons to design a B2B customer journey map:
- Enhanced customer understanding — A customer journey map provides valuable insights into the needs, motivations, pain points, and behaviours of your B2B customers. It helps you better understand their challenges, preferences, and decision-making processes.
- Strategic decision-making — A customer journey map helps businesses make data-driven decisions about their marketing, sales, and customer service strategies. It allows them to identify areas of improvement, optimise touchpoints, and align resources better to serve customers at each stage of their journey.
- Personalised experiences — A customer journey map enables a company to deliver tailored experiences to its B2B customers. This ultimately fosters stronger relationships and dramatically improves customer satisfaction.
- Alignment across teams — A customer journey map is a common reference point for different teams within an organisation. Marketing, sales, customer service, product development, and other departments can become more aligned and collaborative. This ensures consistent, cohesive customer experience across all touchpoints.
- Continuous improvement — Mapping the B2B customer journey is an iterative strategic process. It provides a framework for ongoing evaluation and optimisation of the customer experience to drive better business outcomes.
Key Stages of the B2B customer journey
The B2B customer journey typically consists of the following stages:
In this stage, the B2B vendor aims to raise awareness about what their business offers. The B2B customer, on the other hand, becomes aware of a need or problem they want to address. For example, the company might be planning to attend an industry event in another state. So one of the first things they’ll need to sort out is the transportation for their staff.
Now they’re aware of the need, so they start researching potential solutions and exploring available options.
As the name implies, this is where the customer “considers” their options. In the consideration stage, the B2B customer narrows their choices and evaluates different vendors or providers.
Here, they delve deeper into the features and benefits of each option. They may compare the prices offered by the shortlisted vendors and consider payment options, flexibility, and customisation. At the end of the day, it’s about arriving at an informed decision about who they will purchase from.
Having narrowed down their options, it’s time for the B2B customer to decide what B2B vendor to contact to initiate the buying process.
This is a pivotal moment in the B2B buyer journey. For one, it represents a successful conversion for the vendor, and is a sign that their lead nurturing methods are sound.
After the decision is made, the customer moves into the implementation stage. This involves the buying process, onboarding, and installation/configuration.
Depending on the product or service being provided, this stage may also include special training for specific staff within the B2B customer’s organisation. Once everything is properly set up, the customer integrates the chosen solution into their existing business processes.
With the solution fully implemented, the customer enters the support and relationship management stage. For instance, they might require ongoing technical support or they might be assigned an account manager to handle post-purchase concerns and requests.
This is the B2C equivalent of customer loyalty. In this stage, the B2B customer evaluates their experience with the vendor and decides whether to continue the relationship. Additionally, there may be opportunities for upselling or expanding the scope of services provided to the customer.
It’s important to note that the B2B buyer journey is not strictly linear. This means it’s not uncommon for buyers to move back and forth between stages based on their specific needs and circumstances.
Touchpoints in B2B customer journey mapping
The customer journey mapping process includes several critical touchpoints that occur before, during, and after a sale. Touchpoints are the various customer interactions or moments of engagement with a company throughout the customer journey.
Each one provides an opportunity for the company to leave an impression on the customer and ultimately impact their decision-making process. That’s why optimising touchpoints to deliver a consistent and personalised experience is essential in building strong relationships and fostering customer loyalty.
Source: salespanel.io
These touchpoints can occur through various channels, both online and offline, and are crucial in shaping customer experiences.
Customer touchpoints can occur at different stages of the buying journey. Here are some examples:
- Industry events and conferences — These events are great for learning about new trends, technologies, and potential solutions.
- Online research — Conducting searches on search engines and exploring industry publications and social media communities are great ways to facilitate customer interactions.
- Word-of-mouth referrals — Seeking recommendations and feedback from colleagues, industry contacts, or trusted sources make for great customer touchpoints.
- Company website and landing pages — Visiting the company’s website and landing pages to explore detailed information about potential solutions.
- Product demonstrations or webinars — Participating in live or recorded demonstrations and webinars to gain insights into the functionality and benefits of the offerings.
- Case studies and success stories — Reviewing real-world examples and success stories that highlight how the product or service has helped other businesses.
- Consultations — Engaging in meetings or consultations with sales reps to discuss requirements and solutions.
- Proposal and pricing discussions — Collaborating with the B2B vendor on contract terms and negotiating proposals that align with the B2B customer’s requirements.
- Reference checks — Seeking references from existing customers to validate the company’s reputation and track record.
- Vendor presentations or pitches — Attending presentations or pitches by vendors to assess their expertise and how well they understand the business’s challenges.
- Onboarding and training sessions — Participating in onboarding sessions and training programs to learn how to use the solution effectively.
- Technical support and guidance — Seeking technical support and advice during the implementation stage to resolve any issues that arise.
- Documentation and user manuals — Accessing comprehensive documentation, user manuals, and resources to support the implementation process and user adoption.
- Dedicated account managers or customer success representatives — A designated point of contact is great for nurturing current customers.
- Helpdesk or support ticket systems — Utilising helpdesk or support ticket systems to log and track support requests, ensuring timely resolutions. This is a key part of modern B2B customer expectations and is a leading factor in increasing customer retention.
- Surveys and feedback mechanisms — Providing feedback through surveys or related mechanisms to help the vendor improve their offerings and sales process.
- Contract renewal discussions — Engaging in discussions with the B2B vendor regarding contract renewal terms and potential adjustments based on changing business needs.
- Cross-selling and upselling opportunities — Exploring opportunities to expand the relationship by considering additional vendor offerings.
Mapping the B2B buyer journey
Customer journey mapping requires a thoughtful approach to design truly innovative experiences tailored to the B2B context.
It’s important to look for common pitfalls that typically accompany a journey mapping exercise.
Some businesses make the mistake of overgeneralising the buyer’s journey. This results in them creating a one-size-fits-all customer journey map that doesn’t account for the unique needs of different customer segments.
Another common mistake is focusing primarily on the sales stages and neglecting other key touchpoints of the buyer journey. This makes it difficult to capture the nuances of the buying experience truly.
The ideal customer journey map takes into account all the key stages of the journey with the view to achieving repeat business. It must also contain all the major elements necessary to improve customer touchpoints.
Check out the B2B customer journey map template below for an idea of the mapping process.
Source: slideteam.net
Here are some techniques you can use to map the B2B customer journey:
Start by developing detailed user personas that represent your target B2B customers. The most effective way to create personas is first to identify the pain points, motivations, and decision-making criteria of various customer segments.
This helps you understand their needs and tailor the customer journey map accordingly.
Engaging in one-on-one interviews with existing customers is a surefire way to gather insights about their experiences and interactions with your company. You can also collect customer feedback data through the usual tools — customer satisfaction surveys, feedback forms, focus groups, etc. This helps identify areas of improvement and shape the customer journey map.
Leverage data analytics tools to analyse customer behaviour, engagement metrics , conversion rates, and customer journey progression. This data provides a quantitative understanding of the customer journey and helps identify bottlenecks or areas of improvement.
Involving your sales and customer service teams in the B2B customer journey mapping process is important. They have valuable insights into customer interactions and can provide detailed accounts of the pain points at each journey stage.
Additionally, this collaboration can help buoy your marketing efforts and drive quicker outcomes.
Conduct workshops involving cross-functional teams from all relevant departments. Encourage brainstorming and collaboration to gain different perspectives.
Study the customer journeys of your competitors in the B2B space. Identify areas where they excel or fall short and use that knowledge to differentiate your own customer journey mapping.
Keep in mind that the B2B customer journey is not static, so regularly review your customer journey map. There will always be new customer insights, market trends, and changing customer expectations to incorporate down the line. This ensures your customer journey map remains accurate and relevant.
Download your free “Gamification Guide”
Get your PDF now and start transforming your approach to digital engagement!

Mapping the B2B customer journey is an essential practice for businesses seeking to understand and optimise their interactions with customers. By comprehensively mapping the key stages and touchpoints, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behaviour, preferences, and pain points.
Understanding the B2B customer journey enables companies to align their efforts to deliver a seamless and satisfying experience at every touchpoint. Ultimately, an effective B2B customer journey map serves as a roadmap for success, guiding businesses towards delivering exceptional experiences.
Latest Posts

The impact of machine learning on finance is significant. Thanks to this technology, financial institutions are now equipped to make efficient decisions. Through the analysis of data sets, machine learning […]

Banking compliance training isn’t just another task. It’s the stage where everything else performs. Banks must navigate a myriad of regulations and laws. After all, this is a trust-driven, high-stakes […]

Discover how gamification in fintech is revolutionizing financial engagement, making banking fun & boosting user loyalty.

Comments are closed.
- Marketing evaluation
- Case studies
A complete guide to the B2B customer journey

Daniela Nocker

The B2B customer journey (or B2B buying journey) is a rather complex process that typically involves many different touchpoints on the customer side. It’s important to get this process right, since businesses that understand the B2B customer journey can create a more positive customer experience, which, in turn, can lead to more sales and higher customer satisfaction. And that’s what we all want, right?
If you find yourself lost somewhere along your customer journey, we’re here to help! This blog post explores the B2B customer journey, its stages and pivotal touchpoints. As you’ll see, there are both a conventional way and a recently more prominent way to approach the B2B customer journey. We will also cover:
- The customer journey map
- Strategies to maximise customer satisfaction and loyalty
- An evaluation of a successful B2B customer journey implementation
1. What is the B2B customer journey?
The B2B (business-to-business) customer journey is the process that individuals go through when considering purchasing products or services for their business from other businesses. If you want to read about what B2B marketing is more broadly and how it works, read our complete guide to B2B marketing .
In contrast, the B2C (business-to-consumer) customer journey is the process consumers go through when considering and purchasing products or services from businesses for their private usage. While there are some similarities between the B2C and B2B customer journeys, there are also important differences to highlight:
1.1. Understanding your B2B customer journey
A clear picture of the B2B customer (or user) journey is crucial and allows businesses to:
- Improve customer experience : By understanding customers’ needs and pain points at each stage of the customer journey, businesses can create a more integrated experience for their target audience.
- Optimise marketing and sales strategies : By understanding the different channels and touchpoints potential customers use during their journey, both marketing and sales can plan and execute their strategies more effectively.
- Enhance customer satisfaction and retention : Businesses can increase customer loyalty by providing a positive customer experience throughout the journey.
1.2. The typical (and perhaps outdated?) B2B customer journey stages
The B2B customer journey includes the entire process buyers go through, from the initial awareness stage to the final purchase decision and post-purchase stage. While the specifics may vary across industries and organisations, this more traditional B2B journey (also known as a traditional funnel) generally looks as follows:
- Awareness: At this initial stage, potential B2B customers identify a need or problem and seek solutions.
- Research: During this stage, buyers look for different solutions to their challenges and rely heavily on online resources, search engines, industry publications, and peer recommendations to gather information.
- Consideration: Prospects enter this stage once they are aware of potential solutions. Here, they look at different options, compare features, and assess how well each solution aligns with their unique needs.
- Evaluation: During this stage, prospects delve deeper into the shortlisted solutions and engage with sales representatives.
- Decision: Once the evaluation is complete, buyers commit to a particular vendor and make the purchase.
- Post-decision: The (now) customers use the product or service and evaluate their satisfaction.
With the above stages in mind, it’s important to remember that, in most cases, the customer journey is not linear . Customers may move back and forth between different stages or be stuck in one. Touchpoints might also differ throughout the journey, and, in today’s world, a big part (up until the evaluation stage) is done by the buyers themselves, without any company interaction.
1.3. A more recent approach: Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
Many B2B professionals now consider the above model as a traditional outlook on the marketing funnel or customer journey. It began to face challenges as a decreasing proportion of overall generated leads resulted in sales, making it tough to prioritise it on a larger scale. This is where ABM (Account-Based Marketing) comes into play.
According to HubSpot , “ Account-based marketing (ABM) is a strategic approach focusing on high-value accounts in a market or business. ABM strategies focus on creating personalised buying experiences for better customer acquisition, relationship-building, and business growth. ”
ABM as a strategy has been in existence for many years, but when it comes to actual implementation by businesses, its adoption has been mixed, with many companies only recently beginning to realise its potential. This is partly due to advancements in technology and data analytics, which have made it easier to target and engage specific accounts with personalised content and messaging.
But back to why we speak about ABM in this context. ABM takes the traditional (lead-based) funnel and flips it. The strategy focuses on the following (account-based) funnel stages instead:
- Identify: Your available market is out there and, guess what? They are looking for your solution to their identified challenge, too.
- Expand: Same as above, but now the focus lies on specific target accounts that are trying to solve their identified problem.
- Engage: Potential customers are looking for qualitative content to learn more about specific products or services – now is your time to shine and stand out to them!
- Advocate: For a customer, it’s never the end of the road as it might be internally (sale went through, job done!) – customers still expect to be satisfied throughout all touchpoints.
As you might have noticed now, we’re also looking at a customer journey here – but one from a vendor’s perspective, based on accounts. You can read more about the importance of both vendor and client perspectives in the customer journey later in this article.
2. The B2B customer journey map
The B2B customer journey map visually represents a potential customer’s steps as they interact with a vendor. It shows the user’s thoughts, feelings, and actions at each stage of the journey and the touchpoints, channels, and interactions that occur.
2.1. What is the B2B customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual tool that businesses use to improve the customer experience. It helps companies visually identify the different touchpoints that potential customers have with their brand and understand their needs and expectations at each stage of the journey.
2.2. Identifying touchpoints, channels, and interactions
Touchpoints are when a customer interacts with a company. They can be online or offline, and they can include things like:
- Website visits
- Social media post views
- Content engagement (blog articles, videos, and so on)
- Reach-outs to sales or customer support
Channels are how customers interact with a company. They can include:
- Social media
Interactions are the specific actions that customers take at each touchpoint. For example, a customer might visit the company’s website to browse content or call customer support to ask a question.
3. A visual overview of a customer journey map
Gartner’s B2B customer journey map highlights the idea of non-linearity and unpredictability and emphasises the “loop” that customers engage in across a typical B2B purchase. In fact, we believe you shouldn’t strive to understand how every single customer behaves across every single touchpoint and channel .
Another visual example of the customer journey map is B2B International’s overview , as it shows more details, including perceptions, risks and opportunities.
3.1. The B2B customer journey map (Precis’ version)
As you can see, there are many pretty and informative infographics showcasing customer journey map examples all over the internet. Really, a lot of them.
But most of them are either from the customer or vendor perspectives, rarely both. So we decided to make our own example – one that combines both areas and visualises their interconnectedness. We’ve intentionally adjusted the stages too, to ensure a more coherent integration.
However, it’s essential to remember the B2B customer journey is rarely a straightforward one – and expecting such simplicity would be (unfortunately for us marketers) overly optimistic. Therefore, our diagram should be viewed not as a set-in-stone blueprint, but rather as a flexible framework guiding the alignment of vendors and clients throughout the B2B customer journey. So we recommend you use this as a foundation to develop your own detailed and customised customer journey map based on your own specific needs.
⚠️ The “Advocate” stage should not be seen as the conclusion, but as a pivotal point that ideally feeds back into the “Identify” stage (through positive word of mouth), thereby creating a continuous customer journey loop. ⚠️
3.2. The Precis B2B customer journey map at work
By understanding the details of a customer journey such as in the example above, companies can identify opportunities to improve the experience for their potential customers.
- For example, they might realise that their website is challenging to navigate, or that their sales response times are too long. By addressing such issues, the customer journey will become smoother and, as already highlighted above, overall customer satisfaction will increase.
4. Maximising the B2B customer journey with effective strategies
4.1. how do you create a successful customer journey.
Now that we looked at a customer journey example, let’s dive into effective strategies to create a successful customer journey. In general, the following tactics are key:
- Understand your customers’ needs, pain points, and goals . What are they looking for in a product or service like yours? What challenges are they facing? Once this is clear, you can tailor your marketing and sales efforts to meet their needs and personalise the customer experience for them.
- Offer a consistent omnichannel experience . Buyers expect to be able to interact with you through a variety of channels, including your website, social media, and email. Make sure that your experience is consistent across all channels so customers can easily pick up where they left off.
- Collect and analyse customer feedback . It’s essential for improving the customer journey, so make it easy for customers to provide feedback and use it to make improvements.
To ensure a positive B2B customer experience throughout all journey stages, you can start by implementing the following strategies per stage. If you peek at our infographic above, this would now be the vendor’s point of view:
- Identify : Establish a strong online presence and brand awareness for your business as potential customers might stay in this stage the longest, sometimes even completely unaware of their potential challenge (related to that, read more about Demand Generation ).
- Attract : Provide valuable content through SEO and social media to attract potential customers to your business.
- Engage : Create compelling product pages, industry-focused case studies, and testimonials to showcase the value proposition of your company’s offering and differentiate yourself from competitors.
- Close : Now it’s time to streamline the purchasing process, ensuring it is convenient and transparent for potential customers. Provide comprehensive product information, answer queries, and address any concerns prospects might have. Demonstrating expertise, reliability, and excellent customer support can significantly influence the decision-making process.
- Advocate : The B2B customer journey does not end with the purchase. Now you should focus on nurturing relationships with customers by offering ongoing support, training, and proactive assistance. By doing so, you can foster loyalty, encourage repeat business, and generate positive referrals.
4.2. How do you evaluate the effectiveness of B2B customer journey strategies?
Measuring and optimising key metrics is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of B2B customer journey strategies. By tracking the right metrics, companies can identify areas where they excel and others where they need to improve.
Overall, we shouldn’t measure towards leads but look at the bigger picture instead: sales pipeline and company revenue. However, when talking about the customer journey, which heavily involves a company’s website, content and so on, we suggest tracking and evaluating these key metrics:
- Website traffic : The number of visitors coming to your website
- Conversion rate : The percentage of visitors who take a desired action, such as signing up for a newsletter or contacting sales
- Lead quality : The likelihood of a lead converting into a customer
Additional (and more sales related) metrics to measure can be:
- Sales cycle length
- Customer lifetime value (CLV)
Once you have collected data on the above metrics, you can use it to optimise your customer journey strategies. For example, if your website traffic is high but your conversion rate is low, you may need to improve your landing pages or calls to action.
Also, it is important to note that customer journey optimisation is an ongoing process. As your business grows and changes, your customer journey will change, too. Therefore it’s important to continuously monitor your key metrics and adjust your customer journey strategies accordingly. And that’s done in teamwork – Marketing, Sales and Customer Success all together.
In summary, understanding and optimising the B2B customer journey is essential for enhancing the customer experience and driving sales and satisfaction. This journey is multifaceted, encompassing stages from awareness to post-purchase, often not following a linear path.
The B2B customer journey map visually illustrates these stages and interactions, providing insights for improvement. Effective strategies involve understanding customer needs, ensuring a consistent omnichannel experience, and collecting and analysing feedback.
Measuring key metrics like website traffic, conversion rate, and lead quality helps evaluate strategy effectiveness, enabling ongoing optimisation. In today’s competitive B2B world, understanding the customer journey is crucial for building lasting customer relationships and achieving long-term success.
Psst! We’ve even held a few B2B events, too .
Relevant posts

How to manage SEO during a website migration

Third-Party Cookies and Privacy Sandbox – Explained

Experts eye: Marketing and Sales alignment in the SaaS industry
Are you an agency specialized in UX, digital marketing, or growth? Join our Partner Program
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
A step-by-step guide to mapping the B2B customer journey (with real-life examples)
It’s tricky to effectively map out all the different user personas and purchasing processes in the B2B customer journey. But understanding your customer's experience is key to improving conversions and retaining users.
That’s why it’s essential for B2B companies to follow an effective customer journey mapping process.
Last updated
Reading time.

