How to manage privacy and security settings in Safari on iPhone and iPad
Browsing on the internet is something most of us do just about every day, but there is always a slight element of danger, whether it's viruses, identity theft, or getting spoiled for Game of Thrones (DAMN IT).
If you want to have more control over your privacy and security while using Safari on your iPhone or iPad, here's how!

How to prevent cross-site tracking
How to block all cookies in safari, how to request that websites don't track you, how to get warnings about fraudulent websites, how to allow or deny camera and microphone access, how to see if websites have apple pay set up, how to clear your history and website data, how to remove all website data.
Ever been looking at shoes and then shoe ads suddenly pop up on your Facebook feed? That's cross-site tracking and it's a way of monitoring your online behavior to better cater advertising toward you. If you don't like that, then you can turn it off in Safari like this:
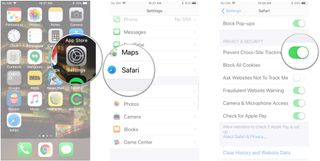
- Launch Settings from your Home screen.
- Tap Safari . You'll have to scroll down to find it.
- Tap the switch next to Prevent Cross-Site Tracking . It's down under Privacy & Security .
Cookies are bits of your information that websites store in order to perhaps customize your experience in future or to save login information so that you don't have to constantly input your email address, for example. If you don't want Safari sites to save any of your info, then you can block all cookies like this:
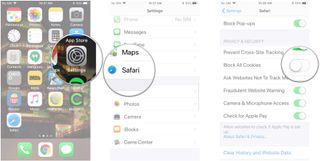
- Tap the switch next to Block All Cookies . It's down under Privacy & Security .
Adding to the above-mentioned cross-site tracking information, you can also get Safari to send requests to websites asking them not to track your behavior. This is added padding in cross-site tracking prevention.
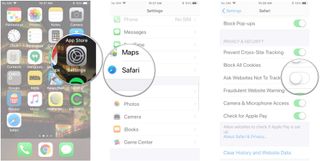
- Tap the switch next to Ask Websites Not To Track Me . It's down under Privacy & Security .
Safari can detect when websites are suspicious or may appear fraudulent, and if you enable the setting, you can get a warning before visiting those sites. You can also just hit "Ignore" if you know the site is legit.
- Tap the switch next to Fraudulent Website Warning . It's down under Privacy & Security . Green is on.
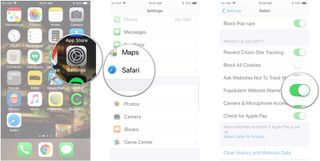
Some websites may want access to your camera and microphone — sites like Facebook — and Safari would therefore need that access. You can completely deny it like this:
Master your iPhone in minutes
iMore offers spot-on advice and guidance from our team of experts, with decades of Apple device experience to lean on. Learn more with iMore!
- Tap the switch next to Camera & Microphone Access . It's down under Privacy & Security .
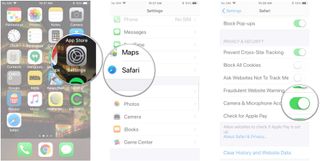
Safari can automatically check to see if the site you're visiting supports Apple Pay. Here's how to enable it:
- Tap the switch next to Check for Apple Pay . It's down under Privacy & Security .
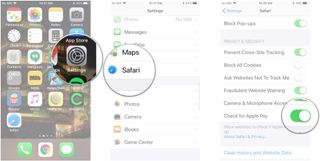
If you've been looking up J-Law's nudes or scheming on Xmas gifts for the wife and she also uses your phone, you can clear your Safari browsing history, which will also clear out your browsing data like cookies, login information, and more.
- Tap Clear History and Website Data .
- Tap Clear History and Data in the pop-up.
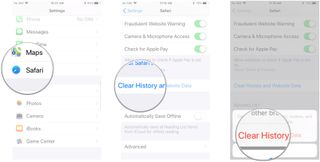
If you want to keep your browsing history but want to remove your data from Safari, you can just delete website data, which will remove cookies, login details, and more.
- Tap Advanced at the bottom of the page.
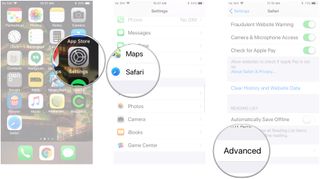
- Tap Website Data .
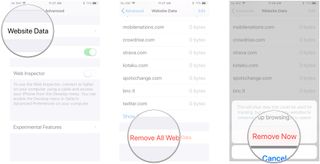
- Scroll to the bottom and tap Remove All Website Data .
- Tap Remove Now .
Let us know in comments below!

○ iOS 14 Review ○ What's new in iOS 14 ○ Updating your iPhone ultimate guide ○ iOS Help Guide ○ iOS Discussion

