- Woopra Logo
- Platform Customers Pricing Resources Company
- Log in Start For Free
- Automations
- Integrations
- Documentation

7 Interesting Real-Life Customer Journey Map Examples

Creating a customer journey map is vital for any business to optimize its sales and marketing processes.
According to Salesforce , “among high-performing teams, 88% say a customer journey strategy is critical to the success of their overall marketing.”
An effective customer journey map will include each customer touchpoint a shopper interacts with on the way to making a purchase.
If you’re looking to create this document from scratch or looking for ways to improve your map, below are some customer journey map examples from highly successful companies.
Customer Journey Map Examples
When doing customer journey mapping, you should think deeply about your business and the customer experience. On that note, let’s dive into some real-life customer journey mapping and walk you through what makes customer journey maps so valuable.
Consumer SaaS Customer Journey Map Examples
Customer journey maps are essential to B2C companies in the SaaS space. It can be expensive to acquire a new customer and each month that you’re able to keep a subscription active deepens your ROI and ROAS.
Understanding each customer interaction, pain points and customer needs is vital for maximizing value throughout the customer lifecycle - and a user journey map will help identify these areas.
Spotify is one of the world’s most popular audio streaming services. When Spotify wanted to improve the music-sharing experience for its customers, it hired a marketing firm to create a customer journey map .
The goal of this user journey map was to determine where music sharing features the best fit into the customer experience .
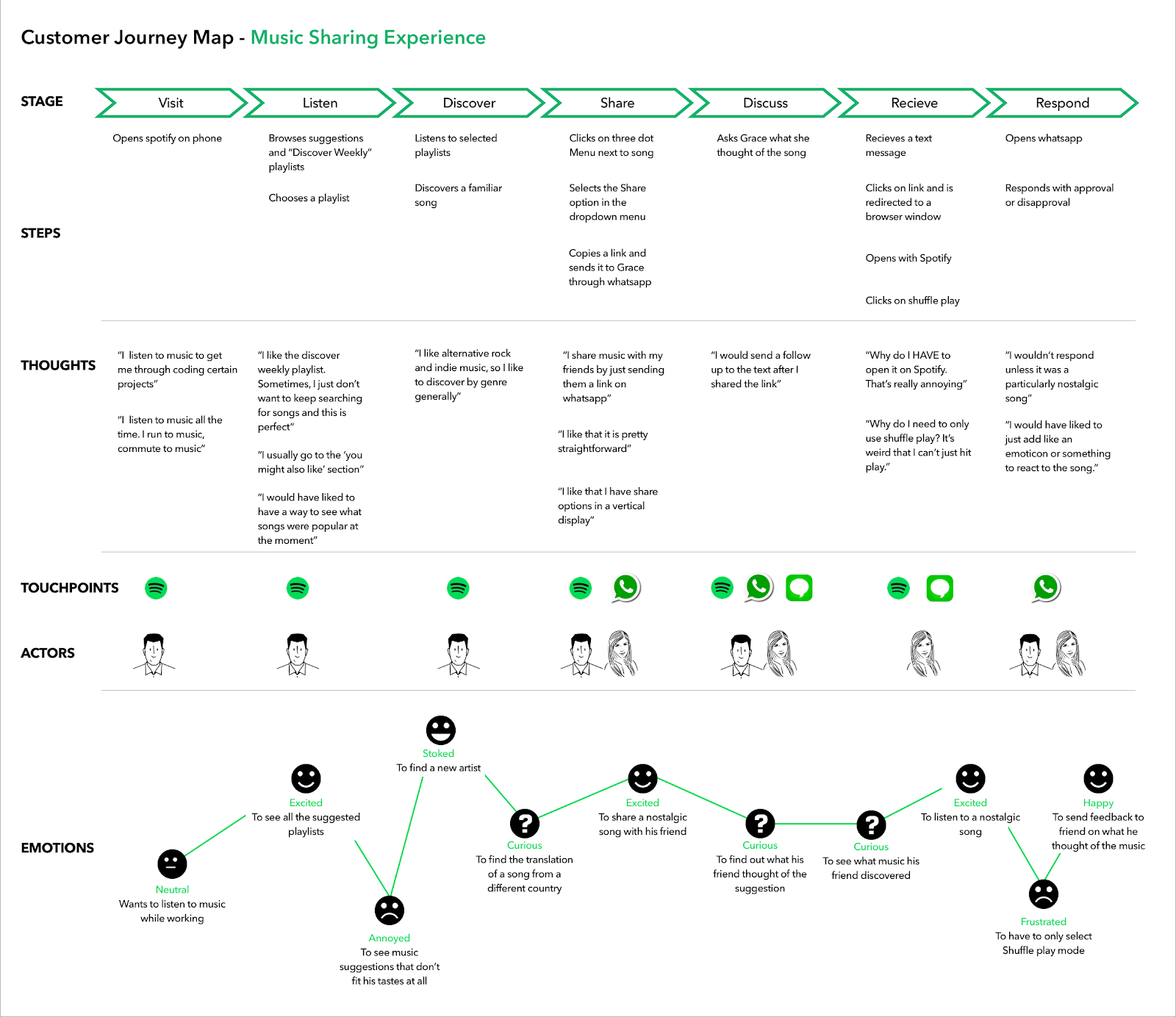
In this example, we see the user experience mapped out from the moment the user first opens Spotify on a mobile device, all the way through to whether they like a song that a friend has shared.
Also Read: Effective Customer Journey Design
Throughout each stage and every touchpoint, the brand lists what a customer is engaging with, doing, thinking, and feeling (something that's commonly done with an empathy map ). The agency used data research and customer surveys to better understand how users felt at each touchpoint in the customer journey to collect this information.
Based on the customer journey map, Spotify was able to identify pain points for users and address those pain points so that the music sharing experience is smooth and seamless, encouraging more users to share music -- and to do it more often. \
This journey map is excellent because it identifies key areas of customer engagement, takes into account customer behavior , and has the goal of making the customer experience as enjoyable as possible.
The end result is significantly higher customer satisfaction, which can have several key benefits, including a smoother buyer journey, greater customer loyalty, and in many cases, existing customers becoming brand advocates.
2. TurboTax
Turbo Tax is a leading online software package for preparing taxes. When the TurboTax team was ready to launch a new product called Personal Pro, they created a customer journey map to better understand the overall customer experience with this new product.
The team used a mix of data research, customer surveys, and key conversations with tax professionals to understand how the product fits into the lives of those using it.
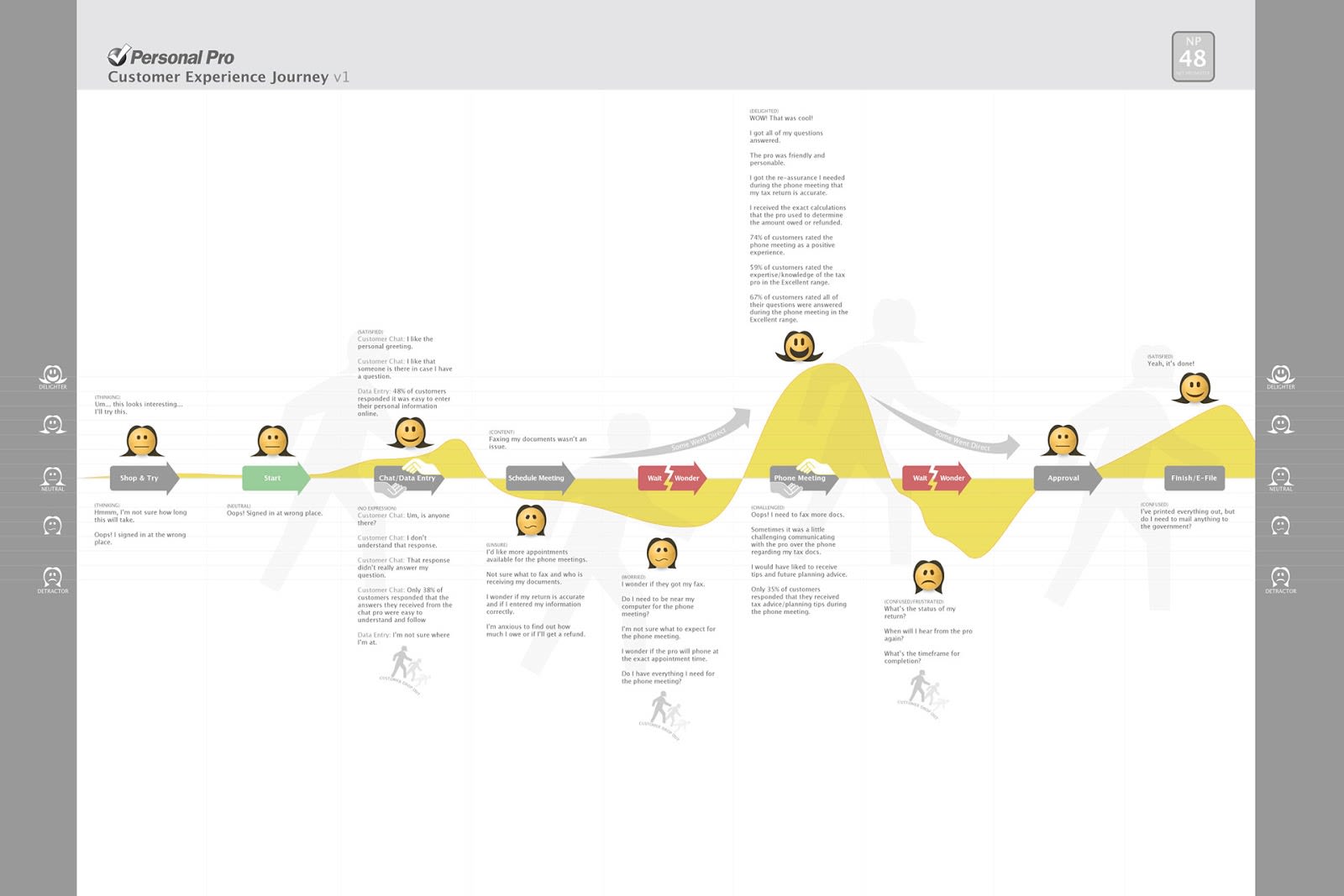
TurboTax’s customer journey analytics exercise starts when someone enters the website and is in the consideration phase through to the completion of the tax filing.
This customer journey map is great because it allows the team to see each customer pain point experienced and, therefore, address these pain points to make the customer experience smoother and more satisfactory.
Ecommerce Customer Journey Map Examples
The Ecommerce space is highly competitive in almost every niche these days. To maximize profit margins while keeping pricing competitive, it’s important to convert as many shoppers that visit your site as possible.
Also Read: Customer Journey Template
In addition to converting first-time customers at high rates, it’s important to have up-sell and cross-sell touchpoints in your customer journey as well. This increases the lifetime value of your customers and drives up the ROI against your acquisition costs.
Customer journey mapping is a vital exercise that can help E-commerce businesses skyrocket conversion rates from all online shoppers and achieve higher customer success.
1. Columbia Road
E-commerce agency, Columbia Road, created this map template for a fictitious online grocery shop . Here the agency demonstrates the core activities, goals, touchpoints, and experiences that a customer will go through during the decision-making process to place an order.
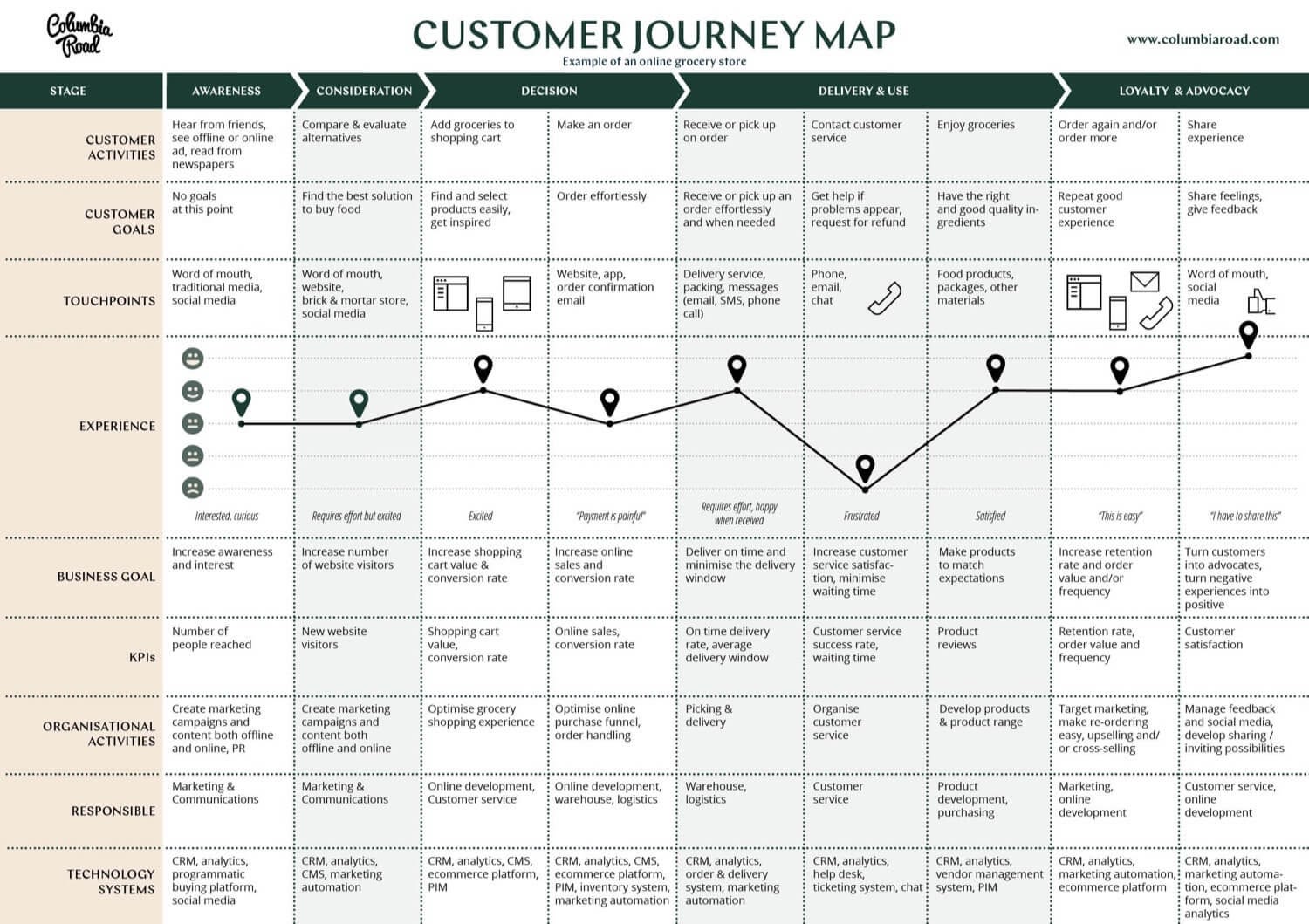
In this customer journey mapping exercise, the Columbia Road team went one step further than others by also including Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and which department is responsible for ensuring a customer has the best experience possible at each stage within the user journey.
Including KPIs is important because it lets you know if your customer journey map template is effective or if it needs to be adjusted to better serve your shoppers.
Amazon is one of the largest E-commerce shops in the world, with its own technology and custom systems in place for moving a customer through the sales journey. Its customer journey map is one of the most complex around and would take most people days to read through and understand each customer journey stage.
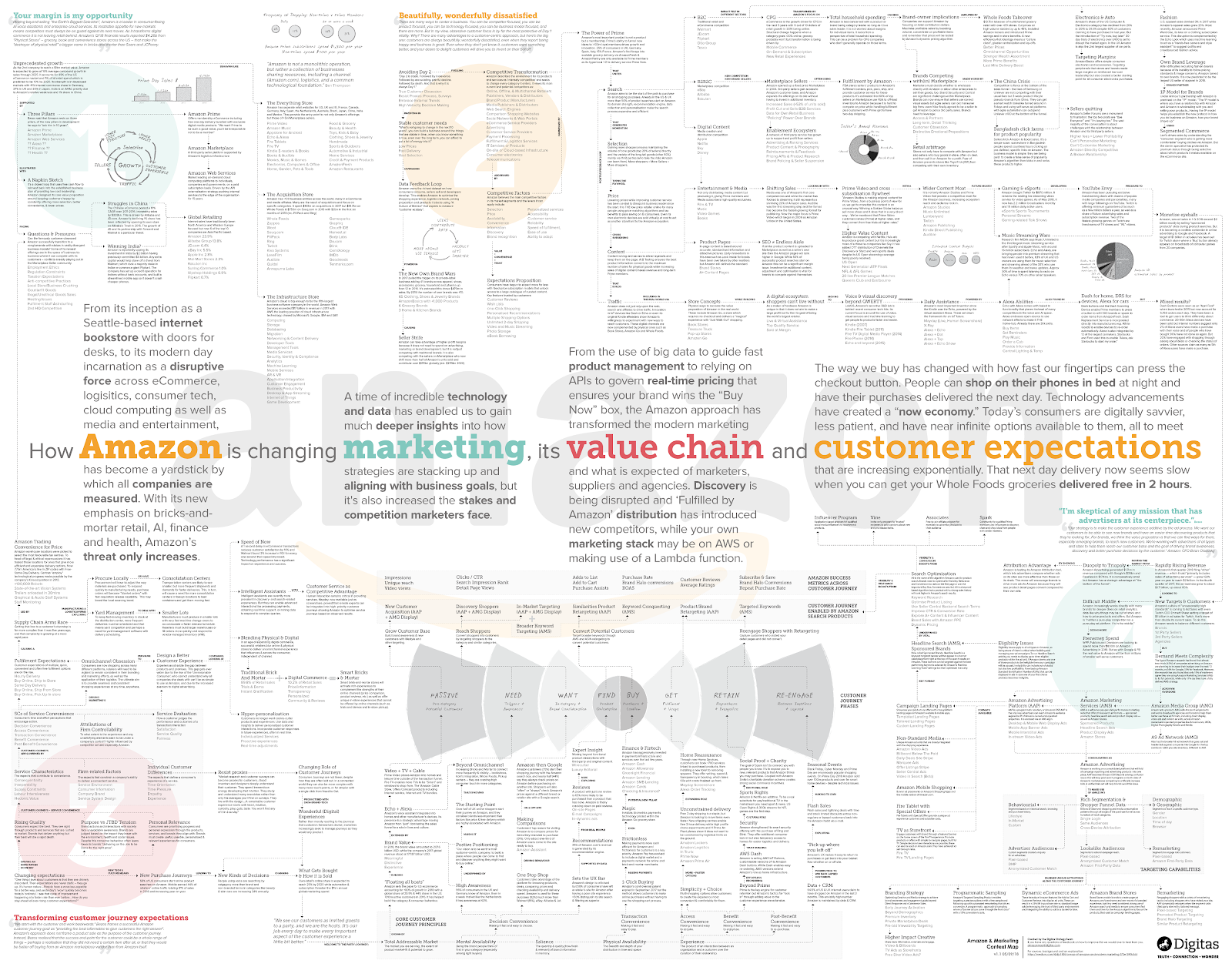
The good news is that the map can be broken down into several more digestible parts for analysis.
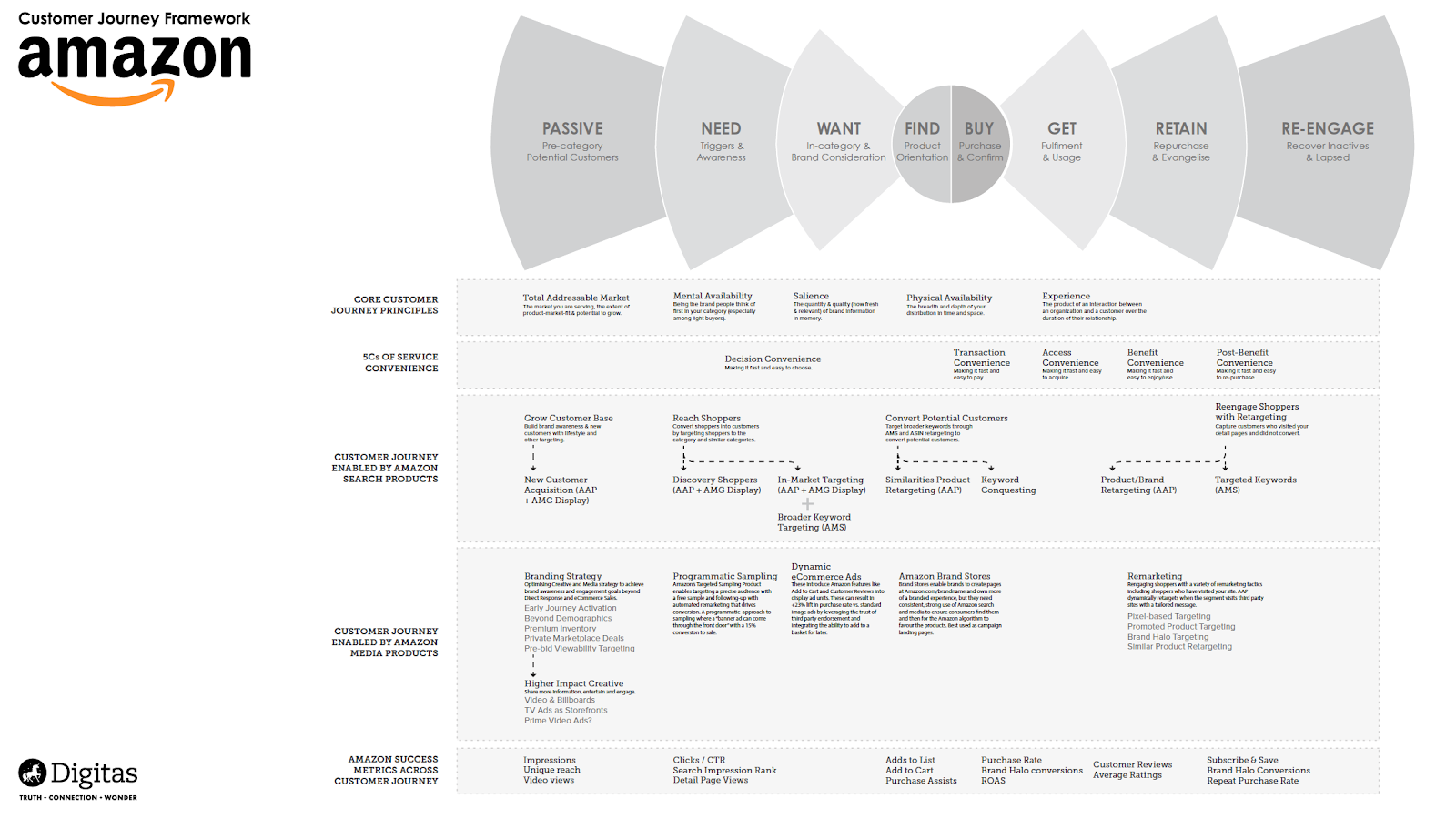
Here we can see Amazon’s customer conversion funnel and how the customer journey is enabled by its own products that push users through the sales funnel to maximize customer engagement.
Most interesting here is how Amazon includes its success metrics for each stage of the customer journey. These are the same success metrics that just about every E-commerce shop should be monitoring:
- Impressions
- Add to list
- Add to cart
- Purchase assists
- Conversion rate
- Subscriptions
- Repeat purchase rates
When conducting your customer journey mapping exercise, be sure to include these key metrics to monitor your success and gain deeper insight into the overall customer experience.
3. A More Common Scenario
If looking at the Amazon customer journey map feels overwhelming to you know that you’re not alone. Most E-commerce businesses will have a much less complicated customer journey to map out.
Here's a customer journey map template for the checkout process for online shops.
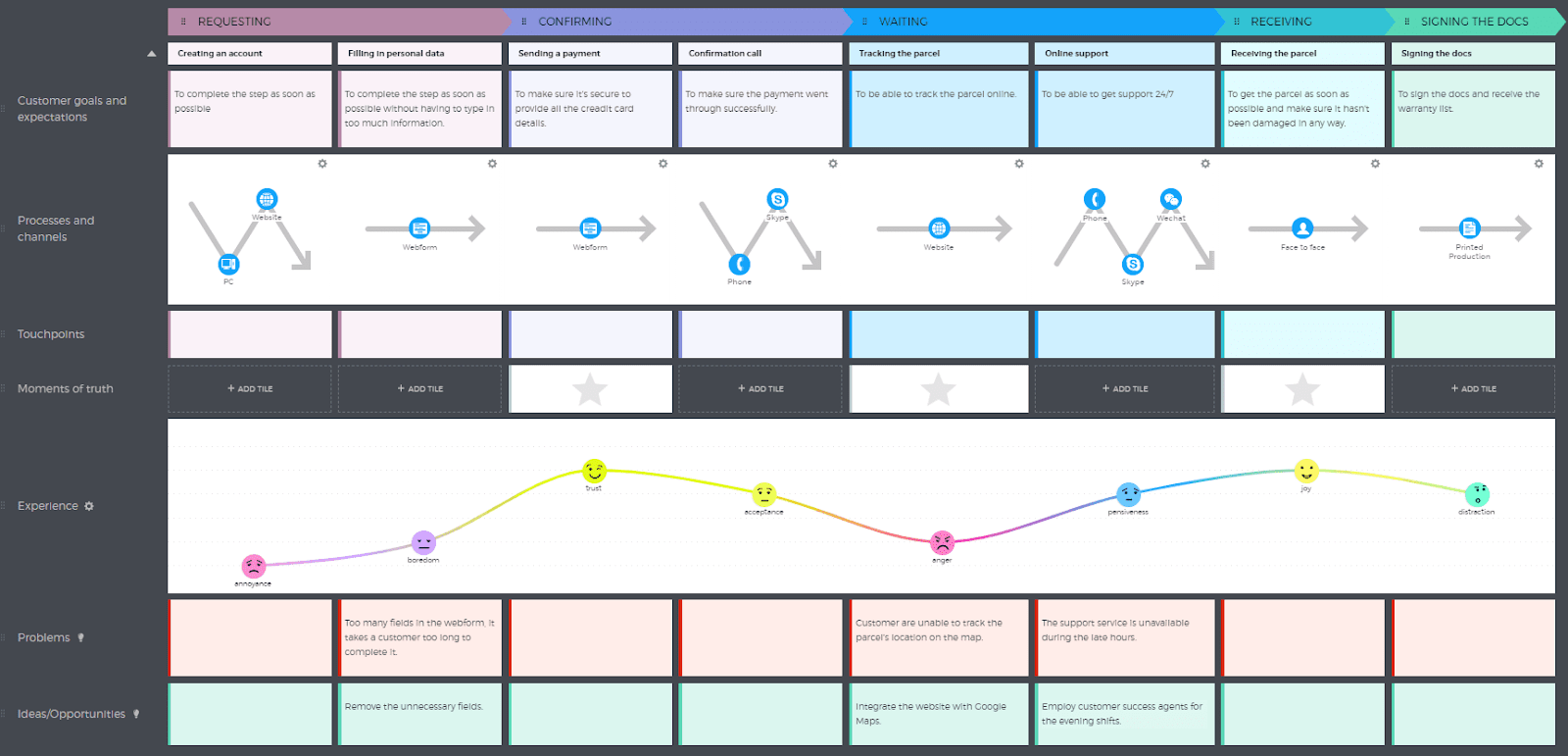
For instance, you see the most important stages of the checkout process, including the technology involved, common customer frustrations, and space to include solutions to make the process smoother.
For example, if a customer finds creating an account to be a barrier to checkout in the very first step - then offering a guest checkout option would be one solution for improving the customer experience.
Start your E-commerce customer journey mapping exercise using the above customer journey mapping template as an outline and then customize it for your own needs.
(If this isn't a good fit for your company, check out these other customer journey templates .)
B2B Customer Journey Map Examples (SaaS)
In the B2B customer journey , the sales cycle can vary significantly based on price point and the buy-in from stakeholders needed to make a business purchase.
When it comes to a B2B SaaS purchase for something reasonably inexpensive like Hootsuite’s social media management platform or the MailChimp email marketing platform, most of the customer journey will happen digitally with minimal to no involvement from a sales representative.