Use our step-by-step guide to create a map for your business-to-business (B2B) company that tracks your users’ unique journeys, giving you key insights into your customers and their needs.
Get valuable insights into your B2B customer journey
Hotjar helps you understand how buyers interact with key web and product touchpoints to improve their experience.
How to map out the B2B customer journey in 5 steps
Mapping the customer journey is essential in understanding your buyers and turning them into loyal customers.
Follow these steps to create an actionable B2B customer journey map that gives insights into who your customers are and helps you build an optimized user experience (UX) for them:
1. Set goals unique to your business
Before you start mapping out the customer journey, define your larger business and customer goals.
To begin, ask yourself what you want your customers to achieve—what are their jobs to be done (JTBD)? Does your business depend on repeat customers, or are your products one-off larger ticket items? Your customer journey will look different if you sell business clients a one-time-purchase product, like a hardware device, versus a subscription service.
For example, different B2B firms—like GE Renewable Energy and Hubspot—will have very different objectives. A company like GE Renewable Energy that sells large equipment to B2B customers may prioritize goals like generating more website conversions and creating brand advocates who recommend GE products to other businesses in the industry.
On the other hand, a software company like Hubspot will need to emphasize the customer journey's onboarding and renewal components to increase customer retention.
Know what your goals are before creating your B2B customer journey map to prioritize the most important steps for your customers and your business.
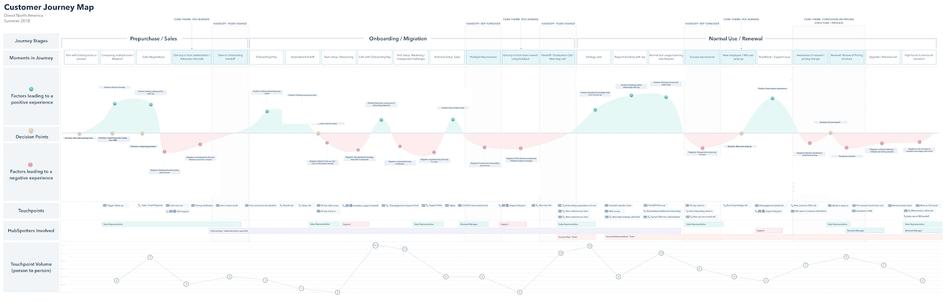
2. Identify your customer segments
The purchasing process is an especially nuanced cycle for B2B businesses, because the end users of your product or service are often not the same people making the purchasing decision .
John Forberger , founder of Forberger Communications , highlights this complexity:
Typically, multiple people have influence over a deal. Maybe one person researches how to replace a current tool, then a second person does a demo, and a third person actually cuts the check.
Don't just focus on the users who’ll try out your product or service, or on the C-level decision makers: understand every stakeholder involved in the purchasing process to map out an accurate B2B customer journey .
Consider the different needs of end users versus purchasers and think about how your user personas may differ depending on company size and type.
Take Canva, for example: the design tool is used by a variety of businesses, from freelancers to large corporations like PayPal and Danone. Understanding different user profiles and needs gave Canva the insight they needed to design their homepage for different B2B customer types who can choose their own adventure and head off on their most relevant user journey.
Pro tip: once you define your user profiles, learn more about different buyer types by asking the right survey questions . Use these questions to dig deeper into user goals and jobs to be done to better design the B2B customer journey.
3. Define the B2B customer journey stages
Once you have clear goals and user personas, it’s time to define the stages of the customer journey. Let’s take a look at a typical 7-stage B2B customer journey, using the popular SEO tool Ahrefs as an example.
Awareness: a buyer becomes aware of their problem and begins to search for solutions, which is when they discover your brand. In our example, a buyer knows they need to improve their website’s SEO performance, so they search for “best SEO tools” and come across Ahrefs. They visit the homepage, where the tool’s value proposition entices them to learn more.
Consideration: customers consider your product or service as a potential solution. Here, the buyer visits Ahref’s website and learns about the brand’s unique selling proposition , reads about features, watches a demo, explores resources like the Ahrefs blog and SEO guide, and weighs up whether Ahrefs is the product solution for them.
Decision: the buyer makes a decision and purchases the product or service that best fits their needs. In the case of Ahrefs, the buyer purchases the subscription (Lite, Standard, Advanced, or Enterprise) that’s right for them. The Ahrefs website guides users in the decision and purchasing process by displaying clear CTAs that encourage users to become paying customers.
Onboarding: the buyer starts to use the product, goes through the onboarding process, and gets familiar with the tool by reading guides and watching demos. They (ideally) start to adopt it into their everyday workflow.
Support: users contact customer teams as they need support. In our example, customers have easy access to customer support agents and the Ahrefs help center to smoothly resolve issues and questions.
Retention: customer retention is a key part of the B2B buyer journey, and at this stage, buyers decide whether or not they’ll remain loyal customers and continue using your product. Ahrefs offers a range of subscription models and gives users who sign up for an annual subscription a two-month free plan.
Advocacy: the final stage in an ideal customer journey is turning customers into brand advocates. Ahrefs has done a good job of this: the homepage shows reviews from real users who recommend the tool, including pro SEOs, content marketers, and agencies.
Pro tip: your product's user journey may look different depending on your company and customer types: a business customer purchasing a one-off product will have a very different journey from a company subscribing to a service.
Oleg Donets , founder and chief marketing officer at Real Estate Bees , points out how the stages of non-SaaS B2B customer journeys can differ from SaaS journeys :
"Since the vast majority of SaaS companies utilize subscription revenue models, this directly impacts the customer journey. B2B customer journeys often scale back a notch shortly after a sale has been made, but that’s when the customer journey of a SaaS company just starts kicking in."
4. List all possible B2B customer touchpoints
Once you map out the steps in your customer’s B2B journey, identify each ‘touchpoint’ where they interact with your company, from social media posts to your homepage CTAs and your product itself.
Let’s go back to the Ahrefs example.
A key touchpoint in the early awareness, consideration, and purchase stages of the B2B customer journey is their homepage and a clear call-to-action (CTA) button. These onsite touchpoints show customers what their next steps in the product experience (PX) should be and give them the information they need to make a decision.
In the next phases—onboarding and support—follow Ahrefs' example by making it easy for users to connect with your B2B business, resolve their issues, and upgrade. On the Ahrefs help center page, customers can reach out to representatives and receive support within minutes.
Make sure you continue mapping out how your users interact with your B2B after they become customers—in the retention and advocacy phases . How can you make it easier for them to renew their subscription? Do you offer any rewards for referrals?
As well as mapping out touchpoints by customer journey phase, consider the different touchpoints experienced by different user personas.
For example, the product experience of high-level executives who make the purchasing decision may not be the same as their employees who are your end-users.
By identifying key B2B customer journey touchpoints for different customers and purchasing stages, you can improve UX, making product advocates out of your buyers.
Pro tip: use Hotjar's Observe tools—like Heatmaps and Recordings —to explore how your users interact with key B2B customer touchpoints on your website and product—and get the insights you need to improve their journey.
Hotjar Session Recordings show you how users experience your page to improve low-performing touchpoints
5. Measure and analyze the success of the customer journey
One of the most important customer journey mapping best practices is measuring the success of your customer journey.
Use the right customer journey mapping tools to help you evaluate the impact of your touchpoints. For best results, combine website analysis tools with software that offers more in-depth product experience insights and user feedback.
Use Hotjar's Observe tools to track how customers are engaging with your touchpoints. Then use Hotjar’s Ask tools—like Surveys and Feedback widgets—to learn what your users really think and feel about their B2B experience.
Tools like Google Analytics also help in mapping and analyzing the customer journey, giving you more general information on the types of users that visit your website and whether they convert or bounce.
Combine Hotjar with Google Analytics to dig deeper into B2B customer touchpoint insights to improve conversion rates and enhance the customer experience .
After you’ve mapped the customer journey, regularly check in on your key goals and what matters most to your customers. Keep measuring the outcomes of your customer journey to understand which aspects of the B2B customer journey are successful and what needs improvement.
Create a brilliant B2B user journey for happier customers
Successfully mapping out the B2B customer journey requires a deep understanding of all your buyers and how they interact with your brand and product.
Adapting these steps to your customers and company helps you create a customer journey map that identifies what your users need at each stage of the buying cycle to provide them with the best possible experience.
Use Hotjar to understand how buyers interact with key web and product touchpoints—and improve their experience with your B2B business.
FAQs about B2B customer journey mapping
Why do you need b2b customer journey mapping.
Visualizing the customer journey is the first step to understanding and improving it. B2B customer journey mapping helps you identify what type of experience customers have with your product at every stage .
Without B2B customer journey mapping, you won’t understand the process of converting potential buyers into loyal customers, meaning you have no way to make adjustments that enhance the customer journey.
How is the B2B customer journey different from other customer journeys?
With the B2B customer journey, there are often more stakeholders involved in the decision-making process than with a B2C customer journey. For that reason, the B2B customer journey is often much longer and depends on various decision-makers .
Plus, the B2B customer journey is often cyclical, as customer retention is such a key goal for many B2B companies.
What are some common mistakes of B2B customer journey mapping?
A big mistake in B2B customer journey mapping is failing to consider all user personas. B2B products often have a number of diverse customer profiles, whether that be different positions within one company (administrator vs. C-level executive) or different types of companies (like a small business vs. an enterprise).
Another common mistake is not taking into account the length and complexity of the B2B customer journey , which often has a lengthy approval process, and requires several different stakeholders to sign off on purchasing decisions.
CJM research
Previous chapter
Next chapter
B2B Customer Journey: Creating a B2B Customer Journey Map

Customer journey map is a versatile tool that allows businesses to walk in their customer's shoes and get a better understanding of how and why customers interact with the business. In long-term B2B relationships, customer journey mapping is essential.
In this blog post, we’ll discuss the importance and intricacies of B2B customer journey mapping. We’ll also provide a list of the key B2B customer touchpoints and walk you through the process of creating a B2B customer journey map.
B2B Customer Journey Map
Customer journey is a holistic representation of all the interactions a customer has with a company, from discovery to purchase and post-purchase. A customer journey map is a visualization of the entire customer journey from beginning to end.
In B2B, a customer journey map highlights all the touchpoints a client has with a company, which allows the sellers to get an insight into the customers’ decision-making process, identify pain points, and optimize customer experience, which ultimately leads to more sales and revenue. The B2B customer journey starts with the customer acknowledging a problem or an unmet need and ends with post-purchase support or ongoing relationship management.
Customer journey B2B vs B2C
While B2B and B2C customer journeys involve similar stages, B2B customer journeys are more complex and multifaceted. Firstly, B2B purchases involve multiple decision-makers that participate in different stages of the decision-making process and have unique expectations. For example, executives might want the most affordable solution that the team might not find as convenient. Secondly, the order value in B2B is usually much higher, so every customer is valuable and can make a big difference for the company. Lastly, the B2B buying journey is more complex and may last for several weeks or even months.
The Importance of B2B Customer Journey Mapping
For B2B relationships, customer journey mapping is particularly important. Here’s why.
Customer centricity
Businesses often make the mistake of focusing too much on their product and not having a deep enough understanding of the customers and their buying process. Customer journey mapping allows businesses to get a bird's eye view of the customer journey and stay focused on customer needs and expectations. A well-crafted customer journey map can help the seller see its product from the buyer’s perspective, provide proactive support, and optimize customer experience .
Understanding complex purchase process
B2B customer journeys are not as straightforward as customer journeys in B2C. While that makes customer journey mapping more difficult, it is also more important and effective when done right. In B2B, you need to impress different employee segments with unique priorities and needs. By creating a customer journey map, you can identify which touchpoints are working in your favor and which ones need improvement.
Personalization
B2B customers expect you to have a deep understanding of their businesses and provide a high level of personalization. By mapping the customer journey, sellers can identify opportunities to deliver tailored experiences, address specific needs, and provide relevant information at each stage. With a detailed customer journey map, you can make sure you’re not neglecting any touchpoint or actor and provide seamless customer experience throughout the customer journey.
B2B Customer Journey Touchpoints
B2B customer touchpoints are the various interactions that occur between a business and its customers throughout different stages of the customer journey. Here's a breakdown of the typical stages in the B2B customer journey and some examples of touchpoints that may occur during each stage. Remember that touchpoints can vary depending on the industry, target audience, and business model.
- Industry conferences and events
- Trade shows and exhibitions
- Online advertising and display ads
- Social media presence and engagement
- Content marketing (blog posts, whitepapers, e-books)
- Search engine optimization (organic search results)
- Consideration
- Webinars and educational events
- Case studies and success stories
- Product demos and free trials
- Comparison charts and feature matrices
- Vendor websites and online product information
- Third-party review sites and testimonials
- Sales presentations and proposals
- Pricing and negotiation discussions
- Customized product demonstrations
- Technical documentation
- References and referrals
- Competitor analysis and benchmarking
- Order placement and invoicing
- Contract negotiation and signing
- Procurement and purchasing processes
- E-commerce platforms or online ordering systems
- Vendor management and due diligence
- Post-Purchase
- Onboarding and implementation support
- Customer training and workshops
- Account management and relationship building
- Help desk or customer support services
- Feedback surveys and satisfaction measurement
- Renewal reminders and upselling/cross-selling opportunities
B2B Customer Journey Map
Creating a B2B customer journey map involves visualizing the entire customer journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase support. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you create a B2B customer journey map:
1. Identify your customer personas
Start by defining the different types of customers or buyer personas you’ll be interacting with. When you understand their characteristics, pain points, goals, and motivations, you can tailor the journey map to specific customer segments .
2. Outline the stages
Identify the main stages in the customer journey based on your typical sales process. Typically, that includes stages like awareness, consideration, evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase but ultimately depends on your specific business model.
3. List customer actions and emotions
For each stage, identify the key actions your customers are likely to take and the emotions they may experience. These actions can include researching solutions, attending webinars, evaluating proposals, making a purchase, etc. Emotions can range from frustration and confusion to excitement and satisfaction.
4. Identify touchpoints
Map out the interactions that customers have with your business at each stage. This includes online and offline touchpoints such as website visits, social media engagement, phone calls, meetings, etc. Consider all possible channels and customer touchpoints throughout the journey.
5. Capture customer goals and pain points
Understand the goals your customers have at each stage and the pain points they encounter. Goals can be things like finding a solution to a specific problem or streamlining their operations. Pain points may include budget constraints, complex decision-making processes, or lack of information.
6. Evaluate customer expectations
Determine what customers expect from your business at each stage. This could be timely and relevant information, personalized assistance, quick response times, or a seamless purchasing experience. Understanding these expectations will help you deliver the right experience.
7. Analyze gaps and opportunities
Compare the customer expectations and goals with the actual touchpoints and experiences you provide. Identify any gaps where customer needs are not being met to find opportunities to enhance customer interactions, streamline processes, or address pain points.
8. Visualize the customer journey map
Create a visual representation of the customer journey map. This can be a flowchart, infographic, or any other format that helps you visualize the stages, touchpoints, customer actions, and emotions.
9. Refine and iterate
Regularly review and update the customer journey map as you gain more insights and feedback. Continuously iterate the map to align with changing customer expectations, market dynamics, and business goals.
B2B Customer Experience Best Practices
Follow these tips to optimize your B2B customer experience.
Measure loyalty and retention
To determine whether your customer relationship management efforts are successful, you need to constantly measure and analyze customer retention and loyalty. By calculating metrics like Customer Retention Rate or Net Promoter Score, you can gauge customer satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
Understand the emotional reasoning
While B2B decisions are less emotional than B2C decisions, it’s important to consider the emotional motivations of your customers. For example, an executive may express that they are looking for a cheap solution because they want to find the most cost-effective tool for their business. If you can demonstrate that investing in a more expensive tool could lead to more sales and higher revenue, the executive might realize that the more expensive tool is actually more cost-effective.
Optimize processes with AI
Using AI-powered tools can help you make the customer experience more convenient and improve your B2B customer retention. Whether your customers are businesses or individuals, every improvement and update should be based on customer feedback. After the purchase, B2B customers are usually interested in continuing and improving their relationship, so they are willing to provide more qualitative feedback. By analyzing that feedback with Essense, you can get valuable suggestions for your business and optimize your B2B customer journey. Powered by AI, Essense turns unstructured data into actionable insights in just a few clicks.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest news and updates.
Related posts
The B2B Customer Journey: Back to The Basics

The B2B customer journey is a complex matter, packed with a host of different touchpoints that affect customer experience. Understanding that complexity is essential in planning your customer service and marketing strategies.
So, how can you analyze your journey and go about improving it in the right way? We’ve come up with an essential guide to help you do just that.
- Definition of B2B customer journey
- B2B customer journey stages
- Difference between B2B and B2C journeys
- Building a customer journey map
- Improve your B2B customer journey
Let’s get started.
What is a B2B customer journey?
The B2B customer journey is the collection of touchpoints and interactions a customer has with a B2B company, from their very first encounter, all the way through to post-purchase.
Consider a B2B buyer who becomes aware of a SaaS software company that can address their particular needs, for example. There’s a whole load of other steps to go through before committing to a purchase. And even after purchasing, there’s still the setup, making sure they're getting the most out of it, and so on. That’s all part of the customer journey.
It’s the lasting impression of this journey that creates the all-important customer experience .
The B2B customer journey stages
The B2B customer journey stages consist of five main areas: awareness, consideration, conversion, loyalty, and advocacy. The exact stages may be broken down further or vary depending on the specific type of business (for example, some companies may require onboarding, or have multiple points of purchase).
Incredibly, throughout this whole journey, most B2B buyers spend only 17 percent of their time actually talking to you, according to Gartner's 2019 Future of B2B Buying Journey Report.
The rest of the journey happens "behind your back" — mostly researching and discussing with their team. That means that quality content is of paramount importance to give buyers access to the information they need to move through the stages.
The table below provides a general overview of how the B2B customer journey could look.

Difference between B2C and B2B journeys
The difference between B2C and B2B customer journeys is essentially that B2B customer journeys are more complex. And of course, they’re selling to different audiences.
That means that although the overall structure, running from awareness through to advocacy, is similar in both, behavior is guided by different motives in B2B. We can therefore make a number of distinctions. The table below shows some of the most important.