Mick is a staff writer who's as frugal as they come, so he always does extensive research (much to the exhaustion of his wife) before making a purchase. If it's not worth the price, Mick ain't buying.
Google shows off new Gemini conversational AI capabilities as it becomes increasingly clear how far Apple's Siri has fallen
Apple realized Siri's failings after execs tested ChatGPT for themselves before refocusing the company on significant iOS 18 upgrades
This updated fan favorite iPad accessory works with the latest models and the Apple Pencil Pro
Most Popular
- 2 Apple Pencil Pro vs Pencil 2: Features, differences, and compatibility explained
- 3 New Apple Pencil Pro features come to the Goodnotes iPad note-taking app including support for its squeeze and barrel roll gestures
- 4 New iPhone 16 Pro Max dummy leak shows just how much your hands will need to grow before launch day
- 5 10 free PlayStation games you can play on Gamma and RetroArch for iPhone, iPad, and Apple TV right now
- Stream Your Favorite Sports
- Where to Watch WNBA Games
How to Control iPhone Safari Settings and Security
Control your settings and security in the iPhone browser
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SamCostello-d7fcf106ec2048ccb06d1e2190b3396d.jpg)
- Ithaca College
In This Article
Jump to a Section
How to Change the Default iPhone Browser Search Engine
How to use safari autofill to fill out forms faster, how to view saved passwords in safari, control how links open in iphone safari, how to cover your online tracks using private browsing, how to clear your iphone browser history and cookies, prevent advertisers from tracking you on your iphone, how to get warnings about potentially malicious websites, how to block websites, ads, cookies, and pop-ups using safari, how to use apple pay for online purchases.
- Take Control of Your iPhone Security and Privacy Settings
What to Know
- To change search engine, go to Settings > Safari > Search Engine . To control links, go to Safari > Open Links .
- To use AutoFill, go to Settings > Safari > AutoFill > turn on Use Contact Info .
- To view saved passwords, go to Settings > Passwords & Accounts > Website & App Passwords .
This article explains how to adjust Safari settings and security on your iPhone or iPad.
Searching for content in Safari is simple; tap the menu bar at the top of the browser and enter your search terms. By default, all iOS devices use Google for web searches, but you can select a different search engine by following these steps:
Open the Settings app.
Select Safari > Search Engine .
Select the search engine you would like to use as the default. Options include Google , Yahoo , Bing , and DuckDuckGo . The setting is automatically saved, so you can search using the new default search engine right away.
Similar to a desktop browser , Safari automatically fills in forms by grabbing information from your address book. This saves time because you don't need to fill out the same forms over and over again. To use this feature, follow these steps:
Select Safari > AutoFill .
Toggle the Use Contact Info switch to on/green.
Your information appears in the My Info field. If it does not, select the field and browse your address book to find your contact information.
Older versions of iOS allowed you to change your username and password info here. If you want to save, edit, or delete usernames and passwords in iOS 13 or later, go to the Passwords & Accounts settings page (select Settings > Passwords & Accounts ).
To save frequently used credit cards to make online purchases quicker, move the Credit Cards switch to on/green. If you don't have a credit card saved on your iPhone, select Saved Credit Cards , and add a card.
Saving usernames and passwords in Safari means you're not forced to memorize login credentials to access a website. As this data is sensitive, iOS takes measures to protect it. If you need to look up a username or password, you can do so by following these steps:
Select Passwords & Accounts > Website & App Passwords .
You are asked to authorize access to this information using Touch ID , Face ID , or your passcode.
A list details all the websites for which iOS has saved login data. Select a site to view the corresponding username and password.
You can choose where new links open by default—in a new window that appears either in front of or behind the page you are currently viewing. Follow these steps to adjust this setting:
Select Safari > Open Links .
Select In New Tab to open links in a new window in Safari and to have that window appear in front of the current tab. Select In Background to open links in a new window that appears behind the page you are currently viewing.
Browsing the web leaves digital footprints. Between browsing history, cookies, and other usage data, you may prefer to cover some of those tracks. The Safari Private Browsing feature prevents Safari from saving information about your behavior—including browsing history, cookies, and other files—while it is turned on.
When you want to delete your browsing history or cookies manually, follow these steps:
Select Safari > Clear History and Website Data .
A menu appears asking if you would like to clear the browsing data. Select Clear History and Data .
Cookies allow advertisers to track you across the web. This lets them build a profile of your behavior and interests to target you with ads better. Here's how to opt-out of some of that tracking data:
Select Safari .
Move the Prevent Cross-Site Tracking switch to on/green.
Older versions of iOS included a Do Not Track feature that asked websites not to track your browsing data. Apple removed this feature, as the request was never mandatory and did not do much to limit the tracking of user data.
Setting up fake websites that look like ones you normally use is a common method of stealing data from users. Safari has a feature to help avoid these sites. Here's how to enable it:
Move the Fraudulent Website Warning switch to on/green.
You can speed up your browsing, maintain privacy, and avoid certain ads and websites by blocking cookies. Here's how:
Move the Block All Cookies switch to on/green, then select Block All to confirm the action.
If you set up Apple Pay , you can use it at any participating retailer to complete purchases. To make sure you can use it at those stores, enable Apple Pay for the web. Here's how:
Move the Check for Apple Pay switch to on/green.
Take Control of Your iPhone Security and Privacy Settings
While this article focuses on privacy and security settings for the Safari web browser, the iPhone has other security and privacy settings. These settings can be used with other apps and features to protect private info stored on your iPhone .
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- How to Change Settings in iOS Dolphin
- How to Find a Wi-Fi Password on an iPhone
- How to Clear Search History on iPhone
- 3 Ways to Clear Cache on an iPad
- How to Manage Browsing History on Safari for iPad
- 4 Ways to Play Fortnite on iPhone
- How to Manage History and Browsing Data on iPhone
- How to Change the Default Search Engine in Safari for iOS
- The Top 10 Internet Browsers for 2024
- How to Add, Edit, and Delete Bookmarks in iPhone's Safari
- How to Enable or Change AutoFill Information on an iPhone
- How to Manage Your Browsing History in Safari
- How to Solve Safari Crashes on the iPhone
- How to Disable JavaScript in Safari for iPhone
- Firefox Focus: What It Is and How to Use It
- How to Clear Cookies on iPad
Tell websites to stop tracking you
Change your search engine to duckduckgo.
- Hide your IP address
Stop using location services
Disable autofill, clear your browsing history, block your cookies, 7 settings you should change in safari to enhance your privacy.
- If you use Safari on your Mac, iPhone, or iPad, you can enable settings to enhance your privacy while web browsing.
- You can easily disable cookies, change your search engine to DuckDuckGo, hide your IP address, and more.
- Here are seven of the top ways to make your online activity more private.
While Apple has allowed alternative browsers on the iPhone and iPad for quite some time, odds are good that if you have one of those devices (or a Mac computer, of course) you frequently use Safari to browse the web. It's relatively safe and private, but you can do much better by tweaking a few settings. Here are seven Safari settings that'll enhance your privacy when you're online.
Almost every step you take online is tracked by websites to target you for ads and to customize your experience. But you can shut most of that down by telling Safari to stop tracking you. On your iPhone or iPad, start the Settings app and then tap Safari . In the Privacy & Security section, enable Prevent Cross-Site Tracking by swiping the button to the right.
On a Mac, start Safari and then click Safari in the menu bar at the top of the screen. Click Preferences in the dropdown menu. In the Preferences window, click the Privacy tab and then click the checkbox for Prevent Cross-Site Tracking .
Google is most people's default, but that search engine fundamentally lacks privacy. If you don't want a large corporation to know your browsing history, switch to DuckDuckGo. On an iPhone or iPad, start the Settings app and then tap Safari . In the Search section, tap Search Engine and choose DuckDuckGo from the options.
If you're using a Mac, start Safari and then click Safari in the menu bar at the top of the screen. Click Preferences in the dropdown menu. In the Preferences window, click the Search tab. Finally, to the right of Search Engine , click the dropdown menu and switch from Google to DuckDuckGo .
Hide your IP address
By default, websites can see your IP address, which can reveal personal details about you including your location. If you prefer, you can hide this from online trackers. On your iPhone or iPad, start the Settings app and then tap Safari . In the Privacy & Security section, tap Hide IP Address and choose From Trackers .
On a Mac, start Safari and then click Safari in the menu bar at the top of the screen. Click Preferences in the dropdown menu. In the Preferences window, click the Privacy tab and then click the checkbox for Hide IP address from trackers .
A lot of your mobile device's secret sauce is based on location services — your iPhone and iPad need to know where you are to make smart suggestions and offer location-based features. But if you don't want Safari to know where you are, it's easy to turn off. On an iPhone or iPad, start the Settings app and then tap Safari . In the Settings for Websites section, tap Location and change the setting to Deny (or, if you want to be asked every time, choose Ask ).
On a Mac, start Safari and then click Safari in the menu bar at the top of the screen. Click Preferences in the dropdown menu. In the Preferences window, click the Websites tab. Choose Location in the pane on the left. At the bottom of the window, configure When visiting other sites by clicking the dropdown menu and choosing Ask or Deny .
Autofill is a great feature if you don't like to enter basic personal information into web forms over and over again, but for that to work, Safari has to record private data. Don't want that? On an iPhone or iPad, start the Settings app and then tap Safari . In the General section, tap Autofill and turn off Use Contact Info and Credit Cards by swiping the buttons to the left.
On a Mac, start Safari and then click Safari in the menu bar at the top of the screen. Click Preferences in the dropdown menu. In the Preferences window, click the AutoFill tab. You can disable autofill data in four categories by clearing the checkboxes.
This one is the traditional, go-to way to enhance your privacy — you can clear your browsing history from time to time to erase records on your device about where you've been online, along with your saved website passwords. On an iPhone or iPad, start the Settings app and then tap Safari . Then scroll down and tap Clear History and Website Data . Conform you want to do that in the popup window.
On a Mac, start Safari and then click History in the menu bar at the top of the screen. Click Clear History in the dropdown menu, choose the timeframe you want from the dropdown menu, and click Clear History .
If you prevent cross-site tracking (see the earlier tip in this article), Safari prevents some third-party cookies. But you can disable all cookies if you want to amp up your privacy — just be aware that your online experience will be less convenient, and some sites won't work properly. To try it on an iPhone or iPad, start the Settings app and then tap Safari . In the Privacy & Security section, enable Block All Cookies by swiping the button to the right.
On a Mac, start Safari and then click Safari in the menu bar at the top of the screen. Click Preferences in the dropdown menu. In the Preferences window, click the Privacy tab. Beside Cookies and website data , click the checkbox for Block all cookies .
- Main content
5 Features in Safari for Mac That Boost Privacy and Security
If you use Safari, you should know about these features that keep your data safe and secure online.
When you’re browsing the internet, it’s easy to forget about safety and privacy issues. You might not always think about how much personal information you’re sharing, or how often you use the same passwords on different sites.
If you use Safari on a Mac computer, it’s actually OK to forget this a bit, because the browser handles some of this for you.
Safari is chock-full of features that keep your data private and your web experience extremely safe. We’re here to tell you all about these, so you can make sure you’re using them smartly.
Safari Features to Protect Your Privacy
Websites love to track users to learn more about them, then market to people effectively by showing them personalized ads. This can be fairly innocuous, but the data accumulated on you can reveal where you live, how old you are, and other information you may not want everyone to know.
How websites do this, as well as when and where the tracking takes place, can be pretty tricky to spot. We’ve written about different ways to check who is tracking you online , which can help you get a clearer picture of online privacy.
But Safari also has many built-in features that help you keep your browsing data to yourself. You can thus better maintain your privacy just by using Safari as your browser and making sure certain settings are turned on in it.
1. Safari's Intelligent Tracking Prevention
One of these features is the Intelligent Tracking Prevention built into Safari. Through machine learning, the browser spots where websites and companies obtain user data, then blocks that data from carrying over onto other sites.
This means any information obtained about you on one site can’t be spread all over the internet. Your data and personal information stay limited to individual sites.
The tracker also minimizes third parties from accessing any data Apple collects on you as a user. And you have a say over how much data Apple can collect from you when you use its devices and software. You can request your personal data from Apple to see how much the company accesses, and alter how much information apps send back to Apple.
The privacy tracker is automatically enabled in the latest versions of Safari. If you want to check that it is, or alter its behavior, head to Safari > Preferences and click on the Privacy tab. Make sure the Prevent cross-site tracking box is checked to keep the protection activated.
2. Privacy Reports in the Smart Search Field
The privacy reports in the Smart Search field at the top of Safari are another feature keeping your information private. The Smart Search field is the address bar in Safari. It’s where you type in or paste URLs to access websites.
And like address bars in most modern browsers, you can also enter text to search the web using your preferred search engine, chosen at Safari > Preferences > Search . Consider choosing a privacy-focused search engine to reduce data collection as you search.
Aside from URL-related suggestions, the search field has a major privacy feature. It can tell you if anything is trying to track your data when you’re on a particular site. This also lets you know if that entity was blocked from getting the information or not.
This information is found in the privacy report. Privacy reports can tell you about active trackers on sites you’re currently browsing, as well as trackers that have been blocked in the past.
To get a privacy report on active trackers, open a website in Safari. Then, click on the shield icon to the left of the Smart Search field. You’ll see a list of any trackers found on the site.
To see a history of data trackers Safari has blocked, and what sites they’ve been on, click on Safari > Privacy Report . You’ll see how many trackers Safari successfully blocked in the last 30 days, the percentage of websites you went to that contacted trackers, and more information you can use to help keep your data private in the future.
3. Private Browsing Windows
Safari also allows you to browse the internet using Private Browsing windows . Private Browsing windows work as default Safari windows do, except they hide even more information from websites and data trackers.
In a Private Browsing window, no search or website information is saved—any sites you visit or terms you search in these windows won’t appear in your Safari history. Autofill information isn’t saved, and webpages can’t be shared or accessed via iCloud or Handoff.
Any data you create while browsing in one private tab won’t affected or be accessible to other private tabs or windows you keep open. This means that even if you log into Facebook in one private tab, you’d have to log in again if you opened Facebook in a second private tab. So you deal with even less tracking than Intelligent Tracking Prevention on its own.
Related: Ways You Can Be Tracked in Incognito or Private Browsing Mode
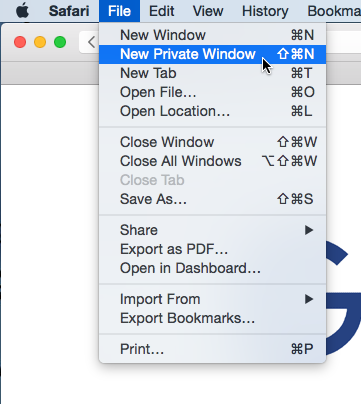
To open a Private Browsing window in Safari, click on File > New Private Window . If you want Safari to default to private windows, go to Safari > Preferences > General . In the Safari opens with dropdown menu, select A new private window .
Safari Features for Better Security
In addition to keeping your information private, Safari also keeps you safe from hackers and malware as you browse the internet.
4. Safari's Password Manager
One of its major security features is its built-in password manager. Like other password managers, there are some steps to complete before you start using it fully. But Safari will safely save passwords for you as you use them on different websites.
Read more: How to Start Using a Password Manager
Those passwords only auto-fill when you log in with your credentials. On Mac computers with Touch ID, your fingerprint can protect autofill for your usernames and passwords. This means not just anyone can log in to your email, social media, or banking sites.
To see your passwords without auto-filling them, you can go to Safari > Preferences > Passwords . Here, you need to input your Touch ID fingerprint or enter your computer password.
In your Safari password list, you can see if any passwords have been compromised or exposed, as long as have the Detect passwords compromised by known data leaks box checked.
If your passwords have appeared around the web, Safari will show a yellow triangle icon that has an exclamation point in it to the right of the password. Seeing this icon usually means you should change that password, which you can do on your account page for the website. Safari will then update its password manager to match.
Safari’s password manager can also help you create strong passwords. Whenever you sign up for a new website, Safari will offer to create and store a super-strong password that’s near-impossible to guess.
If you’re worried about not being able to make strong passwords on your own , this is a fantastic option that keeps your internet experiences safe and secure. And with iCloud, these strong passwords are easy to pass on to iPhone and iPad. Touch ID and Face ID ensure that only you can see your passwords.
5. Popup Blocking in Safari
Safari also offers extensive popup blocking, giving you a less annoying web experience that's also safer. Popup ads can contain all sorts of seedy links, including those that download malware to your Mac.
While macs aren’t known for getting viruses, Mac-specific malware definitely exists. We’ve written before about how to tell if your Mac has a virus , but it's better to make sure you don’t get malware, rather than having to deal with removing it.
Safari has several settings for popups, including blocking all of them outright. You can also have Safari let you know when it blocks one, in case you actually need a popup from a particular site.
To set Safari’s pop-up settings, go to Safari > Preferences and click on the Websites tab. Scroll down the left menu to Pop-up Windows , then set your preferences for various websites using the dropdown menus on the right.
For a default popup setting, set the When visiting other websites dropdown to your preference at the bottom of the window.
For a Private and Secure Browser, Use Safari
Safari comes with many features that keep your personal information and user data well hidden, as well as settings that let you browse the internet safely. It’s a great browser already built into Mac computers, and worth using for these and many other reasons.
Start using Safari regularly, and you can make it your own by learning how to customize some of its elements.

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Safari - Privacy and Security in Safari
Safari -, privacy and security in safari, safari privacy and security in safari.

Safari: Privacy and Security in Safari
Lesson 5: privacy and security in safari.
/en/safari/bookmarking-in-safari/content/
Safari privacy and security
Safari has several security features , including security indicators and malware protection . Because of its advanced security features , Safari offers a safe browsing experience. Safari also allows you to control what information you share online, keeping your personal information private.
Watch the video below to learn the basics of privacy and security in Safari.
Website security indicators
Whenever you navigate to an encrypted website, Safari will display a security indicator to the left of the web address in the address bar.

Understanding this indicator can help you stay safe when entering personal information online.

- If no indicator appears, this means the site is not using a secure connection. This is not important for many websites, like a news source or weather forecast, but you should avoid entering sensitive personal information on these pages.
Safari offers a high level of protection from malicious websites, but you should still use your best judgement when browsing online. Review our Internet Safety tutorial to learn more about staying safe online.
Maintaining your privacy in Safari
Safari takes great care to keep your personal information private. It offers many ways to control your privacy, like modifying your privacy settings , deleting your history , and browsing in a private window.
Privacy settings
Safari allows you to control some of the information you share online, which you can modify in your privacy settings . We recommend not changing Safari's default selections, as they allow for the best balance of privacy and security while browsing. However, you can modify them if you want.
To modify your privacy settings:
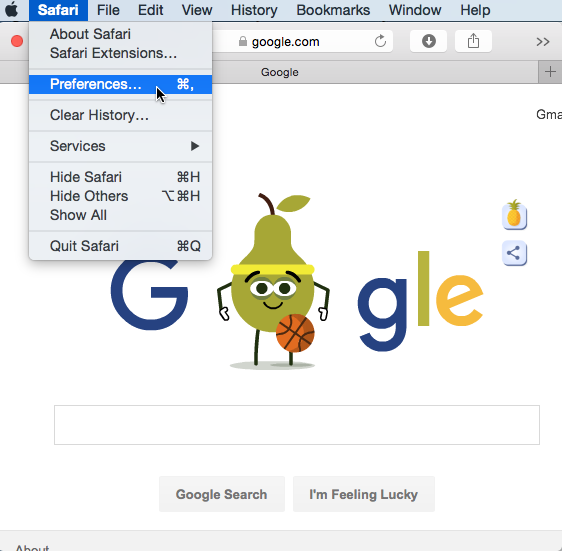
Deleting browsing history
Like all browsers, Safari keeps a record of every website you visit in your browsing history . You may want to remove some or all of your browsing history for the sake of privacy.
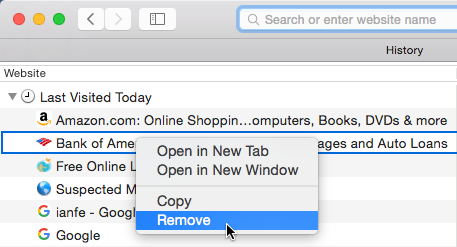
To remove specific sites from history:
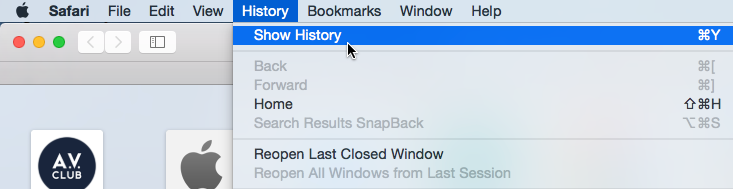
- A new History tab will appear with your full browsing history .
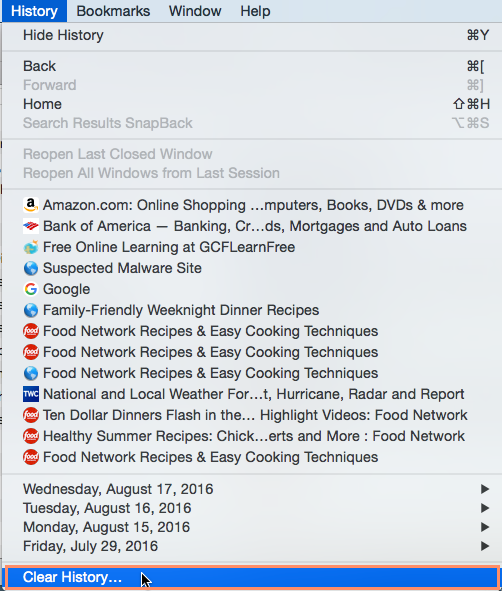
To clear all browsing data:
Safari makes it easy to delete some or all of your history. For example, sometimes you might want to remove only your history from the past hour instead of removing your entire history. You might also want to remove all of your saved pages and cookies but keep your saved passwords.
- The selected browsing history will be cleared.
Private browsing
For added privacy, Safari also offers private browsing , which allows you to browse the web without recording your history or storing cookies. This is a great way to keep your browsing history secret when planning a party or buying a gift for someone who shares your computer.
To create a private window:
Private browsing does not make Safari more secure —it only stops Safari from saving history and cookies for that session. Don't use a private window to view any websites you wouldn't feel safe viewing in a regular Safari window.
Apple announces powerful new privacy and security features