In this case, customer journey maps might be made using a simple Excel spreadsheet.
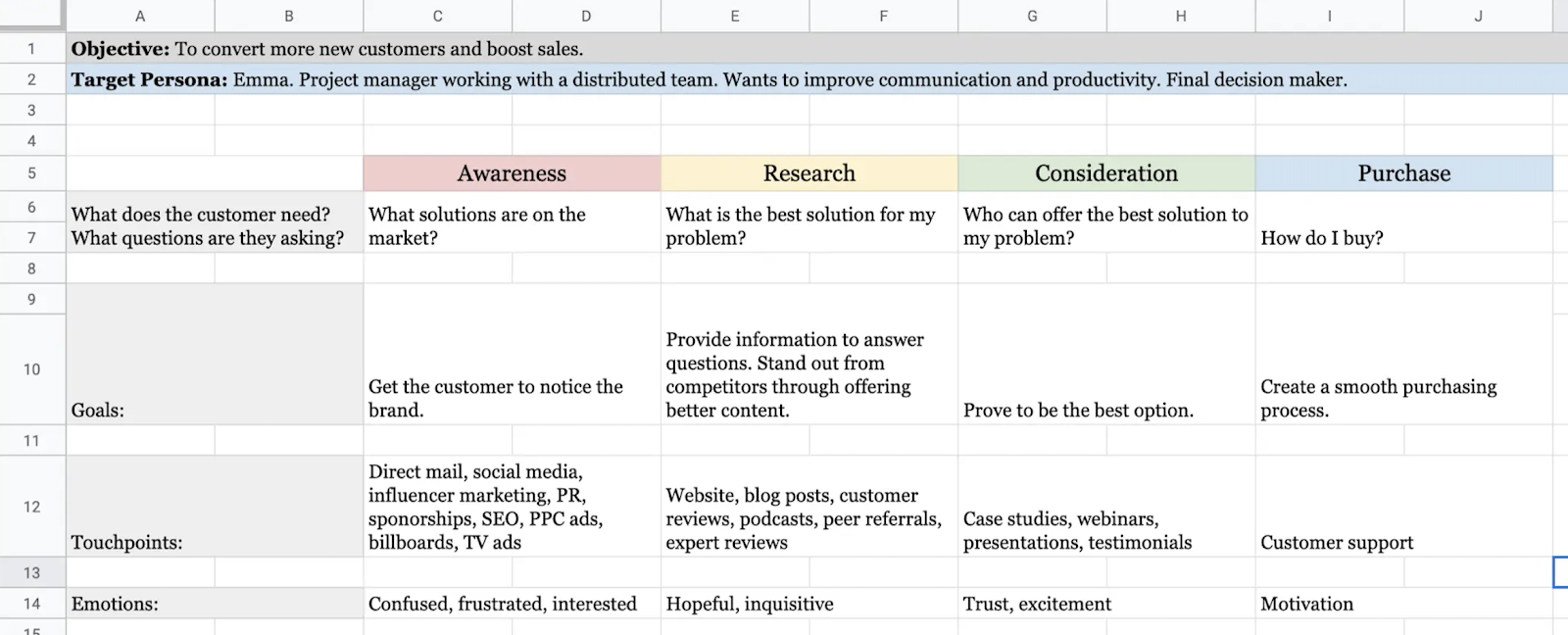
Because there are few high barriers to conversion, the customer sales journey can happen quickly and easily as long as the right digital touchpoints are in place.
The journey map example above shows that touchpoints can all be online assets from social media for awareness, to blog posts for research, to case studies or webinars for consideration. Finally, there might be a personal touchpoint at the very end if someone has a question right before or after purchasing.
If your customers go from Awareness to Purchase (or even Free Trial purchase) quickly, a simple user journey mapping might work for you.
If a B2B SaaS company has a longer sales cycle with a more highly considered product or service, the customer journey map should be more complex and done differently.
Below is an example from HubSpot. The first part of their customer journey map includes the various stages of the journey throughout each customer touchpoint:
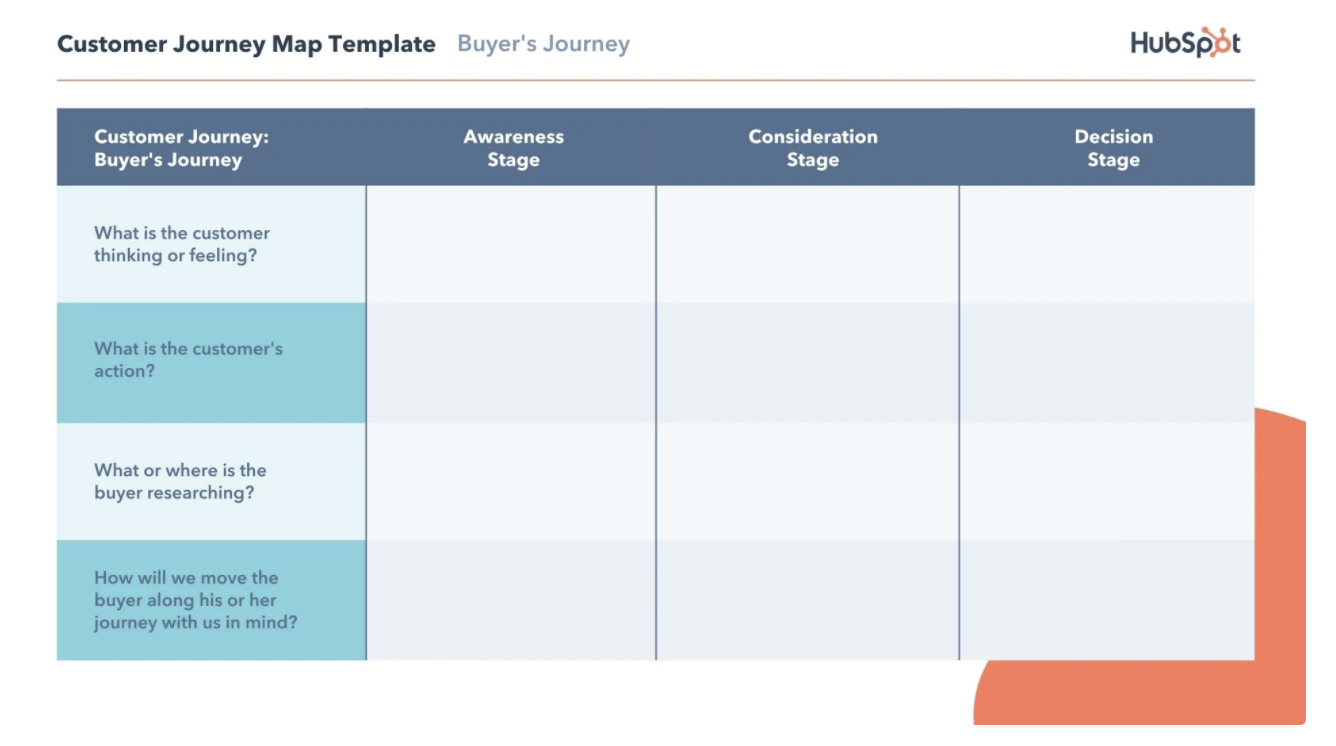
Because this is an example of a journey with a longer sales cycle, it also breaks down the stages into substages to dig further into the mindset of a potential customer.
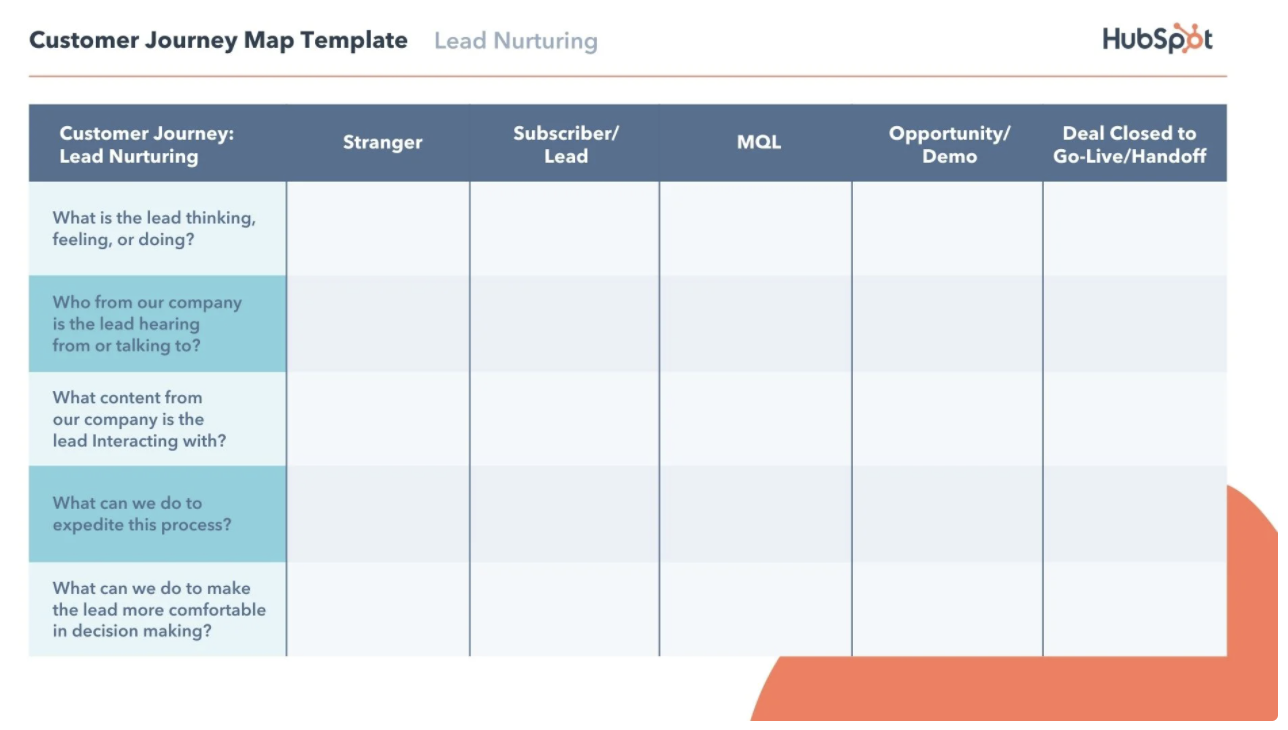
Under the Awareness Stage would be the Stranger. Under the Consideration Stage would be the Subscriber/Lead and MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead). And under the Decision Stage would be the Opportunity and the Deal Closed/Handoff.
As a customer moves from, say, Subscriber to MQL in the Consideration Stage, they will experience different emotions and require different touchpoints to move through the sales funnel.
For example, a blog subscriber or newsletter subscriber might not even be able to afford your product or service, so it wouldn’t make sense to assign them a sales rep and waste that rep’s time.
However, once a subscriber becomes an MQL, and you know they fit your customer profile you can start treating this person as a real potential customer by dedicating more time and resources.
This also makes for a more relevant experience from your customer’s perspective. No one likes to be hassled to buy a product they can't afford.
In the overall customer journey, the subscriber and the MQL are both still in the Consideration Stage but they should be treated in a different way which is why it’s important to break the journey down into smaller stages if you have a longer sales cycle.
What Makes a Good Customer Journey Map
Above we walked through several interesting examples of customer journey maps and discussed the pros and cons. Now, as you get ready to create your own map, let’s talk about key elements to keep in mind for best practices.
1. It Should Be Based on Market Research Plus Real Customer Data
According to a study from Ascend2 in partnership with Ansira, enterprise marketers are using customer feedback surveys (53%) and customer journey marketing research (47%) to build journey maps.
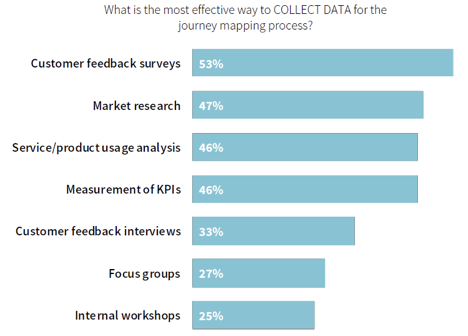
This is a great combination because it includes work based on theory as well as the real-world experiences of shoppers. And having this mix is critical for constructing effective journey maps and ultimately optimizing the customer experience.
Why is this combination key?
Customers don’t always know what they want or what they would prefer if they have never experienced a new product or feature before.
Therefore, it’s up to the business to continuously innovate and present ideas to shoppers. These new products and features should be workshopped based on a customer persona and user research.
Then, once the product or new feature is created, to make it as beneficial to the user as possible, feedback should be collected so improvements can be made.
Because customer journey maps need to take into account the thoughts and actions of users, compiling a document that includes a combination of market research and customer feedback surveys is the best way to get the data you need to make an effective journey map for your ideal buyer persona.
2. It Expands Beyond Your Marketing Funnel
A common pitfall for many companies when customer journey mapping is making a storyboard of the marketing funnel or marketing plan.
The marketing funnel is a good basis for creating a skeleton of the marketing portion of experience maps, but the user journey map should go well beyond marketing.
What does this mean?
The marketing funnel can be broken down into customer journey stages , just like your customer’s journey. It starts with awareness with your target audience and ends with a purchase from your ideal customer persona in the most basic sense (we often like to take this beyond purchase to gaining a loyal customer and getting a repeat purchase).
This means in the awareness stage of your marketing funnel you may talk about social media, Google Ads, and other forms of awareness building.
Then in the interest section, you may discuss email marketing, webinars, and other forms of content that increase interest. And in the consideration phase, you may talk about the UX design of your website, sales demonstrations, customer service, and so on.
A good marketing funnel will detail basic activities that should be carried out at each stage of the funnel for your user persona.
The Customer journey maps goes well beyond these basic activities and also lists out what a customer is thinking, feeling, and doing at each stage of the marketing funnel.
Think of it as a marketing funnel on steroids! It’s a much stronger and more powerful document than just your basic marketing funnel or marketing plan.
Additionally, any customer experience mapping needs to go beyond the marketing funnel. It should include the entire user experience with the product or service, each step in the sales cycle, and the touchpoints a person may routinely have with customer service.
3. It Includes KPIs
Good customer journey maps will include the various stages of the sales and marketing cycle as well as the thoughts, feelings, and actions of the user at each stage. Great customer journey maps will include KPIs for each stage.
Including KPIs is important so that the map can be evaluated by each customer touch point and adjusted when necessary.
Also, note that a customer journey map isn’t a document that is set in stone. It should be updated when new information is learned about:
- Customer behavior
- Customer needs
- Customer goals
- Customer expectations
- Customer satisfaction
- Customer support
- Customer service
It should also be evaluated and adjusted if overall sales and marketing goals are not being met.
Because the world is always evolving, so is the entire customer journey.
Whether you’re using a basic platform like Google Analytics or something more advanced like Woopra that’s specifically designed with the customer journey in mind, it should be capable of tracking all essential KPIs.
Get Started Creating Your Customer Journey Map
There's no better time to start laying the foundation for your customer journey mapping process than today.
By creating a visual representation of the buying process, you’ll gain valuable insight into the customer experience and reasons why customers do and don’t buy from you.
Once you’ve identified customer pain points you can make improvements at the necessary customer journey touchpoints, as well as optimize your customer service blueprint to position your business for sales success.
Remember, the whole goal is to put yourself in your customer’s shoes to create the best possible shopping experience for customer retention!
End-to-End Customer Journey Analytics Tool
Acquire and retain more customers with advanced analytics. Woopra is your single source of truth for tracking your customers.
Related Articles
The beginner’s guide to behavioral targeting to increase conversions.