These differences impact how a B2B company goes about its business.
For example, in the case of selling to multiple people, when you’re talking to a non-decision-maker, it might make sense to talk about how user-friendly your service is, and try to give them the tools they need to make a business case to the decision-maker.
On the other hand, if it’s the actual decision-maker you’re talking to, you might want to think about a strategy that is much more focused on business results and KPIs.
6 Steps to building a customer journey map for B2B
Creating a customer journey map for B2C helps chart the stages your customers go through. It is a crucial first port of call in improving your customer journey, because it allows you to find touchpoints you had neglected before or bottlenecks that appeared. Here are six steps to help you create your B2B customer journey map.
1. Analyze typical buying groups
In a B2B environment, there are often multiple people involved, all with different roles and responsibilities. In fact, the typical buying group for a complex B2B solution involves six to 10 decision makers according to Gartner. And they’ll all have different requirements you’ll have to take on board. Make sure you understand their level of influence on buying decisions, too.
2. Understand your customers’ goals
What needs are your buyers trying to fulfill or what problems are they trying to solve? Take the time to get a handle on their motivations so you can better understand the value you’re going to provide.
3. Leverage data and analytics
Analytics is an extremely useful tool in your B2B customer journey arsenal. It can help you move away from making subjective decisions and ensure you instead deal in cold, hard facts. Use data from multiple sources like your CRM or customer experience platform to get a holistic view of the journey.
4. Build out the B2B customer journey stages
As mentioned previously, your precise customer journey map for B2B will depend on your business’ exact processes. To make things easier, it might help to start from a generic template (you can use the generic stage layout above), and then split that out into more complicated components as you go. It helps to put yourself into your customer’s shoes (perhaps assuming one of your buyer personas) and try to go through the B2B customer journey stages as an experiment.
5. Lay out the different touchpoints
Many B2B touchpoints, for example websites, blog content, and organic search, are shared between B2B and B2C. Others, however, are more specific to B2B. Demos, sales meetings, onboarding — you need to map all that. A digital customer journey may be more commonplace now, but don’t forget to take into account analog channels like print media, too.
6. Define your own goals
It’s useful to keep the end results you want in mind as you go through the process as well. Ultimately you’re going to want results in areas such as retention and customer satisfaction . Gather customer feedback and cross-reference your business analytics to see if you hit these goals.
Note : Depending on your company’s processes, it may make sense to have one customer journey map per major B2B client.
How to improve your customer journey for B2B
According to Gartner’s 2019 report, 77 percent of B2B buyers feel that making a purchase is very complicated and time-consuming. And, ultimately, that is bad for business. To minimize complications, make sure you optimize your B2B customer journey the right way. Here are some ideas to get you going:
- Create buyer personas. When we buy a product, what we’re really doing is ‘hiring’ it to help us do a job, according to Harvard Business School professor Clayton Christensen. A good place to start then is with a list of your customer’s jobs . What is it that they need to do? Consider factors like your contact’s position in their organization, their business needs, and their role within the decision-making process. These days, 60 percent of all B2B tech buyers are millennials (2 percent are even Gen Z) so this is definitely something to take into consideration.
- Stay focused on content creation. More than half of all B2B buyers view at least eight pieces of content during the purchase process, and 82 percent of buyers viewed at least five pieces of content from the vendor prior to purchase, according to Forrester. Make sure each piece of content is aimed at improving the customer journey and sets up the next action you want to see from your buyers to move prospects along the journey. Structure content around the issues that are most important to your customers.
- Identify and remove roadblocks. Make targeted interventions to remove friction and improve results by working backward to pick out anything from your customer journey that could get in the way of a sale. Factors nearest to the purchase point are often the lowest-hanging fruit.
- Qualify your leads properly. Don’t take any old form-fill to be a qualified lead. At the end of the day, pushing a lead through the process when they’re not ready is going to be damaging for everyone, your business included.
- Get onboarding right. Make sure your onboarding process is as smooth as possible. It will help you stand out from the crowd and lay the path for customer success.
- Stay front of mind. Nurturing current customers is crucial. Keep in touch so they stay engaged, update them on how things are going, and give them access to useful reports. And when it comes to renewal dates, make sure you send out timely reminders.
Learn from the B2C journey
Customer journeys tend to be thought of in terms of B2C. In fact, the reality is that in B2B, buyers are not only looking for but expect a buying experience like that of a B2C customer. And if there’s one thing B2C does well it’s personalization.
Yet, can you think of a time you’ve had a truly personal B2B interaction? To really stand out from the crowd with your B2B customer journey, always keep in mind that behind every brand logo are actual human beings.
What are your thoughts about the B2B customer journey? Let us know with a comment.
Looking to better manage your customer experience and gain greater insight into your customer journey? See what the Acquire platform could do for you by booking a demo with our team of experts.
Related Articles
These Are the Customer Journey Phases in B2B
In the age of digital marketing, a B2B customer's journey from initial contact with a brand or product to purchase has become much more complex than in the past. However, the phases of the B2B customer journey extend far beyond this buying process.
Marketing on a wide variety of channels, blogs, social media sites, review and comparison portals, and many other touchpoints between companies and customers have ensured that the B2B customer journey can take many more routes these days.
Only rarely does the customer journey lead directly from initial contact to purchase. This presents companies with special challenges.
What Is the Customer Journey?
The term customer journey is one of the most central concepts in marketing. It describes the customer's journey from the first contact with a company, a brand or a product to the purchase and finally to the use of the product or service.
The customer journey, which runs in cycles, includes all the touchpoints that customers have with a company during the purchase decision process . In today's age of digital media, a customer journey is much more complex than in the past.
Companies not only have direct touchpoints with customers, such as through advertisements, a phone consultation or a video demo, but usually also a variety of indirect touchpoints. These include rating portals, company blogs and forums where customers inform themselves about companies and their products.
Against the backdrop of the increased complexity of the customer journey, the customer's journey is now also much more flexible in terms of time.
Depending on the number and intensity of direct and indirect touchpoints, the customer journey can last from just a few days to several months.
For companies, an in-depth understanding of all customer journey phases and the individual touchpoints is a basic prerequisite for a customer-oriented orientation of marketing and sales.
Countless studies have looked at all the details of the customer journey in recent years. Two of the most important study results that companies should definitely keep in mind are:
only 2% of customers buy a product from a brand after an initial contact.
Customers interact with a brand an average of six to eight times before becoming its customers.
Companies that do not know the journey of their (potential) customers will thus have the greatest difficulty in acquiring new customers, as well as retaining existing customers in the long term.
Source: incomplete Customer Journey according to Pedalix
Customer Journey Phases at a Glance
The detailed mapping of a customer journey and an in-depth understanding of all phases of the customer journey are decisive prerequisites for aligning one's own marketing and sales in a customer-oriented manner.
The clear separation of all phases and the full representation of all possible touchpoints contribute to a company's ability to successfully accompany a customer throughout his entire journey.
The correct understanding of the customer journey and customer centricity is therefore an important contribution to increasing sales figures, increasing customer satisfaction and extending the customer relationship in every company.
Customer Journey According to AIDA
In recent years, various models have been developed to map the customer journey. These models differ in terms of their division into phases and the adoption of perspectives.
Marketing and sales professionals face the challenge of finding the most appropriate customer journey model for their company or brand.
Source: Own representation based on the AIDA model
The first description of the customer journey goes back to the American advertising strategist Elmo Lewis. As early as the end of the 19th century, he developed a model for advertising effectiveness that is known today by the acronym AIDA.
The four letters stand for the terms
and Action.
According to the Customer Journey AIDA model, customers pass through four stages on their customer journey:
In stage 1 (Attention), the customer's attention is gained. Through advertising or other interaction, he learns of the existence of a brand or product.
In stage 2 (Interest) the customer's interest is aroused. He begins to show interest in a market or a product.
In the third stage (Desire) the interest turns into a concrete desire. The customer wants to own a product.
In stage 4, the customer converts his desire to own the product into a purchase (action).
However, the AIDA model, as well as the classic sales funnel, fall short, as they stop at the conclusion of the purchase or contract
On the one hand, countless scientific studies in recent decades have shown that the monocausal stimulus-response model underlying the AIDA theory rarely corresponds to reality. The human stimulus-response pattern has been shown to be much more complex than the AIDA model suggests.
And secondly, the number of touchpoints between companies and customers has increased many times over in the age of the Internet and extends far beyond the purchase.
Against this backdrop, the customer's travel route has become much less straight and much more "curvy".
Extension of the Customer Journey Phases
As an extension or update of the AIDA model to the present day, it is recommended to use a revised 4-phase customer journey model.
Source: Customer Journey according to Pedalix
It starts with the Attract phase. A customer has a problem and becomes aware that a product or service can solve the problem.
This awareness can come through various touchpoints, such as advertising, social media, or word of mouth.
So during this phase, the potential customer is attracted via their interest.
The second phase is the Engage phase. The customer informs himself in detail about the topic relevant to him and the associated solutions.
Information can also be obtained from a wide variety of sources, such as search engines, blogs or rating portals.
The potential customer searches for further information that deepens his basic knowledge and provides him with a sound basis for decision-making.
Phase three of the model is the conversion phase. The potential customer decides to contact a sales representative who accompanies him through the closing phase of the sales funnel .
Here, too, there can be several possibilities as to which touchpoints are used to complete the actual purchase.
Examples might include a face-to-face sales call, an online form, or a phone sales process.
The last phase, which is new compared to the AIDA model, is the Delight phase. The customer uses the product, is satisfied with the performance and becomes a returning buyer.
Provided the customer is delighted with the product, he is likely to recommend it to industry peers and possibly a wider audience.
Touchpoints for the Delight Phase are, for example, newsletters, reviews and surveys or customer service.
This four-phase model of a customer journey has the advantage that it fully maps all phases of customer contact before, during and after the purchase.
The more accurately a company maps the individual touchpoints with the customer within the different phases, the more precisely and specifically it can address the customer's individual needs.
Furthermore, a comprehensive representation of the customer journey makes it easier for companies to successfully accompany customers from phase to phase.
Related Posts
Shortening the b2b sales cycle: here's how it works.
Achieving a contract more efficiently is a focus for every company. However, this is often not so easy. To effectively shorten the B2B sales cycle,...
Your B2B Customer Journey Has these Touchpoints
You know your direct sales channels, of course. But what about touchpoints earlier in the B2B buying process? Do you have a strategy in place to...
10 Steps to an Efficient B2B Sales Funnel
A well-filled and smoothly functioning B2B sales funnel is the basis for a sustainable B2B company. We show you how to turn your sales funnel into...
B2B Customer Journey: Mapping the Path to Purchase Success
Understanding the B2B customer journey is crucial for companies operating in the business-to-business domain. It encompasses the complete experience a business customer goes through when interacting with a company, from the first point of contact to post-purchase engagement. This journey is multifaceted, often involving a longer sales cycle and multiple decision-makers, which requires a strategic approach to effectively cater to each stage.
Mapping out the B2B customer journey enables businesses to identify key touchpoints, understand customer needs and pain points, and optimize the overall experience. By doing this, companies can enhance their customer interactions, foster long-term relationships, and ultimately drive growth. Given its complexity, the B2B customer journey differs significantly from the B2C journey, involving specialized strategies tailored to professional clientele.
The challenge for B2B organizations is to constantly analyze and improve their customer journey, acknowledging that B2B buyers expect a seamless, personalized experience as much as individual consumers do. Insights gained from examining this journey help businesses in anomaly detection, predicting buyer behavior, and adjusting their marketing and sales efforts accordingly to better meet the expectations of their business clients.
Understanding the B2B Customer Journey
The B2B customer journey encompasses the various phases a business undergoes from initial awareness to post-purchase evaluation when engaging with another business’s products or services. Understanding and mapping this journey is essential for B2B companies to effectively meet the needs of their clients.
Defining B2B Customer Journey
B2B customer journey represents the steps businesses take when purchasing from other businesses. It frequently involves multiple stakeholder interactions and a series of strategic decisions. The steps in this journey include awareness , consideration , decision , and post-purchase . Each of these steps can be mapped for clarity and to improve interaction with potential clients. A clear understanding of the B2B customer journey allows companies to pinpoint specific customer needs and pain points, and tailor their marketing and sales strategies accordingly.
Key Differences Between B2B and B2C Customer Journeys
The B2B customer journey differs from the B2C customer journey in several key aspects:
- Complexity and Length : B2B journeys tend to be more complex, involving more decision-makers and a longer sales cycle.
- Decision-Making Process : While B2B decisions are typically rational and value-driven, B2C purchases can be more impulsive and influenced by emotions.
- Relationship Focus : B2B relationships are long-term and based on building trust and strategic partnerships, as opposed to the often transactional nature in B2C.
By recognizing these differences, businesses can better align their strategies with appropriate B2B customer journey mapping techniques to foster successful B2B relationships.
Stages of the B2B Customer Journey
The B2B customer journey is a structured process addressing various stages from the initial discovery to the eventual loyalty. This seamless progression ensures businesses can effectively engage with potential clients at each crucial phase.
Awareness Stage
At the beginning, the Awareness Stage , potential customers recognize a need or challenge within their business. They become aware of possible solutions, starting their quest for information. Here, content such as blogs, whitepapers, and webinars play a pivotal role in drawing attention to a company’s offerings.
Consideration Stage
During the Consideration Stage , buyers start comparing different solutions to their identified problems. They engage with case studies, product videos, and customer testimonials, which help them understand how each solution can address their particular needs.
Decision Stage
In the Decision Stage , informed customers are ready to make a purchasing decision. They weigh factors like price, capabilities, and service support. Engaging sales presentations and detailed proposal documents often sway the decision towards the most compelling offering.
Service and Onboarding
Service and Onboarding are about setting customers up for success. Effective training programs, clear implementation guides, and responsive customer service teams ensure a smooth transition to using the new product or service.
Retention and Loyalty
Finally, ongoing customer support and account management contribute to Retention and Loyalty . Regular follow-ups, exclusive offers, and customer feedback loops help maintain a strong relationship, turning one-time buyers into long-term partners and advocates.
B2B Customer Journey Mapping
In B2B Customer Journey Mapping, the goal is to chart the course a client takes from initial awareness to final decision, capturing key touchpoints and decision-making moments. This process relies on data to build a comprehensive flowchart that embodies the customer’s experience.
Creating a B2B Customer Journey Map
To create a B2B Customer Journey Map , one begins with outlining the goals that align with the business objectives. Then, a detailed flowchart is designed, representing each stage of the journey. This flowchart should be informed by both qualitative and quantitative data, ensuring it mirrors the real-world experiences of B2B customers.
Identifying Touchpoints and Moments of Truth
Identifying Touchpoints and Moments of Truth is crucial since these are the interactions and critical decisions that define the relationship between a business and its clients. Touchpoints can range from website visits to direct communications, while moments of truth are those pivotal interactions that can sway a customer’s decision.
Using Data to Inform Journey Maps
Incorporating data into journey maps allows businesses to substantiate the steps of the customer journey with real evidence. Utilizing analytics, businesses can discern patterns and preferences, turning them into actionable improvements within the journey map. Data ensures that the created journey map is not just a theoretical construct but a living document that evolves with customer behavior and feedback.
Tailoring the Experience to Customer Segments
In the B2B landscape, successfully tailoring the customer journey hinges on a deep understanding of different customer segments. This approach optimizes customer interactions and aligns with the unique needs of each group.
Importance of Personas and Buyer Personas
Creating accurate personas and buyer personas is the cornerstone of segmenting the B2B customer journey. Personas are constructed through comprehensive research , incorporating demographic data, behavior patterns, motivations, and goals. They enable businesses to empathize with their customers at a granular level. For example, a software company may identify several buyer personas such as the tech-savvy innovator, the cost-conscious manager, or the feature-focused user, tailoring messaging and solutions accordingly.
Understanding Decision-Makers and Stakeholders
In B2B transactions, identifying key decision-makers and stakeholders is crucial. They often have different concerns and influence over the purchasing process. A decision-maker might be focused on ROI and long-term viability, while other stakeholders could be concerned about implementation and ease-of-use. Understanding their roles helps in crafting a journey that addresses each segment’s unique challenges and drives them towards making a purchase decision.

Optimizing Touchpoints Across Channels
Effective optimization of touchpoints across various channels is pivotal for enhancing B2B customer journey experiences. It requires a targeted approach to strategy, measurement, and technological integration.
Channel Strategy and Customer Engagement
Crafting a channel strategy that prioritizes customer engagement is essential. B2B entities should identify which channels their customers frequent and determine the most impactful touchpoints within those channels. From direct sales interactions to online platforms, each channel offers distinct opportunities for engagement. For example, enhancing the customer experience on professional networks can lead to stronger relationships and increased trust.
Measuring and Enhancing Touchpoint Effectiveness
It’s important to regularly perform touchpoint analysis to measure the effectiveness of each customer interaction. This may involve collecting data on customer satisfaction, conversion rates, and other key performance indicators. Companies can then utilize this data to refine their touchpoints. For instance, insights from a CRM system could pinpoint a need for improved customer service protocols on social media platforms.
Leveraging CRM Systems
Utilizing CRM systems effectively is crucial for managing customer interactions and data across multiple channels. These systems can track interactions and provide valuable analytics that inform decisions about where to optimize touchpoints for better engagement. They enable a seamless flow of information that can help in tailoring communication and sales approaches to individual client needs.
Integrating a CRM strategy with channel management ensures that customer data informs engagement tactics, leading to more personalized and targeted customer experiences.
Sales and Marketing Alignment
In a well-orchestrated B2B environment, sales and marketing alignment is pivotal for enhancing conversion rates and achieving the shared goals of the business. This synergy involves a systematic approach to unifying customer views, sharpening messaging and content, and ensuring both efforts are customer goal-centric.
Collaborating for a Unified Customer View
Sales and marketing teams bring different perspectives to the customer journey. By collaborating, they generate a comprehensive view of the customer’s needs and behaviors. Sales teams contribute insights from direct interactions, while marketing teams offer analytics-driven data. When combined, these insights lead to a more targeted and effective conversion strategy.
Tools and Strategies:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems for sharing information.
- Regular cross-departmental meetings to sync on customer feedback and experiences.
Strategies for Effective Messaging and Content
Effective messaging and content creation are at the heart of marketing efforts . These materials should address the specific pain points and challenges of the target audience. The marketing team’s strategic content backed by the sales team’s on-the-ground insights can create a powerful narrative that resonates with customers.
Key Elements:
- Consistent language and themes across all materials.
- Educational content that positions the company as a thought leader.
Aligning Sales and Marketing Efforts with Customer Goals
The ultimate aim of both sales and marketing is to guide customers towards their goals. Aligning these departments ensures that each touchpoint in the customer journey is coherent and purposeful. This alignment not only supports the customer’s path to purchase but also creates a seamless brand experience.
Action Steps:
- Define common goals for sales and marketing departments.
- Develop shared metrics to measure the success of aligned efforts.
About The Author
Andrei Kholkin
Related posts.

Bing Ads Conversion Tracking: Optimize Your Campaigns for Better ROI

Enterprise Ecommerce Platforms: Optimize Your Business for Scalability and Success

Break Even ROAS Calculator: Optimize Your Ad Spend for Maximum Profitability
5 Stages Of The Customer Journey
Discover the 5 key stages of the B2B customer journey: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Advocacy. Learn practical strategies to enhance engagement and drive conversions at each stage, with insights from Factors.ai.

Customer centricity is at the heart of a successful business. Delivering value to buyers at every customer journey stage drives sales conversions and retention. This, however, is easier said than done — especially in the case of B2B customer journeys.
Understanding the customer journey is crucial for modern marketing and sales strategies. With evolving customer behaviors and preferences, it's essential to adapt and refine approaches to address the complexities of how customers interact with brands.
This journey is no longer a straightforward path but a complex, often non-linear process. To effectively engage with potential customers, businesses need to grasp the intricacies of each stage, especially awareness, consideration, and decision. This blog explains these stages, offering practical insights and strategies based on current industry understanding and research.
- Understanding the customer journey is crucial for B2B marketing and sales success due to its complexity and non-linear nature.
- Customer journeys map out various buyer interactions to track how and why prospects become paying customers.
- The customer journey consists of 5 broad stages: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Advocacy.
- Delivering relevant material along each stage ensures that prospects feel understood and valued. This, in turn, contributes to successful journeys and provides practical insights and strategies for each stage.
- Businesses can enhance engagement and build long-term relationships by addressing customer needs and behaviors throughout the journey.
- Factors.ai connects the dots across campaigns, websites, and CRM to map the customer journey using path analysis and account timelines.
The Evolution of Customer Journey Stages
The B2B sales cycle involves several stakeholders and touch points across campaigns, social media, organic efforts, offline events, and more. A customer journey maps out these interactions to track how and why prospects become paying customers.
Since B2B sales cycles tend to be lengthy, non-linear experiences, it can be challenging to map them accurately without the right tools and frameworks.
Learn more about customer journey mapping here: The Complete Guide To Customer Journey Mapping .
Traditionally, the customer journey was viewed as a linear process, with prospects moving through clearly defined stages: awareness, consideration, and decision. However, modern perspectives reflect a more nuanced view. Today’s customers might navigate through these stages in a circular or even chaotic manner, reflecting the complexities of contemporary decision-making.
According to Gartner , only 17% of a customer journey is spent directly conversing with the vendor. The remaining 83% takes place through independent research and internal deliberation. Hence, businesses must distribute relevant value at each journey stage — even outside discovery sessions and demo calls.
Understanding the Awareness Stage
The awareness stage is where the customer journey begins. At this point, potential customers become aware of a problem or need but have not started actively seeking solutions. It's crucial to recognize that potential customers need help understanding the scope or urgency of their issue during this stage. They may be exploring general trends or innovations without a clear sense of how these relate to their specific needs.
Customers in the awareness stage primarily gather information. They might browse blogs, read articles, and engage with introductory content. Marketing efforts in this stage should focus on educational content that introduces customers to new concepts or challenges. Content such as informative blog posts, eBooks, and webinars can effectively capture their interest and lay the groundwork for further engagement.

Transitioning to the Consideration Stage
As customers move from awareness to consideration, they start recognizing the need for a solution. This transition is often triggered by an internal realization, such as remembering the inefficiency of current processes or the impact of emerging trends. This is a critical phase for businesses where prospects evaluate various solutions to address their identified needs.
During the consideration phase, customers will likely seek detailed information about potential solutions. They will look for case studies, ROI calculators, and in-depth product details to compare options. Effective marketing strategies during this phase should provide comprehensive resources that assist decision-making. This includes offering detailed product descriptions, customer testimonials, and interactive tools that help prospects understand the benefits and value of different solutions.
A few questions to ask here would be:
- Is the value of my product easy to grasp?
- Can people find my business without hassle?
- How does my product compare against competitors in terms of pricing and features?
- What is my unique selling point to convince buyers to pick me over the competition?
At this stage, it’s important to highlight why your product outshines the others with relevant case studies, product webinars, FAQ documentation, and more.

Navigating the Decision-Making Process
The decision stage is where customers are ready to finalize their purchase. At this point, they compare different solutions and make a final choice. However, it's important to note that the decision-making process is sometimes linear. Customers may revisit earlier stages if they encounter new information or if internal factors, such as budget constraints or organizational changes, influence their decision.
The decision stage involves evaluating competitors and making a purchase decision. Marketing efforts should be geared towards removing any final obstacles to purchase. This includes providing clear pricing information, offering competitive comparisons, and addressing any lingering objections. Strong calls to action and easy-to-navigate purchasing processes can significantly impact the final decision.

Circular and Non-Linear Customer Journeys
Modern customer journeys are often circular or iterative rather than strictly linear. Customers might revisit earlier stages as they gather more information or reassess their needs. HubSpot supports this perspective , noting that the customer journey can involve looping back to previous stages, reflecting the dynamic nature of modern decision-making.
To effectively manage this non-linear journey, businesses must be adaptable and responsive. Implementing tools for account scoring and path analysis can help identify where prospects are in their journey and adjust marketing strategies accordingly. For instance, if a prospect shows renewed interest in a particular product feature, it may indicate a return to the consideration phase.
Leveraging Customer Feedback and Data
Collecting and integrating customer feedback is crucial for refining the customer journey. Feedback at various stages provides valuable insights into customer needs and preferences. By incorporating this feedback, businesses can better align their marketing strategies with customer expectations and improve overall engagement.
Implementing tools for feedback collection, such as surveys and user reviews, can help businesses understand pain points and areas for improvement. Regularly analyzing this data allows for continuous optimization of marketing efforts and enhances the overall customer experience.
Enhance Customer Experience with Personalization
Personalization plays a vital role in managing the customer journey effectively. Tailoring content and interactions based on customer behavior and preferences can significantly enhance engagement. Using data to personalize email campaigns, website content, and product recommendations can create a more relevant and engaging customer experience.
Personalization should be based on insights gained from customer interactions and feedback. Data analytics involves understanding customer behavior, preferences, and pain points. Personalized content can address specific needs and concerns, making it more likely to resonate with the target audience.
The Role of Technology in Managing the Customer Journey
Technology plays a significant role in managing and optimizing the customer journey. Customer relationship management (CRM) systems, marketing automation tools, and analytics platforms are essential for tracking and analyzing customer interactions. These tools can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and engagement patterns.
Implementing CRM systems allows businesses to manage customer relationships more effectively by tracking interactions, managing leads, and analyzing data. Marketing automation tools can streamline communication, and nurture leads through personalized content and targeted campaigns. Analytics platforms provide insights into customer behavior, helping businesses make data-driven decisions and optimize their marketing strategies.
Integrating Omnichannel Marketing for a Seamless Journey
In today's digital age, customers interact with brands across multiple channels. Integrating an omnichannel marketing approach ensures a seamless and consistent experience throughout the customer journey. This involves unifying marketing efforts across various platforms such as social media, email, and in-store experiences.
An effective omnichannel strategy involves synchronizing marketing messages and ensuring that customer interactions are consistent regardless of the channel. This enhances the customer experience and provides a holistic view of customer behavior, enabling better decision-making and more personalized interactions.
Difference Between Customer Journey and Sales Funnels
While the customer journey and sales funnel are often used interchangeably, they represent different aspects of the purchasing process.
The sales funnel is a linear model that outlines a customer's stages, from awareness to purchase. It typically includes stages such as awareness, interest, decision, and action. The funnel model focuses on guiding customers through a sequence of steps toward a final conversion. It's a valuable tool for visualizing and managing the sales process but can oversimplify the complexity of modern customer interactions.
In contrast, the customer journey is a broader concept encompassing all customer interactions with a brand, from initial contact to post-purchase experiences. It acknowledges that customer interactions are not always linear and may involve multiple touchpoints and feedback loops. The customer journey model emphasizes the importance of understanding and optimizing the entire experience, including emotional and contextual factors, rather than just focusing on driving conversions.
The Importance of Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping is a valuable tool for visualizing the customer experience. It helps businesses understand customers' various touchpoints and interactions with the brand. By mapping out the customer journey, companies can identify potential pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Creating detailed customer journey maps is essential to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences. These maps should include all journey stages, from initial awareness to post-purchase interactions. Regularly updating and analyzing these maps allows businesses to stay attuned to evolving customer needs and optimize their marketing strategies.
Tracking Customer Journey Maps with Factors.ai
Factors.ai provides a robust platform for tracking and analyzing customer journey maps. This tool offers valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and interactions across various touchpoints.
With Factors.ai, you can:
- Visualize Customer Journeys
Create detailed maps illustrating how customers interact with your brand through different stages. This visualization helps identify critical touchpoints and understand the overall customer experience.
- Analyze Customer Behavior
Track customer actions, preferences, and engagement patterns. Factors.ai provides data-driven insights that inform your marketing and sales strategies, allowing you to tailor your approach based on actual customer behavior.
- Optimize Touchpoints
Use the insights gained from journey maps to optimize customer touchpoints and enhance the overall experience. Factors.ai enables you to identify pain points and improvement areas, helping you refine your strategies for better results.
- Measure Impact
Assess the impact of interactions and touchpoints on customer satisfaction and conversion rates. Factors.ai offers tools to measure the effectiveness of your efforts and make data-driven decisions to drive better outcomes.
By leveraging Factors.ai , you can better understand the customer journey and make informed decisions to enhance engagement and drive success.
Building Long-Term Customer Relationships
The end goal of managing the customer journey effectively is building long-term customer relationships. This involves facilitating a smooth journey from awareness to a decision and ensuring ongoing engagement and satisfaction post-purchase. Loyalty programs, personalized follow-ups, and excellent customer service are crucial to fostering long-term relationships.
Post-purchase engagement is crucial for maintaining customer loyalty and encouraging repeat business. This can include sending personalized thank-you emails, offering exclusive discounts, and providing excellent customer support. Companies can turn satisfied customers into brand advocates who contribute to long-term success by continuously nurturing customer relationships.
In a nutshell
Navigating the modern customer journey requires a comprehensive understanding of the various stages and an adaptable approach to marketing. The transition from awareness to consideration is a critical phase that demands targeted strategies to address evolving customer needs. Businesses can better engage with prospects and drive successful outcomes by focusing on educational content, detailed product information, and practical decision-making support.
Understanding that the customer journey is often non-linear and iterative allows businesses to remain flexible and responsive. By focusing on each stage and addressing your customers' unique needs and behaviors, you can achieve long-term success and foster a positive relationship with your audience.
Factors.ai can help track each stage, from awareness to advocacy. To see Factors.ai in action, book a personalized demo here!
Related posts
%20(2).avif)
Top 5 Demandbase Alternatives to Boost ABM in 2024
%20(1).avif)
Everything You Need to Know About SaaS Google Ads

Top LinkedIn Agencies in North America
See factors in action.
Schedule a personalized demo or get started for free
Let's chat! When's a good time?
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Customer Journey Marketer Blog
The Art and Science of Aligning Digital Marketing with the Modern Customer Journey
Gary DeAsi / January 5, 2017
- 65 Questions for Understanding the B2B Customer Journey
Stages are just half the battle. Get the ultimate list of 65 questions to help you fully understand the B2B customer journey for your customers & business.