Privacy Features Give Users Greater Control of Their Data
Features Designed to Help Protect User Safety
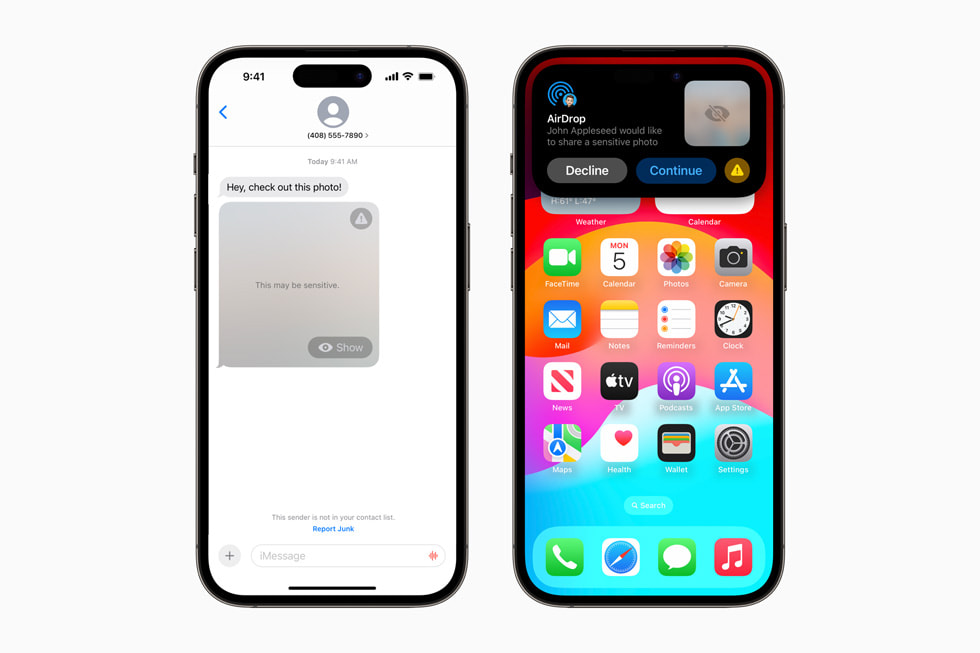
Powerful Security Protections to Safeguard User Data
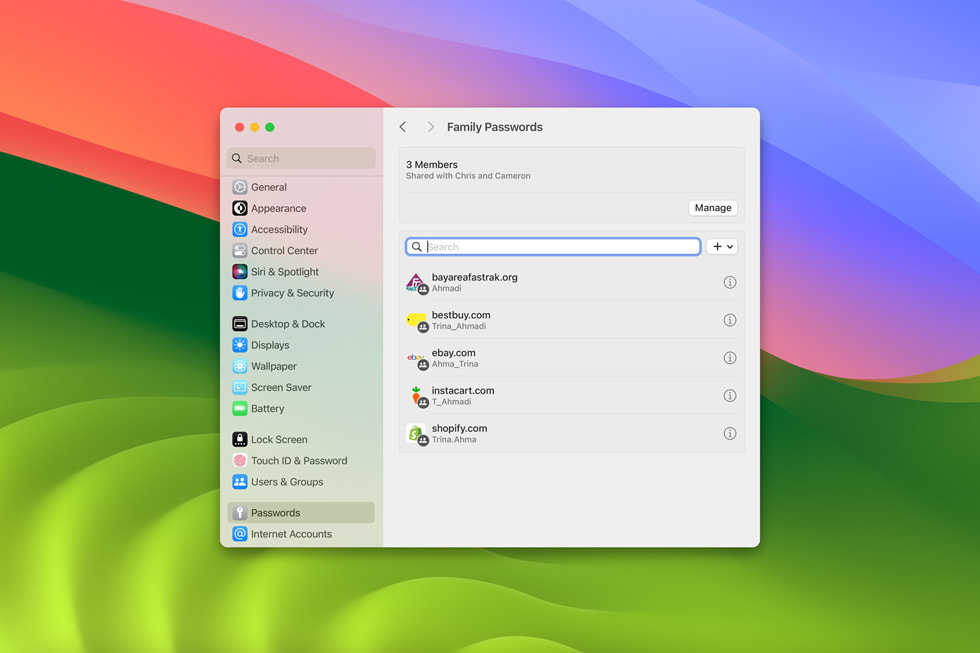
Additional Features Designed with Privacy and Security at Their Core
- Check In makes it easy for users to let friends or family members know they’ve reached their destination safely. Once turned on by the user, Check In automatically detects when the user has reached their intended destination, and will let selected contacts know via Messages. In the case that something unexpected happens while the user is on their way, Check In will recognize that the user is not making progress toward their declared destination and check in with them. If they don’t respond, the feature will share useful information — like the user’s precise location, battery level, cell service status, and the last active time using their iPhone — with the contacts the user selected. In addition to making it easier to get help if needed, Check In is designed around privacy and security, keeping the user in control by letting them choose whom to share their information with, including the destination and time duration that they set. Users can end the Check In session at any time. Information sent with Check In is end-to-end encrypted so only the user’s family member or friend can read it, not Apple or anyone else.
- With NameDrop , a new AirDrop experience, a user can hold their iPhone near another to share their contact information with only their intended recipients. Users can also choose the specific contact details they want to share — and, importantly, what information they don’t want to share. Users can also share content like photos or links the same way. Apple Watch users can also use NameDrop by tapping the Share button in My Card in the Contacts app, or by tapping the My Card watch face complication, and then bringing Apple Watch face to face with someone else’s Apple Watch. As with all AirDrop experiences, these new features securely share content over an encrypted connection.
- Live Voicemail makes it easier to know when to answer a phone call. When someone calls and starts to leave a message, users will see a live transcription as the caller speaks. If the user wants to talk to the caller, they can pick up the call at any time. When Silence Unknown Callers is turned on, calls from unknown numbers will go directly to Live Voicemail without ringing. Calls identified as spam by carriers won’t appear as Live Voicemail, and will instead be instantly declined. This gives the user more peace of mind that spam, scams, or calls that may be invasive of privacy, can be ignored without missing important calls. Thanks to the power of the Neural Engine, Live Voicemail occurs entirely on device, and this information is not shared with Apple.
Text of this article
June 5, 2023
PRESS RELEASE
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA Apple today announced its latest privacy and security innovations, including major updates to Safari Private Browsing, Communication Safety, and Lockdown Mode, as well as app privacy improvements. Additionally, Apple introduced new features designed with privacy and security at their core, including Check In, NameDrop, and Live Voicemail. These new efforts are the latest manifestation of Apple’s deeply held belief that privacy is a fundamental human right and that good privacy is built on a foundation of strong security.
“Privacy is designed into every new Apple product and feature from the beginning,” said Craig Federighi, Apple’s senior vice president of Software Engineering. “We are focused on keeping our users in the driver’s seat when it comes to their data by continuing to provide industry-leading privacy features and the best data security in the world. This approach is evident in a number of features on our platforms, like the major updates to Safari Private Browsing, as well as the expansion of Lockdown Mode.”
Major Updates to Safari Private Browsing Safari introduced private browsing years before any other browser. This year, a significant update provides even greater protection against trackers as users browse the web and from people who might have access to their device. Advanced tracking and fingerprinting protections go even further to help prevent websites from using the latest techniques to track or identify a user’s device. Private Browsing now locks when not in use, allowing a user to keep tabs open even when stepping away from the device.
Photos Privacy Permission Improvements A new embedded Photos picker can help users share specific photos with apps while keeping the rest of their library private. When apps ask to access the user’s entire photo library, the user will be shown more information about what they’ll be sharing, along with occasional reminders of their choice.
Link Tracking Protection in Messages, Mail, and Safari Private Browsing Some websites add extra information to their URLs in order to track users across other websites. Now this information will be removed from the links users share in Messages and Mail, and the links will still work as expected. This information will also be removed from links in Safari Private Browsing.
App Privacy Improvements New tools give developers more information about the data practices of third-party software development kits (SDKs) they use in their apps, allowing them to provide even more accurate Privacy Nutrition Labels. These changes also improve the integrity of the software supply chain by supporting signatures for third-party SDKs to add another layer of protection against abuse.
Communication Safety Communication Safety, designed to warn children when receiving or sending photos in Messages that contain nudity, now covers video content in addition to still images. A new API lets developers integrate Communication Safety right into their apps. Additionally, the feature will now help keep kids safe when they’re sending and receiving an AirDrop, a FaceTime video message, and when using the Phone app to receive a Contact Poster and the Photos picker to choose content to send. All image and video processing for Communication Safety occurs on device, meaning neither Apple nor any third party gets access to the content. These warnings will be turned on for the child accounts in their Family Sharing plan, and can be disabled by the parent.
Sensitive Content Warning Sensitive Content Warning helps adult users avoid seeing unwanted nude images and videos when receiving them in Messages, an AirDrop, a FaceTime video message, and the Phone app when receiving a Contact Poster, all using the same privacy-preserving technology at the core of Communication Safety. The feature is optional and can be turned on by the user in Privacy & Security settings. As with Communication Safety, all image and video processing for Sensitive Content Warning occurs on device, meaning neither Apple nor any third party gets access to the content.
Passwords and Passkeys Updates For easier and more secure password and passkey sharing, users can create a group to share a set of passwords, and everyone in the group can add and edit passwords to keep them up to date. Since sharing is through iCloud Keychain, it is end-to-end encrypted. Additionally, one-time verification codes received in Mail will now automatically autofill in Safari, making it easy to securely log in without leaving the browser.
Lockdown Mode Lockdown Mode expands to provide even more protections for those who may be targeted by mercenary spyware because of who they are or what they do. New protections encompass safer wireless connectivity defaults, media handling, media sharing defaults, sandboxing, and network security optimizations. Turning on Lockdown Mode further hardens device defenses and strictly limits certain functionalities, sharply reducing the attack surface for those who need additional protections. Additionally, Lockdown Mode will be supported on watchOS.
These features will be coming in free software updates this fall.
Press Contacts
Apple Media Helpline
Images in this article
- VPN & Privacy
Ultimate guide to browser security: Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Edge, and Safari