How to get Started with Analytics

From Emails to Customers — Woopra Campaign Tracking
5 actionable methods to engage mobile customers, explore topics.
© Woopra, Inc. 600 California St 11th Floor San Francisco, CA 94108
- Request a demo
- Product Analytics
- Customer Analytics
- Customer Journey Analytics
- Google Analytics F.A.Q.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of service
What is a Customer Journey Map? [Free Templates]
Learn what the customer journey mapping process is and download a free template that you can use to create your own customer journey map.
Table of Contents
Mapping the customer journey can give you a way to better understand your customers and their needs. As a tool, it allows you to visualize the different stages that a customer goes through when interacting with your business; their thoughts, feelings, and pain points.
And, it’s shown that the friction from those pain points costs big: in 2019, ecommerce friction totaled an estimated 213 billion in lost US revenue .
Customer journey maps can help you to identify any problems or areas where you could improve your customer experience . In this article, we’ll explain what the customer journey mapping process is and provide a free template that you can use to create your own map. Let’s get started!
Bonus: Get our free, fully customizable Customer Experience Strategy Template that will help you understand your customers and reach your business goals.
What is a customer journey map?
So, what is customer journey mapping? Essentially, customer journey maps are a tool that you can use to understand the customer experience. Customer journey maps are often visual representations showing you the customer’s journey from beginning to end. They include all the touchpoints along the way.
There are often four main stages in your sales funnel, and knowing these can help you create your customer journey maps:
- Inquiry or awareness
- Interest, comparison, or decision-making
- Purchase or preparation
- Installation, activation, or feedback
Customer journey maps are used to track customer behavior and pinpoint areas where the customer experiences pain points. With this information uncovered, you can improve the customer experience, giving your customers a positive experience with your company.
You can use customer journey mapping software like Excel or Google sheets, Google Decks, infographics, illustrations, or diagrams to create your maps. But you don’t actually need customer journey mapping tools. You can create these maps with a blank wall and a pack of sticky notes.
Though they can be scribbled on a sticky note, it’s often easier to create these journeys digitally. That way, you have a record of your journey map, and you can share it with colleagues. We’ve provided free customer journey mapping templates at the end of this article to make your life a little easier.
The benefits of using customer journey maps
The main benefit of customer journey mapping is a better understanding of how your customers feel and interact with your business touchpoints. With this knowledge, you can create strategies that better serve your customer at each touchpoint.
Give them what they want and make it easy to use, and they’ll keep coming back. But, there are a couple of other great knock-on benefits too.
Improved customer support
Your customer journey map will highlight moments where you can add some fun to a customer’s day. And it will also highlight the pain points of your customer’s experience. Knowing where these moments are will let you address them before your customer gets there. Then, watch your customer service metrics spike!
Effective marketing tactics
A greater understanding of who your customers are and what motivates them will help you to advertise to them.
Let’s say you sell a sleep aid product or service. A potential target market for your customer base is young, working mothers who are strapped for time.
The tone of your marketing material can empathize with their struggles, saying, “The last thing you need is someone asking if you’re tired. But we know that over half of working moms get less than 6 hours of sleep at night. While we can’t give you more time, we know how you can make the most of those 6 hours. Try our Sleep Aid today and sleep better tonight.”
Building out customer personas will show potential target audiences and their motivation, like working moms who want to make the most of their hours asleep.
Product advancements or service improvements
By mapping your customer’s journey, you’ll gain insights into what motivates them to make a purchase or prevents them from doing so. You’ll have clarity on when or why they return items and which items they buy next. With this information and more, you’ll be able to identify opportunities to upsell or cross-sell products.
A more enjoyable and efficient user experience
Customer journey mapping will show you where customers get stuck and bounce off your site. You can work your way through the map, fixing any friction points as you go. The end result will be a smoothly-running, logical website or app.
A customer-focused mindset
Instead of operating with the motivation of business success, a customer journey map can shift your focus to the customer. Instead of asking yourself, “how can I increase profits?” ask yourself, “what would better serve my customer?” The profits will come when you put your customer first.
At the end of the day, customer journey maps help you to improve your customer experience and boost sales. They’re a useful tool in your customer experience strategy .
How to create a customer journey map
There are many different ways to create a customer journey map. But, there are a few steps you’ll want to take regardless of how you go about mapping your customer’s journey.
Step 1. Set your focus
Are you looking to drive the adoption of a new product? Or perhaps you’ve noticed issues with your customer experience. Maybe you’re looking for new areas of opportunity for your business. Whatever it is, be sure to set your goals before you begin mapping the customer journey.
Step 2. Choose your buyer personas
To create a customer journey map, you’ll first need to identify your customers and understand their needs. To do this, you will want to access your buyer personas.
Buyer personas are caricatures or representations of someone who represents your target audience. These personas are created from real-world data and strategic goals.
If you don’t already have them, create your own buyer personas with our easy step-by-step guide and free template.
Choose one or two of your personas to be the focus of your customer journey map. You can always go back and create maps for your remaining personas.
Step 3. Perform user research
Interview prospective or past customers in your target market. You do not want to gamble your entire customer journey on assumptions you’ve made. Find out directly from the source what their pathways are like, where their pain points are, and what they love about your brand.
You can do this by sending out surveys, setting up interviews, and examining data from your business chatbot . Be sure to look at what the most frequently asked questions are. If you don’t have a FAQ chatbot like Heyday , that automates customer service and pulls data for you, you’re missing out!
Get a free Heyday demo
You will also want to speak with your sales team, your customer service team, and any other team member who may have insight into interacting with your customers.
Step 4. List customer touchpoints
Your next step is to track and list the customer’s interactions with the company, both online and offline.
A customer touchpoint means anywhere your customer interacts with your brand. This could be your social media posts , anywhere they might find themselves on your website, your brick-and-mortar store, ratings and reviews, or out-of-home advertising.
Write as many as you can down, then put on your customer shoes and go through the process yourself. Track the touchpoints, of course, but also write down how you felt at each juncture and why. This data will eventually serve as a guide for your map.
Step 5. Build your customer journey map
You’ve done your research and gathered as much information as possible, now it’s time for the fun stuff. Compile all of the information you’ve collected into one place. Then, start mapping out your customer journey! You can use the templates we’ve created below for an easy plug-and-play execution.
Step 6. Analyze your customer journey map
Once the customer journey has been mapped out, you will want to go through it yourself. You need to experience first-hand what your customers do to fully understand their experience.
As you journey through your sales funnel, look for ways to improve your customer experience. By analyzing your customer’s needs and pain points, you can see areas where they might bounce off your site or get frustrated with your app. Then, you can take action to improve it. List these out in your customer journey map as “Opportunities” and “Action plan items”.
Types of customer journey maps
There are many different types of customer journey maps. We’ll take you through four to get started: current state, future state, a day in the life, and empathy maps. We’ll break down each of them and explain what they can do for your business.
Current state
This customer journey map focuses on your business as it is today. With it, you will visualize the experience a customer has when attempting to accomplish their goal with your business or product. A current state customer journey uncovers and offers solutions for pain points.
Future state
This customer journey map focuses on how you want your business to be. This is an ideal future state. With it, you will visualize a customer’s best-case experience when attempting to accomplish their goal with your business or product.
Once you have your future state customer journey mapped out, you’ll be able to see where you want to go and how to get there.
Day-in-the-life
A day-in-the-life customer journey is a lot like the current state customer journey, but it aims to highlight aspects of a customer’s daily life outside of how they interact with your brand.
Day-in-the-life mapping looks at everything that the consumer does during their day. It shows what they think and feel within an area of focus with or without your company.
When you know how a consumer spends their day, you can more accurately strategize where your brand communication can meet them. Are they checking Instagram on their lunch break, feeling open and optimistic about finding new products? If so, you’ll want to target ads on that platform to them at that time.
Day-in-the-life customer journey examples can look vastly different depending on your target demographic.
Empathy maps
Empathy maps don’t follow a particular sequence of events along the user journey. Instead, these are divided into four sections and track what someone says about their experience with your product when it’s in use.
You should create empathy maps after user research and testing. You can think of them as an account of all that was observed during research or testing when you asked questions directly regarding how people feel while using products. Empathy maps can give you unexpected insights into your users’ needs and wants.
Customer journey map templates
Use these templates to inspire your own customer journey map creation.
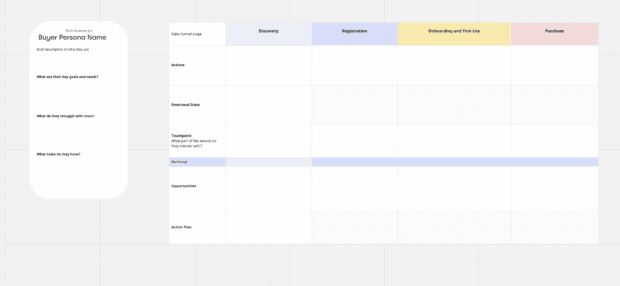
Customer journey map template for the current state:
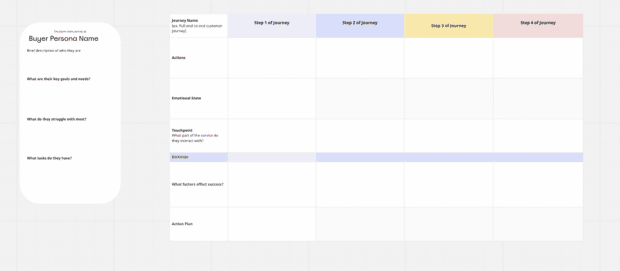
The future state customer journey mapping template:
A day-in-the-life customer journey map template:

An empathy map template:
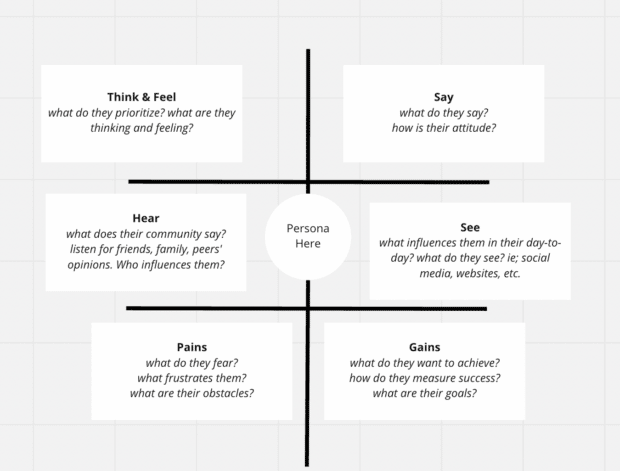
A customer journey map example
It can be helpful to see customer journey mapping examples. To give you some perspective on what these look like executed, we’ve created a customer journey mapping example of the current state.
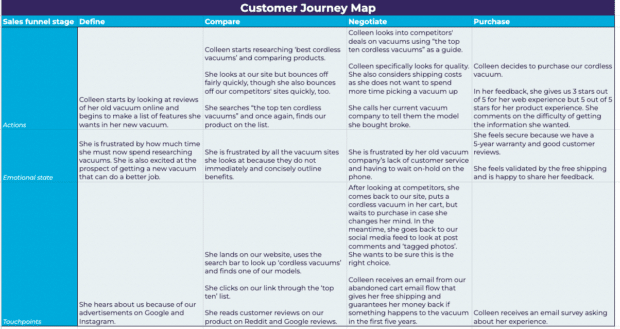
Buyer Persona:
Curious Colleen, a 32-year-old female, is in a double-income no-kids marriage. Colleen and her partner work for themselves; while they have research skills, they lack time. She is motivated by quality products and frustrated by having to sift through content to get the information she needs.
What are their key goals and needs? Colleen needs a new vacuum. Her key goal is to find one that will not break again.
What are their struggles?
She is frustrated that her old vacuum broke and that she has to spend time finding a new one. Colleen feels as though this problem occurred because the vacuum she bought previously was of poor quality.
What tasks do they have?
Colleen must research vacuums to find one that will not break. She must then purchase a vacuum and have it delivered to her house.
Opportunities:
Colleen wants to understand quickly and immediately the benefits our product offers; how can we make this easier? Colleen upholds social proof as a decision-making factor. How can we better show our happy customers? There is an opportunity here to restructure our website information hierarchy or implement customer service tools to give Colleen the information she needs faster. We can create comparison charts with competitors, have benefits immediately and clearly stated, and create social campaigns.
Action Plan:
- Implement a chatbot so customers like Colleen can get the answers they want quickly and easily.
- Create a comparison tool for competitors and us, showing benefits and costs.
- Implement benefit-forward statements on all landing pages.
- Create a social campaign dedicated to UGC to foster social proof.
- Send out surveys dedicated to gathering customer feedback. Pull out testimonial quotes from here when possible.
Now that you know what the customer journey mapping process is, you can take these tactics and apply them to your own business strategy. By tracking customer behavior and pinpointing areas where your customers experience pain points, you’ll be able to alleviate stress for customers and your team in no time.
Turn customer conversations and inquiries into sales with Heyday, our dedicated conversational AI chatbot for social commerce retailers. Deliver 5-star customer experiences — at scale.
Turn customer service conversations into sales with Heyday . Improve response times and sell more products. See it in action.
Become a better social marketer.
Get expert social media advice delivered straight to your inbox.
Colleen Christison is a freelance copywriter, copy editor, and brand communications specialist. She spent the first six years of her career in award-winning agencies like Major Tom, writing for social media and websites and developing branding campaigns. Following her agency career, Colleen built her own writing practice, working with brands like Mission Hill Winery, The Prevail Project, and AntiSocial Media.
Related Articles
FAQ Chatbot: The Best Way to Save Time on Customer Service
FAQ chatbots are bots designed to answer common questions people have about a product or service. They are used on websites or in customer service applications.

Customer Service Metrics: 2024 Guide + Free Template
Customers expect to get support wherever they look for and they expect it fast. To keep up, track the customer service metrics that matter.

Create a Customer Experience Strategy [FREE TEMPLATE]
This step-by-step template makes it easy to deliver a well-laid-out customer experience strategy that can give you planned, targeted growth.