When people talk about understanding the B2B customer journey, it seems to me that the majority of the time we tend to do so primarily in the context of stages – the various phases customers encounter at different points throughout their journeys.
As I outlined in a previous article about the stages of the new digital marketing funnel , there’s no question that having a well-defined stages model is absolutely essential for customer journey mapping. It’s a must.
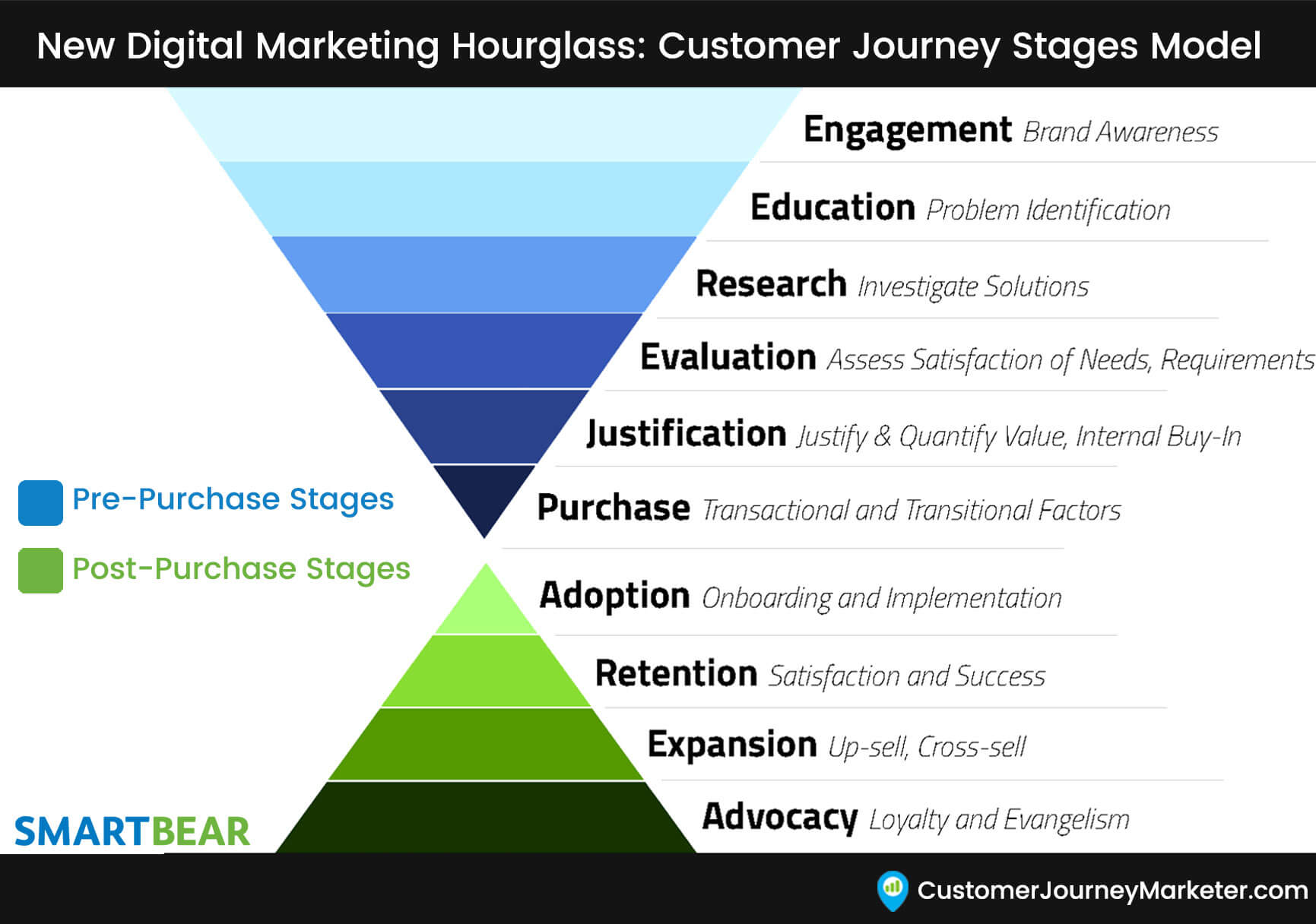
Customer Journey Stages Are Not Enough
Critical as they are, stages models are certainly not all there is to it when it comes to really getting a complete picture of the B2B customer journey. Far from it.
There are many other important variables and considerations that you need to understand that are specific to your business and customers that can drastically change the nature of the path customers take in their journey, the obstacles and barriers they encounter along the way, and thus the marketing approach that should be taken accordingly.
At SmartBear, our customer journeys varied incredibly across all of our different products, markets and audiences, so of course we needed to understand this in order to apply different marketing strategies for each.
Below I’ve compiled a list of question examples that you may look to answer in order to get a more complete understanding of what the B2B customer journey looks like for your customers and organization.
65 Questions for Understanding the B2B Customer Journey [Ultimate List]
I. understanding your customers, customer persona questions.

- Demographic information: Age? Gender?
- What are their job titles?
- What are their work responsibilities?
- What knowledge and skill sets are required to do their job?
- What tools do they use?
- What are their career goals?
- What motivates them? Why do they get out of bed in the morning?
- What do they like and dislike most about their job?
- What does their day-to-day look like?
- Where do they spend most of their time?
- What are their top work priorities?
- What keeps them up at night?
- Who is their boss?
- What does their team look like?
- How is their job measured?
- Who do they trust? Look up to? Respect?
- What traits and characteristics do they admire in organizations?
- What are their hobbies and interests outside of work?
Customer Organization Questions
- Key industry verticals?
- Company size: How many employees? Annual revenue?
- What is their business model?
- What does their technology stack look like?
- What is their organizational structure?
- What are their geographic locations?
- Who are your customers’ customers?
- Who are your customers’ competitors?
Online Behavior and Preferences Questions
- What blogs and online publications do they read?
- What online communities do they belong to?
- Which social media networks and platforms do they use?
- In what format do they prefer to consume content?
- What thought leaders, writers, bloggers, and industry experts do they follow?
- How do they research vendors online and in general?
II. Understanding your Business
Problem and before scenario questions.
- What are the common problems and pain points customers experience that your product/service can help alleviate?
- How do they solve (or cope with) the problem before using your solution?
- What are the common buying triggers, or common events or conditions that often set customers off in search of a solution?
- What language and terminology might they use when talking about your solution?
- What keywords and search phrases do they use when looking for a solution?
17 Proven Ways to Generate More Leads that Convert to Sales
Your Product/Solution Questions
- What are the most important values the product/service provides customers?
- What are your key value propositions?
- What are the most important features/capabilities provided in the product/service?
- What are the different use cases for why/how different customers use it?
- How complex is the solution to use? To implement?
- What level of knowledge, skills or experience do customers need?
Technical Considerations Questions (If applicable)
- What are the key 3rd party technology integrations or partnerships?
- What key technologies does or doesn’t the product support?
Your Sales and Purchasing Process Questions
- What is your sales model?
- What is your pricing model/structure?
- Average length of sales cycle?
- Average deal size?
- Common sales barriers and objections?
- Complexity of purchasing decision?
- What are the different internal roles involved with the purchasing process?
- Who are the users? The influencers? The decision maker? Champion?
Your Market and Competitive Landscape Questions
- Market maturity stage?
- What is your Sirius Decisions Demand Type ? (see chart below)
- What does the competitive landscape look like?
- What is your market share? Positioning?
- What are your top strengths, differentiators and advantages vs leading competitors?
- What are your top weaknesses and disadvantages vs leading competitors?
- What key trends are happening in the marketplace?
Sirius Decisions Demand Spectrum
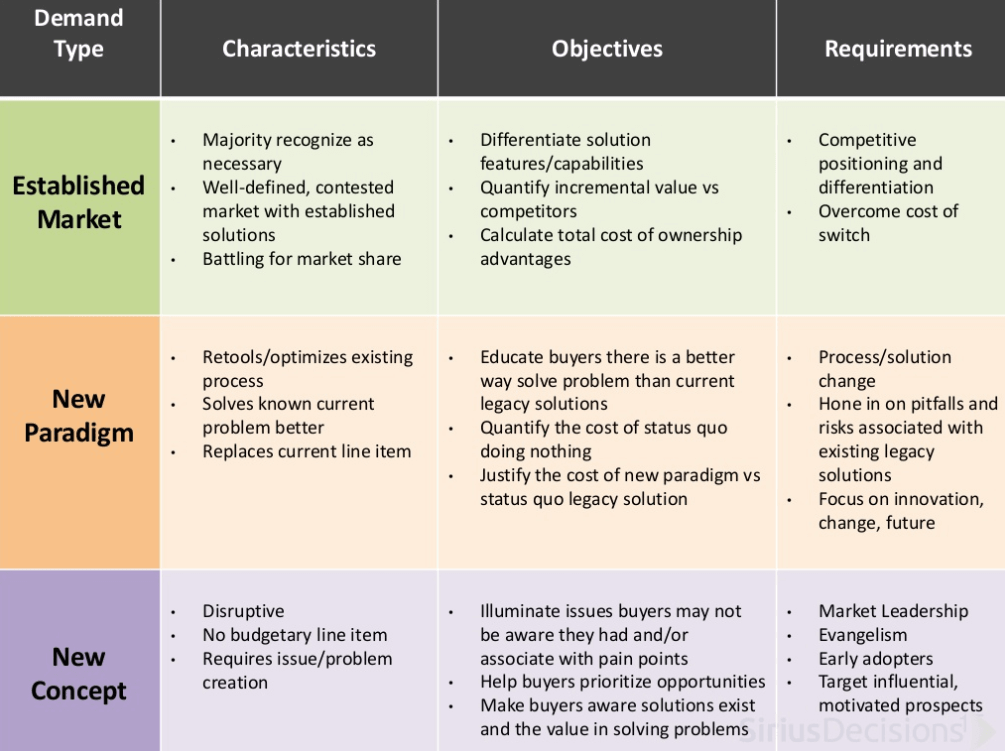
Once you have all of this juicy info on customer personas and organizations, your business and the market landscape, add this to the customer journey stages knowledge, and we will then have a much more complete view and understanding of the B2B customer journey.
But first we have to get the answers to these questions somehow…
How Do You Get All this Information?
You’ll most likely need to collect information from a number of different sources, which might range from online surveys and interviews with customers and internal experts, networking , research and data analysis .
However you decide to go about doing the research, I would strongly encourage making sure customer interviews is a regular part of the process. In fact, I believe marketers should take the opportunity to hop on the phone and talk to customers as often as the opportunity arises. The qualitative information you often dig up in those conversations with customers is just absolute gold, and stuff you commonly won’t be able get anywhere else.
I actually interviewed 22 different customers last year as a part of a brand project I was working on, and I probably learned just as much valuable info from a demand gen and customer journey perspective as I did in relation to the brand.
Customer Journey “Battlecards”
Once you’ve done your research and collected all this great knowledge, its important to get the info into the hands and heads of each member of your team so they can start putting it to good use.
One approach I took for this which was pretty effective for us was creating what I internally called “ Customer Journey Battlecards .”

I worked with product marketing managers to get much of the missing info filled out on these pages, and then held a marketing team training series to help educate the team, which we also recorded and added to the wiki pages.
Putting in the Time to Do Your Research
As Steve Offsey pointed out in a recent interview about customer journey mapping misconceptions , far too often marketers don’t invest the time and energy to conduct the necessary research required to truly understand their customers and the B2B customer journey.
Without ever even getting input from the actual customers, or conducting substantial external research, teams frequently construct their marketing strategies and customer journey mapping programs based entirely on their own internal perceptions and point-of-view.
Click To Tweet
Regardless of customer journey mapping, I think few would argue that there is little if anything more vital to the effectiveness of marketing than understanding your target customers.
So, I’m not suggesting that you need to answer every single question on this list in order to understand the B2B customer journey, but the more of this kind of knowledge you do have about your customers, business, and market, the more vivid (and accurate) your picture will be.
Customer journey stages are just half the battle. If you haven’t already, take the time to do the important research that really helps you complete your holistic view and truly understand your customers and their journeys!
In the likely case that you don’t have the bandwidth to drop everything for a large scale research project anytime soon, you can always break it up over time and do little by little (in fact, it really should be a recurring exercise.)
We did the “battlecard” project over a period of six weeks. Easy peasy.
What questions do you think are most important for understanding the B2B customer journey? Any others you would add to the list?
- Recent Posts
- Report: The State of Customer Journey Management and CX Measurement - June 10, 2019
- 10 Powerful Behavioral Segmentation Methods to Understand Your Customers - March 27, 2018
- How to Use Customer Behavior Data to Drive Revenue (Like Amazon, Netflix & Google) - February 27, 2018
You might also be interested in:
- Report: The State of Customer Journey Management and CX Measurement
- 10 Powerful Behavioral Segmentation Methods to Understand Your Customers
- How to Use Customer Behavior Data to Drive Revenue (Like Amazon, Netflix & Google)
- How to Use Growth Hacking to Skyrocket Your Marketing Results
Subscribe to Customer Journey Marketer
Enter your email address and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
ABOUT Customer Journey Marketer
Follow & connect.
- Home > Publications > Customer Journey Mapping in B2B Markets: A Comprehensive Guide
Customer Journey Mapping in B2B Markets: A Comprehensive Guide

Customers are organizations’ biggest asset – without customers to buy products and services – there is no business at all. In recent years, customer experience has become a focal point for organizations, to encourage customers to spend more, pay a premium for that service, and recommend the supplier based on the experience it delivers. There is a strong correlation between poor customer experience and switching suppliers for better experience and service, and therefore understanding the journey that customers go through, and where improvements could be made – is now commonplace in many organizations.
What is Customer Journey Mapping?
To understand the current customer experience, it is essential to map the touchpoints that customers go through with the supplier. Through doing this, we can then build an understanding of where the customer might be facing points of delight or frustration, which can help organizations to drive improvement for customers.
A customer journey map is a visual representation of these customer interactions with an organization. To effectively build the map, it is crucial to step into the shoes of the customer to try and understand how our processes impact on the experience that the customer has with the supplier. That is – not only what might encourage the customer to make a purchase, but what emotions they are feeling at each stage of their journey with a supplier, as we know that emotions are a top driver of loyalty to a brand (even over aspects of the journey like ease of business).
It is a blueprint for the journey taken by the customer, marking all touchpoints. It should extend from touchpoints designed to raise awareness and interest – including advertising and marketing efforts, PR, etc. – through to the touchpoints associated with usage e.g. sales reps, accounts teams, support services complaints handling, etc. It should also extend to the cessation of the relationship with the company e.g. closing a bank account, switching to an alternative provider, etc. as the handling of this stage can be critical in turning around experiences and inviting future return to usage.
A Customer Journey Map (CJM) should therefore include:
- A flowchart or diagrammatical representation of the journey which customers take.
- All interactions and interfaces (touchpoints) between the customer and the company/brand
- Likely “pain points” in the journey i.e. areas where the customer is likely to experience difficulties or negative emotions.
- Key “moments of truth” i.e. areas where there is the opportunity to “make” or “break” the relationship.
Once maps have been developed, it is also common to then populate them further, to include:
- Identification of departments, regions, and people responsible for the delivery of the customer experience at each touchpoint (e.g. customer service, technical support, HR, sales and marketing, etc.)
- Linkages between touchpoints
- Emotions elicited and desired in the customer at each touchpoint.
- Importance ratings for each touchpoint. This can include looking at the internal perception of importance compared to customer measures.
- Performance of the company/brand at each touchpoint. As with importance, the gap between the internal and external perception can be identified.
Customer journey mapping is evolving to be more sophisticated in driving action. The use of AI in customer journey mapping is on the horizon, to allow us to more accurately predict customer behavior based on past data – which can in turn help organizations to improve customer experience and satisfaction through anticipating what the customer will need. It is certain that customer journey mapping will be even more relevant to drive customer satisfaction and retention in the future.
Contact Us >
Why Conduct Customer Journey Mapping?
Most large corporations operate in ways which separate different functions of the service delivered to its customers e.g. ordering, technical support, complaint handling, warranty claims, general inquiries, etc. This is generally felt to be necessary to build expertise and manage operations. However, unless the various functions are joined up, the customer can feel this disconnect or even fall between departments or functions. By tracking and describing the customer’s experience at each stage of this ‘journey’, a company is able to:
- Deliver seamless, streamlined products and services that cut across departments within the company.
- Tailor services to meet the needs of both customers and the business.
- Understand the experiences, thoughts, and feelings of customers.
- Develop compelling propositions.
Customer journey mapping has obvious advantages within a company, not least in developing a customer culture and the internal buy-in with the brand. Customer experience journey mapping exercises focus the business on the customer. Simply by spending the time considering what the customer’s lifetime experience is with the company highlights the strategic positioning the customer has within the company, the customer culture, and the degree to which the customer is considered in service design and delivery. This can help to unite siloed departments or teams on improving the overall experience of the customer, and how they can work together to do so.
In recent years, we have become more attuned with the importance of empathizing with customers’ emotions throughout the customer journey, as positive emotions and feelings towards suppliers are directly related to future purchases from the supplier. Customers with a stronger emotional connection to the supplier as well as strong satisfaction, are more profitable for suppliers. Along the customer journey, we should think about ways to measure and enhance the customer’s emotional connection with the brand.
To do this, we might want to include on our CJM:
- The baseline emotional state of the customer
- Examples of what could enrich the experience at each stage (resulting in a more positive emotional response)
- Examples of what would be a poor experience at each stage (resulting in a more negative emotional response)
Many brand strategies are developed in the absence of the customer and yet it is the customer who lives the brand. Their perception of the brand comes not only from the messaging, imagery, and promotions, but also from the experience they have with the company and its products. Whilst this philosophy can now be seen in the imagery of the mass promotional campaigns of some leading brands, it must be backed up by the experience delivered when interacting with the supplier. A company that understands the customer journey in detail is able to design “ideal” experiences and orientate the operations and the people delivering these to engage its customers with the brand and build loyalty.
Moreover, we have seen that in recent years, especially since the Covid-19 pandemic, that customers’ expectations of the brands that they work with have increased. This has resulted in a gap between what the customer expects from the brands they are working with, and what can realistically be delivered by the supplier. To narrow this gap, it is critical to highlight where the gaps are largest between expectations and experience when customer journey mapping – organizations need to be prepared to meet expectations as closely as possible to avoid this ‘customer expectation gap’ growing larger.
Figure 1: The customer expectation gap
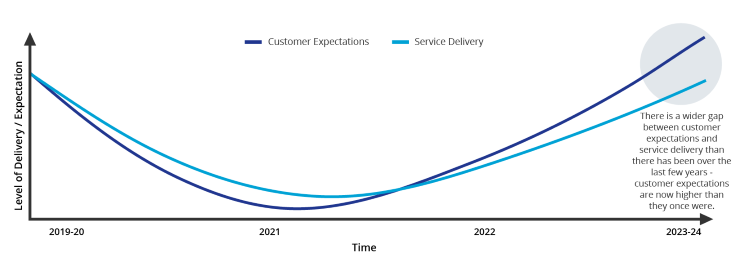
Problems and Pitfalls with Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping and touchpoint analysis is not without its problems. Knowledge and perceptions, both internal and external, are required to develop the Customer Journey Map, particularly in more complex B2B markets. Pitfalls which can be experienced when embarking on the process can include:
- Getting buy-in from senior management.
- Getting co-operation from staff who are responsible for the various elements of the customer journey (and aligning on actions based on customer journey mapping)
- Availability of resources to undertake the process, and drive action based on research findings.
- “Blank sheet syndrome” – having difficulty getting started.
- Lack of understanding of customers’ emotional connection with the brand and how to tap into this.
- The complexity of customer journeys – every customer can take a different journey, so maps can be complex!
Types of Customer Journey Maps Used in B2B Markets:
Customer Journey Maps can take several forms, depending on the needs of the business and the extent to which business processes are incorporated into the map.
Typical customer journey mapping:
A map that provides a strategic overview of the stages of the B2B customer journey, along with the component B2B touchpoints where a customer can interact or engage with the company at each stage of the journey.
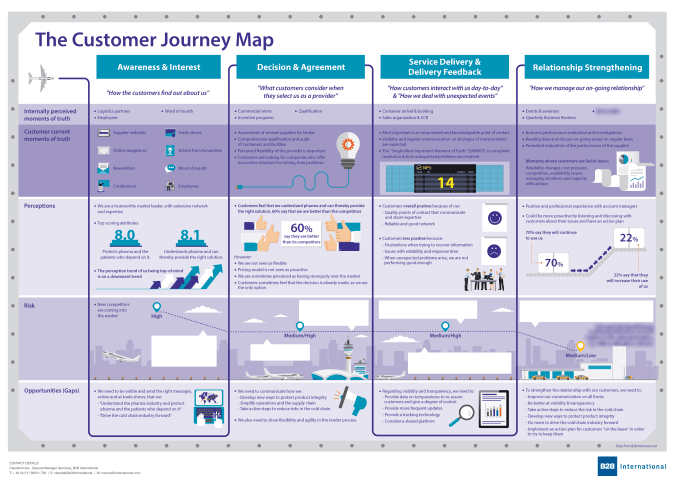
Tactical customer journey mapping:
The tactical B2B customer journey map focuses on a particular touchpoint (or cluster of B2B touchpoints) to highlight the journey that the customer goes on at that stage. This is particularly useful when looking at an important (or painful) touchpoint where performance needs to be at a high standard. Tactical maps can also be a useful tool for training teams that are responsible for a particular stage of the customer journey.
The performance map is similar to the tactical journey map, though it goes into more detail about the performance at each step of a process, and provides key recommendations at each stage. These are invaluable when identifying “pain points” and “bottlenecks” for the customer, and identifying how processes impact on customers. Therefore, they can be very useful for circulating information to those responsible for making the improvements on a day-to-day basis. These maps can also be helpful to design touchpoint research or surveys, to measure performance trends at the ‘painful’ touchpoint.
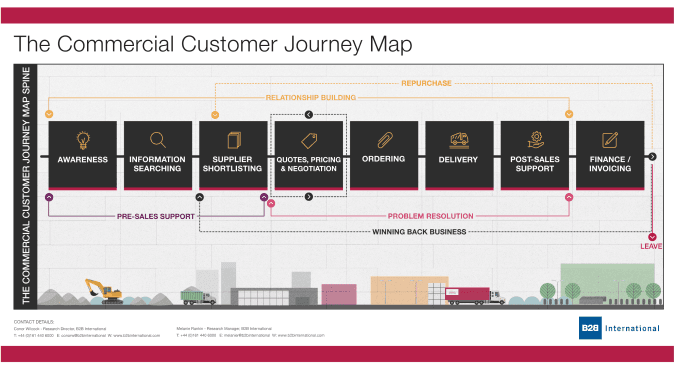
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
A customer journey map details all the individual touchpoints and interactions that customers have with a specific business.
Whilst all customer journey maps are unique to a business and its different customer groups, the process in creating these journey maps is broadly the same. If an end-to-end customer journey map has not been created, then it can be useful to map this out starting with how a customer becomes aware of a business or brand (such as through the website or a word-of-mouth recommendation), right through to service delivery and ultimately, what happens at the point at which a customer wants to exit the relationship or indeed, return and continue doing business. It might even be useful to consider the emotions and the processes that the customer goes through before they start to research brands (e.g., what problem(s) would the product or service be solving?).
Alternatively, a business may want to instead focus on one part of the customer journey (rather than the end-to-end journey) to understand this better and to explore this in more detail. As an example, if a business is happy with the sales process upfront but is more concerned about understanding the after-sales customer experience, then it may wish to build a map to explore specific interactions that occur at this point in the journey to examine where they are performing well, where there are potential problems or customer “pain points” and which departments are responsible for owning each of these specific customer interactions or experiences.
A key point to bear in mind is that the focus should always be on the customer, i.e. the customer journey map must be produced through the lens of a customer. In other words, it should represent the interactions the customer sees and experiences, rather than the internal processes that may occur behind the scenes within a business, which the customer does not see. For example, a customer may order a product for delivery, but they might not see how that order is specifically processed by the organization internally.
Creating the customer journey map
Depending on the industry in which a company operates, the range of its operations and the type of products and services it offers, the starting point will be to define the different groups of customers and to establish how different their “journey” with the company can be. Typical approaches to customer experience journey mapping here are to segment B2B customers on firmographics (i.e. classifications which make them different such as geography, age, SIC code), behaviors (i.e. what they buy) or needs (what they are looking for). This exercise is required before any journey mapping can take place. It may even be the case that these customer groups are overseen by different departments within the organization; in some cases, it makes sense to create multiple customer journey maps to avoid data overload.
The next step is to map the journey of each of the customer segments from end to end, detailing all the customer touchpoints with the company, and the customer responses to these.
The key overarching stages of the customer journey form the “spine” of the customer journey map. Under each key stage of the “spine” is where you list all the individual touchpoints or interactions a customer may have at that stage. Touchpoints may have connections with different stages of the “spine”, depending on the journey that the customer is taking.
As an example, under the “awareness” stage of the spine, the individual interactions a customer may experience in becoming aware of the brand may include some or all of the following:
- The company website
- Social media
- Trade publications
- Word-of-mouth recommendations
- Branded vehicles or delivery trucks
- Seeing the brand at sponsored events
Post-it notes and flip charts (or similar) are useful for capturing all this information. We would always advise that one post-it note is used for each touchpoint, as when doing this as an internal group exercise, then you will likely want to add or remove individual touchpoints, or potentially move these around or group them together. The key here is to keep reminding yourself that these touchpoints should all represent experiences through the eyes of the customer and so if a customer does not experience it (i.e. it’s an internal process they do not see), then it should not be included.
Heat-mapping performance
With multiple touchpoints and interactions mapped against each key stage of the “spine”, a customer journey map can shed light on the hundreds of specific interactions a customer can have with a business. Knowing what these are is a vital basis for formulating a plan or allocating resources appropriately towards effectively managing the customer experience across these different interactions.
However, a useful exercise in helping a business understand where attention is required, is to heat-map performance of these touchpoints. Once again, it’s important to put yourself in the shoes of the customer and then decide (either in groups or individually) which touchpoints can be classified into the following:
Customer pain points: Those touchpoints where there are challenges faced by the customer or where a business feels it fails to meet customer needs and expectations now. This point is important given how crucial customer emotion and brand connection is for customer retention.
Moments of delight: On the flip side, those touchpoints where a business feels that it delights customers by doing a good job or exceeding their needs or expectations.
Moments of truth: The touchpoints which are the most important or critical because they have the most impact on the longer-term loyalty of a customer. These points in the journey map can simultaneously be pain points or moments of delight.
When heat-mapping, it is not necessary that every single touchpoint is classified into one of the above and some may be left blank because they could be somewhere in the middle – neither a pain point nor a moment of delight. Equally, it is ok if some touchpoints are marked as a pain point and a moment of delight as well as a moment of truth, since this might represent that this touchpoint is important, but there are extreme inconsistencies in the experience of the customer here.
Of course, this exercise captures an internal perspective only, so it’s important to also test this out by speaking directly to customers. By doing this, it can be a powerful catalyst for change to conduct gap analysis on what we think internally versus what customers feels in practice. These insights can be used to help a business prioritize its resources on where these are needed most and where these could have the most positive impact on longer-term customer loyalty.
To overcome the barrier of the mapping exercise being based on internal views only, validating the customer journey map by speaking to customers allows us to better understand the sentiment that customers feel at the various stages of the customer journey, as well as giving us the ability to understand variations in the decision-making unit at different points in the customer journey. We can ask customers about changing dynamics in the decision-making unit throughout the journey, as well as when something goes wrong, for example. Customers may not travel through a linear customer journey map, so it is useful to understand discrepancies and variations in the customer journey taken, and the impact of these on the customer.