As your main point of access to the World Wide Web, your browser is exposed to potential online attacks every time you use it. The browser is a great channel for hackers to get access to your personal data, to manipulate your connections, to get tracking software onto your computer, and even to access your computer directly.
Contents [ hide ]
Browser security overview
Network settings, security weaknesses in browsers, browser privacy mode, malicious extensions, security extensions, online protection, stay safe on the web.
As an entry point to your computer, your browser is constantly vulnerable to hacker attack. Hackers and the producers of malware pay close attention to the code that creates browser programs, and they also examine ways to manipulate the various programming languages that run in browsers in order to sneak malware onto your computer.
The producers of browsers are aware of these threats and research security weaknesses, trying to spot them before hackers do. In many cases, they only discover an exploit once a hacker has already launched a worm that uses it. However, browser producers regularly produce updates to their products that close off these loopholes.
The main security procedure that you can implement in your browser is to allow automatic updates. This will keep you ahead in the cat and mouse game against hackers.
Browser security falls into two main areas:
- Protection against browser weaknesses that can let in malware
- Protection against snoopers that covertly collect information about you and your online activity
In order to address the issue of browser weaknesses, you can easily close off the entry points that hackers use by altering the settings of your browser.
Snooper attacks are harder to deal with because these can be implemented outside of your browser, either on the internet or through the network procedures of your computer. With just a few network settings adjustments, a hacker can hijack all of the traffic that passes in and out of your browser and control all of your web access.
To reduce the amount of information stored in your browser, we’ll show you how to remove browser history, cached data, and cookies. Each browser contains a settings menu that allows you to clean out this information. However, you can prevent this data from accumulating in your browser by using its privacy mode.
The next sections of this guide will show you:
- How to use the privacy modes of your browser
- How to remove data stored in your browser.
- How to check your network settings to make sure that your internet traffic is not being hijacked,
- How to remove the capabilities of your browser to play JavaScript programs, Flash files, or display PDFs — both Flash and PDF files have become conduits used by hackers to sneak worms onto your computer.
Although the network settings on your device do not pertain directly to browser security, some browser behavior is set by routing preferences that are dictated in the network settings of your operating system. These settings can sometimes be altered by viruses, Trojans, and worms. Even if your antimalware system detects the operation of this malware, once the network settings of your device have been altered the damage those viruses can do to your computer will still continue to operate.
Traffic redirection gives hackers the option of sending fake copies of well-known websites that exist to harvest your login credentials, force advertising on you, or sneak extra programming code onto your computer.
The two key settings that you need to address here are the proxy settings and the DNS settings.
Proxy settings
A proxy server mediates all of your internet traffic. Ordinarily, you should not have a proxy nominated in your network settings. If one is there, then all of your traffic on the web is being channeled through that server. The owner of the proxy server can block requests for web pages, or send back altered pages that look like the pages that you want but actually are fakes controlled by a hacker. If your proxy settings have been altered, your internet actions will be monitored and manipulated until you remove this setting.
DNS settings
A DNS server translates website names to the actual internet address of the server that hosts that website. When you enter the address for a web page in your browser, the first step in accessing that page is to lookup the internet address for that site. The root of a web address is called a “domain.” For example, “comparitech.com” is the domain of this web page. “DNS” stands both for “domain name system,” which is the network that provides internet address for given domains, and for “domain name server,” which is the computer that your browser will refer to when looking for the IP address of the page you want to see.
Ordinarily, the DNS server that you access is dictated by your internet service provider.
However, that preference can be overridden in the network settings of your computer. If a virus alters the DNS settings of your computer, a hacker-owned DNS server can return a different address. So, you may type in yahoo.com, but instead of getting the real Yahoo home page, the hacker DNS returns the address of a copy of that page held on the hacker’s server. If you then log into that fake page, you will just be passing your login credentials to the hacker. When you are looking at the fake page, your browser will show the web address of the real page, so it is very difficult to spot DNS hijacking.
Check network settings on Windows
In order to prevent both proxy and DNS hijacking, you need to make a point of visiting the network settings of your device to check that you haven’t been hit. If you have, all you need to do to restore your browser privacy is delete the values in your proxy and DNS settings.
The DNS settings and proxy settings on Windows are set in two different places. Firefox has its own proxy settings system.
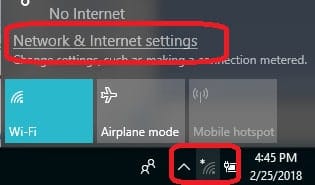
- Click on the network symbol in the system tray. Select Network and Internet settings .
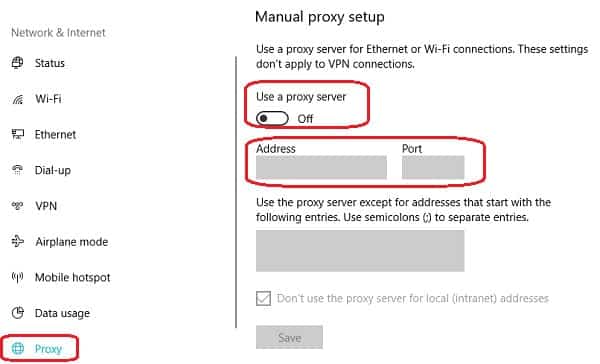
- In the Network Settings screen, click on Proxy in the left-hand menu.
- Scroll down to the Manual proxy setup section. Make sure that the Address and Port fields are blank and that the Use a proxy server slider is set to Off .
- Click on Status in the left-hand menu and then select Change Adapter Options . This will open a folder with a list of all the connection types available to you.
- Click on the connection you use the most. For example, Wi-Fi . If you use several different connection types you will have to perform the following sets for each.
- Right-click on the connection definition and select Properties from the context menu.
- In the Properties screen, select the Internet Protocol Version 4 item and click on the Properties button.
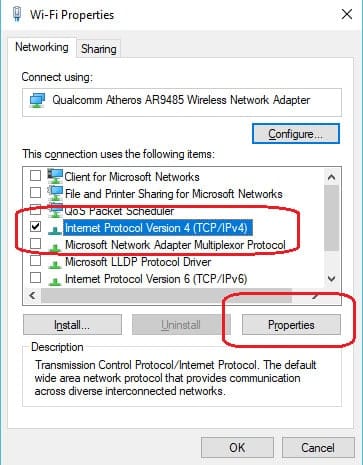
- In the next screen, make sure that the two DNS address fields at the bottom of the window are blank. The Obtain DNS server address automatically radio button should be active.
- Click OK to close down the Internet Properties window and then press OK in the WiFi Properties window to close it.
If you use Firefox, you need to go into the settings of that browser to make sure than there hasn’t been a proxy server address entered there.
- Open Firefox and click on the Hamburger menu symbol at the end of the address bar. Select Options from the drop-down menu.
- Scroll to the bottom of the Options page to the Network Proxy section. Click on the Settings button.
- In the Connection Settings window, make sure that the No proxy radio button is active.
- Click on OK to close the Connection Settings window.