Customer Experience Management Explained [11 Top Tips]
Turn that frown upside down! Keep your customers smiling with a strong customer experience management strategy.
- Case studies
- Expert advice
How to create a customer journey map — a step-by-step guide with examples
Learning more about client experience is the best way to understand and improve it. As you are reading this article, you already know that 😉
Here, you will find a detailed step-by-step guide on making a customer journey map (CJM), examples, expert tips, templates, and a PDF guide to download and save for later.
- 1 What is a customer journey map?
- 2 Benefits of client journey mapping
- 3.1 Step 1: Define your persona
- 3.2 Step 2: Set customer journey stages
- 3.3 Step 3: Define journey map sections
- 3.4 Step 4: Set customer goals
- 3.5 Step 5: Define touchpoints
- 3.6 Step 6: Processes and channels
- 3.7 Step 7: Problems and ideas
- 3.8 Step 8: Emotional graph
- 3.9 Step ?: Be Creative!
- 4 Customer journey map examples
- 5 A customer journey mapping checklist
- 6 The free guide to download
What is a customer journey map?
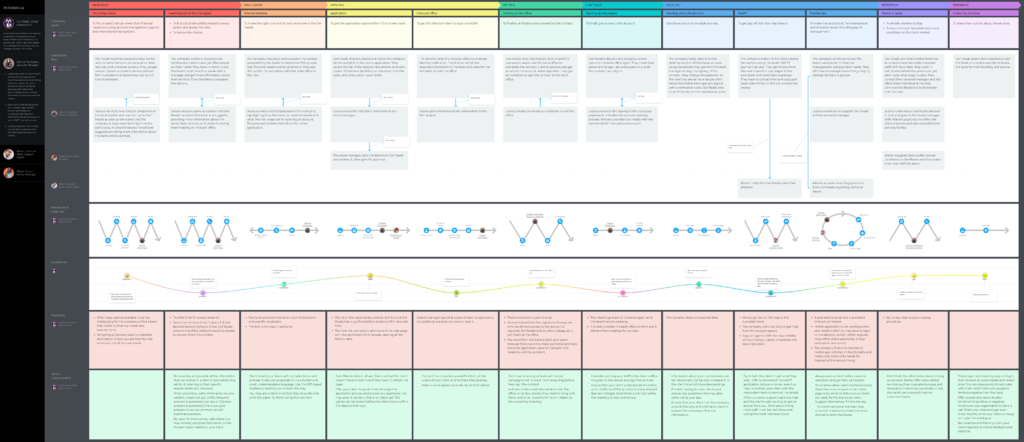
A customer journey map is the final output of the collaborative visualization process called customer journey mapping. This process lets you reveal typical experiences the customers have over time when interacting with your organization, service, or product. A finished map provides insights into their actions, processes, goals, needs, channels, emotions, and many other aspects shaping the customer experience.
Journey maps can be of different scopes. For example, a broad-scope map would include multiple customer journey stages like ‘Awareness’, ‘Decision’, ‘Purchase’, ‘Support’, and ‘Renewal’. In contrast, a map with a narrower focus would look at a few specific stages like ‘Decision’ and ‘Purchase’.

CJMs focusing on the current experience are AS-IS maps, while journey maps visualizing the future, desired, state of the experience are called TO-BE maps.
There’s also a similar technique, customer experience mapping, which is often used interchangeably with journey mapping. Experience maps are variations of CJMs, but they typically cover a wider range of interactions and contexts beyond a specific consumer-business relationship.
Benefits of client journey mapping
Why make journey mapping your tool of choice? There are plenty of reasons, the major of which include:
- Gaining a deeper understanding of your customers
For instance, a high-end fashion retailer may discover that its younger customers prefer online shopping, while older customers enjoy the in-store experience.
- Getting a single view of your customer within the organization
Journey mapping will help you turn a fragmented vision of the customer experience into a unified, organization-wide one. It will have a massive impact on the decision-making process, encouraging you to consider how your actions will affect your clients and become customer-focused.
- Breaking corporate and cross-department silos
To make the way toward delivering a great customer experience, you will need to collaborate with others. Understanding why this collaboration is essential, departments and employees will be more inclined to participate in conversations and collaborate.

- Improving customer experience, retention, and loyalty
While working on a map, you will discover customer pain points at different stages of their journey with you. Fixing the most crucial one as quickly as possible will do you a good turn by eliminating the reasons for leaving you. If fixes take much time, look for quick wins first.
For instance, adding details about your shipping policy on the website will take a developer half an hour, while it will set the right expectations among customers. They won’t be expecting the delivery the next day anymore, bombarding your customer support team with frustrated messages. Another example is a subscription-based video streaming service that can personalize content recommendations to keep subscribers engaged and less likely to cancel their subscriptions.
- Better conversion and targeting of your target customers
Sometimes, it makes sense to focus on a specific segment or, talking journey mapping terms, specific personas. Customer journey insights will help you with this endeavor by giving you a glimpse into these people’s minds and ensuring the higher effectiveness of your marketing.

How to build a customer journey map
Although there is no gold standard for creating a customer journey map, we’ll try to create a somewhat generalized map. So that you can use it as a reference when making maps of your own.
We’ll be using our CJM Online tool along the way for two reasons. Because it’s easy to use and lets you create a CJM fairly quickly without wasting time setting up the environment. Oh, and there's a Personas building tool that comes with it 😉

We’ll take a pizza restaurant as an example of business and learn how to make a customer journey map together.
Step 1: Define your persona
Creating personas is a crucial part of customer experience service and journey mapping in particular. We won’t go into details — you can find them in this post about defining personas .
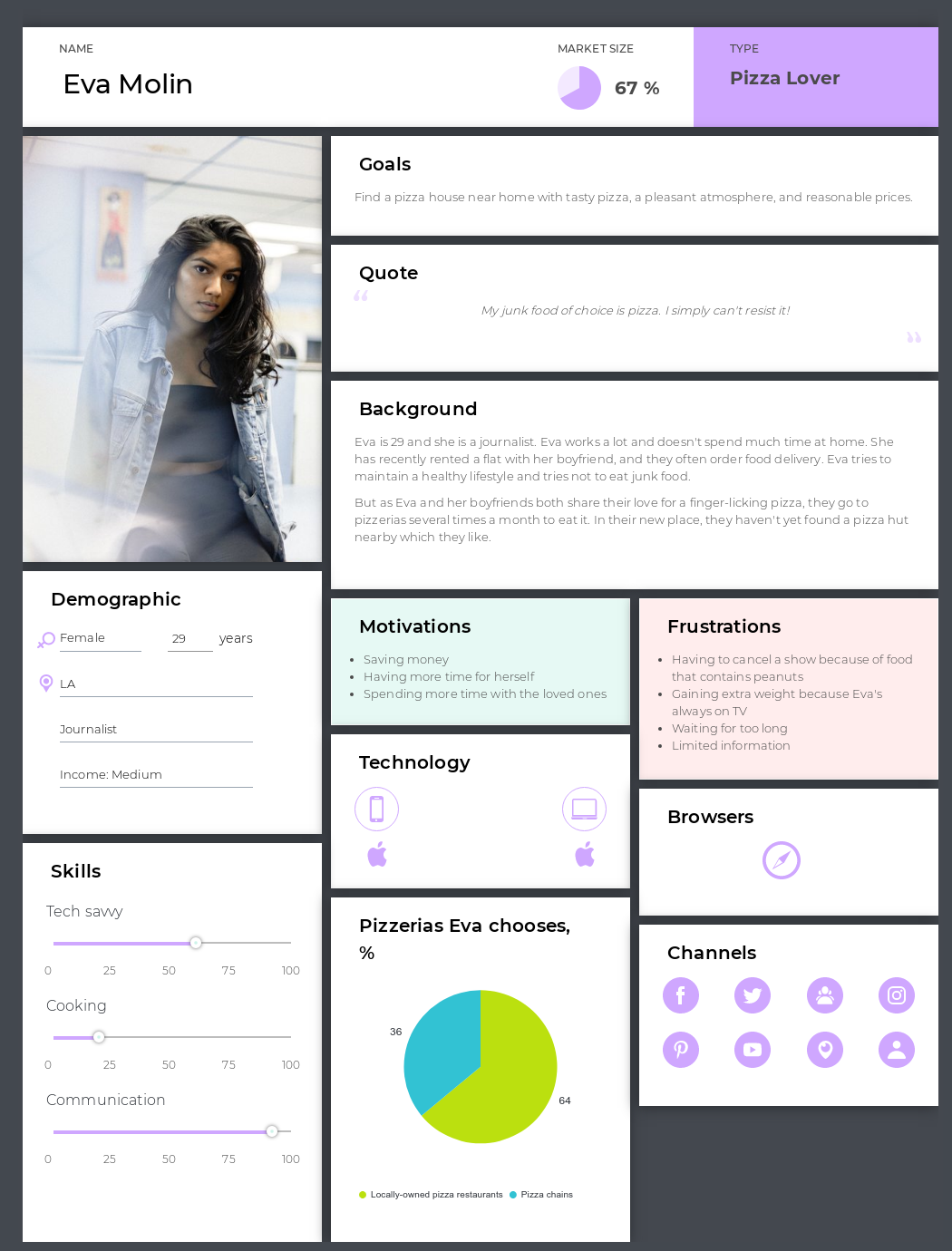
Let’s just say that our persona’s name will be Eva Moline — 29, works as a journalist and loves pizza. Eva is not really tech-savvy, and she tries to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Step 2: Set customer journey stages
Stages are the steps customers take when interacting with a business. The easiest way to identify them is to think of all the actions the person has to take throughout their journey, organize them into logical groups, and name these groups. These will be your map stages.
The number of stages varies from business to business, but we’ll take 8 for this example:
💡 Expert tips:
- If you’re unsure about the order or names of the stages, don’t worry about that. You can change both at any time when working on the map.
- If your stages are complex, you can break them into smaller ones. Read this blog post about defining customer journey stages to learn more.
Step 3: Define journey map sections
Sections are horizontal rows with data that, together with the stages you defined, make up a customer journey map.
When picking sections for a map, your choice will depend on your journey’s type and purpose.
As for UXPressia’s Journey Map tool, it offers a set of more or less universal sections for all kinds of maps.
We’ll use some of the sections in the current example.
Step 4: Set customer goals
Setting customer goals at each stage is great for multiple reasons:
- It helps you understand how your business goals align with the goals of your customers.
- You can meet your customers’ needs better, gaining their loyalty by helping them achieve their goals at each stage.

Above, you can see some of the goals we set for Eva. They are self-explanatory, so there’s no need for extra details.
Step 5: Define touchpoints
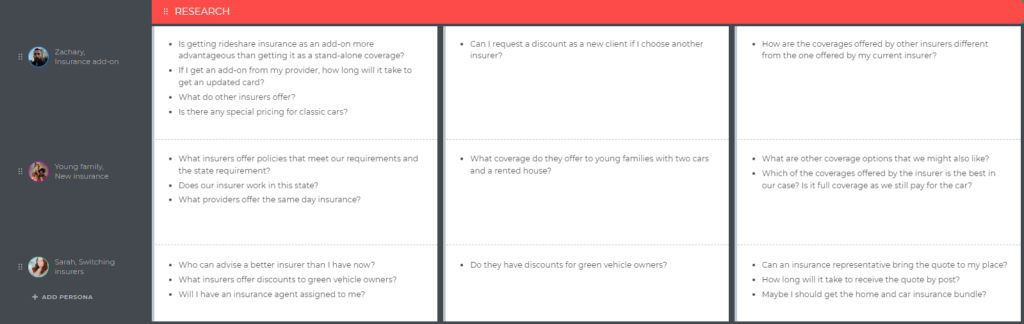
Touchpoints are encounters that happen between your business and customers. In the pizza restaurant example, touchpoints happen:
- At the Awareness phase, when Eva is actively looking for a pizza place nearby. She is asking around, searching locations on Google Maps, etc.
- At the Research phase, when she is trying to find out what people say about the place by asking her friends and reading online reviews.
- At the Arrival stage, when Eva searches for a parking spot and enters the restaurant to get seated after parking the car.
- At the Order stage, when she makes an order and waits for it.
- Time to eat! At this stage, touchpoints occur when Eva is being served and when she is eating her meal.
- At the Leave stage, Eva interacts with the waiter, pays for the meal, etc.
- At the Feedback stage, she goes to the pizzeria’s website and drops a few lines on Instagram.
- At the last stage, Eva gets a promo email from the restaurant with discounts or other special offers.
Defining all the touchpoints is critical because each touchpoint leaves some impression, and your main goal is to keep it up to the mark.
You can also have a separate section to describe the actions your persona takes:
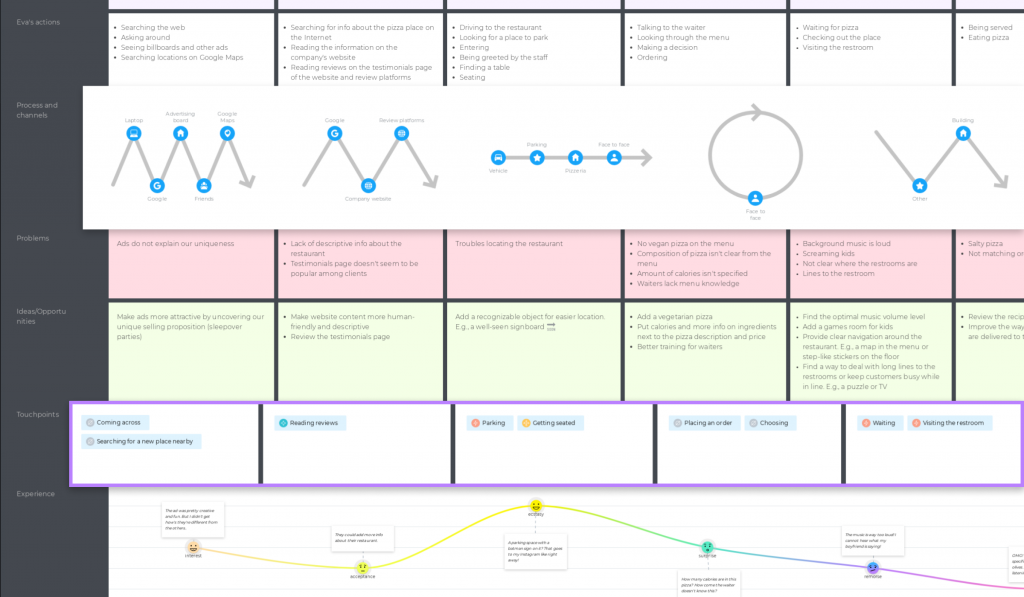
Step 6: Processes and channels
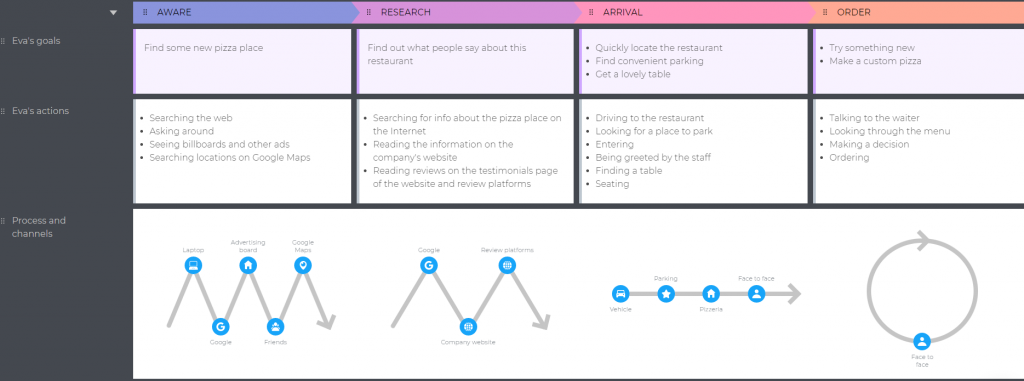
Now, you may want to add some processes and channels to the map. Just to see what channels your persona uses and what types of processes are in their journey. Luckily, our tool lets you do it in the most awesome way. Processes can be linear, non-linear & time-based, cyclic, or bi-directional. In UXPressia, you can specify up to 10 channels per process.
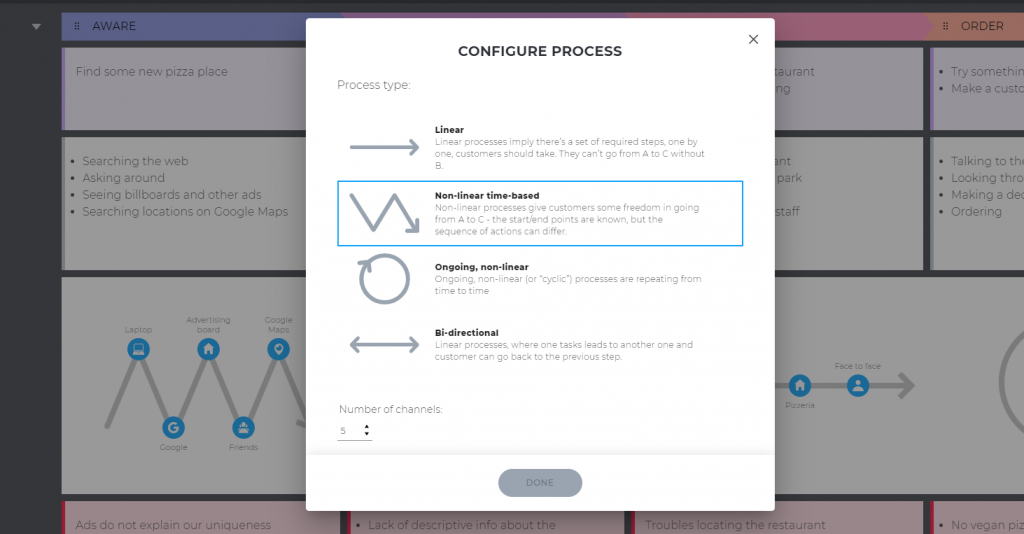
Step 7: Problems and ideas
It’s time to explore problems Eva might have when using our service. It could be a lack of info about the pizza house. Few reviews and ads do not show how our pizza differs from others.
Upon arriving, Eva may struggle with locating the place due to unclear information on signboards or just because of a hard-to-find location.
When making her order, Eva may look for detailed info on dish ingredients to learn whether it contains peanuts she’s allergic to. Descriptions may not be as detailed as she’d want them to be.
While waiting for the pizza, Eva may want to check out the place. Finding a restroom can turn into a nightmare if you don’t have clear signs showing what’s where in the restaurant.
Once you’re done with problems, it’s time to find solutions to these problems. Brainstorm for some ideas on how this or that problem can be solved. Here’s what we brainstormed for Eva’s case:

Step 8: Emotional graph
Never underestimate the power of visualization. And our Customer Journey tool is all about it. We added an emotional graph to see where our service example shines and where it stinks. Plus, we filled text boxes with Eva’s thoughts:
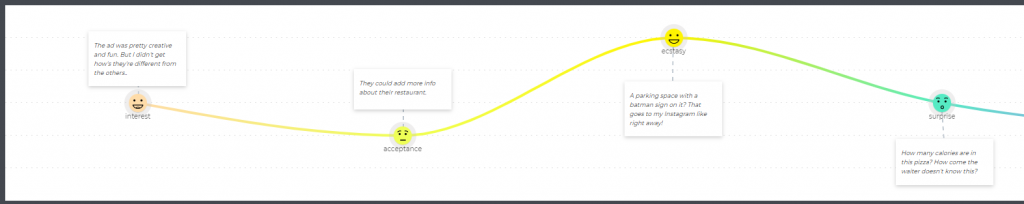
There’s also a special section ( “Think & feel” ) to put personas’ thoughts.
Step ?: Be Creative!
This is a good start, but the map is far from being complete. So, keep exploring Eva’s journey to find more insights and then add all of them to the map.
If you use our tool (which we highly recommend you to do), check out other CJM sections:
- Image section for screenshots, photos, or any other relevant imagery. You can even turn it into a storyboard , describing the journey from beginning to end with your images or those from our library.
- Charts section for communicating data in a visual and meaningful way, just like we did it in the persona:
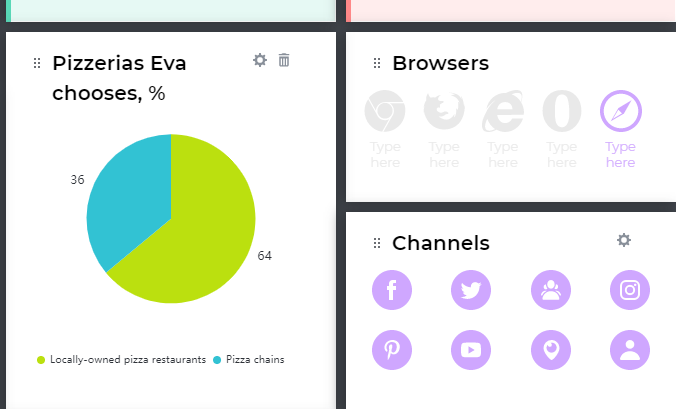
- Video and document sections for journey-related videos and documentation (e.g., an annual marketing report).
- Personas section for visualizing different personas’ interactions within the same journey.
💡 Expert tip: The section with the persona’s questions works like a charm for marketing and content purposes. So be sure to add one 😉
Customer journey map examples
There are also a whole lot of free CJM templates for all sorts of journeys in our library. Here are three examples we picked for you.
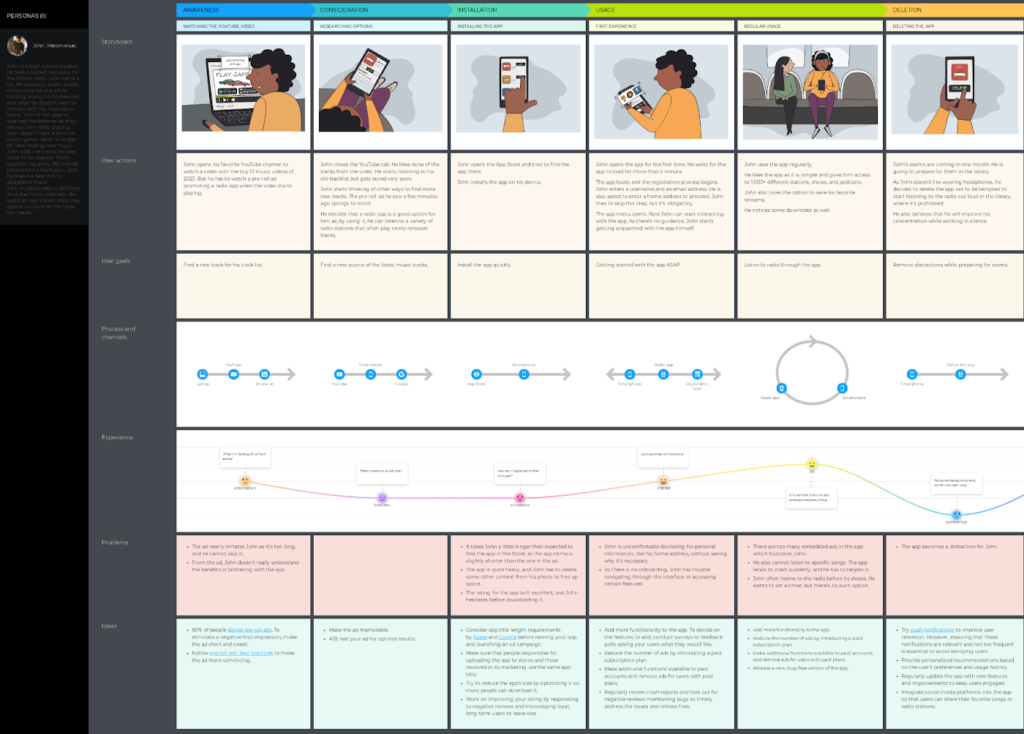
- Example 1: a mobile user journey
This user journey map template covers the digital experience of the persona who discovers a new mobile app, installs it, and uses the app for some time before deleting it.
- Example 2: a client journey map for a corporate bank
This free template is an example of a multi-persona, B2B customer journey. The key persona is a newly opened company looking for a bank to run their business. The CJM also visualizes interactions between the personas involved.
- Example 3: a digital customer journey
This customer journey map example shows the digital journey of three customer personas who want to buy a new pair of sneakers online. They go through the same stages, but if you look at the map, you will be able to see the differences in customer behavior, goals, and actions. It’s also a multi-persona journey map .
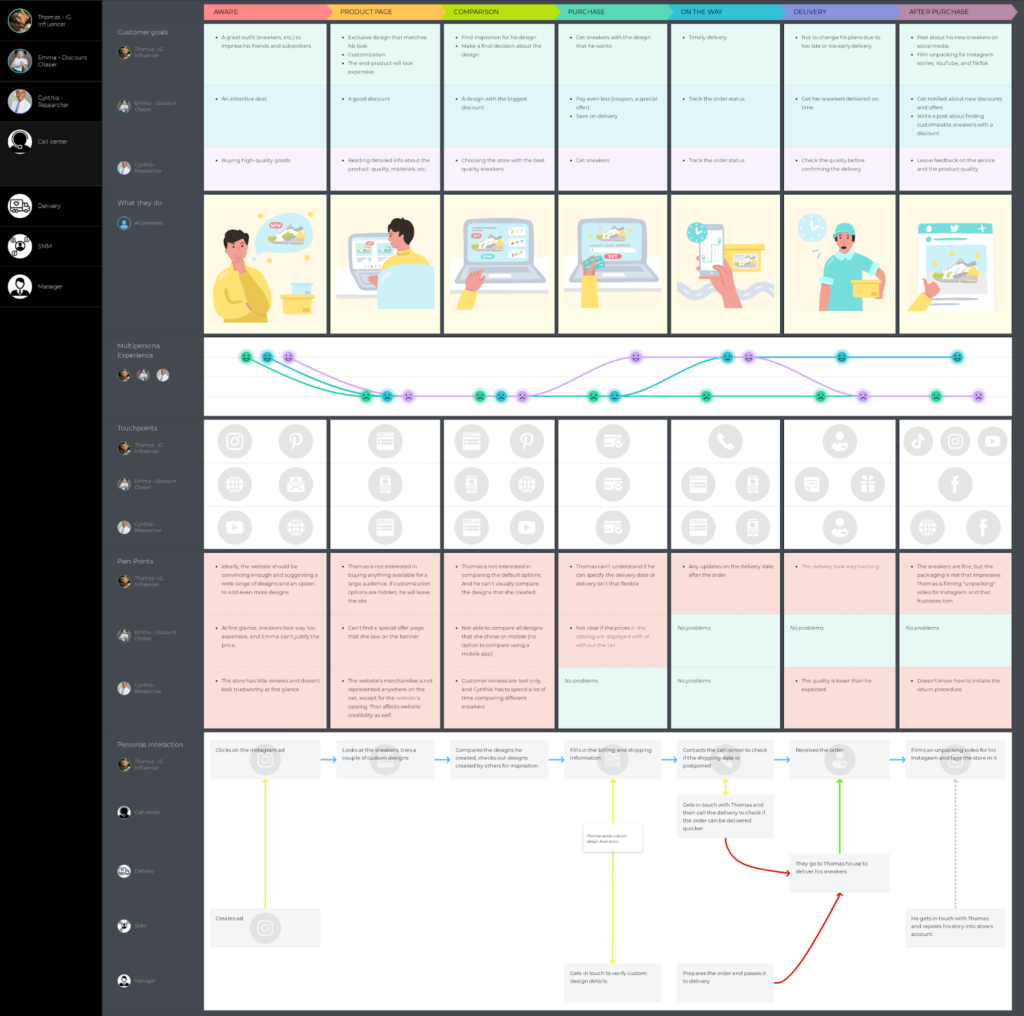
A customer journey mapping checklist
As a quick recap, here is a checklist with key steps to follow when creating a customer journey map:
- Do research
To represent real people, your real customers, and visualize their journeys, you must base your personas and journey maps upon actual data.
- Define your customer persona(s)
Identify your target personas. Create detailed profiles focusing on information relevant to your journey mapping initiative. Include such details as background, customer needs, motivations, channels, etc.
- Specify journey map stages
Determine the stages you want to have on your map and come up with their names.
- Decide on the map sections
Determine which sections to include in your map (e.g., actions, touchpoints, emotions, channels).
- Set customer goals for each stage
Make sure that it is your customers’ goals, not your business goals.
- Identify touchpoints between the persona(s) and your organization, product, or service
Consider both online and offline interactions.
- Map out processes and channels
Visualize the journey-specific processes and the channels your customers use at each stage. Include both digital and physical channels.
- Highlight problems and look for opportunities
Identify any pain points and issues customers might encounter. Brainstorm potential solutions and quick wins to improve the experience.
- Add details about the emotional experience
Visualize the persona’s emotional journey. Include thoughts and feelings where it’s relevant.
- Use more sections
Include illustrations, images, and charts to make the map visually engaging and easy to understand. Enrich your journey map with more data, like KPIs related to journey stages.
Feel free to tailor this checklist to the specific context of your business and your project's needs.
The free guide to download
As a bonus, download our free customer journey mapping guide. Fill in the form below to get a PDF file as an email.
Related posts
The post was originally written in 2017.
Rate this post
first of all, excellent example and I’m very happy to I could understand how to create user journey map, due to for a long time I can’t understand it and how, many thanks for your efforts 🙂 I have some question about ser journey map. I hope to open your chest for me,
1-no there are rules for user journey map? 2-I need another example ?(for example Uber)?further understand 3-have I create user journey map without customer?
Hello, Karim!
I am very glad that this article helped you understand customer journey mapping 🙂
In regards to your first question, I would say that journey maps differ from business to business. However, they tend to have the same structure give or take. So no matter what industry you make a CJM for, you will end up having several stages and a bunch of sections we mentioned in this post.
If you’re looking for CJM examples of Uber customers, here is one: https://www.mindomo.com/doc.htm?d=92be818b774d422bad7eab790957ebc0&m=7d286174ccf1450bbb77c921a609ff65 Plus we have a lot more on our template page: https://uxpressia.com/templates
As for your last question, yes. You may have a journey map without a customer (persona) and use target audience segments instead (or have a generic map without personas at all, though I don’t recommend the latter as in this case it will be hard to empathize with real people). So you will certainly have to introduce a customer down the road to gain a deeper understanding of the journey.
many thanks for your reply to me and again I have some questions
1-why you don’t use in your example? user experience, empathy maps such as use goal touch point, and how to create it 2-As for the previous example (Uber) very confuse for me not as your example
Could you please rephrase your first question? And as for the Uber map, well, that’s all I managed to find. 🙂 But again, here you can find a hundred of map examples of all stripes and colors: https://uxpressia.com/templates
welcome again, my question is? what’s different between Aware and Research
The differences come from the names.
At the aware stage your client realizes that there’s a need for a service/product. Or they find out that your company exists and offer a desired service.
While at the research stage they either do research on your business (e.g. visit your website or ask their friends if they used your service) or they research what is out there on the market that can help them.
Makes sense? 🙂
Thank you for this,
I am wondering , Have you done examples on B2B services. I work in Accreditation & Certification, this seems to be the least visited topic in marketing platforms and blog sites.
We have some B2B templates in our Template Library . Type B2B tag in the search placeholder and you will see all categories with the fitting templates. You can also explore the B2B mapping guide here .
Good luck and happy customers!
Great article, well articulated and detailed. I am starting off with service design and was wondering if I could get some advice mapping out a customer journey for a specific project. I was mapping out how do one approach to repair services?
Hi Shreya, glad you liked the article!
If you’re dealing with home repair, I might suggest our pre-filled template for an interior design agency customer journey: https://uxpressia.com/templates/real-estate . Templates can be a great starting point even if they’re not a 100% match to your use case.
Other than that, you will need to create a persona. If you don’t have any research data yet, do it based on your assumptions. Then, try to visualize what their experience across all stages and interactions with the repair service might be. Once you have the first draft, you can proceed with validating it and adding more data as it comes in.
If you have more context on the project, I can look into it and come up with specific tips 🙂
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Thank you for sharing, it was something I researched.
Hi Rok! Happy mapping 🙂
Learn / Guides / Customer journey mapping (CJM) guide
Back to guides
Customer journey mapping in 2 and 1/2 days
How to create a customer journey map that improves customer success.
Last updated
Reading time.
There’s a common saying that you can’t understand someone until you’ve walked a mile in their shoes—and that’s exactly what customer journey maps do: they help you put yourself in different customers’ shoes and understand your business from their point of view.
Why should you do it? How should you do it? Find the answers in this guide, which we wrote after interviewing 10+ customer journey experts who shared methodologies, dos and don’ts, and pro tips with us.
On this page:
What is a customer journey map?
How to create a customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
4 benefits of customer journey mapping for your business
In later chapters, we dive deeper into customer journey analytics, workshops, and real-life examples.
Start mapping your customer journey
Hotjar lets you experience the customer journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
A customer journey map (CJM) is a visual representation of how customers interact with and experience your website, products, or business across multiple touchpoints.
By visualizing the actions, thoughts, and emotions your customers experience, a customer journey map helps you better understand them and identify the pain points they encounter. This is essential if you want to implement informed, customer-focused optimizations on your site.
Mapping the customer journey: narrow vs. wide focus