The role of internal employees and customers in customer journey mapping
Customer experience journey mapping can be done using a variety of methods which engage stakeholders involved in the process, and ensures their input into the development of the maps. A combination of workshops, staff interviews or focus groups, and customer interviews are normally used. These are then validated externally with customers (current, potential, and sometimes lost) to ensure the maps encapsulate the customer experience, and no critical touchpoints are missing.
Sessions can be conducted either in-person or virtually, so that we can capture as much knowledge as possible, even when teams are spread across the globe. We can use virtual whiteboards to map the journey, and encourage participation from everybody in the session. There is often some debate on what the journey looks like when sessions are conducted, whilst teams try to align on what the experience of the customer looks like, how they experience the journey, and which touchpoints are painful, positive or moments of truth.
Internal workshops (usually senior management) can help to:
- Establish a high-level view of the customer journey
- Establish buy-in at senior level
- Start thinking about things from the customer’s point of view
Internal interviews (usually departmental) can help to:
- Validate the high-level map
- Ascertain more touchpoints at particular stages
- Understand pain points and important touchpoints
Customer (current and/or lost) input – interviews and focus groups can help to:
- Validate the journey both in terms of stages and touchpoints
- Understand important touchpoints for customers
- Understand pain points for customers
- Understand gaps in internal vs. external perception
- Highlight expectations so we can estimate the customer expectation gap
- Understand feelings at each stage of the journey (when things go right, and when things go wrong)
- Demonstrate how decision-making units can change throughout the customer journey
Visualizing the Customer Journey Map
As customer journey maps can be complex, it is critical to design a clear visualized map that can be understood and used across departments.
There are a variety of ways to design the customer journey map to make the data simple, clear, and actionable. You may choose to use:
Large posters which can be placed in offices or other places of business to encourage engagement of all staff in the customer experience
Booklets which can focus on different personas or customer types through the customer journey
Excel spreadsheets or detailed tables of the customer journey (especially for customer experience teams who need the detail to drive improvement in the customer journey)
Digital outputs such as interactive infographics or videos, which can be shared across teams and/or regions. These outputs are especially useful now with online and hybrid working being common practice – staff can still be engaged in customer journey and experience improvement without being in a physical workspace.
The Value of Customer Journey Mapping & Challenges in B2B Markets
Customer journey mapping is just one stage in the move towards a customer centric approach. It marks the starting point; placing the experience of the customer at the heart of what the company does and how it operates. It provides a single overview of how customers interact with the business, focusing the company’s thinking on the customer and how the service appears from an external perspective. It is all too easy for large corporations to think in terms of departmental tasks, and so it facilitates cross-departmental working to understand the impact on the journey for the customer, and consider the “desired” emotional response from the customer at each point (as well as the impact if this desired emotional response is not achieved).
However, customer experiences, rather than being neat and linear, are often convoluted and complex, particularly in B2B markets where tendering, multi-site requirements, and technical product and service requirements often define journeys. These complexities can confound the customer journey mapping team, resulting in maps which are either overly complex or overly simplified, failing to capture the most important B2B touchpoints from the customer perspective and the emotional response to these from the customer. Resultant actions can then be process- rather than experience-driven.
The outputs from customer experience journey mapping deliver a tool for identifying outstanding and problematic areas, as well as “delight” and “choke points” in the journey. Using the customer experience management (CEM) process cycle (see below), the next stages are to design the “ideal” experience, put in place the processes and people addressed to deliver it, and develop a feedback mechanism to measure progress. As a result, valuable resources can be targeted where they will have the greatest impact for the customer coupled with efficiency for the business.
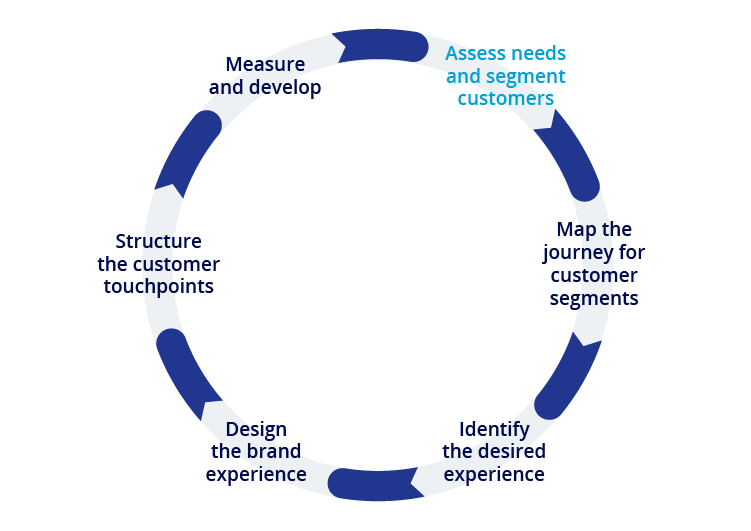
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
Customer journey mapping is an excellent tool to help an organization redesign its customer experience. It can help an organization piece together the current structures and processes affecting the customer and, by listening to customer feedback, identify gaps from the ideal experience. However, customer journey mapping is not an easy process, and getting it wrong can ultimately leave you with a lack of direction. Below are 5 tips to ensuring a successful project:
What does success look like?
You need to be upfront and clear about what your true objective is for undertaking the project, and this needs to be aligned within the business. This makes sure that the customer journey mapping work stays focused. Customer journey mapping can capture a wide range of information, and therefore it is important that the ultimate goal is kept in mind during the initial planning stages.
Identify complexities early
You need to think about your business and whether any intricacies in the way you operate will affect the journey mapping process. For example, different product groups or different customer segments may have different journey maps. The journey mapping exercise needs to take these into account, and it could be appropriate to design different journey maps to take these into account. Think about your customer segments before mapping starts!
Preparing for the workshop
Ahead of the workshop, enough groundwork needs to be done to make the customer journey mapping exercise run smoothly. You may want to hold stakeholder conversations ahead of the workshop to make sure there is internal alignment. You also need to ensure all of the right people are going to be present at the workshop – a healthy cross-section of different teams who are knowledgeable about the customer. You also want to have the right exercises in place that will ensure your output contains everything you were looking for. An interactive online whiteboard can be a useful tool to collaborate and get some ideas floating around before the customer journey mapping workshop itself.
Validating the customer journey map
As well as gathering the internal view, it is important to speak with customers to learn more about the processes from their experiences. It is often only necessary to do a small number of depth interviews to achieve this. Again, looking back at ‘what does success look like’ will inform the design. You may only need to speak to customers about a certain element of the journey, or speak to certain types of decision-makers to gather an understanding of customer sentiment, and identify where improvements can be made.
Visualizing the output
We would recommend that much consideration is given to the final output. Ultimately this is what you and your colleagues will be using to improve the customer experience. There are many creative ways that the map can be visualized – from giant posters, booklets, excel spread sheets or videos. It needs to be easy to understand, easily shared and can generate the actions you want.

Closing Thoughts
As a key element of Customer Experience Management, customer journey mapping is a “step back” exercise, and one which affords the opportunity to design truly innovative experiences which differentiate. It has real value in engaging staff at all levels within a business with its customers and their experience of the company and brand.
Customers are the greatest advocates of a brand or specific product or service: they tell stories and they make recommendations. They have the power to infect others with their enthusiasm for adoption, but also have the ability to influence against adoption, and hence focus on them is essential for long-term strategic growth.
Increasing customer expectations mean that it is more important than ever to understand customers’ emotions, behaviors and needs throughout the customer journey, to avoid increasing the gap between their expectations and what suppliers can realistically deliver. Understanding the customer journey in detail means that customers’ behaviors and next steps can be anticipated, and an experience can be designed to delight the customer.
Learn More About Customer Journey Research >
Readers of this article also viewed:
Customer Satisfaction Surveys & Research: How to Measure CSAT How to Determine the Strength of Your B2B Brand A 5-Step Framework for Driving Action and Seeing Results from your CX Programs
To learn how we can help your organization to create a customer journey map
Speak to an expert...
- Keep up to date with our latest research
- First name *
- Last name *
- Company name *
- By subscribing to this newsletter, you are opting in to our marketing communications. Read our privacy policy for more information.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Privacy Overview
Chicago 875 N Michigan Ave Chicago, IL, 60611
How To Create A B2B Customer Journey Map And Meet Evolving Client Needs

Brian Decoded
President at alpha efficiency.
Join me at the forefront of web design and digital marketing innovation. I am obsessed with web design, business philosophy and marketing performance. I write Conversion Insider newsletter.
Follow me on LinkedIn
Follow me on X
Follow me on Instagram
Subscribe to Conversion Insider
Do you find it difficult to attract high-quality B2B leads and convert them into loyal clients? Does it feel like your digital marketing strategies are floating without direction?
You’ve got a great product, and you’re investing in marketing campaigns, but somehow, clients keep choosing competitors. And when they choose you, it’s a struggle to build deeper relationships and do repeat business.
Ten years ago, I was struggling in the B2B sphere, too. I started my own web design agency in Chicago , and whenever I was close to landing a new client, an obstacle would arise unexpectedly. I learned the hard way that in B2B, it’s not just about selling a product. It’s about the whole B2B customer journey – getting to know your clients, understanding their needs, and ensuring you’re there with the right solutions at the right time.
In this article, I’ll show you how to create your B2B customer journey map . You’ll have a practical, actionable plan to draw in clients and build lasting, meaningful relationships with them. You’ll understand the challenges in the B2B customer journey and gain a holistic view of how to bring structure to your digital marketing efforts.
Table of Contents:
What makes the b2b customer journey unique – b2c vs b2b journeys, how can b2b customer journey mapping drive your success, four types of b2b customer journey maps and when to use each, step 1: define the ideal clients you want to attract by creating detailed buyer personas, step 2: define all customer touchpoints with your company, step 3: map out b2b customer journey paying attention to 5 crucial stages, how to optimize your b2b customer journey to boost sales, final thoughts.

Selling products or services to individuals is different from selling to businesses.
If B2B is a marathon, B2C is more like a sprint. The end goal is the same – creating exceptional customer experiences and fostering long-term customer relationships. Yet, the path to reaching this goal differs vastly between the two.
In B2C transactions, the focus is typically on individual customers making personal purchasing decisions. This journey is often shorter, more impulsive, and driven by emotional factors. The strategies you’d employ here lean towards mass marketing, with an emphasis on creating an immediate connection with the product.
In contrast, the B2B customer journey is usually longer and involves more challenges:
- Complex Processes : B2B transactions often involve multiple layers of decision-making. You must count on several stakeholders, each with unique customer pain points and requirements.
- Larger Deals : The stakes are higher in B2B, with deals typically larger and more complex than in B2C.
- Longer Sales Cycles : B2B sales cycles often stretch over months or even years, as purchasing involves considerable deliberation and approval processes.
- Sensitive Documents and Information : B2B transactions frequently require the exchange of sensitive information and documents, adding a layer of complexity to the relationship.
- Challenging Mass Marketing : Mass marketing strategies that work in B2C are less effective in B2B, where personalized and targeted approaches are crucial.
- Higher Customer Acquisition Costs : Acquiring a new B2B customer generally costs more, given the extended sales cycles and the need for tailored solutions.
- Two-Way Communication : Effective B2B relationships demand ongoing, two-way communication, ensuring that the needs and expectations of both parties are continuously aligned.
For those in the B2B sphere looking to enhance their strategy, focusing on B2B conversion rate optimization becomes a pivotal aspect. It’s about fine-tuning every interaction and touchpoint to align with potential customers’ specific needs and pain points.
By mapping the B2B customer journey, you gain invaluable insights that can transform your approach and ultimately fuel growth.
Build Deeper Relationships By Showing That You Understand Client Needs
Understanding your target audience is critical to growing your business. By mapping the B2B customer journey, you delve into the specifics of your client’s needs and pain points.
You’ll be able to tailor your interactions and solutions, demonstrating a deep understanding of your customer base. The result? Stronger, more trusting relationships you can count on long-term.

Increase Sales And Deal Sizes By Providing A Personalized Experience
A well-mapped customer journey enables you to provide highly personalized experiences. When you understand the nuances of your customer’s buying experience, you can craft offers and solutions that resonate more deeply with each segment of your customer base.
A map also helps you analyze the B2B customer journey more efficiently and identify leaks in your inbound marketing funnel .
This level of personalization not only boosts sales but can also lead to larger deal sizes, as clients are more likely to invest in solutions that feel tailor-made for them.
Retain More Clients
Customer retention is critical to sustainable business growth.
Through journey mapping, I identified key stages where clients felt less engaged and took steps to address these gaps.
This process is crucial for you to maintain and enhance the overall experience of your clients, thus increasing retention. It’s not just about getting clients; it’s about keeping them.
Discover New Opportunities For Connecting With Other Businesses
Through journey mapping, you can identify unmet needs or untapped areas within your customer segments. This can open up new opportunities for connecting with other businesses, either through partnerships, new product lines, or customized services. Understanding customer needs from a business perspective allows you to spot these opportunities early and act on them.
Achieve Better ROI On Your Marketing Efforts By Identifying The Most Effective Channels
By understanding where and how your clients interact with your brand, you can invest your marketing budget more wisely and see a better return on your investments.
In B2B marketing, understanding and creating customer journey maps is fundamental. However, it’s not a one-size-fits-all approach. Different types of journey maps serve various purposes and are used at different stages of strategy development. Let’s break down four primary types of B2B customer journey maps and understand when each is most beneficial.

1. Linear Customer Journey Maps:
These maps represent the customer’s journey in a straightforward, step-by-step progression.
This type is ideal for the initial stages of planning and strategy development in the B2B buyer journey.
They help identify potential sticking points or bottlenecks in the journey.
For example, a Linear map is useful when you need to understand the basic flow of customer interactions from the first contact to the final purchase decision.

2. Circular Customer Journey Maps:
Unlike linear maps, circular ones depict the journey as a series of loops or cycles.
This type is more suited for detailed analysis and troubleshooting within the B2B buyer journey.
They’re particularly effective in identifying areas where customers might be getting stuck or where they repeatedly engage with your business.
Circular maps are great for understanding recurring sales or long-term engagement patterns.
3. Hierarchical Customer Journey Maps:
These maps use a tree-like structure to show different stages and branches of the customer journey.
They are beneficial for understanding how various parts of your organization impact the customer experience.
Hierarchical maps are handy when analyzing the effects of different business units or departments on the customer’s journey and how these interactions layer over each other.

4. Network Customer Journey Maps:
Network maps focus on the relationships and interconnectedness between different customers and touchpoints.
They’re used to understand how various channels and customer interactions work together to create a comprehensive experience.
These maps are invaluable for businesses that operate in multi-channel environments and need to understand how these channels converge to impact the customer journey.
Each of these maps plays a critical role in mapping customer journeys and creating customer journey strategies. They provide different lenses through which you can view and analyze the complex B2B buyer journey, offering insights to drive informed decisions and strategic improvements.
3 Steps To Create Your B2B Customer Journey Map And Bring Structure To Your Success
In the upcoming sections, I’ll guide you through three essential steps to construct a robust and effective customer journey map. Each step is designed to bring clarity and focus to your growth strategy, helping you attract and retain the ideal clients for your business.

The first step in B2B journey mapping is to clearly define your ideal buyer personas and the different paths they might take when interacting with your business. Your industry and the type of products or services you offer will have the most significant impact here.
Creating buyer personas will help you optimize your marketing strategies to draw in ideal clients and subtly push away those you don’t want to work with. In my experience running a digital marketing agency , engaging with clients who didn’t align with our values and approach cost us time and caused considerable stress.
But how do you start creating detailed buyer personas? I usually advise my B2B clients to segment their audience by:
- Firmographics: This involves categorizing your target customers based on factors like geographic location, industry type, company size, structure, and performance. These firmographics help in tailoring your strategies to suit different business models and industry needs.
- Demographics: While it may seem more relevant to B2C, demographics are crucial in B2B as well. Remember, at the end of the day, you’re dealing with individuals making decisions. Defining the age, gender, job title, and education level of these decision-makers helps in creating more targeted marketing campaigns.
- Behaviors: Understanding the behavior patterns of your target personas is key. This includes their buying habits, brand interactions, and how they engage with your type of product or service. Behavioral analysis helps in predicting future trends and making informed marketing decisions.
- Psychographics: This delves into the psychological attributes of your buyer personas, such as their values, interests, and lifestyle. Psychographics give you deeper insight into what drives the decision-making processes of your target audience.

The next step is to define all B2B touchpoints for each of your audience segments. This means identifying every point of interaction they have with your business throughout their journey.
In both B2C and B2B contexts, some touchpoints overlap, like blog posts, social media engagements, and PPC ads. However, the B2B customer journey often involves more intricate touchpoints. These include product demos (having a well-designed schedule a demo landing page is crucial to converting more leads), sales meetings, and the onboarding process.
At this step, you should also consider if your web design branding aligns with the ideal client you want to attract.
Consider all the stages of your customer journey – from initial discovery and consideration, through the purchasing process, to post-purchase support and repeat engagement. For each stage, identify the key customer journey touchpoints. These might include:
- Initial engagement through content marketing or social media
- First contact with a sales representative
- Interaction with your website
- Experiencing a product or service demo
- Ongoing support and communication channels post-purchase
It’s essential at this step to ensure that your touchpoints are numerous and cohesive. They should all speak the same language – your brand’s language. Paying attention to your web design branding is critical. Your website, as a primary business channel, should reflect the essence of your brand and resonate with your ideal client.
By carefully defining and optimizing each of these touchpoints, you ensure that every interaction a potential client has with your business is meaningful, consistent, and aligns with the overall objectives of your B2B customer journey.