Check network settings on macOS
In macOS the DNS and proxy settings are organized per connection type, so if you use both a cable connection and wifi, you will have to follow these instructions for each type.
- Select System Preferences from the dock and click on the Network pane.
- Select the network type and click on the Advanced button to get the Advance Network window.
- Click on the DNS tab. Make sure all of the DNS entries are blank. Highlight each entry and press the minus sign at the bottom left of the window.
- Click on the Proxies tab in the network type screen. Uncheck all protocols in the left-hand list. Click Apply at the bottom right of the Network settings window to save your changes.
Check network settings on routers
Unfortunately, there are many router manufacturers and they all have different user interfaces for their software, so here I will show you an example of one router’s console and you will need to explore the user manual of your own router to find the same screens.
If you can’t find the manual, there are some basic tricks that you can try to get into your router’s settings. Open the Task Manager on your computer and click on the Performance tab. Scroll down to the WiFi section in the left-hand menu. Note down the IPv4 address shown in the main screen beneath the performance monitor.
Enter that address in your browser. However, change the last number to 1. So if your address is shown as 192.168.0.12, enter 192.168.0.1 in the address field of your browser. This should get you into the router’s console.
If you don’t know the username and password for your router, try user/user, system/admin admin/password, admin/admin, or system/password. In some cases you can even leave the password field blank.
If you don’t have the manual, you will need to explore the menu system of your router to get to the right screen. However, you need to look for the Network Configuration page.
If your router has been hijacked by a virus, that malware could also report back to a hacker when you modify the router’s settings. Before making any changes, reset the router to its factory settings to wipe out any malware.
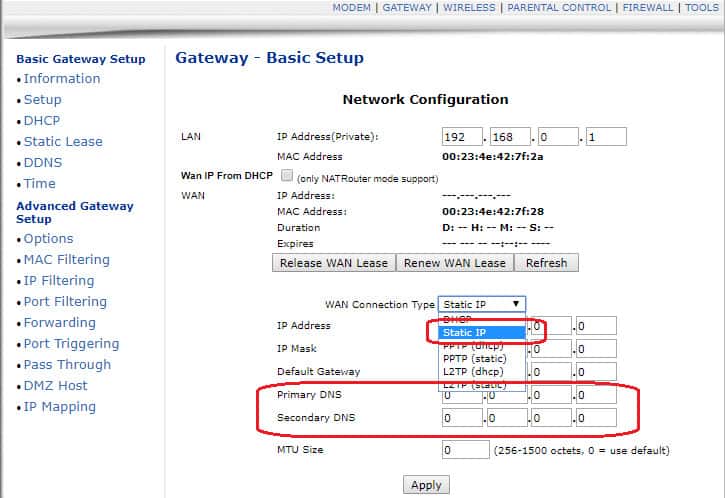
The DNS configuration is not available for DHCP settings. You have to switch to Static IP to change the DNS settings. So, if you arrive at the network settings and see that it is classified as DHCP, then you are safe. If your settings say Static IP, you need to look at the Primary DNS and Secondary DNS fields. If these have values, you need to set them to 0.0.0.0.
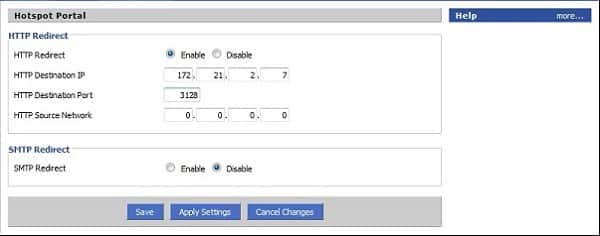
Look for the Hotspot Portal section of your router’s control panel. You need to disable HTTP redirects. If there is no Enable/Disable option, set the Destination IP to 0.0.0.0 and delete the port number. Press the Save button once you have finished.
Check network settings on Android
On Android, the proxy setting relates to each network that you connect to, so you have to follow these instructions for each.
- Swipe down from the top of the screen to expand the Settings menu. Click on WiFi . Tap on More Settings at the bottom of the list of available networks.
- Long press on the network that you want to check the settings for. Select Modify Network in the popup that appears.
- Tap on Advanced options in the next screen and then tap on Proxy . Click on Manual to see whether any proxy server has been set up for that connection.
- Check the Proxy hostname and Proxy port fields. If they have proxy.example.com and 8080 in them, you don’t need to do anything. If there are any other values in these fields, delete them.
- Check the IP settings field. This should be DHCP . You cannot specify a DNS server with this setting. If this field says Static , scroll down to the fields DNS1 and DNS2 . If these fields have the values 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 you don’t need to worry. If there are any other values in those fields, delete them. Change the IP settings back from Static to DHCP .
- Tap Save at the bottom of the Advanced Options screen.
Check network settings on iOS
As with Android, the iOS network settings for proxy and DNS servers apply to the network, so the network you want to check needs to be in range and you have to repeat these instructions for every network that you connect to.
- From the Home screen, tap on Settings . Select Wi-Fi from the Settings screen.
- In the Wi-Fi screen click on the right-arrow next to the name of the network that you want to check.
- In the network settings screen, look for the DNS field. This should read 8.8.8.8 . If there is any other value in that field, tap on it and delete it.
- Scroll down in the network settings screen to the section. Make sure that the Off button is active.
There are four basic problems with browsers that you can fix very easily by changing your browser settings:
- SSL security weaknesses
- Flash video cloaking for viruses
- PDF cloaking for viruses
- Malicious popups
In this section of the browser security guide, we’ll first explain those weaknesses and then show you how to secure your browser.
De-list SSL compatibility to use TLS
SSL was invented by Netscape Corporation as part of HTTPS. HTTPS is the Hypertext Transfer Protocol/Secure and you know that it is in operation on your web transfers when you see “https://” in front of a web page’s address. This system has been very successful on the internet. It includes server authentication procedures and encrypts all contents of internet communications. SSL stands for the Secure Socket Layer. This created ways to check whether the server that a browser connects to really is that computer and it makes it difficult for interceptors of internet traffic to pose as the intended destination of a connection.
The Secure Socket Layer was discovered to have a security flaw and so it was replaced with Transport Layer Security. This was because it was possible with SSL to provide a fake authentication certificate that changed the encryption key that the browser should use to secure all data sent over the connection. If a hacker can dictate the security key, he will know how to decrypt all subsequent communications.
Unfortunately, TLS was created with backwards compatibility to SSL. So if you use TLS and contact a site that is still using SSL, your browser will rollback to SSL and the old security exploit will be exposed. You can close down that weakness by de-listing SSL compatibility from your browser. You also need to prevent your browser from using the first version of TLS to block off the rollback to SSL.
Block Flash and PDF files from loading in your browser
The Flash video standard and the PDF file format are both products of Adobe Systems. Unfortunately, both encoding formats include programming constructs that can provide cover for virus invasion. So, you need to block both Flash and PDF files from loading in your browser.
Block popups
Popups are more of an annoyance than a security weakness. However, they can be used to trap you into a site, add malware to your computer, and can even be deployed recursively to overload your computer. It is better to block popups .
So, let’s tighten up the security of your browser by preventing SSL backwards compatibility, blocking Flash and popups, stopping PDFs from opening in your browser, and stripping out JavaScript.
The menus for closing off some of the security weaknesses are exactly the same for Internet Explorer and Chrome, you just arrive at that screen by a different route in each case. However, if you have closed off these weaknesses in Chrome, then you already have done all the work to protect Internet Explorer and vice versa.
How to secure Chrome
- Click on the three dots symbol at the end of the address bar. In the drop-down menu select Settings . This will open a new tab.
- Scroll down in the Settings screen to the bottom and click on Advanced . The screen will extend. Scroll down to find the System section and click on Open proxy settings . This will open the Internet Properties window.
- Click on the Advanced tab and scroll down in the Settings window. Make sure that Use SSL 3.0 and Use TLS 1.0 are de-selected.
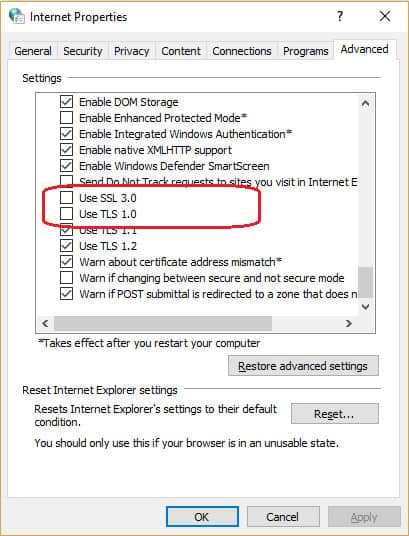
- Click on OK in the Internet Properties window to save the changes.
- Return to the Advanced Settings screen in Google Chrome and look for the Privacy and security section. Click on the arrow next to Content settings .
- Click on the arrow next to JavaScript and in the next screen, click on the slider to turn it to Blocked . Click on the back arrow at the top of the JavaScript screen to return to Content Settings.
- Click on the arrow next to Flash — this is the next entry down from the JavaScript setting. In the next screen, click on the slider so the message next to it reads Block sites from running Flash . Click on the back arrow at the top of the screen to get back to the Content Settings list.
- Scroll down to Popups and click on the arrow in that line. Click on the slider so that you see that popups are blocked. Click on the back arrow at the top of the screen.
- Scroll down to PDF documents , which is the next to last entry in the Content Settings list. Click on the arrow on that line. Click on the slider so that the message next to it reads Download PDF files instead of automatically opening them in Chrome .
RELATED : Best VPNs for Chrome
How to secure Firefox
Make sure that you have Firefox version 57 or above. This newer version of Firefox automatically blocks PDFs from opening in the browser. In order to prevent Flash from running in the web pages that you visit with Firefox, you should install the Flashblock add-on.
To block of the SSL backwards compatibility exploit, follow these steps.
- Enter about:config in the address field of the browser. You will be shown a warning about proceeding. Click on I accept the risk .
- In the Configuration screen, enter security.tls in the Search field. Look for the entry for security.tls.version.min .
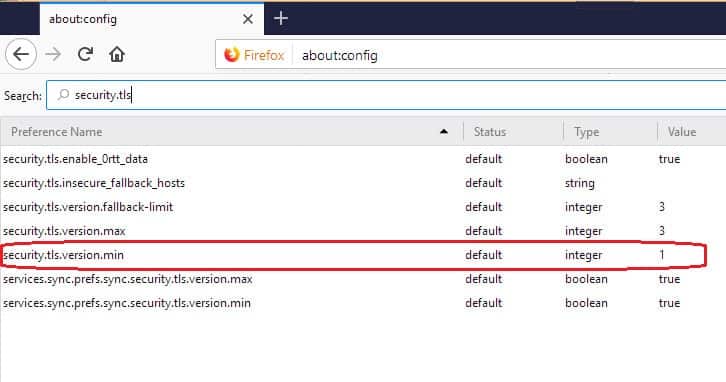
- Double click on the line and enter 2 in the popup box for the value in this field. Click OK to close the popup.
You can block popups through the browser options system:
- Click on the Hamburger menu at the end of the address bar. Select Options from the drop-down menu.
- Select Privacy & Security in the left-hand menu. Scroll down to the Permissions section and check the box for Block pop-up windows .
How to secure Internet Explorer
You remove backwards compatibility for SSL in Internet Explorer with the same screen as that used for Chrome. So, if you have already closed off this exploit for Chrome, you don’t have to do it again. If you don’t have Chrome, follow these instructions.
- In Internet Explorer, click on the cog symbol at the end of the address bar. Click on Internet Options in the drop-down menu. This will open a settings window.
- Click on the Advanced tab and scroll down through the list of settings.
- Uncheck Use TLS 1.0 and Use SSL 3.0 . Click OK to close the window.
To block Flash in Internet Explorer you need to control the ActiveX settings.
- Click on the cog symbol at the end of the address bar in the Internet Explorer browser.
- Click on Safety in the drop-down menu. If there is a check mark next to ActiveX Filtering in the Safety submenu, this setting is already blocked. If not, click on this line in the menu to activate it.
To prevent PDF files from loading in the browser, follow these steps.
- In Internet Explorer, open the cog menu and select Manage Add-ons . This will open the Add-ons Manager screen.
- Select Toolbars and Extensions for the Add-on Type and pick All add-ons from the Show drop-down list.
- Click on then entry for Adobe PDF reader in the main panel of the screen.
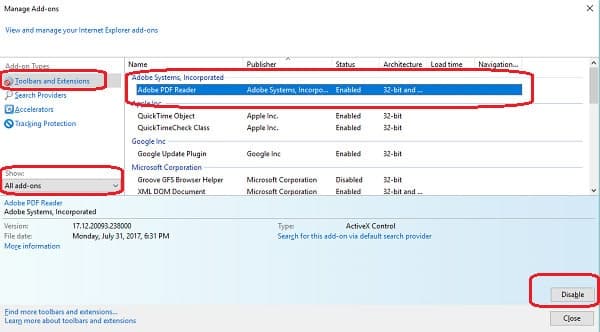
- Click on the Disable button at the bottom of the screen. Click on Close to get out of the Add-ons Manager.
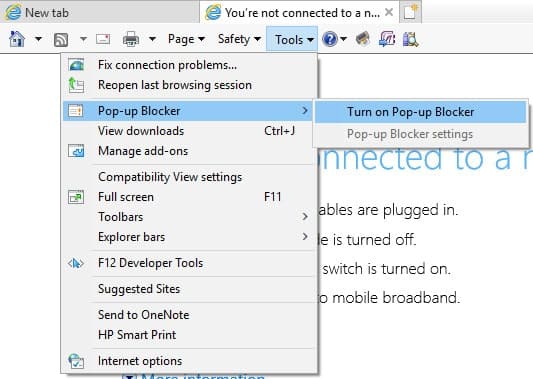
To block popups, you need to look for the Tools menu.
- Click on Tools in the utilities menu at the top of the open tab in Internet Explorer.
- Select Pop-up Blocker in the drop-down menu and then click on Turn on Pop-up blocker .
How to secure Microsoft Edge
You don’t need to worry about SSL backward compatibility in Microsoft Edge, because that option does not exist in this new browser. There is also no option to prevent PDFs from opening in the Microsoft Edge browser.
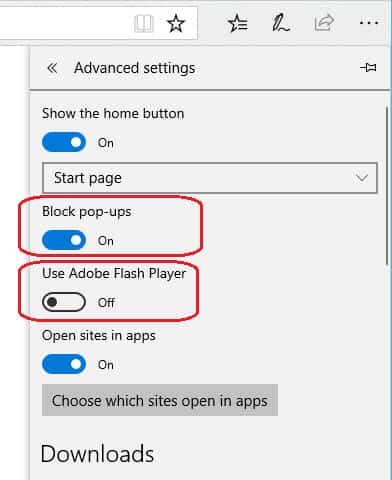
To stop pop-ups and block Flash in Edge, follow these instructions:
- Click on the three dots symbol at the end of the address bar. Scroll to the bottom of the drop-down menu and click on Advanced Settings .
- In the Advanced Settings menu, set the Block pop-ups slider to On and the Use Adobe Flash Player slider to Off .
How to secure Safari
Safari doesn’t include backwards compatibility for SSL, so you don’t need to do anything about that security weakness. However, here are some actions you can take to make your Safari browser more secure.
- Click on Safari in the top menu bar and select Preferences .
- Select Security and then click on Manage Website Settings .
- Select Adobe Flash Player and choose Block from the When visiting other websites drop-down list.
- Click on the General tab in Preferences. Uncheck Open “safe” files after downloading .
- Click on the Advanced tab in Preferences. Under Proxies , click on Change Settings . This will open a new window.
- Uncheck all the protocol entries. Click OK to exit the Proxies window.
RELATED : Best VPNs for Safari
Each browser type has a different name for its privacy mode. However, in each case, this mode performs the same functions. It will delete your private data from storage together with passwords, cached page information, cookies, and browser history once you close the browser window. However, in order to take full advantage of this feature, you must remember to periodically quit the browser.
Here is how to invoke each browser type in privacy mode:
Microsoft Edge privacy mode
Right-click on the program icon and select New InPrivate window from the context menu.
If you already have Microsoft Edge open, click on the three dots symbol at the end of the address bar to get the browser menu. Click on New InPrivate window . You can also open an InPrivate window by pressing Control-Shift-P together.
Internet Explorer privacy mode
Right-click on the program icon and select Start InPrivate browsing from the context menu.
If you already have an IE browser wind open, Press Control-Shift-P together to open an InPrivate browser windows. Alternatively, click on the cog symbol at the end of the address bar to get the browser menu. Select Safety and then click on InPrivate Browsing from the Safety submenu.
Google Chrome privacy mode
The privacy mode of Chrome is called Incognito. If you have Chrome pinned to your taskbar, right-click on the icon and select New incognito window from the context menu.
If you already have a regular Chrome window open, press Control-Shift-N together to open a new incognito window. You can open an incognito window through the menu system: click on the three dots menu symbol and select New incognito window from the menu.
Mozilla Firefox privacy mode
The privacy mode in Firefox is termed a “private window.” If you have Firefox pinned to your taskbar, right-click on the icon and select New private window from the context menu.
If you have a regular Firefox session open already, you can open a private window by pressing Control-Shift-P together. You can also open a private session through the browser menu. Click on the hamburger symbol at the end of the address bar and select New Private Window from the menu.
Safari privacy mode
You can set the preferences of Safari so that it always opens in Private Browsing mode. To do this, click on Safari in the top menu bar and select Preferences . Under the General tab, click on Safari opens with and select A new private window .
If you already have a Safari session open, Click on Safari in the top menu bar and then select Private Browsing from the drop-down menu.
Malicious browser extensions are very difficult to spot. As we grow accustomed to smartphone apps telling us that they want access to data sources such as phone contact lists, we become desensitized to all the requests to access the operating system and data held in other apps. This has become a common occurrence in bona fide browser extensions and, as Zach Miller of online security firm, Cyberpoint explains , people tend to continue with the installation of a browser extension even when the browser points out the security risks.
Browser extensions have a surprising amount of power and control over a browser and the content that is displayed. An extension can inject scripts into rendered pages, create, redirect, or block web requests, or steal information that is entered into online forms.
-Zach Miller, Cyberpoint.
The system and services access that many legitimate browser extensions require really should make you stop and think before adding any extra functionality to your browser, no matter how useful and respectable it may seem.
Some malware uses browser extension functionality to hijack browsers. In January 2018, antimalware company, Malwarebytes reported on a clickjacking worm that directs victims to YouTube pages against their will. This malware extension is called Rogue.ForcedExtension and the Chrome and Firefox extension that it operates through is called Tiempo en Colombia en Vivo. You may think that you would be safe from this malware simply by choosing not to install that extension. However, none of the victims of this malware knowingly chose the extension. To this date, it is not known which action gets this extension installed.
Worse still, malicious extensions are able to defend themselves from removal. They can block access to the extensions and add-on management pages and redirect you away from searches in how to combat these forms of malware. Basically, once malware extensions get onto your browser, they are not going to let go.
Some malware extensions advertise themselves with the same name as legitimate utilities. Many of these fake extensions even manage to make it onto the Google Chrome Web Store.
Regular and recommended extensions can get hijacked. You might read good reviews of an extension and decide to install it. However, on installation you will be warned that the extension will be able to read and change your data on the web, read and change your browser history, modify text in your clipboard, and change the settings of your browser.
Although you may have trusted that company at that point, that trust should not be ongoing.
Chrome and other browsers will automatically update the extensions you have installed and they remain active without you knowing that the program has changed.
If the permissions required by the extension have changed with the new update, then the browser will disable that extension until you have approved the permission changes. The default requirements for system access that extensions regularly ask from you are more than enough for a hacker to get malware onto your system.
This makes extension updates a really easy route for hackers — not only do they piggyback on the large user base of popular extensions, but they only require one file to be uploaded to a server in order to proliferate millions of computers and phones. An example of this phenomenon occurred with an update to the Web Developer extension in August 2017 . A hacker managed to get his own version with malware onto the update server, thus downloading his malicious software onto more than a million computers.
Another danger with useful browser extensions is that they are often developed by small companies or individuals that make no money out of them. Ask yourself, how often do you pay for a browser extension? The low income that developers derive from these facilities makes them vulnerable to offers to purchase the system.
Hackers and darkside marketers generate a lot of income from ransomware, DDoS-for-hire attacks, and pay-per-click marketing scams. It makes sense for them to reinvest some of that revenue into buying access to millions of computers for very little money. They only need to update that excellent utility by inserting a little bit of extra code, and their scam is installed automatically as a legitimate browser extension update. This is exactly what happened when the browser extension Particle for YouTube was sold off in July 2017.
Given that extensions are ongoing security weaknesses in your browser, it is better to practice caution and try to avoid adding them.
After you just read advice not to install browser extensions, it may seem odd that this next section gives recommendations on extensions you should install. However, these extensions will help you improve the security of your browser, rather than impair it.
Although it is possible to block tracking software in your browser settings, these options are not very comprehensive. It is better to install extensions in order to fully block tracking codes. Many tracker blocking extensions also block adverts. Standalone ad blockers are also popular with web surfers.
Blocking JavaScript is also a good idea. Although there is the option to prevent JavaScript from running in Chrome, the implementation of JavaScript blockers as extensions generally works better.
Other security extensions listed in this section include systems to generate passwords for you so you don’t make the mistake of using the same password for all of the sites that you visit. You can also read here about extensions that will check the security of the pages that you visit .
HTTPS enforcement
As explained above, the HTTPS schema protects your data during transfer. However, not all sites use HTTPS and those that still use HTTP don’t offer very good security.