A customer journey map can have a very narrow focus and only look at a few, specific steps of the customer experience or buyer’s journey (for example, a product-to-purchase flow on a website), or it can take into account all the touchpoints, online and offline, someone goes through before and after doing business with you.
Each type of customer journey map has its advantages:
A CJM with a narrow focus allows you to zero in on an issue and effectively problem-solve
A CJM with a wide focus gives you a broader, holistic understanding of how customers experience your business
Regardless of their focus, the best customer journey maps have one thing in common: they are created with real customer data that you collect and analyze . The insights are usually organized into a map (hence the name), diagram, or flowchart during a group workshop, which is later shared across the entire business so everyone gets a clear and comprehensive overview of a customer’s journey.
How to create your first customer journey map in 2 and ½ working days
The process of creating a customer journey map can be as long or short as you need. Depending on how many people and stakeholders you involve, how much data you collect and analyze, and how many touchpoints there are across the business, you could be looking at days or even weeks and months of work.
If you’re new to customer journey mapping, start from a narrower scope before moving on to mapping every single customer touchpoint .
Here’s our beginner customer journey mapping framework to help you create your first complete map in 2 and ½ working days:
Day 1: preliminary customer journey mapping work
Day 2: prep and run your customer journey mapping workshop.
Final ½ day: wrap up and share your results
Download your free customer journey map checklist (as seen below), to mark off your tasks as you complete them.
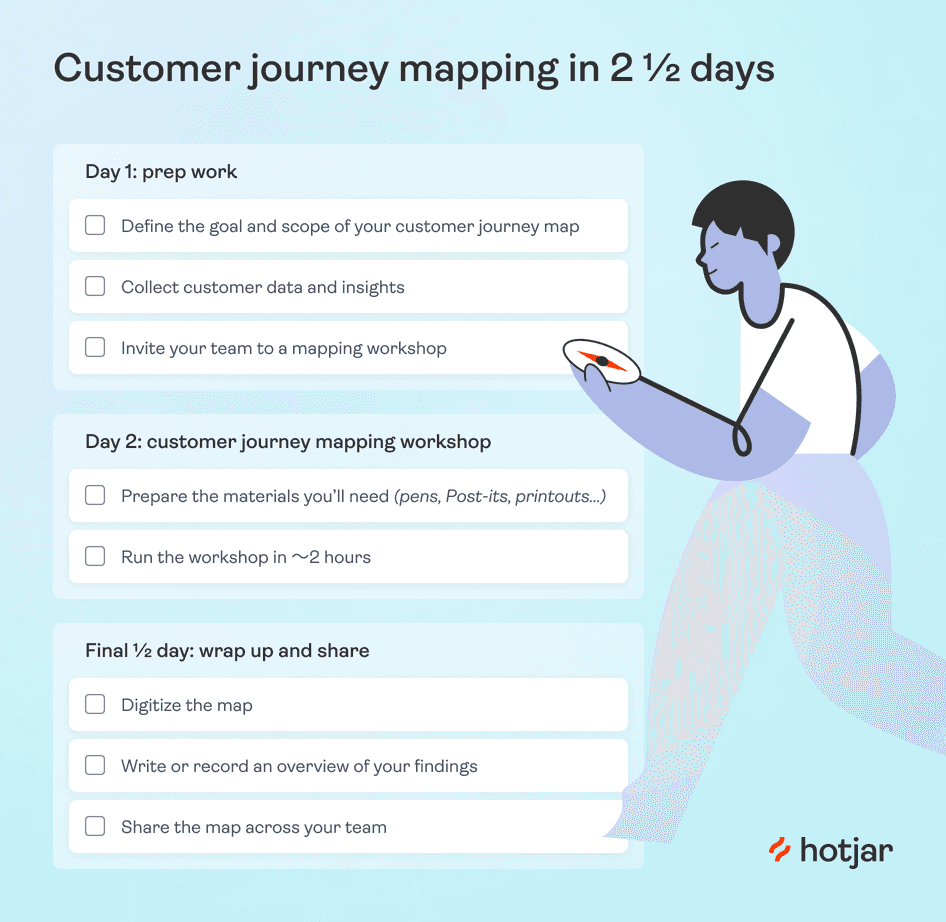
On your first day, you have three essential tasks:
Define the goal and scope of your CJM
Collect customer data and insights
Invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
Step 1: define the goal and scope of your CJM
Clarifying what part(s) of the journey you're looking at, and why, helps you stay focused throughout the mapping process.
If this is your first map, start from a known issue or problematic area of your website. Keep the scope small, and focus on anything you can break down into four or five steps. For example:
If you have a high drop-off on a pricing page with five calls-to-action, each of which takes users to a different page, that’s enough for a mappable journey
If your purchase flow is made of five self-contained pages, each of which loses you potential customers, that’s a good candidate for mapping
✅ The output: a one- or two-sentence description of what your map will cover, and why, you can use whenever you need to explain what the process is about. For example: this map looks at the purchase flow on our website, and helps us understand how customers go through each step and the issues or obstacles they encounter. The map starts after users click ‘proceed to checkout’ and ends when they reach the 'Thank You' page .
Step 2: collect customer data and insights
Once you identify your goal and scope, the bulk of your first day should be spent collecting data and insights you’ll analyze as part of your mapping process. Because your map is narrow in focus, don’t get distracted by wide-scale demographics or data points that are interesting and nice to know, but ultimately irrelevant.
Get your hands on as much of the following information as you can:
Metrics from traditional analytics tools (such as Google Analytics) that give you insight into what’s happening, across the pages and stages your customer journey map covers
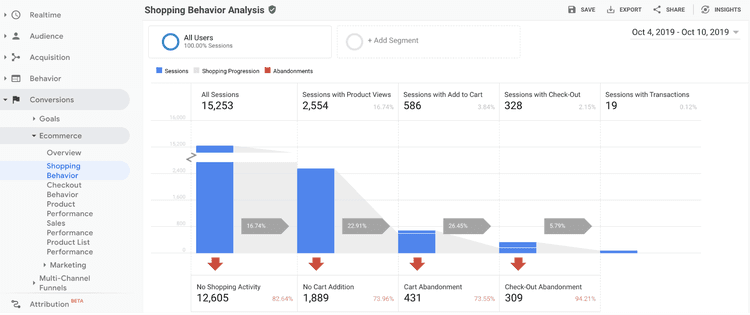
Data from analyzing your conversion ‘funnels’ , which record how many visitors end up at each stage of the user journey, so you can optimize those steps for potential customers and increase conversions
Behavior analytics data (from platforms like Hotjar) that show you how people interact with your site. For example, heatmaps give you an aggregate view of how users click, move and scroll on specific pages, and session recordings capture a user’s entire journey as they navigate your site
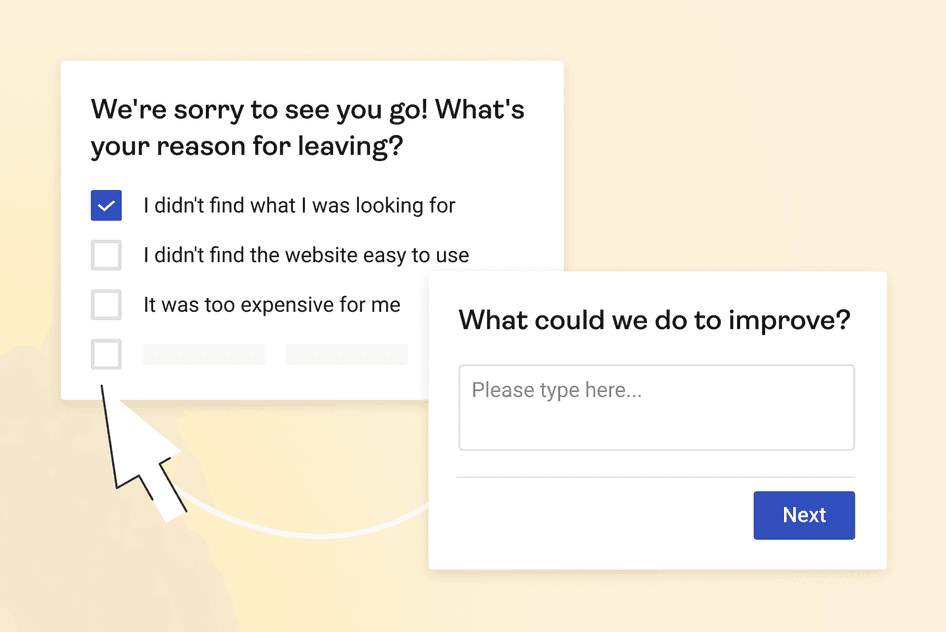
Quantitative and qualitative answers to on-site surveys relevant to the pages you’re going to investigate, as customer feedback will ultimately guide your roadmap of changes to make to improve the journey
Any demographic information about existing user and customer personas that helps you map the journey from the perspective of a real type of customer, rather than that of any hypothetical visitor, ensuring the journey makes sense for your target audience
Any relevant data from customer service chat logs, emails, or even anecdotal information from support, success, and sales teams about the issues customers usually experience
✅ The output: quantitative and qualitative data about your customers' interactions and their experiences across various touchpoints. For example, you’ll know how many people drop off at each individual stage, which page elements they interact with or ignore, and what stops them from converting.
💡Pro tip: as you read this guide, you may not yet have most of this data, particularly when it comes to heatmaps, recordings, and survey results. That’s ok.
Unless you’re running your CJM workshop in the next 12 hours, you have enough time to set up Hotjar on your website and start collecting insights right now. The platform helps you:
Learn where and why users drop off with Funnels
Visualize interactions on key pages with Heatmaps
Capture visitor sessions across your website with Recordings
Run on-site polls with Surveys
When the time comes for you to start your customer journey mapping process, this data will be invaluable.
Step 3: invite your team to a customer journey mapping workshop
In our experience, the most effective way to get buy-in is not to try and convince people after things are done—include them in the process from the start. So while you can easily create a customer journey map on your own, it won’t be nearly as powerful as one you create with team members from different areas of expertise .
For example, if you’re looking at the purchase flow, you need to work with:
Someone from the UX team, who knows about the usability of the flow and can advocate for design changes
Someone from dev or engineering, who knows how things work in the back end, and will be able to push forward any changes that result from the map
Someone from success or support, who has first-hand experience talking to customers and resolving any issues they experience
✅ The output: you’ve set a date, booked a meeting space, and invited a group of four to six participants to your customer journey mapping workshop.
💡Pro tip: for your first map, stay small. Keep it limited to four to six people, and no main stakeholders . This may be unpopular advice, especially since many guides out there mention the importance of having stakeholders present from the start.
However, when you’re not yet very familiar with the process, including too many people early on can discourage them from re-investing their time into future CJM tasks. At this stage, it’s more helpful to brainstorm with a small team, get feedback on how to improve, and iterate a few times. Once you have a firm handle on the process, then start looping in your stakeholders.
On workshop day, you’ll spend half your time prepping and the other half running the actual session.
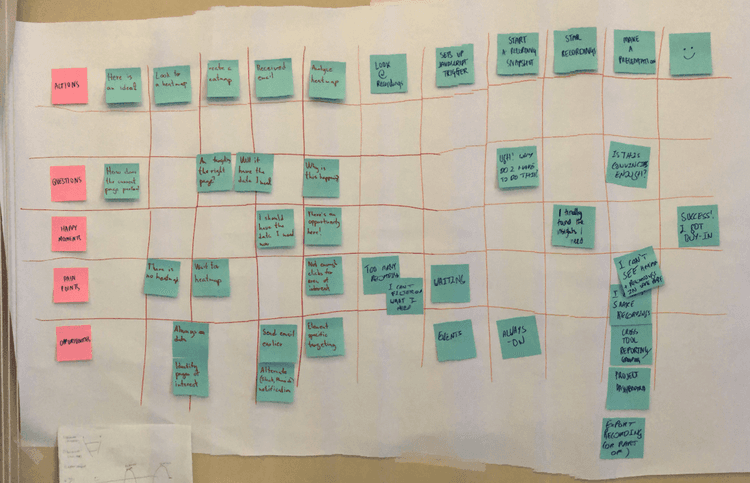
Step 1: prepare all your materials
To run a smooth workshop, ensure you do the following:
Bring stationery: for an interactive workshop, you’ll need basic materials such as pens, different colored Post-its, masking tape, and large sheets of paper to hang on the wall
Collect and print out the data: use the data you collected on Day 1. It’s good to have digital copies on a laptop or tablet for everybody to access, but print-outs could be the better alternative as people can take notes and scribble on them.
Print out an empathy map canvas for each participant: start the workshop with an empathy mapping exercise (more on this in Step 2). For this, hand each participant an empty empathy map canvas you can recreate from the template below.
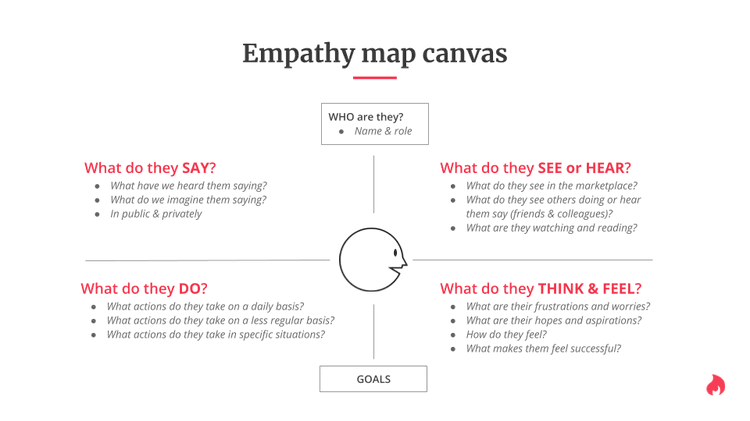
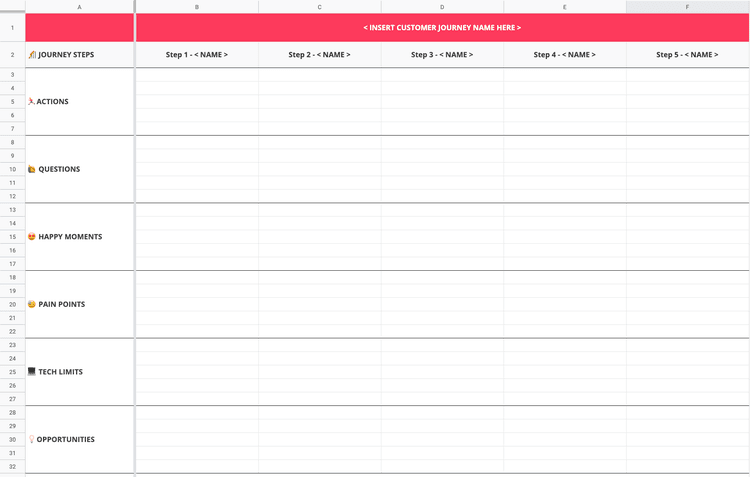
Set up a customer journey map template on the wall: use a large sheet of paper to create a grid you'll stick to the wall and fill in as part of the workshop. On the horizontal axis, write the customer journey steps you identified during your Day 1 prep work; on the vertical axis, list the themes you want to analyze for each step. For example:
Actions your customers take
Questions they might have
Happy moments they experience
Pain points they experience
Tech limits they might encounter
Opportunities that arise
Step 2: run the workshop
This is the most interactive (and fun) part of the process. Follow the framework below to go from zero to a completed draft of a map in just under 2 hours .
Introduction [🕒 5–10 min]
Introduce yourself and your participants to one another
Using the one-two sentence description you defined on Day 1, explain the goal and scope of the workshop and the activities it will involve
Offer a quick summary of the customer persona you’ll be referring to throughout the session
Empathy mapping exercise [🕒 30 min]
Using the personas and data available, have each team member map their observations onto sticky notes and paste them on the relevant section of the empathy mapping canvas
Have all participants take turns presenting their empathy map
Facilitate group discussions where interesting points of agreement or disagreement appear
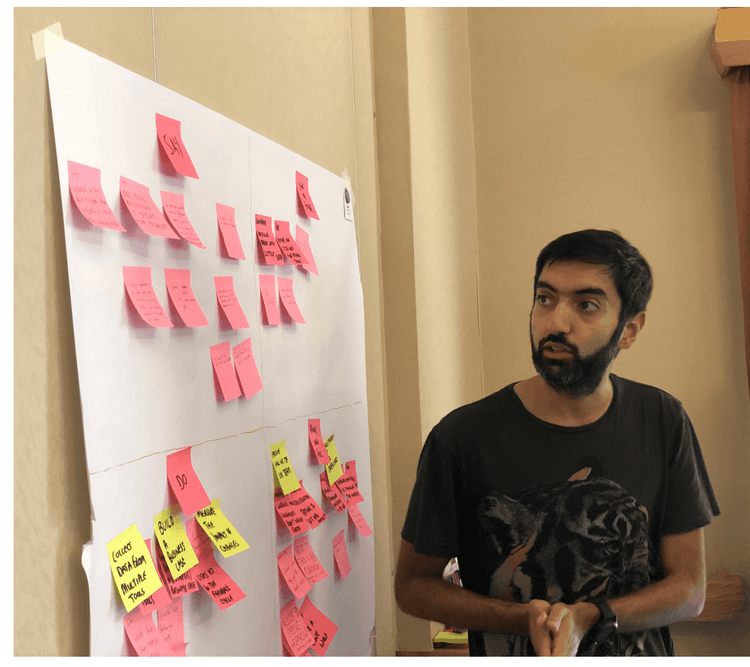
Customer journey mapping [🕒 60 min]
Using Post-its, ask each participant to fill in parts of the map grid with available information. Start by filling in the first row together, so everybody understands the process, then do each row individually (15–20 min). At the end of the process, you should have something like this:

Looking at the completed map, encourage your team to discuss and align on core observations (and take notes: they’ll come in handy on your final half day). At this point, customer pain points and opportunities should become evident for everybody involved. Having a cross-functional team means people will naturally start discussing what can, or cannot, immediately be done to address them (35–40 min).
Wrap up [🕒 5 min]
Congratulations! Your first customer journey map is complete. Finish the session by thanking your participants and letting them know the next steps.
Final half-day: wrap up and share
Once you’ve gone through the entire customer journey mapping workshop, the number one thing you want to avoid is for all this effort to go to waste. Instead of leaving the map hanging on the wall (or worse: taking it down, folding it, and forgetting about it), the final step is to wrap the process up and communicate the results to the larger team.
Digitize the map so you can easily update and share it with team members: it may be tempting to use dedicated software or invest time into a beautiful design, but for the first few iterations, it’s enough to add the map to your team’s existing workflows (for example, our team digitized our map and added it straight into Jira, where it’s easily accessible)
Offer a quick write-up or a 5-minute video introduction of the activity: re-use the description you came up with on Day 1, including who was involved and the top three outcomes
Clearly state the follow-up actions: if you’ve found obvious issues that need fixing, that’s a likely next step. If you’ve identified opportunities for change and improvement, you may want to validate these findings via customer interviews and usability testing.
4 benefits of customer journey mapping
In 2023, it’s almost a given that great customer experience (CX) provides any business or ecommerce site with a competitive advantage. But just how you’re supposed to deliver on the concept and create wow-worthy experiences is often left unsaid, implied, or glossed over.
Customer journey maps help you find answers to this ‘How?’ question, enabling you to:
Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
Create cross-team alignment around the business
Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
We’ve done a lot of customer journey work here at Hotjar, so we know that the above is true—but don’t just take our word for it: all the people we interviewed for this guide confirmed the benefits of journey mapping. Let’s take a look at what they shared.
1. Visualize customer pain points, motivations, and drivers
It’s one thing to present your entire team with charts, graphs, and trends about your customers, and quite another to put the same team in front of ONE map that highlights what customers think, want, and do at each step of their journey.
I did my first customer journey map at MADE.COM within the first three months of joining the company. I was trying to map the journey to understand where the pain points were.
For example, people who want to buy a sofa from us will be coming back to the site 8+ times over several weeks before making a purchase. In that time, they may also visit a showroom. So now I look at that journey, at a customer’s motivation for going to the website versus a physical store, and I need to make sure that the experience in the showroom complements what they're doing on-site, and vice-versa, and that it all kind of comes together.
The map helps in seeing that journey progress right up to the time someone becomes a customer. And it also continues after: we see the next touchpoints and how we're looking to retain them as a customer, so that they come back and purchase again.
A customer journey map is particularly powerful when you incorporate empathy into it, bringing to light specific emotions that customers experience throughout the journey.