Now, it’s time to delineate and understand the five foundational stages of a B2B customer journey. These stages serve as a guideline. You can customize them according to your business’s unique needs and customer life cycle. Let’s delve into each stage, exploring the mindset of potential customers and effective strategies for engagement and conversion.
1. Awareness Stage:
Customers in this stage are often seeking information. They may be experiencing certain pain points but haven’t yet identified the exact problem or the solution. Your role is to capture their attention and help them better understand their issues.
The key here is to create quality content that educates and informs. This could be through:
- Infographics
- Social media content
At this stage, your conversion goal is typically about capturing interest rather than making a sale. Goals may include website visits, content downloads, newsletter sign-ups, or social media engagement.
Focus on the ‘why’ and ‘what’ rather than the ‘how.’ Highlight common issues or challenges that your target customers might face. Use storytelling to make your content relatable and engaging. Remember not to appear too pushy.
2. Consideration Stage:
Now, your potential customers are evaluating their options. They are looking more deeply into the pain points they’ve identified and the available solutions. Your potential clients compare different products or services, assess their features, benefits, and costs, and consider how well each aligns with their specific needs. Here, more detailed and specific content can be effective:
- Case studies
- Product demos
- Email marketing
In the Consideration stage, conversion goals focus on deepening engagement. This might include actions like downloading a whitepaper, signing up for a webinar, or requesting a product demo.
Shift the focus from general industry problems to specific solutions your product or service offers.
Provide content that highlights your unique value proposition.
Use this stage to educate potential customers about your product or service, focusing on how it addresses their specific needs and pain points.
3. Conversion Stage:
The Conversion stage is the critical point in the B2B customer journey. It’s where consideration turns into decision-making. Potential clients have gathered enough information and are ready to make a purchasing decision. They are one inch away from deciding whether to make a purchase or enter into a business relationship with you. However, they seek that final push or reassurance confirming their choice.
Here’s what you need to do at the conversion stage:
- Personalized Communication: By now, you’ve probably learned more details about each potential client. Personalizing your emails, direct sales calls, or proposals can be very effective.
- Clear Call-to-Action (CTA): Ensure that your marketing materials, especially on digital platforms, have clear, compelling CTAs that guide the customer toward making a purchase or getting in touch.
- Streamlined Purchasing Process: Simplify the purchasing process to make it as smooth and hassle-free as possible. This could involve optimizing your online checkout process, providing clear pricing information, and offering flexible payment options.
- Risk Reduction Measures: Implement measures to reduce perceived risks, such as offering guarantees, free trials, or demos. This should alleviate any remaining doubts or concerns.
The aim is to facilitate the customer’s decision-making process and lead them to a confident purchase decision.
Focus your content on the tangible benefits and ROI that your product or service offers. Highlight success stories and case studies that demonstrate real-world results.
Moreover, you can try evoking a sense of urgency with limited-time offers to encourage quick decision-making. Incentives like special pricing for early sign-ups can also be effective.
Finally, make it clear that your team is ready to assist with any queries or concerns during and after the purchasing process.
4. Service Stage:
Once a customer has made a purchase, the Service stage of the B2B customer journey begins. This stage is critical for maintaining satisfaction, building long-term relationships, and setting the stage for repeat business or upselling.
After buying your products or services, customers expect their needs to be met effectively and efficiently. They are looking for validation of their choice through high-quality service and support. You must address any post-purchase doubts or issues to ensure continued satisfaction.
- Onboarding: Implement a structured onboarding process for new customers. Guide them on how to use the product or service, whom to contact for support, and what to expect in the coming days or weeks.
- Responsive Customer Support: Ensure your customer support is easily accessible, knowledgeable, and responsive. Quick and effective resolution of any issues is crucial in maintaining customer trust and satisfaction.
- Regular Check-Ins: Proactively reach out to clients for feedback, offer help, and update them on new features or services. Show them that you value their business and are invested in their success.
- Resource Availability: Give customers access to user guides, FAQs, training sessions, and community forums to help them fully utilize your product or service.
In the Service stage of the B2B customer journey, you focus on exceeding customer expectations and strengthening the foundation for a long-term relationship. Show customers that their satisfaction and success are your top priorities, which in turn nurtures loyalty and opens doors to future business opportunities.
5. Advocacy Stage:
Here, satisfied customers become champions for your brand, sharing their positive experiences with peers and contributing to your business’s growth through word-of-mouth and referrals.
Customers in this stage have a high level of trust and satisfaction with your product or service. They are more likely to recommend your business to others.
- Encourage Testimonials and Reviews: Ask satisfied customers to share their experiences. Make it easy for them to leave reviews or provide testimonials, which can be powerful tools for attracting new customers.
- Implement a Referral Program: Create a referral program that rewards customers for bringing in new business. This encourages them to advocate for your brand and shows appreciation for their support.
- Engage in Co-Marketing Efforts: Collaborate with customers on case studies or joint marketing initiatives. This not only showcases their success but also strengthens your partnership.
- Keep the Dialogue Open: Maintain regular communication with your most loyal customers. Keep them informed about new developments and involve them in feedback sessions or beta tests for new products.
In the Advocacy stage, the conversion goals shift towards generating new leads through referrals and enhancing brand reputation. Monitor metrics like referral rates, the number of testimonials received, and the impact of case studies on lead generation.
Use your platforms to share customer success stories.
Offer special content, insights, or offers to your advocates as a token of appreciation and to keep them engaged.
You might also want to try building a community where your most loyal customers can interact, share their experiences, and feel like a part of your brand’s journey.

If you’ve mapped out a B2B customer journey and are now wondering, “ Why is my conversion rate so low? ” – there are several things you can do to turn things around in your favor.
Simply laying out the stages of your customer journey doesn’t automatically guarantee improved sales or conversions. Think of your customer journey map as a living, breathing entity. Based on customer feedback and data-driven insights, it needs regular nurturing, updates, and tweaks.
Optimizing your B2B customer journey is an ongoing process. It involves delving into each journey stage, analyzing performance metrics, identifying bottlenecks, and experimenting with new strategies to enhance the overall customer experience. It’s about asking the right questions:
Are you targeting the right audience? Is your messaging resonating with your potential customers? Are there any touchpoints where prospects drop off more than others?
In this section, I’ll give you tips for refining your approach, enhancing customer experiences, and boosting your sales figures.
Optimize Your Website For B2B Customers
Your website often serves as the first point of contact between your business and potential customers. Optimizing your website goes beyond aesthetic appeal. You must create a functional, user-friendly platform that resonates with business clients. Understanding the difference between B2B vs B2C website design is crucial here.
- User Experience (UX): B2B website visitors typically seek specific information to help them make informed business decisions. Ensure your site is easy to navigate, with a clear structure and intuitive menu. Information should be easy to find, and the overall user experience should be seamless.
- Content: Tailor your content to address B2B concerns. This includes detailed product information, case studies, whitepapers, and industry insights. The content should establish your expertise and trustworthiness in your field.
- Call-to-Action (CTA): Your CTAs should be clear, compelling, and relevant to your B2B audience. Whether scheduling a demo, downloading a whitepaper, or contacting a sales representative, ensure these actions are prominent and straightforward.
- Lead Generation Tools: Implement effective lead generation tools such as contact forms, newsletter signups, or free resource downloads. Place them strategically to capture leads without appearing intrusive.
- Mobile Optimization: With the increasing use of mobile devices in the business world, ensure your website is fully optimized for mobile. This means fast loading times, responsive design, and mobile-friendly navigation.
- SEO Strategies: Employ robust SEO strategies to enhance your visibility to a B2B audience. Optimize your website for industry-specific keywords, maintain a blog with regular, high-quality content, and ensure your website is technically sound.
- Social Proof: Incorporate social proof elements like client testimonials, partner logos, and case studies. These build credibility and reassure potential customers of your expertise and experience.
Leverage Analytics Tools To Find Out How People Interact With Your Brand Across Different Channels
One crucial yet often overlooked part of the customer journey mapping process is to test if things turn out as planned. It’s essential to set up and use web analytics early on to monitor different marketing channels and how your audience interacts with your brand.
Pay attention to user behavior on your site. Which pages are they spending the most time on? What is the journey they take through your website? This information is vital to understanding what captures their interest and where they might be dropping off.
Conducting a CRO audit from time to time can also help you identify bottlenecks in your funnel and improve your customer journey.
Utilize the insights from your analytics and CRO audits to test different strategies. This could involve A/B testing on your website, experimenting with different email marketing tactics, or trying new approaches on social media.
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Traffic Sources: Understand where your visitors are coming from. Are they finding you through organic search, social media, referrals, or paid ads? This insight helps in allocating resources more effectively.
- User Behavior: Track metrics like page views, bounce rates, and average time spent on your site. This data will show you how engaging your content is and which pages are most (or least) effective in retaining visitors.
- Conversion Rates: Monitor how well your website converts visitors into leads and customers. Look at the performance of different pages and CTAs to understand what works best.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Keep an eye on the cost of acquiring new customers. This metric is crucial for evaluating the efficiency of your marketing efforts and ensuring sustainable growth.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Understand the long-term value of each customer. This helps determine how much you can afford to spend on acquiring and retaining new customers.
Use CRM To Store All Information
In my own journey of scaling Alpha Efficiency, adopting a CRM system, specifically HubSpot, was a transformative decision. Besides allowing us to store data, a dedicated CRM helped us build a foundation for meaningful customer interactions and streamlined operations.
HubSpot became our single source of truth. All customer interactions, from initial contacts to ongoing engagements, were meticulously logged. This organization meant we spent less time searching for information and more time acting on it.
Using a CRM helps you uncover patterns in customer behavior. These insights enable you to tailor our services more effectively, anticipate needs, and address issues proactively, significantly boosting customer satisfaction.
Check my article on small business tools to find the CRM that best suits you.
B2B customer journey mapping is not a static or one-time activity. It’s a continuous, dynamic process that evolves with your business, market, and most importantly, customers.
The insights and strategies I gave you in this article are designed to guide you through understanding and improving each stage of your customer’s journey. However, every business is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. It’s about finding the right balance and approach that aligns with your business goals and customer needs.
If you’re looking to dive deeper into analyzing your current digital presence or seeking ways to attract and retain more clients, I’m here to help. I invite you to schedule a call with me for a personalized consulting session. Together, we can assess your current strategies, identify areas for improvement, and develop a tailored plan to enhance your B2B customer journey, ultimately driving better results for your business.
Also, to stay in touch with the latest trends in digital marketing and receive weekly advice on improving your online success, join my Conversion Insider community for free.
Related posts:
- Conversion Rate Optimization Checklist: Boost Your Website Profit
- Is rel = “noopener noreferrer” the same as “nofollow”?
- Website Builders or Hard Coding: Which Fits Your Business The Best?
- Create A Website: Development Steps From Concept to Profits
- Form UI Design: 13 Tips That Can Triple Your Conversion Rates
Recent Post

Brian Dordevic
How To Use Isometric Web Design To Increase User Engagement
Have you tried adding depth and personality to a website design while prioritizing a clean aesthetic? Then you know what a challenging endeavor that c...

How To Get Web Design Clients (Even If You're Not Good At Sales)
Do you fear that not knowing how to get web design clients will prevent you from ever achieving the freedom you've been hoping for? Tired of sendin...

UI Screens: Design Principles for Maximizing App User Engagement and Retention
In the digital world, screens take center stage. Well-designed UI screens can boost mobile app conversion rates by nearly 200%. That's probably why th...

Infinite Deals
Eliminate uncertainty.

Strategy Session
Embrace the opportunity.

Website Essentials
Work with me and my team.

ConversionHUB
Operations docs for your firm.

Fresh inspiration is a fingertip away, Download Our Portfolio.
Download Our Portfolio
Chapter 1: The B2B Customer Journey + Buying Process

Welcome to Chapter 1 of A Master Guide To B2B Content Marketing .
Understanding the B2B customer journey is the first step to building an effective content marketing strategy.
The art of B2B content marketing involves aligning your business goals with your audience's needs. A good B2B content marketing strategy caters to your audiences' personalized interests within specific phases of the buying process and sales funnel.
Let’s run through the top 10 factors that define B2B customer journeys, looking at the buying process in particular.
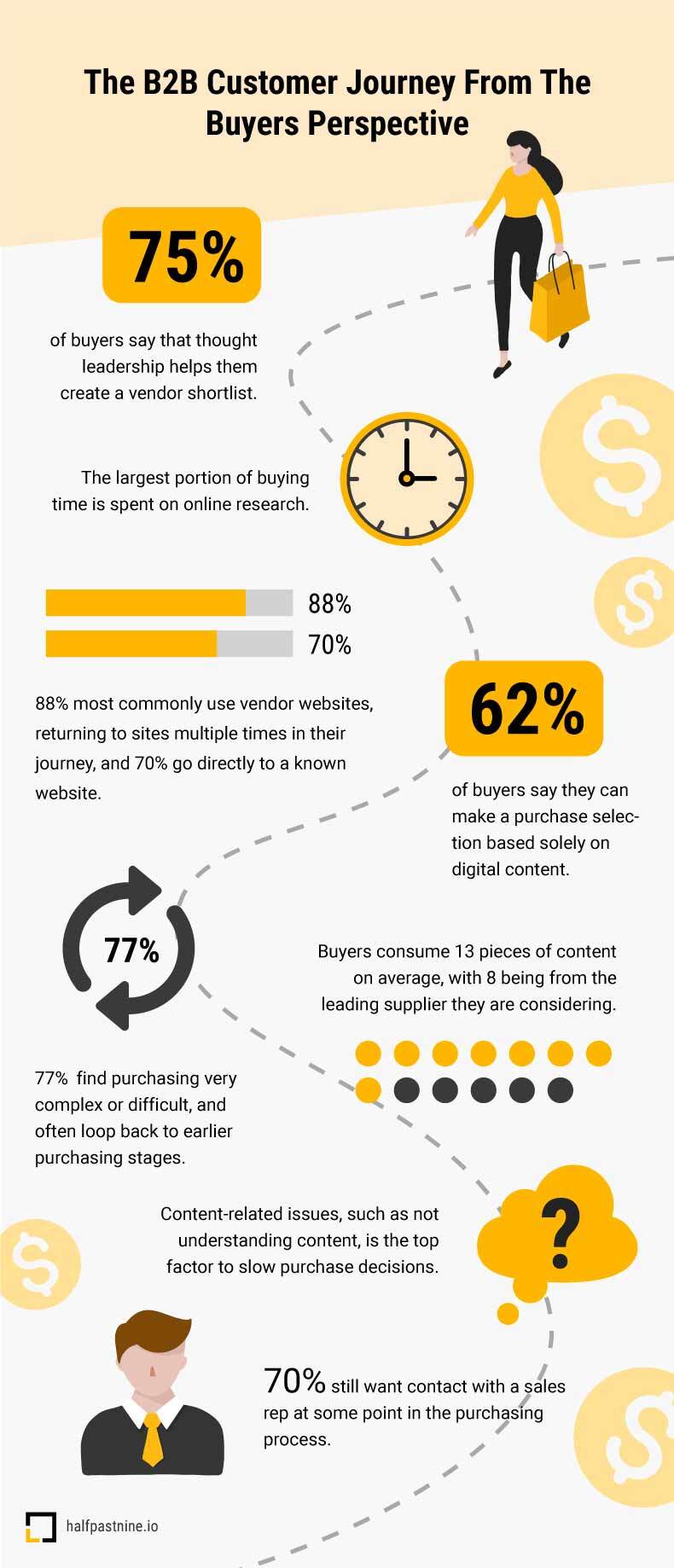
1. Longer Nurturing Times
B2B sales conversions are not immediate impulse buys. They are highly logical decisions that require multiple data inputs, and will be considered at more than one level of an organization.
- Gartner found that 77% of B2B buyers found purchasing very complex or difficult. The process is not linear, with buyers typically looping back to previous stages.
- On average, 75% of B2B companies take at least 4 months to win a new customer, but more complex deals can take much longer.
It takes time to fully define purchasing criteria, explore options, and weigh them up before reaching a final decision. That’s why the B2B customer conversion process is a sustained effort that requires a diversity of content to support effective lead nurturing strategies.

2. Multiple Buyer Roles With Differing Priorities
Collective purchasing decisions will make or break a business, so of course, it’s not taken lightly. A B2B buying process will potentially involve multiple departments and job roles.
- Data from 2017 found that an average of 6.8 people were involved in purchasing decision making, up from the previous year. (Of course, this depends on the size of your target customers’ businesses.)
- Today, 73% of people involved in the B2B buying process are millennials, and 81% of non-C-suiters have a say in purchase decisions.
Your content library needs to target decision-makers for conversion, but equally cater to influential researchers and end users as crucial players within the process. If you're only marketing to the highest level, you're overlooking people who need to notice you before things progress to the decision-making stage.
There are typically 4 main buyer roles:
1. Influencer or Initiator - A person close to the process who identifies the need for an outside solution and whose opinion counts in the buying decision. They could be an end user, a team manager, or act in an advisory capacity.
2. Information Gatekeeper - A person who controls the flow of information and communication in the organization, whether a manager or a tasked assistant. They typically control access to decision makers.
3. Decision maker - The person who makes a final call and approves the purchase. They aren’t often an end user, but sit higher up within the managerial hierarchy with priorities that could differ from an end user or manager.
4. End User - The people who will actually use your solution or service in an operational capacity. They might become the main contacts for the relationship on a day-to-day basis after purchase.
3. Online Research Is the Biggest Purchasing Activity
It is vital that your brand shows up during the online research process. In 2019, Gartner found that 27% of the complete B2B buying process is spent on online research. This is the largest portion of time spent on purchasing activities.
- The amount of time spent on online research increases in line with the value of the purchase, but is 20 hours on average.
- Your sales reps may get as little as 5% of total buyer time during the whole process. B2B buyers can carry out over half of the buying process through digital touchpoints before they establish contact.
- In terms of making a decision, buyers will progress more than 70% of the way to making a final decision before engaging sales representatives.
- 62% of B2B buyers say they can make a purchase selection based solely on digital content.

4. Vendor Websites Is the Favored Research Channel
Most B2B buyers will use your website as their primary research tool.
When it comes to channels for purchase planning specifically, a 2018 Statista survey of global B2B marketing professionals found:
- 88% of buyers most commonly used vendor websites, returning to sites multiple times in their journey.
- 70% go directly to a known website.
- 67% conduct a general internet search.
- 53% go to social media to find purchasing information.
- 50% used LinkedIn to research vendor content.
5. Buyers Want Content To Guide Them
When it comes to online research, 32% of buyers said they couldn’t find the information they needed, and 37% said there was not enough information relating directly to purchase.
Creating clear and streamlined content flows for defined buyer personas according to their interests, roles and needs is a crucial goal to work towards.
- C-level executives ( 60% ) and VPs (82%) report that content-related issues - such as not understanding the content or not being able to share content internally - are the top factors slowing down purchase decisions.
- 45% of buyers said they want a personalized content portal to help them find relevant content.
Content personalization is a trend that continues to grow as inbound marketing evolves, raising customers’ expectations.

6. Several Pieces of Content Are Required (But Not Too Many)
Key content touch points must be planned to progress users within a B2B buying process to completion. Expanding your customer touch points while portraying your brand authority consistently at every journey stage is a key part of building brand awareness and then trust.
More B2B marketing touch points are required than B2C on average. We’re talking around 10 digital touch points before first contact as a general rule of thumb. And most buyers ( 77% ) will consume more than 3 pieces of long-form content before making contact.
However, content provision needs to be strategically considered with relevance prioritized over volume. There is a sweet spot for deeper-funnel content volume in terms of driving conversion.
- Buyers have been found to consume 13 pieces of purchasing content on average, with 8 being from the leading supplier they are considering.
- 86% of buyers get overwhelmed when there are more than 10 pieces of purchasing content to read from an individual supplier.
7. Trust Is the Most Important Factor
The larger and longer-term investments typically involved in B2B mean that buyers need to build trust before they make any commitments. Relationship building for extracting high lifetime value is a much larger part of the equation. Your leads are evaluating your company for the commitment to serve their best interests and deliver what they expect over time with consistency.
- Over 90% of decisions to buy from another business depend solely on the trust created.
- 84% of buyers say they would be more likely to purchase from a supplier they had a good relationship with, even if their competitors had better sales terms.
- 75% of B2B marketers found that content marketing was successful for building trust during 2021.
8. Industry Trends and Tech News Is Favored
The B2B customer journey can start long before an active buying process. Building topical authority within your niche helps you reach the relevant people to build brand awareness and credibility. You want your brand to come top of mind when a buying process is activated.
- Learn more about brand awareness and how to measure it .
Most buyers ( 75% ) say that thought leadership helps them create a vendor shortlist, and 49% of decision-makers say thought leadership has directly led them to do business with a company.
B2B audiences regularly spend time consuming content:
- 88% of B2B professionals consume business-related content online at least once a week and are prepared to spend time consuming content.
- A 2019 study found that 34% of buyers would invest 30-60 minutes in a content session, and 26% spent as long as it took if the content was great.
- In 2021 overall B2B content consumption increased by 22% .
In terms of topics, B2B buyers are most interested in industry trends, especially backed up by data and metrics:
- Clutch found that the leading reasons for consuming content was to stay up to date with industry trends ( 45% ) and industry technology (45%), followed by 24% looking for small business topics.
- IT and tech buyers are particularly driven to stay up to date with new trends. Isoline’s 2019 survey of IT buyers found that 66% of respondents were aiming to learn about industry developments, and 56% read for purchase planning.
- 66% of surveyed B2B buyers say they want vendors to use more data and research to support their content.