Browser Cleaners
It is possible to delete all cookies and temporary storage from all browser types. If you use the privacy modes that the browsers offer, then you don’t need to delve into the settings of your browser to clean out all of that data. If you are not that keen on the idea of using privacy mode, you can install a browser cleaner to get rid of all of that hidden information for you. Even if you do use privacy modes, not all records of your site visits are deleted when you close the browser.
Here is a selection of data cleaners.

JavaScript Blockers
Web pages are written in a code that is called the Hypertext Markup Language, or HTML for short. HTML only contains instructions for formatting text. It is not a programming language. However, it is possible to embed scripts in HTML code, and scripts include programming constructs. JavaScript was invented to enable small programs in web pages .
Those little bits of programming code are all that a hacker needs in order to download a gateway program on your computer or manipulate the operating system in such a way that rootkit programs can get in and control the functions of your operating system. You need to block JavaScript from running in your browser.

Password protection
One of the easiest ways that hackers can get into your email account or other online services is to just try some of the standard weak passwords, which include “1234567890,” qwerty,” and “password.” You not only stand to compromise your privacy to hackers through weak passwords, but these are also a gift to stalkers and former friends.
You need to use more complex passwords for each of the sites that you visit and you need to make the password for each site unique . This task can be difficult to manage. You will find it difficult to remember the password for each site and keeping all of your passwords on a piece of paper in your computer or phone case is another bad idea.
Password vaults (also called password managers ) solve the problem of knowing what constitutes a strong password and they also enable you to generate a different password for each site that you use. A password vault browser extension will store all of your passwords , so you only need to remember the master password for the vault. When you go to a site that has a password stored in the vault, the extension will fill in that field for you. Here are some of the best password vaults available right now.

There is a free version of Blur that doesn’t include the above two services, but it still creates a very comprehensive online privacy service. There is a password manager module in blur that is every bit as complete as the service offered by LastPass. The utility also includes a browser fingerprinting prevention system. Tracking by social media buttons is blocked by Blur and the system also includes a tracker and ad blocker.
You can get an email address from blur to use when you sign up for online services. The mail sent through to that account is forwarded on to your regular email address. This ensures that you are very difficult to trace online.
Blur is available in both free and paid version for Internet Explorer, Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.

Tracker blockers
Retargeting has become a major marketing tool on the web. This method puts a little marker on your computer in the form of a cookie when you visit a website. Trackers usually go hand in hand with targeted advertising.
If you visit a website that participates in retargeting, you will notice that many of the subsequent sites that you visit display ads for that site or service. This is enabled by the website checking for one of its advertising service’s cookies on your computer before it loads content into the advertising panels on the page. Google is one of the biggest operators of retargeting advertising and it has developed the method into a very lucrative income stream.
Social media buttons and website analytics tools also practice tracking.
Although some argue that trackers enable people to see ads that they will find useful, rather than just promotions for random services, this method creates a privacy issue and the secretive way that retargeting is implemented angers many. Although businesses may claim that the method is only used for targeting adverts and no information about visitors is collated, marketers are notorious for monitoring the performance of ad campaigns and use trackers to gather data on your internet activities as much as they use them to deliver adverts.
The technology behind retargeting provides an excellent avenue for snoopers and data gatherers. The selective delivery of ads can be hijacked by browser viruses to earn hackers money and they can even be used to redirect your browser to show substitute pages rather than the sites that you thought you were visiting. All in all, it is better to block tracking libraries.
All the major browsers now include settings to allow you to enable tracker blocking or to send a “do not track me” request. However, knowing that retargeting is a major source of revenue for very large corporations, those browser developers didn’t really make their blocking systems completely foolproof. For example, Apple made its tracker blocker in Safari so that it allowed the trackers, but deletes them after 24 hours if you don’t visit any page on the same domain within that period. Rather than blocking tracking, this methodology gives a supreme advantage to the two biggest retargeting systems that are run by Google and Facebook.
Tracker blocking is better when it is implemented by extensions rather than by relying on the settings in your browser.

Ad blockers
As explained above, retargeting, with the use of trackers, has become a major technique for advertisement management used on the web. The tracker blockers will prevent retargeting agencies from loading the adverts of their clients in your browser because the delivery processes won’t find any of those essential tracking cookies on your computer.
Tracker blockers are often advertised as tracker and ad blockers. However, they usually focus on blocking ads that use tracker codes and that doesn’t cover all online advertising. It is better to use both a tracker blocker and an ad blocker.

Security checkers
If you can live without all of the above extensions then just focus your attention on this category.
The extensions in this category will examine the contents of the web pages that you visit and give you reports on the trackers and other privacy and security weaknesses that each page includes. In the case of CyberSec and Secure.link, the extension will prevent your browser from encountering dangerous web pages.

If you are not a web programming or networking expert, you may find these details a little overwhelming. However, once you become familiar with the report format that is displayed in the extension’s drop-down panel, you will learn to graze the information made available to focus on the important bits.

The extension also monitors for botnet activity. Even if your computer has already been infected, CyberSec will block your communications with the Command and Control mechanism that launches attacks on other computers. This extension will also block trackers, pop-ups, ads and videos. The NordVPN browser extension is available for Chrome and Firefox.