2. Create cross-team alignment around the business
The best, most effective customer journey maps are not the solo project of the user experience (UX) or marketing team (though they may originate there).
Customer journey maps are a quick, easy, and powerful way to help everybody in your business get a clearer understanding of how things work from a customers’ perspective and what the customers’ needs are—which is the first step in your quest towards creating a better experience for them.
Our first goal for preparing a customer journey map was to improve understanding customers across the company, so that every employee could understand the entire process our clients go through.
For example, people from the shipping department didn't know how the process works online; people from marketing didn't know how customers behave after filing a complaint. Everything seems obvious, but when we shared these details, we saw that a lot of people didn't know how the company itself works—this map made us realize that there were still gaps we needed to fill.

If we discover that customers have a pain point in a specific section of the map, different teams can look at the same section from several angles; customer support can communicate why something is not possible, and engineering can explain why it’s going to take X amount of effort to get it done. Especially in cross-functional teams where we all come from really different disciplines, I find these maps to be an incredible way for us all to speak the same language.
3. Remove internal silos and clarify areas of ownership
As a company grows in size and complexity, the lines of ownership occasionally become blurry. Without clarity, a customer might get bounced like a ping pong ball across Sales, Success, and Support departments—not great for the seamless and frictionless customer experience we all want to offer.
A central source of ‘truth’ in the form of a customer journey map that everybody can refer to helps clarify areas of ownership and handover points.
We were growing as a team, and we realized we needed to operationalize a lot of the processes that, before then, had just been manually communicated. We did it through a customer journey map. Our goal was to better understand where these hand-off points were and how to create a more seamless experience for our customers, because they were kind of being punted from team to team, from person to person—and often, it was really hard to keep tabs on exactly where the customer was in that entire journey.
4. Make improvements and convert more visitors into customers
A customer journey map will take your team from 'It appears that 30% of people leave the website at this stage' to 'Wow, people are leaving because the info is incomplete and the links are broken.' Once everyone is aligned on the roadblocks that need to be addressed, changes that have a positive impact on the customer experience and customer satisfaction will happen faster.
The customer journey map brings it all together: it doesn't matter who you've got in the room. If you’re doing a proper journey map, they always get enlightened in terms of ‘Oh, my word. I did not know the customer's actually experiencing this.’ And when I walk out of the session, we have often solved issues in the business. Accountability and responsibilities have been assigned, and I find that it just works well.
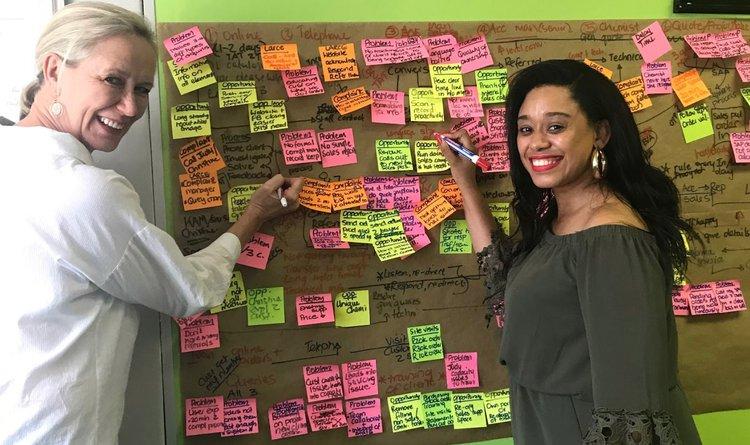

Shaheema (right) working on a customer journey map
Collect the right data to create an effective customer journey map
The secret of getting value from customer journey mapping is not just building the map itself: it's taking action on your findings. Having a list of changes to prioritize means you can also measure their effect once implemented, and keep improving your customers' experience.
This all starts with collecting customer-centric data—the sooner you begin, the more information you’ll have when the time comes to make a decision.
Start mapping your customer journey today
Hotjar lets you experience your customer’s journey through their eyes, so you can visualize what’s working and what needs improvement.
FAQs about customer journey mapping
How do i create a customer journey map.
To create a useful customer journey map, you first need to define your objectives, buyer personas, and the goals of your customers (direct customer feedback and market research will help you here). Then, identify all the distinct touchpoints the customer has with your product or service in chronological order, and visualize the completion of these steps in a map format.
What are the benefits of customer journey mapping?
Customer journey mapping provides different teams in your company with a simple, easily understandable visualization that captures your customers’ perspective and needs, and the steps they’ll take to successfully use your product or service.
Consider customer journey mapping if you want to accomplish a specific objective (like testing a new product’s purchase flow) or work towards a much broader goal (like increasing overall customer retention or customer loyalty).
What is the difference between a customer journey map and an experience map?
The main difference between an experience map and a customer journey map is that customer journey maps are geared specifically toward business goals and the successful use of a product or service, while experience maps visualize an individual’s journey and experience through the completion of any task or goal that may not be related to business.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
By Teresa Anania, Staff writer. Last updated June 10, 2024. Download free templates. What is a customer journey map? A customer journey map is a visual representation of the various stages a consumer goes through during their relationship with a business.
In this article, you’ll learn what a customer journey map is, why you need one and how to build a customer journey map that helps you achieve your goals. We’ve also included examples and templates along the way so you can easily create a customer journey map for your own business.
Spotify, Columbia Road, and Hubspot all serve as very interesting customer journey map examples. We cover B2C, B2B, SaaS & ecommerce examples.
5 great examples of customer journey mapping. A good customer journey map identifies buyers’ actions, desires, and experiences at every key touchpoint—from when a customer lands on your webpage all the way to conversion, onboarding, and beyond.
A customer journey map example. Mapping the customer journey can give you a way to better understand your customers and their needs. As a tool, it allows you to visualize the different stages that a customer goes through when interacting with your business; their thoughts, feelings, and pain points.
Here, you will find a detailed step-by-step guide on making a customer journey map (CJM), examples, expert tips, templates, and a PDF guide to download and save for later.
A customer journey map example for a theater company that investigates a theatergoer’s journey, from booking a ticket online to attending a show. Regardless of their focus, the best customer journey maps have one thing in common: they are created with real customer data that you collect and analyze.
Image source. Why is a customer journey map important? A customer journey map allows you to identify the micro-moments that make up the full experience of your brand.