9. Content Must Integrate With Sales Processes
While B2B buyers spend most time researching online, 70% still want contact with a sales rep at some point in the buying process. B2B is significantly more dependent on people relationships for conversion.
Marketing content should integrate with your sales team’s processes for a smooth wooing and conversion process. Your business's financial success depends on how easy it is for buyers to move through the funnel and convert. Every part needs to function together, with a smooth hand over to sales staff for qualified leads.
Automated marketing tools can really help you with this, but more on that in Chapter 4!
Given the importance of online content marketing for building B2B brand awareness and nurturing the buying process, your business can’t afford not to show up online!
Search engines are particularly important at the starting point of a buying process. However, pre-building brand awareness among your target audience using online thought leadership puts you 10 steps ahead of competitors who don’t do this as well. You want buyers to come directly to your website as the first port of call.
Getting to grips with what your audience are most interested in and providing genuinely helpful content relevant for your offering will make sure they think of you first when a buying process is activated. To achieve this, leverage online channels where your audience spends time consuming business content, such as LinkedIn, online media publications, eNewsletters and Google.
Once a buying process starts, your job is to provide clear content for the consideration + action stages by explaining solutions, the value they deliver and supporting evidence.
- Data visualization is a crucial tool for understanding and optimizing how your marketing content performs.
- Learn how to build your marketing data inputs .
And this concludes our exploration of the B2B buyer customer journey.
Discover more of this four-part series below, designed to help you achieve your content marketing goals. Or why not bookmark them for later?
More In This Series:
- Chapter 2: Building Your B2B Content Marketing Strategy
- Chapter 3: How To Create B2B Marketing Content
- Chapter 4: Distribution Tactics for B2B Marketing Content

Unlock Revenue Growth With Data
Knowing where to invest marketing budget to increase contribution margin and overall revenue growth is the #1 pressing challenge for any marketing or growth leader.
As multichannel complexity and media budgets grow, attribution becomes one of those topics we really can’t ignore.
To truly understand the most valuable customer journey design, relying on default attribution reporting within ad platforms or Google Analytics just doesn’t cut it. In fact, it can even do more harm than good due to misattribution and double attribution - a big problem with these uncensored (and self-serving) tools.
The trouble with free on-platform attribution reporting (like Facebook or Google Analytics) is that they are siloed walled gardens that work in isolation with their own limited data sets. Your most powerful and valuable attribution analysis needs to cover everything, directly tied back to revenue results.
Without a proactive attribution strategy that connects all your customer journey and conversion data, optimized customer journey design will remain an elusive mystery. Highly influential channels like dark social or offline interactions are often underestimated or completely missing, while non-profitable campaigns are over-indexed.
The difference in business results can easily stack up to millions of dollars in wasted budget and lost opportunities - especially where larger paid media budgets are involved.
Let’s explore how marketers can master attribution to start hitting revenue targets with much greater confidence and certainty.
The Impact of Not Using Accurate Attribution Reporting
The impact of not using attribution reporting - or using it poorly - is worth understanding. It can have multiple negative impacts on decision-making and overall business performance.
The common consequences are:
Incomplete Customer Insights Cause Poor CX
An incomplete understanding of customer preferences, motivations, and pain points hinders the ability to tailor marketing strategies to effectively engage and convert customers.
This can result in a lack of adequate content personalization and a poorer customer experience (CX), meaning your brand gets overlooked in favor of others by potential customers.
Unprofitable Resource Allocation
Struggling to accurately identify the marketing channels, campaigns, or touchpoints that are driving conversions or desired outcomes results in less effective use of resources.
For example, over-investing in underperforming channels, and underinvesting in high-impact touchpoints, wasting budget in the process.
Poor Revenue Growth and Limited Brand Equity
Incorrect assumptions about the impact of specific touchpoints or channels results in suboptimal marketing performance and missed opportunities.
If marketing efforts fail to engage and convert customers effectively over time, the business can suffer from stunted revenue growth, also putting a cap on brand equity.
Understanding the Challenges for Accurate Attribution
Marketers can’t fully rely on free attribution solutions for the insights they need to drive significant optimizations. Results can be significantly misleading when solely using free on-platform attribution reporting.
On-platform attribution issues:
- No Cross-Channel Visibility - On-platform attribution doesn't have full visibility into the performance of other channels, or wider customer journey outside of their own ecosystem, acting as walled gardens. This limited view can make it difficult to understand the true impact of each channel on conversions and ROI (or ROAS).
- Double Attribution - When using multiple platforms, there's a risk of double attribution - where more than one platform takes credit for the same conversion. This overlapping attribution may cause businesses to overestimate the performance of certain channels or campaigns, and consequent overinvestment stunts overall marketing ROI.
- Inconsistent Attribution Methods - Different platforms apply different attribution rules, leading to inconsistencies in how they assign credit to various touchpoints. This inconsistency can make it challenging to accurately compare the performance of different marketing channels or campaigns.
- Tracking Limitations - With increasing data privacy regulations, third-party platforms may face challenges in accurately tracking user behavior across channels. A custom attribution model can help overcome some of these limitations by incorporating first-party data and other tracking methods.
- Lack of Customization - On-platform attribution reporting may not be tailored to your specific needs, goals, and marketing strategy. A custom attribution model, on the other hand, can be designed to accurately reflect a business's unique customer journey, allowing for more precise insights into the performance of each marketing channel and campaign.
There is a compelling case for marketers to invest in their own customized attribution solutions. Especially when paid media investments start becoming more significant.
However, accurate attribution modeling isn’t one of the most straightforward tasks for a marketing department to tackle.
There are several hurdles to overcome to extract and benefit from the most valuable insights:
1. Tracking Data Across Complete Journeys
A typical user journey involves multiple devices, channels, platforms, and time breaks between visits, making it difficult to track a complete customer journey path from the first touchpoint to conversion. Cross-device tracking techniques are needed, such as device matching or probabilistic modeling.
2. Data Privacy
Tracking restrictions and cookie limitations can limit the ability to track customer interactions across marketing channels, sometimes requiring workarounds. Yet it's essential to adhere to data privacy regulations, maintain transparency and obtain appropriate consent from customers when collecting and utilizing their data.
3. Offline Data Tracking
Marketers may need to implement strategies such as unique identifiers, coupon codes, QR codes, or call tracking to link offline interactions to specific customers and attribute them properly. However, implementing and managing these tracking mechanisms may require additional resources and operational adjustments, including manual data entry from both customers and staff.
4. Data Quality and Completeness
Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the data is crucial for building reliable attribution models. Marketers must establish data quality control measures, address data gaps, and perform regular data validation to maintain the integrity of the data.
5. Data Integration
Integrating data from various sources, both online and offline, can be complex. Offline data sources such as in-store purchases, call center interactions, or direct responses may not be easily captured and linked to other digital data. Marketers need to develop data integration processes to build a unified view of complete customer journeys.
6. Attribution Modeling Complexity
Choosing the best-fit modeling approach for marketing goals, and accounting for multiple touchpoints both online and offline, adds complexity to attribution modeling. Marketers need to understand statistical models that can properly attribute credit to different touchpoints based on their real impact on conversions. This requires analytical expertise, plus the budget for necessary data tools as marketing complexity grows.
Types of Attribution Data
Data attribution models are nothing without the data that you feed into them.
There are 2 main sources of attribution data.

1. Software-based Attribution Data
This utilizes digital tracking tools, such as analytics platforms or marketing automation software, to track and record user interactions and automatically attribute conversion actions to specific marketing touchpoints.
Pros - It provides objective and granular data on user interactions and conversions, and enables real-time tracking and analysis of customer journeys. The reliance on voluntary self-reporting and subjective recall is reduced.
Cons - Aside from missing touchpoints that are not digital or easily trackable by software, it can be complex to implement and require technical expertise. You’ll need the right tracking set up for accurate data and reliable insights, and the analytics tools.
2. Self-reported Attribution Data
This is data collected directly from your customers and leads, who share information about the touchpoints that influenced their decision-making process. It’s usually collected via an online form or survey but can also be collected in direct conversation with customer-facing staff and then recorded in a CRM.
Pros - It allows for qualitative data collection, using direct insights from the individuals themselves to capture subjective factors and nuances that software-reported attribution may miss, such as offline interactions or word-of-mouth referrals.
Cons - It relies on individuals' willingness to provide information, and their memory and perception which may not always be accurate or complete. This type of data can be more time-consuming and resource-intensive to collect and analyze.
Hybrid Attribution Data
Combining both self-reported and software-based data sources into attribution modeling is what is known as hybrid modeling. It’s the ideal solution to mitigate the drawbacks of each data type, providing the most fully comprehensive understanding of your customers journeys.
Next, depending on your marketing activity and data tracking sophistication, you’re going to have some of the following types of data sets to work with.
The best way to categorize your data inputs is to split it into channel data and event data.

1. Event Data (What Happened?)
Event data typically includes:
- Conversion Data - Conversion data includes information about the desired actions taken by users, such as purchases, form submissions, or sign-ups. Conversion goals need to be set for each journey stage.
- Behavioral Data – Any data related to customers' online behavior, such as organic website visits, page views, time spent on site, clicks, search queries, and interactions with specific content or features.
- Clickstream Data – This is a record of each click a consumer makes while browsing online. Tracking all these actions can help brands form an accurate understanding of the most effective consumer journey design.
- Ad Impressions and Clicks - Ad impressions combined with click data provides information on the number of times an ad was displayed to users, and the corresponding clicks made. This data helps gauge the effectiveness of specific ads.
- CRM and First-Party Data - This data provides long-term insights into customer behavior and can include survey responses, purchase history, and any interactions with the brand. CRM data is necessary to link the direct impact on revenue generation and CLV.
Note, there are two common ways to give credit to touchpoints within a conversion sequence: post-click, or post-view.
Post-click Conversion Data - If attribution is done on a post-click (not necessarily last-click) basis, clicked touchpoints will get a part of the conversion credit as long as the action happens within the defined lookback window.
Post-view (or view-through) Conversion Data – Here, the content a user viewed (impressions) within the specified lookback window also gets part credit for a conversion. Most of the advertisers who advertise on multiple channels will have video and social media as part of the conversion journey. These channels usually are not driving clicks, but still contribute to outcomes. This data is more challenging to accurately collect.
The lookback window is how far back a conversion action is included, usually measured in days. So a 7-day lookback window would only include advert impressions or clicks 7 days before the customer converted. In low-cost eCommerce transactions where the selling cycle is short, the most relevant lookback window only might be 7 – 14 days. Whereas for more complex sales like business software, a lookback window of 60 days could be used.
2. Channel Data (Where Did It Happen?)
Channel source data typically includes:
- Referral Data - This identifies the source that referred users to your website (or app). It can attribute from the high-level referral sources, such as search engines, social media or email, right down to the specific pieces of content.
- Device and Platform Data – This gives information about the devices and platforms used by users during their customer journey. It allows marketers to track cross-device interactions and attribute conversions across different devices. Device data is also helpful for providing location information.
- Offline Data - This gives information about customer interactions outside of digital channels, such as in-store purchases, phone calls, word of mouth, events, direct mail responses, etc. Offline data is typically captured through mechanisms like unique identifiers, coupon codes, or CRM systems.
An attribution model is essentially used to link these two types of data together to show which marketing touchpoints deliver the best results.
Types of Attribution Models
There are several types of attribution models to feed your data into. Applying the right modeling for the goal or KPI is key.
A model essentially joins up your event data (what happened) to your channel data (where it happened) to show you the most profitable journey connections.
The difference between attribution models is where they place most credit for achieving a desired conversion goal (like submitting a contact form, generating an MQL or closing a sale). Conversion goals should be set up for each stage of the customer journey to feed attribution analysis.
Multi-touch models attribute results to more than one touchpoint, allowing for the influence of consecutive touchpoints to be considered as part of a process that led to the final conversion.
A model either uses:
- Rule-based methodology - Analyzes data in a completely static approach.
- Data-driven modeling - Typically uses AI and machine learning to help automatically customize multi-touch attribution based on the influence of touchpoints.

Here’s a breakdown of the most common attribution models:
Last Touch (or Last Click) Attribution
This model assigns all the credit for a conversion to the last touchpoint (or channel) that the customer interacted with before making a purchase or completing the desired action.
When to use it? - To understand which touchpoints are most influential for prompting people to take the final step in completing a conversion goal (e.g., submitting a contact form or making a purchase).
Limitations? – Although easy to use and collect data for, it’s not a great stand-alone model for longer and more complex sales cycles where conversion still heavily relies on the preceding touchpoints, particularly in B2B.

First Touch (or First Click) Attribution
The first touchpoint (or channel) the customer engaged with receives 100% of the credit for the conversion.
When to use it? - To understand which early journey touchpoints are best at first reaching new audience members who will eventually convert.
Limitations? – It ignores the influence that mid to late journey touchpoints have for final conversion. Data accuracy can also be more difficult to assure depending on your data tracking methods and lookback window

Linear Attribution
Equal credit is given to each touchpoint in the customer journey, recognizing the role of all channels in driving conversions.
When to use it? – To understand how touchpoints and journey architecture work together to nurture conversions over time, including cross-departmental touchpoints between marketing and sales for B2B.
Limitations? – The data collection process is more intensive and may require cooperation with other departments to capture all touchpoints, taking time to implement fully. This may include qualitative touchpoints through manual data entry. Distributing credit evenly doesn’t account for which touchpoints have most influence.

Time Decay Attribution
More credit goes to touchpoints that occurred closer to the conversion event, with the assumption that recent interactions have a greater impact on the decision-making process.
When to use it? – For longer, more complex customer journeys where later touchpoints are most influential. Equally, it can be useful for very short sales cycles where decisions are made quickly and you want to see which touchpoints have immediate effect for impulse conversion.
Limitations? – The influence of earlier touchpoints for creating brand awareness or intent won’t be accounted for.

U-Shaped (Position-Based) Attribution
A higher percentage of credit goes to the first and last touchpoints in the customer journey, while the remaining credit is distributed evenly among the other touchpoints. It's based on the idea that the first and last interactions play a more significant role to create new leads and drive conversions.
When to use it? – When you want to understand which channels generate most new leads, and which drive most conversions.
Limitations? – Again, the influence of in-between touchpoints will not be fully understood, and it requires data collection to cover all touchpoints within the journey.

W-Shaped Attribution
Equal credit goes to three key touchpoints: the first interaction, the lead creation event (e.g., form submission), and the final conversion event. The remaining credit is divided among the other touchpoints.
When to use it? – To highlight the key journey milestones from early journey, mid journey and late journey.
Limitations? – The influence of intermediary touchpoints is not fully understood

Data-Driven Attribution
Data-driven models use advanced analytics, machine learning, or artificial intelligence to analyze customer journey data and assign credit to various touchpoints based on their estimated influence on conversions. This can be done by off-the-shelf software solutions specifically designed for marketing attribution. There are two widely accepted data-driven models for attribution: Shapley value model, and Markov chain model.
When to use it? – For more accurate full-journey attribution across multiple touchpoints, providing greater flexibility for integrating multichannel data silos and more balanced weighting criteria.
Limitations? - An attribution software subscription is required, some of which can be costly. How the algorithms are coded and applied is sometimes proprietary information that is not made fully clear or adaptable. Data sources still need to be set up and connected, including offline touchpoints. It can take months of work to fully set up and implement a data-driven model covering all marketing channels.

Fully Customized Attribution Modeling
Custom-built models are also data-driven, but can include as much complexity and adaptability as you’d like. They allow for full visibility and control of the combined data sets, rules and weighting in use. It allows the layering of many rules and granular data analysis so you can deeply understand and drive growth to a level that isn’t available any other way.
When to use it? - For larger media budgets where small adjustments see the $ results impacted by millions.
Limitations? - Fully customized attribution requires a specialist to implement because of the complicated algorithms and calculations, along specialized statistical software and coding. Like off-the-shelf data-driven solutions, it can take several months to fully implement.

Choosing Data and Models to Match Goals
For multichannel marketing across the customer lifecycle, marketers will have several different goals and KPIs, so there isn’t a one-size fits all when it comes to using attribution modeling.
For example, marketing goals will vary by campaign, but also business lifecycle stage. As a business matures and can afford to allocate more budget in demand creation, longer payback periods become feasible in the name of sustainable growth.
For the most accurate results, several rules and weighting criteria may need to be layered together. This requires an understanding of how to choose the most appropriate combination for each goal or data set.
Here are examples of how different goals could affect the overall approach for assessing attribution against KPIs:
Brand Awareness - The main objective is to build familiarity rather than immediate conversions, so attribution models that consider upper-funnel touchpoints using a longer lookback window are most helpful.
Conversion Rate Optimization - Last touch attribution can provide insights into the most influential touchpoints in driving conversions for any journey stage.
Customer Acquisition – With a focus on identifying marketing efforts that drive most new customers, attribution models that emphasize first touch and last touch before sale conversion are a good fit.
Customer Retention and CLV - Attribution models that consider multiple touchpoints over the customer lifecycle are best. Time-based attribution models such as linear or time-decay attribution can help identify touchpoints that contribute to CLV over time.
Cost Efficiency - Attribution modeling using cost-per-click (CPC) or cost-per-acquisition (CPA) data provides insights into the cost of acquiring customers through different channels.
Channel Optimization - Models like time-decay attribution or position-based attribution can help evaluate the effectiveness of various channels throughout the customer journey.
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) - Attribution that uses revenue conversion data along with position-based or data-driven models are most suitable for calculating ROAS. These models can help isolate the impact of an advertising campaign against other touchpoints.
Customer Engagement - Attribution models fed with click data are most valuable. Models like engagement-based attribution or position-based attribution can help attribute credit to touchpoints that generate higher engagement levels.
Campaign or Event Success - Campaign-based attribution or event-based attribution allow marketers to filter conversion data specifically for the corresponding campaign (or event) identifier.
Demographic Targeting - Companies that target audience segments based on demographic data, such as geography, need to be able to filter customer event data for segment-based attribution.
Social Media Influence - Models using multi-touch attribution with social media weighting can help more accurately attribute conversions or engagements specifically to social channels.
Experimentation with attribution models will help you find the most suitable approach for each reporting use case.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Building Custom Attribution Models
A customized approach to attribution modeling allows hybrid data usage to give the most complete and accurate view of your marketing effectiveness. (Reminder - a hybrid approach combines multiple online and offline data sources, reducing the risk of misleading insights).
With customized approaches, you can get journey clarity at the individual level. For example, you could isolate a new customer to see that their first website visit was 9 months ago, and they were exposed to 37 ads across 5 platforms. You can also use heat map tools to confirm how channels work together in order to predict where prospects will go next, targeting content messaging accordingly.
Here are the 6 steps to create custom attribution reporting that will truly allow you to start optimizing your marketing investments:
Step 1 - Clearly Define Your Goals
Identify the specific objectives that your marketing efforts aim to achieve, such as increasing conversions, driving brand awareness, or improving customer retention. They can be different for each channel or audience segment. As discussed, these goals will guide the rule options for your attribution model.
For each goal, decide what you consider to be a conversion for the journey stages, and whether you will need to include post-view data in addition to post-click data. The type of conversion is important, so you’ll want to identify the conversion events to look at for each specific goal, including the lookback window that will be most relevant.
Attributing marketing activity to revenue is the ultimate aim – this will give you the most powerful information to improve ROI and drive growth.
Step 2 - Identify All Your Data Sources
Start with accurately and consistently collecting all the data you possibly can for all customer interactions across all your active channels and platforms. You’ll need to UTM tag every link that matters, and have tracking pixels installed for all active marketing platforms.
Here’s a quick checklist of data sources:
- Social media (organic)
- Paid media campaigns
- Email marketing
- CRM system and revenue data
- Customer feedback
- Call tracking
- Offline touchpoints
- Third-party data providers
- Self-reported attribution is most valuable when free text only.
- B2B buying decisions usually involve multiple people, so it’s better to track the customer journey at the account level instead by combining individual user data.
Step 3 - Bring in the Necessary Data Capabilities
Marketers need to have a deep understanding of marketing concepts and principles to be able to set up effective attribution models and make data-driven decisions.
You will need access to strong data analysis skills to be able to set up, manage and interpret the data for customized attribution models. Some technical knowledge is required to select, set up and configure attribution software tools, integrating them with existing data sources and systems. Knowledge of statistics is also necessary to understand, interpret and communicate the results of attribution models.
If in-house attribution data specialists are not in budget (or available), It can be more economical to use specialized data agencies to support you.
Step 4 - Chose + Activate Your Data Tools
Available resources are a big part of your consideration here. You’ll need to consider what is within means for your company in terms of ease of use, data integration capabilities and subscription cost.
There are 2 options here:
- Off-the-shelf attribution software
There are several software tools available that can help marketers combine marketing attribution data from different sources.
Tools with in-built machine learning and AI are better suited to help you analyze and weigh the contribution of different touchpoints and channels in your custom hybrid attribution model. This will give you more accurate insights.
Google Analytics (or Campaign Manager 360) are the best known off-the-shelf providers. However, data integration from other sources can be much more of a challenge with GA. Some other off-the-shelf options which offer better data integration capabilities include Northbeam, Wisely, Adobe Analytics and Improvado.
However, the drawbacks are that you’re still handing over power to a platform that uses its own proprietary algorithms, not always allowing complete visibility or flexibility in how rules are applied or data is weighted.
- Build your own custom modeling
Depending on your resources, building custom modeling offers the greatest control and visibility of exactly how data is being weighted and analyzed for each scenario.
If you’re doing this independently, you’ll need a data connector/warehouse solution to import and store your data from across your multichannel data sources. Custom coding and statistical tools can be utilized for advanced capabilities, allowing for layered algorithms and models tailored to any specific need or data set, including fully customized weighting criteria for data sets such as self-reported attribution.
The benefits over any other solution is the most accurate attribution possible, with completely granular insights depending on any criteria you’d like, allowing complete flexibility as variables such as channels, campaigns and customer or market dynamic shifts, and fully aligned for any goal you set.
With customized approaches, you can get journey clarity at the individual level. For example, you could isolate a new customer to see that their first website visit was 9 months ago, and they were exposed to 37 ads across 5 platforms. You can also use heat map tools to confirm how channels work together in order to predict where prospects will go next, targeting content messaging accordingly.
Step 5 - Integrate Your Data Sources
Using your selected attribution tools, start collecting and integrating data from your multichannel sources.
This involves setting up data integrations between the attribution software and the data sources, whether through configuring API connections (recommended) or importing data files.
Automate the most relevant model-based analysis into dashboards, reporting on each of your specific marketing goals whether by revenue, channel, journey stage, customer segment, etc.
Step 6 - Test and Iterate
Continuously test and refine your attribution model, adjusting the weights and methodologies as necessary. Monitor the performance of your model and make data-driven adjustments to improve its accuracy and effectiveness over time.
For example, data capture often relies on UTM tags, which requires links to be clicked before they are reported. This means some early-journey channels that rely on impressions rather than clicks (mainly social media and display advertising) will be underrepresented without qualitative self-reported data and weighting adjustments. Lift tests need to be run to help assess weighting criteria.
To test the influence of unclicked impressions, which is common for early-journey touchpoints and channels, you can use lift tests. Lift tests use test and control groups, only showing adverts to the test group. The difference in conversions between the two groups is known as lift, indicating the channel's real impact, and providing a helpful weighting metric. (Audience sample size and segment characteristics are important for statistically valid comparisons.)
Incrementality is a complementary metric to lift.