The secure.link system is also integrated into the Windscribe VPN browser extension where it give you the option to generate a safety report on every page that you visit on the web.
This extension also includes an ad blocker, a cookie cleaner, and a tracker blocker. Another feature will scramble your browser’s user agent information to prevent browser fingerprinting and you can also elect to let the extension strip out social media buttons. The Windscribe browser extension is available for Chrome and Firefox.
As an entry point to the computer from the internet, your browser is one of the most vulnerable pieces of software that you have on your computer.You canblock off the avenue of attack into your computer by using an online service called a VPN . You will probably remember that there have already been three VPN services mentioned in this guide: TunnelBear, Windscribe, and NordVPN. All three services can be operated through an app or through a browser extension.
A VPN establishes an encrypted link between your computer and the VPN server. Going out from the VPN, all of your traffic has that server’s internet address on it and not yours. The VPN software on your device takes control of your network card, so no internet communication can get into your computer unless it first passes through the VPN server. This adds massive security to your browser as well as other apps that use the internet.
Being very selective about the extensions you install is probably the best way to keep your browser secure. Make regular checks on the proxy and DNS server settings of your browser to ensure that your internet traffic is not being hijacked. Also, make sure that your browser updates automatically to keep up with the latest version and install a good antivirus program .
Now you are aware of the potential threats to your browser, you will be better equipped to prevent intrusion and modification. Enjoy the web, but be cautious about what you download and what you install.
1 Comment Leave a comment
Leave a reply cancel reply.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Roundup - best VPNs for
Privacy alert: websites you visit can find out who you are.
The following information is available to any site you visit:
Your IP Address:
Your Location:
Your Internet Provider:
This information can be used to target ads and monitor your internet usage.
Using a VPN will hide these details and protect your privacy.
We recommend using NordVPN - #1 of 72 VPNs in our tests. It offers outstanding privacy features and is currently available at a discounted rate.
How to remove malware from Safari browser
This guide includes comprehensive information on malicious code targeting Safari and provides effective techniques to remove malware from Safari browser.
The design, user-friendliness, speed, energy efficiency and other pros of the Safari browser are out of the question. Apple devices go equipped with this remarkable Internet navigation tool by default, and the overwhelming majority of Mac and iOS users stay dedicated to it as their primary web surfing software. According to a report by the StatCounter firm, this browser’s overall market share as of January 2017 amounted to 14.54%. People in the cybercrime underground, obviously, stay on top of these statistics as well. These sleazeballs know what’s popular and focus on firing their attacks against digital environments used by many. Furthermore, it turns out that installing toxic apps on Safari without admin’s consent isn’t nearly as tough an objective as compromising other components of Mac OS X architecture. With all the pros of Safari in place, it is currently the weakest link in the overall protection setup of the average Mac.
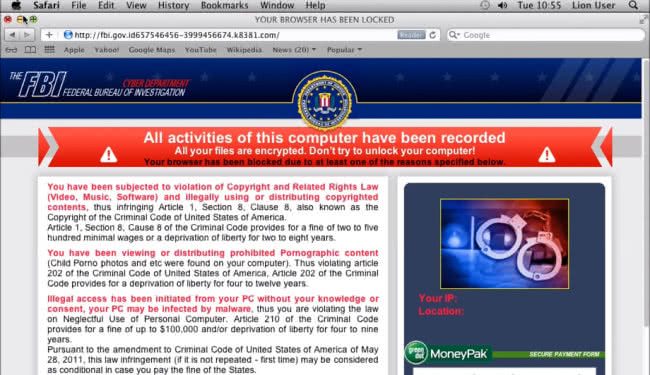
It wouldn’t be correct to classify the malware targeting Safari as a top-notch cyber adversary. Most of the time, these are low-impact hijackers that replace the homepage, new tab and search preferences with certain predefined values. Some of these infections engage in phishing and suchlike types of social engineering, so they are manipulative and annoying rather than dangerous. An example is the nefarious FBI virus that impersonates the apropos law enforcement agency and persistently makes victims end up on a deceptive warning page (see screen capture above). These rogue sites are nothing but bluff, stating that the user has violated the Copyright and Related Rights Law or committed some other computer-related felony. The goal of this hoax is to make victims pay a fee for their purported wrongdoings. Obviously, the correct way to go about this type of attack is to get rid of the Safari browser hijacker, which isn’t difficult to do at all.
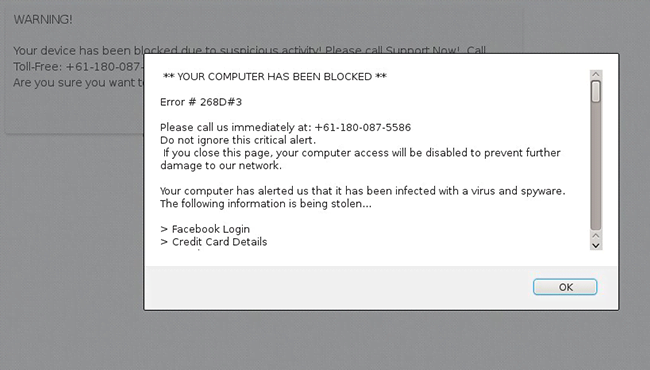
Some types of Safari hijackers reach the brainwashing effect in a somewhat different way. They cause recurrent redirecting of web traffic to misleading sites that report critical system errors or spyware. Popups triggered on such pages may instruct victims to call “tech support” for assistance, with the telephone number being indicated there. If an unsuspecting user actually dials the number, an impostor on the other end will do their best to make the victim pay for the spoof troubleshooting services.Whereas the modus operandi of these perpetrating programs may vary, the common denominator is a piece of malware that attacks the browser and wreaks havoc with it.
Adware is another widespread sub-type of Safari threats. These are intrusive plugins that display redundant ads on web pages visited by a victim. Essentially, adware generates an inconspicuous virtual layer over the original content of a site. This layer may contain arbitrary elements, and it’s up to the attackers what those elements will be. The infected user will encounter a slew of deals, coupons, freebies, comparison shopping boxes and banners wherever they go on the Internet. Search engine results will typically also contain ads that shouldn’t be there. To top it off, adware can trigger interstitial advertisements assuming the shape of separate browser windows. In-text ads pose one more side effect of the activity of these PUPs (potentially unwanted programs).
To handle the aftermath of any malware attack on Safari, removing the troublemaking app, plugin or script is a must. The ad injection instances described above are isolated to a specific machine and have nothing to do with visited websites, so the issues won’t vanish until virus cleanup is performed on the Mac. The same applies to browser hijackers. The sections below cover the entirety of tips to get rid of Safari malware for good.
Remove malware from Safari manually
The starting point for eliminating malicious activity in Safari is to uninstall the offending extension or plugin. This route, however, only works for low-impact browser malware that’s displayed on the list of add-ons and isn’t too persistent to be trashed in the regular way. Anyway, try the steps below first.
1. Uninstall malicious extension in Safari
• Go to Safari menu and select Preferences on the drop-down list
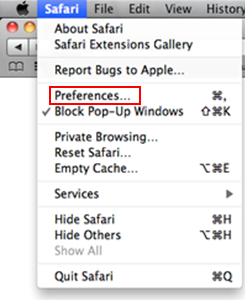
• Click on the Extensions tab on Safari Preferences screen. Scroll down the installed extensions list in the left-hand section of the interface. Select the one that’s causing trouble and hit the Uninstall button as shown below
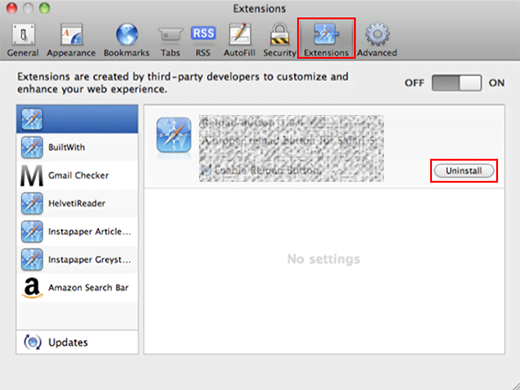
• While on the same screen, select the General tab. Choose your preferred search provider and define the right Safari homepage
• Save the changes and restart Safari. Check whether the issue has been fixed. If so, you’re now good to go. If the problem perseveres, proceed to the next step to handle the malware in a more thoroughgoing way
2. Reset Safari
• Open the browser and go to Safari menu . Select Reset Safari in the drop-down list
• Make sure all the boxes are ticked on the interface and hit Reset
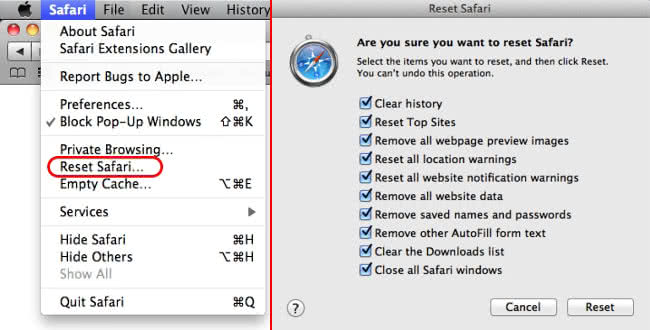

Get rid of malware from Safari using Combo Cleaner automatic removal tool
The Mac maintenance and security app called Combo Cleaner is a one-stop tool to detect and remove malware virus. This technique has substantial benefits over manual cleanup, because the utility gets hourly virus definition updates and can accurately spot even the newest Mac infections.
Furthermore, the automatic solution will find the core files of the malware deep down the system structure, which might otherwise be a challenge to locate. Here’s a walkthrough to sort out the malware issue using Combo Cleaner:
Download Combo Cleaner
By downloading any applications recommended on this website you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy . The free scanner checks whether your Mac is infected. To get rid of malware, you need to purchase the Premium version of Combo Cleaner.
- Open the app from your Launchpad and let it run an update of the malware signature database to make sure it can identify the latest threats.
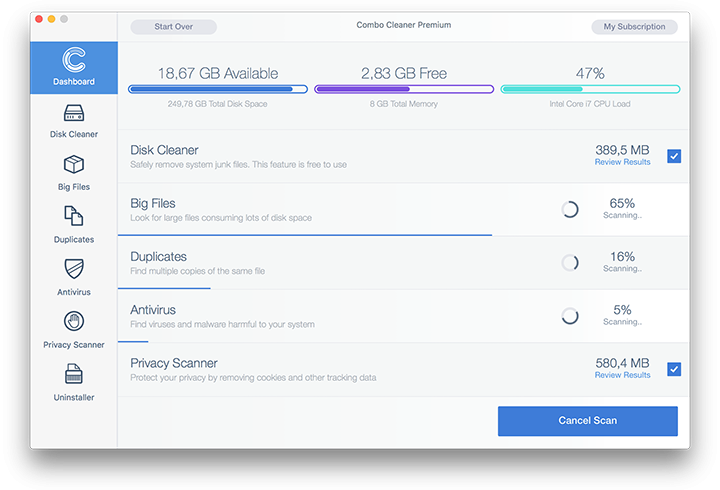
- Once you have made doubly sure that the malicious app is uninstalled, the browser-level troubleshooting might still be on your to-do list. If your preferred browser is affected, resort to the previous section of this tutorial to revert to hassle-free web surfing.
Was this article helpful? Please, rate this.
How to remove iWorm trojan virus from Mac
How to remove xagent mac malware, authentication required.
You must log in to post a comment.
'ZDNET Recommends': What exactly does it mean?
ZDNET's recommendations are based on many hours of testing, research, and comparison shopping. We gather data from the best available sources, including vendor and retailer listings as well as other relevant and independent reviews sites. And we pore over customer reviews to find out what matters to real people who already own and use the products and services we’re assessing.
When you click through from our site to a retailer and buy a product or service, we may earn affiliate commissions. This helps support our work, but does not affect what we cover or how, and it does not affect the price you pay. Neither ZDNET nor the author are compensated for these independent reviews. Indeed, we follow strict guidelines that ensure our editorial content is never influenced by advertisers.
ZDNET's editorial team writes on behalf of you, our reader. Our goal is to deliver the most accurate information and the most knowledgeable advice possible in order to help you make smarter buying decisions on tech gear and a wide array of products and services. Our editors thoroughly review and fact-check every article to ensure that our content meets the highest standards. If we have made an error or published misleading information, we will correct or clarify the article. If you see inaccuracies in our content, please report the mistake via this form .
The best secure browsers to protect your privacy online in 2024