The Main Takeaways
Marketing attribution is critical to understand the impact of different touchpoints on customer behavior and conversions.
While various simplistic attribution models exist, building customized data-driven models provides marketers with the greatest control and insight accuracy for their attribution analysis. This is essential to ramp up marketing spend with certainty of generating the required revenue results.
Custom data-driven attribution models offer several advantages over on-platform and Google Analytics reporting:
1. Report Against Goals - Marketers can tailor custom models to their specific business goals, customer behavior patterns, and available data sources. This level of customization enables a more accurate reflection of the complexities of the customer journey and the unique dynamics of the market.
2. Understand Touchpoint Influence Across Whole Journeys - Custom data-driven models empower marketers to attribute credit to touchpoints based on their true contribution to conversions, rather than relying on predefined rules or assumptions. And by integrating multiple (hybrid) data sources that include online and offline interactions, marketers can operate with a significant competitive advantage to drive growth forwards.
3. Allow Flexibility For Refinement - Custom models also provide the flexibility to adapt and refine the attribution process as the business evolves. You can more easily incorporate new data sources, update algorithms, and fine-tune attribution rules to ensure the model remains aligned with changing market dynamics and marketing activities.
Implementing a custom data-driven attribution model requires robust data integration and advanced analytical capabilities. However, the benefits of improved accuracy, granular insights, and informed decision-making make the investment worthwhile, potentially adding millions of dollars of additional annual growth. Particularly where larger advertising budgets are involved.
By leveraging the power of custom attribution modeling, marketers can achieve industry-leading business outcomes.
If you need any support scoping, setting up or managing your attribution analytics, the team at Half Past Nine are here to help. We live and breathe marketing data! Just reach out.
What To Read Next:
The new era of personalization explained; a guide to building profitable customer journeys with digital intent signals.
- Marketing Data Visualization To Fully Leverage Your Sources of Truth
- Switching to First-Party Data: It’s Time to Stop ‘Renting’ and Start Owning Customer Data
The Ultimate Attribution Playbook in 2023
Imagine a future where paid media actually adds real and welcomed value in people’s lives.
Where the information someone needs appears at exactly the right time to help them find what they want. Or while they’re browsing, learn about something that they weren’t aware could solve a pressing need.
And in the process, brands spend less money putting content in front of people who don’t want or need it, radically driving up the profitability of media spend to deliver maximized revenue growth.
This future is possible, even without third-party cookies. It will be built on a mindset shift, where the rigid parameters of the sales funnel are no longer paramount, and dynamic customer journeys become the north star.
Where as marketers, we can cater to real people who don’t behave in linear ways, with empathetic understanding of what their goals might be and providing real value when it’s wanted.
If your goal is to improve customer engagement and fuel new revenue growth, this article is for you. Let’s explore how to build highly profitable customer journeys using digital intent signals.
Building Personalized Customer Journey Architecture
Our job as marketers is to get the right touchpoints and messaging in the right place to progress our prospects from first introduction to converted and loyal customers.
The basics of the customer journey remain the same under the tried-and-true framework of Awareness > Interest > Consideration > Decision > Retention > Advocacy.
The 3 journey stages for customer acquisition are:
- Early Journey (creating awareness)
- Mid Journey (nurturing interest and consideration)
- Late journey (prompting action)

However, customers can move through buying stages in very different timelines. They may regularly loop back to previous stages, with pauses in-between. In our digital era, journeys can be incredibly fragmented across devices and platforms, and many journeys are completely unique.
The typical customer journey today is actually a 3-dimensional process that can shift in any direction, rather than a straight line from A to B. They can resemble pyramids, diamonds, or even hourglasses, rather than a linear funnel.
A linear sales-funnel philosophy fits with the old approach of the stereotypical sales-led company. It’s not that a sales-led approach isn’t right for any business - but an overemphasis on sales goals can cause counterproductive tactics. For example, immediately jumping to harassing prospects with unwanted phone calls or emails, or running a generic sales ad to the widest audience possible and having to pay above average CPM/CPC due to poor engagement.
That’s why the most successful approach to fueling revenue growth is a dynamic and responsive customer journey framework, rather than a funnel approach.
It allows for the individual to engage with relevant content while on their own unique path, maximizing the number of conversion routes and potentials at any one point in time.

Naturally, the simplicity (or complexity) of a typical journey will vary greatly by the value and importance of the purchase being made.
For ecommerce brands, a customer could leap from awareness to an impulse purchase in the space of 5 minutes in the right circumstances. Or a B2B sale could take many months from initial touchpoint. (Learn more about the B2B customer journey and buying process .)
Regardless of journey timeframes, marketers building any type of customer journey architecture will still need to understand:
- What are the common challenges, needs, goals, and desires of each audience segment?
- What channels and platforms have best reach for the target audience at the specific journey stages?
- What corresponding messages will work best for each journey stage and platform?
- How do cross-channel and platform touchpoints work together to facilitate complete journeys for each segment?
Learning to Read Behavioral “Tells”
How can brands really get to grip with personalization across platforms?
Firstly by recognizing that the old way of building a sales funnel - assuming everyone who enters it will behave the same way - doesn’t reflect reality. We can’t assume that all people in a target market will be relevant leads, use the same platforms, automatically be ready to consider buying after showing interest, or that their consideration process will always follow the same path.
It’s the equivalent of walking up to a colleague in the middle of a phone call and expecting them to answer your question immediately. Or approaching someone perusing the vegan section of a store to offer them a promotional ham sample, then continuing to follow them around after they’ve said “No thank you”.
The need for observation, active listening and empathy applies as much to marketing and sales activity as it does anywhere else in life.
That’s where intent data comes in. Intent data is the marketers means of observing what people are doing, before we “decide” if and how to approach them.
Using intent data to target users will outperform targeting by demographics alone. Users who show intent are typically closer to making a buying decision, making them high-quality leads. By targeting these users, businesses can increase the likelihood of conversions to generate quicker and higher ROI.
And the more digital and mobile customers have become, the more helpful intent data they generate for us. Of course, it still depends on a brand’s ability to manage and analyze the data… But with a solid data strategy, brands can tap into intent data to engineer hockey-stick moments of sustainable growth.
Introducing Digital Intent Signals
Just like in life offline, the key is to observe people’s “body language” within their digital world, building a picture of what might be happening for them in the moment.
We call these digital actions “intent signals”.
Being able to read them allows us to connect with only the most relevant people, using tailored messages that are most likely to resonate in that particular moment.

The majority of buyer journeys start with some type of intent. Although…, your ideal prospects might not always start out directly looking for your type of solution or product.
For example, a person Googles healthy meal recipes. Their goal is to improve their nutrition and lose weight. They aren’t looking for complete nutrition shakes. But if we were to reach the user with content highlighting the quick and easy benefits of complete nutrition shakes to improve health and lose weight, we’re far more likely to capture their attention and create intent to buy.
These types of people with relevant but indirect intent may represent a large portion of your serviceable/addressable market.
Demand is much easier to create with the right message that talks to a pressing goal, at the exact time a person has that goal front of mind. It’s always the goal we need to understand and talk to.
And to be clear, intent signals aren’t KPIs or “vanity metrics”. We use intent signals to deduce intent, and then target or exclude people accordingly. Intent signals should actively inform real-time content targeting when used correctly.
Types of Digital Intent Signals
The intent signals we can gather spans internal and external sources. It crosses organic and paid content, to owned and third-party platforms.
- First-party Data – CRM, website, app and email data (learn more about first-party data )
- Second-party Data – Audience interaction on non-owned channels (E.g. Facebook)
- Third-party Data – Data Companies (E.g. Nielsen)
Some signals can be very overt. Especially at late journey stages, such as filling out a contact form or adding an item to the basket. Whereas other signals are less obvious, like running a Google search to learn about a related topic, or following a competitor’s social media account.

The type of intent signal can give you clues about a person's journey stage to build real-time customer segments. It’s helpful to identify which intent signals feature most prominently at each stage of your brand’s customer journey paths.
Split targeted signals up according to the campaign goals they fit with, whether that's demand capture (late journey) or demand creation (early journey) campaign goals.
For example, if a website visitor is behaving like a user that typically converts after another couple of weeks, you can target them with the right tone of nurturing content accordingly. But if you were targeting someone showing an interest in a competitor that hadn’t been included in your campaigns previously, you could show them content that introduces your brand with the comparative benefits of your brand/product/solution over the competitors.

Here are the most common intent signals that can be tracked:
Content Engagement:
- Reading or viewing content related to specific products or services.
- Downloading or sharing content.
- Commenting on or liking blog posts or social media content.
- Subscribing to a blog, newsletter, or YouTube channel.
Search Behavior:
- Searching relevant keywords.
- Searching for reviews or comparisons related to a product or service.
- Searching for the brand name or specific products.
Social Media Engagement:
- Following or liking a brand's social media pages.
- Engaging with posts by liking, commenting, or sharing.
- Mentioning the brand in posts or comments.
- Clicking on social media ads or sponsored content
Ad Interaction:
- Clicking on digital ads.
- Video ads watch time.
- Clicking on retargeting ads
Event Participation:
- Registering for webinars or online events.
- Participating in trade shows or conferences.
- Engaging in live Q&A sessions or forums.
Website Interactions:
- Traffic source
- Visiting a website multiple times (yours or competitors).
- Spending a significant amount of time on the site or on specific pages.
- Checking product pages or service descriptions.
- Downloading content such as ebooks, whitepapers, or product brochures.
- Returning to the website after a period of inactivity.
- Using online tools, calculators, or configurators.
- Completing quizzes or self-assessments.
App Interactions:
- App downloads.
- App usage patterns and content engagement.
- Search queries.
- Abandoned carts.
- Registration or subscription.
- User reviews and ratings.
Shopping Behavior:
- Adding items to a shopping cart or wishlist.
- Repeatedly viewing a specific product or service.
- Starting but not completing a purchase process.
- Checking the availability or location of a product.
Email Engagement:
- Opening marketing emails.
- Clicking on email links.
- Responding to surveys or filling out forms.
- Forwarding emails.
Customer Support Interaction:
- Contacting sales.
- Using live chat or chatbots.
- Requesting a demo, quote, or more information.
How to Use Digital Intent Signals to Inform Customer Journey Architecture
The process for incorporating intent signals into real-time, personalized media targeting requires the following steps:
Data Collection and Analysis
The first step is to collect data on your audience’s behavior across your channels, including offline touchpoints where possible.
This data needs to be analyzed to identify patterns and understand what specific actions might indicate a user's intent to purchase or engage further. What are the main actions taken within journeys, and what conversion goals can help you qualify people at each stage?
Data tools such as connectors and warehouses will help you merge data from multichannel sources for more holistic understanding and analytical power, whether historical or predictive.
A note here on data collection. User tracking and targeting across multiple advertising platforms can be achieved through more than one method. This means that what a user does on one platform can be used to target them appropriately with relevant content on another platform via:
- First-party Data - Advertisers can import their customer segments into an advertising platform using Customer Match targeting. This matches identifying information that customers have shared with the advertiser, such as an email address, to target specific ads to those customers, and also other people that behave like them (look-alike audiences). This allows advertisers to narrow in on the highest intent/value customers.
- Cross-device Targeting - Also known as people-based marketing, this approach uses Device IDs or User IDs to anonymize user data while still allowing people to be targeted individually (without cookies), so advertisers can track and target a user across multiple devices. Pixels are used for this type of targeting.
A combination of these data collection methods will give brands the most precise targeting power and best results.
Segmentation
Once you've identified key intent signals and conversion goals, you can segment your audience based on their behavior.
For instance, users who have abandoned their shopping carts might be in one segment, while users who have spent a significant amount of time on product pages might be in another.
Personalization
Each segment will have different needs and will be at different stages of the customer journey.
Create personalized paid and organic content for each segment, addressing their specific goals or challenges, guiding them towards the next step in their journey with defined conversion goals for qualifying. Content that matches keywords and the audience’s language directly performs best.
Leverage Media Technology + Automation Tools
There are a number of built in AI and automation tools within the bigger ad platforms for marketers to take advantage of.
Setting campaign goals and conversion goals allow platforms like Google and Meta to automatically optimize targeting to achieve them. Dynamic ads can use AI and machine learning to improve their targeting and optimize ad copy tailored exactly to user search terms. And machine learning already drives real-time programmatic buying, where advertising inventory is bought and sold via an instantaneous auction.
There are various independent solutions that can be used for paid media targeting, such Blueshift and 6sense, including intent data for account-based marketing (ABM) needs.
Testing and Optimization
It's important to continually split test and optimize your campaign creatives and targeting based on performance.
Look at which intent signals are most predictive of conversion, and which types of content are most effective for each segment. Use this information to refine your targeting and personalization strategies. How you use attribution modeling is also a crucial part of your media optimization process.
Recognizing and leveraging customer intent signals in the creation of personalized customer journeys is not just a valuable strategy - it's a business imperative for advertisers seeking to drive revenue growth.
As the advertising landscape becomes increasingly digital and competitive, the brands that will rise to the top are those that truly understand their customers, meeting them where they are and providing what they need at every stage of the journey. By harnessing the power of customer intent signals, marketers can enhance customer experiences, build stronger relationships, and ultimately, achieve sustainable revenue growth.
This shift towards a more customer-centric approach rooted in data insights is not just the future of advertising; it is the present.
If your team needs support gathering, analyzing and incorporating intent signal data into your media strategy, Half Past Nine would love nothing more than to help you realize their transformative power on your bottom line. It’s what we get out of bed for! Just get in touch.
What to Read Next
- Flipping Your Brand Into a Media Company: Content Marketing That Fuels Growth
- Upgrade Your Online Advertising Strategy: The Best Advertising Platforms in 2023
- Does AI Copywriting Work? We Tested ChatGPT Against 6 of The Best AI Writing Softwares So You Don't Have To
Customer Journey Maps: How to Create Really Good Ones [Examples + Template]
Updated: April 17, 2024
Published: May 04, 2023
Did you know 70% of online shoppers abandoned their carts in 2022? Why would someone spend time adding products to their cart just to fall off the customer journey map at the last second?

The thing is — understanding your customer base can be very challenging. Even when you think you’ve got a good read on them, the journey from awareness to purchase for each customer will always be unpredictable, at least to some level.

Download Now
While it isn’t possible to predict every experience with 100% accuracy, customer journey mapping is a convenient tool for keeping track of critical milestones that every customer hits. In this post, I’ll explain everything you need to know about customer journey mapping — what it is, how to create one, and best practices.
Table of Contents
What is the customer journey?
What is a customer journey map, benefits of customer journey mapping, customer journey stages.
- What’s included in a customer journey map?
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
Steps for creating a customer journey map.
- Types of Customer Journey Maps
Customer Journey Mapping Best Practices
- Customer Journey Design
- Customer Journey Map Examples
Free Customer Journey Map Templates
.webp)
Free Customer Journey Template
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free templates.
- Buyer's Journey Template
- Future State Template
- Day-in-the-Life Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The customer journey is the series of interactions a customer has with a brand, product, or business as they become aware of a pain point and make a purchase decision. While the buyer’s journey refers to the general process of arriving at a purchase, the customer journey refers to a buyer's purchasing experience with a specific company or service.
Customer Journey vs. Buyer Journey
Many businesses that I’ve worked with were confused about the differences between the customer’s journey and the buyer’s journey. The buyer’s journey is the entire buying experience from pre-purchase to post-purchase. It covers the path from customer awareness to becoming a product or service user.
In other words, buyers don’t wake up and decide to buy on a whim. They go through a process of considering, evaluating, and purchasing a new product or service.
The customer journey refers to your brand’s place within the buyer’s journey. These are the customer touchpoints where you will meet your customers as they go through the stages of the buyer’s journey. When you create a customer journey map, you’re taking control of every touchpoint at every stage of the journey instead of leaving it up to chance.
For example, at HubSpot, our customer’s journey is divided into three stages — pre-purchase/sales, onboarding/migration, and normal use/renewal.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Maximize Your Success with a Customer Experience Platform
![customer journey phasen b2b How to Measure Customer Experience: 8 Metrics 1000+ Service Reps Prioritize [+Data]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/customerexperiencemetrics.webp)
How to Measure Customer Experience: 8 Metrics 1000+ Service Reps Prioritize [+Data]
![customer journey phasen b2b How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/ai%20image%20misuse%20the%20willy%20wonka%20experience%20%281%29.png)
How AI Image Misuse Made a World of Miscommunication [Willy's Chocolate Experience]

7 Ways to Delight Your Customers This Holiday Season

14 Customer Experience Fails that Companies Can Learn From
![customer journey phasen b2b How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/future-of-customer-experience.png)
How Customer Experience Has Evolved Over the Last Decade [+ 2024 Trends]
![customer journey phasen b2b Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/augmented%20reality%20customer%20experience.png)
Memorable Examples of AR in Customer Experience [+Tips for Implementing the Technology]

Digital Customer Experience: The Ultimate Guide for 2024
![customer journey phasen b2b How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/hybrid%20customer%20service_featured.png)
How to Implement a Hybrid Customer Service Strategy That Works [Expert Tips]

User Flows: 8 Tips For Creating A Super Smooth User Experience
Outline your company's customer journey and experience with these 7 free customer journey map templates.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The 5 stages of the B2B customer journey. The customer journey describes all the interactions that take place between a customer and a business. It starts before a customer discovers your product and continues beyond the point of sale. While they're are key distinctions, both (B2B) and (B2C) customer journeys share the same five basic stages:
A typical B2B customer journey consists of five stages namely: awareness, consideration, decision, retention, and advocacy. Let's discuss each of them briefly. 1. Awareness. This customer journey stage begins when buyers become aware of a challenge and start researching potential solutions.
You can use tools like Churnfree to gather customer feedback. 4. Map the Journey. Draw a map of a customer's life cycle and mark the most significant milestones with reference to the case. If possible, utilize a B2B customer journey map template; otherwise, design it yourself by using flowcharts and diagrams.
The B2B SaaS customer journey outlines how prospects become customers. It's often visualized as a funnel: Top of Funnel (TOFU) - Awareness: Prospects discover your brand. Middle of Funnel (MOFU) - Consideration: Prospects compare you to competitors. Bottom of Funnel (BOFU) - Decision: Prospects are ready to buy.
The B2B customer journey stages outline the actions and choices a potential customer must make before becoming a paying client. Learn how to optimize it for enhanced business outcomes.
The B2B customer journey highlights the touchpoints of one business (the vendor) with another (the customer). One of the key focuses of mapping this journey is to provide a better experience to customers from research to post-purchase. Mapping the B2B journey helps your business better understand the customer's path during their decision ...
Nivedha Thangaraj. June 28, 2024. By 2025, 80% of B2B sales interaction is expected to occur digitally. Where does that leave the industry? According to a report by Gartner, the industry has been shifting towards a buyer-centric, digital model. In other words, like B2C, the customer and their experience are starting to take the front seat.
Here are the key reasons to design a B2B customer journey map: Enhanced customer understanding — A customer journey map provides valuable insights into the needs, motivations, pain points, and behaviours of your B2B customers. It helps you better understand their challenges, preferences, and decision-making processes.
The B2B customer journey is a tapestry woven from various interactions. Let's break down the key elements that make it up: Touchpoints: These are the moments where a customer comes into contact with your company. They can be either online (website visits, social media engagement) or offline (phone calls, in-person meetings). ...
2. The B2B customer journey map. The B2B customer journey map visually represents a potential customer's steps as they interact with a vendor. It shows the user's thoughts, feelings, and actions at each stage of the journey and the touchpoints, channels, and interactions that occur. 2.1.
Mapping the customer journey is essential in understanding your buyers and turning them into loyal customers. Follow these steps to create an actionable B2B customer journey map that gives insights into who your customers are and helps you build an optimized user experience (UX) for them: 1. Set goals unique to your business.
Customer journey B2B vs B2C. While B2B and B2C customer journeys involve similar stages, B2B customer journeys are more complex and multifaceted. Firstly, B2B purchases involve multiple decision-makers that participate in different stages of the decision-making process and have unique expectations. For example, executives might want the most ...
The B2B customer journey stages consist of five main areas: awareness, consideration, conversion, loyalty, and advocacy. The exact stages may be broken down further or vary depending on the specific type of business (for example, some companies may require onboarding, or have multiple points of purchase).
In the age of digital marketing, a B2B customer's journey from initial contact with a brand or product to purchase has become much more complex than in the past. However, the phases of the B2B customer journey extend far beyond this buying process. Marketing on a wide variety of channels, blogs, social media sites, review and comparison portals ...
B2B customer journey represents the steps businesses take when purchasing from other businesses. It frequently involves multiple stakeholder interactions and a series of strategic decisions. The steps in this journey include awareness, consideration, decision, and post-purchase. Each of these steps can be mapped for clarity and to improve ...
The customer journey consists of 5 broad stages: Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Advocacy. Delivering relevant material along each stage ensures that prospects feel understood and valued. This, in turn, contributes to successful journeys and provides practical insights and strategies for each stage.
Diese fünf Phasen einer Customer Journey B2B mit möglichen Touchpoints für Anbieter*innen (Quelle: Concept Draw) 1. Awareness (Bewusstmachung): Ein Auslöser/Problem führt dazu, dass potenzielle B2B-Kund*innen nach einer Lösung suchen. Hier steht der Kaufabschluss noch nicht im Vordergrund, sondern zunächst eine unverbindliche Recherche ...
Get the ultimate list of 65 questions to help you fully understand the B2B customer journey for your customers & business. When people talk about understanding the B2B customer journey, it seems to me that the majority of the time we tend to do so primarily in the context of stages - the various phases customers encounter at different points ...
The Value of Customer Journey Mapping & Challenges in B2B Markets. Customer journey mapping is just one stage in the move towards a customer centric approach. It marks the starting point; placing the experience of the customer at the heart of what the company does and how it operates. It provides a single overview of how customers interact with ...
3 Steps To Create Your B2B Customer Journey Map And Bring Structure To Your Success. Step 1: Define the Ideal Clients You Want To Attract By Creating Detailed Buyer Personas. Step 2: Define All Customer Touchpoints With Your Company. Step 3: Map Out B2B Customer Journey Paying Attention To 5 Crucial Stages.
Unlike B2C, the "customer" in B2B is not a single person, but rather a group of people representing the company (also known as an account). Multiple persons (and their opinions) need to align and agree on buying into your company's product or service. 2. Too many overlapping channels and touchpoints that create a non-linear buyer journey.
Understanding the B2B customer journey is the first step to building an effective content marketing strategy. The art of B2B content marketing involves aligning your business goals with your audience's needs. A good B2B content marketing strategy caters to your audiences' personalized interests within specific phases of the buying process and ...
Download them today to start working on your customer journey map. 2. B2B Customer Journey Map Example. This customer journey map clearly outlines the five steps Dapper Apps believes customers go through when interacting with them. As you can see, it goes beyond the actual purchasing phase by incorporating initial research and post-purchase needs.