Web browsers have become flooded with ad-sponsored content, making browsers a key battleground for end-user privacy. While Chrome is the most widely used browser in the world, there are alternative browsers and ways to improve your security available to help you stay anonymous online.
Data is one of today's key ingredients for generating revenue. Online advertising companies can use web browsing histories to fingerprint individual browsers over time, creating shadow user profiles to reveal information including a user's interests, product searches, and more -- which can lead to targeted advertising. When you look for a privacy-focused browser, you will want to investigate how advertising trackers and cookies are managed, whether or not search histories are stored or shared, and whether or not the browser developer has a transparent privacy policy in place.
Also: The best VPN services (and why you need one to protect your privacy)
What is the best secure browser for privacy in 2024?
ZDNET experts have kept a finger on the pulse of the secure browser market for decades and many of us have tried and tested different options throughout the years. Brave is our top pick for the best browser for privacy based on its approach to user privacy, ad tracking prevention, privacy settings, usability, and speed.
Below, you will find other recommendations for secure browsers that can protect your privacy -- not only from cyberattacks, but also from businesses that scrape, store, and sell your data.
Best secure browsers for privacy in 2024
Best browser for privacy overall.
- Not in the traditional online ad business
- Privacy-focused by default
- Chromium challenger
- Some users report compute resource issues
Brave f eatures: Chromium-based | Blocks third-party ad trackers | Blocks cookies | Incognito windows | Onion routing | VPN | Off the record browsing
Brave is a Chromium-based browser that blocks ads, fingerprinting, and ad trackers by default.
Brave supports millions of users worldwide. The organization's business model relies on privacy-protecting ads that pay publishers and users when users pay attention to ads. The company is transparent about this revenue stream, and it is optional -- with users rewarded in crypto tokens if they opt in to ad viewing.
Brave has several privacy-enhancing settings, including options to block third-party ad trackers, upgrade unsecured connections to HTTPS, as well as block cookies and fingerprinting. Invasive ads and trackers are disabled, which the company says then improves loading times on desktop and mobile.
Also: The best web hosting services for building your dream website
Brave removed Google code from its Chromium to improve user privacy, including some account integration, background sync, and inline extensions. There is also a "Tor mode" available for use, which provides anonymized onion network routing.
The browser developer also offers a VPN and firewall service which protects sessions even outside of the browser. Many users say the browser exceeds expectations, although others find some functionality, such as VPN connectivity, could use improvement.
Brave also offers a feature called " Off the Record " (OTR) for users who may be victims of intimate partner violence. The browser developer says the feature "aims to help people who need to hide their browsing behavior from others who have access to their computer or phone."
Mozilla Firefox
Most secure browser for tracking protection.
- Enhanced tracking prevention
- Focus on accessibility
- Trusted by millions of users
- Strict tracking protection may break websites
- May require heavy PC resources
Mozilla Firefox f eatures: Enhanced tracking protection | Firefox Focus for mobile | Strict privacy standards | DNS queries sent to a secure resolver service | Focus on accessibility | Encrypted Client Hello
Firefox is a must-have for individual browser privacy across multiple devices.
One of Firefox's most important privacy features is enhanced tracking protection. Mozilla has borrowed Tor techniques to block browser fingerprinting, and Firefox developers are constantly seeking to improve tracking-prevention features.
Firefox is rich with choices to customize the browser for privacy. It blocks social media trackers, cross-site tracking cookies, tracking in private windows, crypto miners, and fingerprinting scripts. There is a "strict" mode, too, that might break some sites when trackers are hidden in content -- but there are ways to allow enhanced tracking protection for trusted sites. Furthermore, a recent improvement is the introduction of Encrypted Client Hello (ECH).
Users enjoy Firefox's privacy focus but note that it can be a resource hog.
The other option for Firefox fans is Firefox Focus , a privacy-focused browser for iOS and Android that blocks trackers and has a built-in ad blocker.
Mozilla also offers a VPN , with the option to connect up to five devices to over 500 servers in 30 countries.
The Tor browser
Best for anonymous browsing.
- High levels of anonymity
- DuckDuckGo integration
- Constant updates and improvements
- Learning curve to use
- Can be slow
The Tor browser f eatures : Onion routing | DuckDuckGo integration | Access to websites outside of the clear web
Another great choice for improving your privacy on the web is the Tor browser, a non-profit project focused on anonymizing users online.
Its proprietary web browser disguises a user's IP address and activity by relaying it through a network of servers (nodes) run by volunteers. Bouncing your information around makes it exceptionally difficult to track, which is great if you don't want your ISP or anyone else spying on your online activity.
Tor can be a crucial tool for whistleblowers, journalists, activists, and people avoiding censorship. The Tor browser is also a popular choice for accessing the deep web: A collection of websites and pages that are inaccessible through traditional means, like search engines, in what is known as the "clear" web.
Also: How to use Tor browser (and why you should)
The Tor browser's default search engine is DuckDuckGo, which will not log or store your search queries.
While it isn't a mainstream choice, the Tor browser is a well-regarded browser for people who don't want to be tracked across the web, and it gets updated frequently by the Tor Project . Users applaud the network's tough approach to privacy but note slow speeds and occasional problems with Captchas.
Page loads in the Tor browser can be slower and some sites might not work well due to the architecture of the Tor network. Nonetheless, the Tor browser is a privacy-preserving browser worthy of consideration.
Best browser for private searches
- Available across different operating systems
- Solid commitment to user privacy
- Email protection settings
- Bland browser design
DuckDuckGo f eatures: Chrome and Firefox supported | Mobile and desktop private browser | Does not collect user data | AI experiments | No search engine query trackers
When it comes to DuckDuckGo, user privacy comes first.
The privacy-focused search engine and browser is a vocal supporter of consumer privacy rights and now handles millions of user search queries daily.
There is a growing appetite for privacy-focused alternatives to tech giants like Facebook and Google. DuckDuckGo's Privacy Essentials extension for Chrome , Firefox , and Microsoft's Edge has also proven popular. Its reputation is built on the idea that it does not collect user data but can provide the same search results as those that do.
DuckDuckGo used to be a search engine rather than a full browser, but then released a mobile-friendly browser app and, now, a desktop version. The organization's browser provides a private search, website protection and blockers, web encryption, and more.
DuckDuckGo is experimenting with AI-assisted technologies to improve the search experience and has recently upgraded its browser . Users appreciate the firm's privacy focus, although some complain of censorship -- a concept DuckDuckGo staunchly denies .
Mullvad Browser
Best for use with a vpn.
- Two heavyweight privacy developers
- Fingerprint, tracker blocks
- Tor-based privacy features
- New, so less thoroughly tested
Mullvad Browser f eatures : Fingerprint masking approach | Removes online identifiers | Private mode enabled by default | Blocks trackers, cookies
Mullvad is a relatively new entry to the secure browser market.
Not to be confused with the Tor browser, the Mullvad Browser is marketed as the "Tor Browser without the Tor network." The browser is built by the Tor Project team and distributed by Mullvad, a respected Swedish virtual private network provider.
The idea behind the browser is to emulate the Tor network by creating a similar fingerprint for all users, improving anonymity. Furthermore, the browser comes with a private mode out of the box, tracking and cookies are blocked, and online functions used to extract information from visitors -- such as device identifiers -- are prevented.
You can use the browser as a standalone product, or you can combine it with Mullvad VPN . Users have given generally positive reviews, although you may find yourself signing up for the VPN for the best setup -- and it's not the cheapest on the market.
However, you should keep in mind that Mullvad was subject to a search warrant by the National Operations Department (NOA) of the Swedish Police in 2023. Mullvad staff said that as the customer data did not exist, law enforcement was left with nothing (and no customer information).
What is the best browser for privacy?
Brave is our top pick for the best browser for privacy based on its approach to user privacy, ad tracking prevention, the wide range of privacy settings on offer, usability, and speed. However, no browser is perfect, so you must decide which option suits you best.
Which is the right browser for privacy for you?
Not one size fits all, so be sure to reference the table below to better understand which browser suits your use case.
Factors to consider when choosing a secure browser
When you are switching to a more secure browser, there are some important factors to consider:
- Online identifiers : You should check to see if the browser tracks any of your activities, visits, or search queries. This data can be used to create profiles for targeted advertising and may be used to track you across different websites.
- Audits : The best secure browsers will conduct frequent security audits and have consistent patch releases to fix vulnerabilities and bugs that could expose users to risk.
- Speed vs. security : Some browsers will route your traffic through a number of servers to vastly reduce the likelihood of you being tracked. However, you will need to decide how slow you're willing the connections and browsing to be.
- VPN : If you want to use a VPN, consider whether or not the browser works well with one -- or if the browser offers a built-in solution.
How did we choose these browsers for privacy?
While investigating the best browsers for privacy in 2024, we compared each of these browsers and extensions to determine what makes them different and which is best for different use cases.
- Balance : The balance between managing user privacy and funding a business can be a tricky one for companies to manage, but as we've shown, many developers are willing to wave the security flag on behalf of users over potential opportunities to generate more revenue.
- User experience : We reviewed customer feedback to ensure that the majority of users find the browsers easy to install and use.
- Features : We like to see additional privacy-enhancing features, like onion routing. We chose providers who offer more than standard browsing experiences.
- Platform support : We selected browsers offering a range of support for different operating systems and platforms, as well as mobile coverage.
How does a privacy browser work?
A privacy browser works by automatically erasing your browsing and search history and cookies. It also may limit web tracking, and some even help hide your location (IP address). Privacy-focused browsers may also promote virtual private network (VPN) usage and may include features designed to bypass censorship blocks and keep users as anonymous as possible, such as access to onion routing and refusing to log site visits or web searches.
Do I need a privacy browser?
If you are concerned about your online privacy, you should install a privacy browser or at least an extension. We have to take responsibility for our own privacy online these days, and you can't rely on companies to do the job for you.
Also: How to delete yourself from internet search results and hide your identity online
We can recommend a few basic steps to take: Download one of the privacy-first browsers listed above that doesn't log your queries and activities, install a VPN, and use messaging apps with end-to-end encryption.
Does using a private browsing window hide my IP address?
If you're using Chrome, an incognito window doesn't hide your IP address. It simply doesn't store your browser history, information you've entered into forms, or what permissions you've given to sites you've visited. Microsoft Edge, Firefox, and Opera all use a similar form of "anonymous" web window for browsing, but they aren't truly hiding your online identity.
Also: The best VPN services (and whether it's worth trying free VPNs)
If you want to block your IP address from being viewed or tracked, you can download a VPN , which masks your IP address so your service provider (or anyone else, for that matter) can't see what you're doing.
What is the most common personal web security risk?
Honestly? Putting your personal or contact information on social media. If you have your full name, phone number, address, or place of work anywhere on your social media, someone can use it to wreak havoc on your personal accounts.
To prevent this, avoid using your real name online where possible, turn off location tracking, and don't post about your place of work if you can help it. All it takes is a single piece of personal information for someone with very bad intentions to get ahold of your entire online presence -- and so if you're posting photos of you away from home and on holiday, for example, you're letting people know your home is vulnerable.
Also: The best security keys
Those innocent-looking name generator memes are another big issue; the ones that have you type out your first pet's name and your childhood street name (or something similar) to make up a gnome (or whatever) name. These are answers to common password recovery questions, so by letting the world know that your Christmas elf name is Fluffy Elm Street, you could be handing over all of your personal accounts to internet criminals.
Are there other browsers worth considering?
Online privacy and security are hot topics today. The amount of data quietly collected on each and every one of us is staggering -- and beyond targeted advertisements, you may not realize it.
The browsers we've recommended above can help tighten up your defenses against tracking and online monitoring, but as no browser is a perfect solution, you may also want to consider the alternatives below:
ZDNET Recommends
The best mobile vpns: expert tested, the best vpn services of 2024: expert tested, the best travel vpns: expert tested.
Apple fixes Safari WebKit zero-day flaw exploited at Pwn2Own
Sergiu gatlan.
- May 14, 2024

Apple has released security updates to fix a zero-day vulnerability in the Safari web browser exploited during this year's Pwn2Own Vancouver hacking competition.
The company addressed the security flaw (tracked as CVE-2024-27834) on systems running macOS Monterey and macOS Ventura with improved checks.
While Apple only said that the vulnerability was reported by Manfred Paul, working with Trend Micro's Zero Day Initiative, this is one of the bugs the security researcher chained with an integer underflow bug to gain remote code execution (RCE) and earn $60,000 during Pwn2Own.
"An attacker with arbitrary read and write capability may be able to bypass Pointer Authentication," Apple explains in a Monday advisory.
Pointer authentication codes (PACs) are used on the arm64e architecture to detect and guard against unexpected changes to pointers in memory, with the CPU triggering app crashes following memory corruption events linked to authentication failures.
While Safari 17.5 is also available for iOS 17.5, iPadOS 17.5, macOS Sonoma 14.5, and visionOS 1.2, Apple has yet to confirm if it also patched the CVE-2024-27834 bug on these platforms.
If you run macOS Ventura or macOS Monterey, you can update Safari without updating macOS by going to > System Settings > General > Software Update and clicking "More info…" under "Updates Available."
Pwn2Own Vancouver 2024
Security researchers collected $1,132,500 after exploiting and reporting 29 zero-days at this year's Vancouver hacking contest.
Manfred Paul emerged as the winner and earned $202,500 in cash after demoing an RCE zero-day combo against Apple's Safari web browser and a double-tap RCE exploit targeting an Improper Validation of Specified Quantity in Input weakness in the Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge web browsers during the first day of the hacking competition.
On the second day, Manfred Paul exploited an out-of-bounds (OOB) write zero-day bug to gain RCE and escaped Mozilla Firefox's sandbox via an exposed dangerous function weakness.
Google and Mozilla fixed the zero-days exploited at Pwn2Own Vancouver 2024 within days after the contest ended, with Google releasing patches five days later and Mozilla after just one day .
However, vendors rarely hurry to fix security flaws exploited at Pwn2Own since Trend Micro's Zero Day Initiative publicly discloses bug details after 90 days.
On Monday, Apple also backported security patches released in March to older iPhones and iPads, fixing an iOS zero-day tagged as exploited in attacks.
Related Articles:
Apple backports fix for zero-day exploited in attacks to older iPhones
Google fixes third actively exploited Chrome zero-day in a week
Apple blocked $7 billion in fraudulent App Store purchases in 4 years
PoC exploit released for RCE zero-day in D-Link EXO AX4800 routers
Microsoft fixes Windows zero-day exploited in QakBot malware attacks
- Previous Article
- Next Article
Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment.
Not a member yet? Register Now
You may also like:

FBI seize BreachForums hacking forum used to leak stolen data

Help us understand the problem. What is going on with this comment?
- Abusive or Harmful
- Inappropriate content
- Strong language
Read our posting guidelinese to learn what content is prohibited.
- Cyber Attack
- Vulnerability
- Data Breaches
- Privacy Policy

- Cyber Security News
Apple Safari Zero-Day Flaw Exploited At Pwn2Own : Patch Now

Apple has released security updates to address a zero-day vulnerability in its Safari web browser that was exploited during this year’s Pwn2Own Vancouver hacking competition.
This issue, identified as CVE-2024-27834, was fixed by enhanced checks on macOS Monterey and macOS Ventura systems.
Master of Pwn winner Manfred Paul reported this vulnerability in collaboration with Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative.
Details Of The Apple Safari Zero-Day Flaw
The vulnerability in Safari WebKit is identified as CVE-2024-27834, where an attacker with arbitrary read and write capability may be able to bypass the pointer authentication.
Free Webinar on Live API Attack Simulation : Book Your Seat | Start protecting your APIs from hackers
“An attacker with arbitrary read and write capability may be able to bypass Pointer Authentication,” Apple said .
If this vulnerability is successfully exploited, an attacker may be able to bypass security measures, possibly gaining unauthorized access to the system or running malicious code on it.
During Pwn2Own , Manfred Paul used an integer underflow flaw to obtain remote code execution (RCE) and earn $60,000.
This issue is fixed in iOS 17.5 and iPadOS 17.5, tvOS 17.5, Safari 17.5, watchOS 10.5, macOS Sonoma 14.5.
Update Now!
Update to the latest patched versions of iOS 17.5, iPadOS 17.5, tvOS 17.5, Safari 17.5, watchOS 10.5, or macOS Sonoma 14.5 to mitigate this vulnerability.
Apple released several upgrades for its iOS and macOS operating systems to start the May release cycle. The most noteworthy update for iOS 16.7.8 and iPadOS 16.7.8 addresses CVE-2024-23296.
If you’re using a device with an affected OS, make sure you get the update. This flaw is reportedly under active attack.
On-Demand Webinar to Secure the Top 3 SME Attack Vectors: Watch for Free
Managed WAF
Find us on google news.

Latest News
Royal tiger group with spoofed phone numbers stealing credit..., logicalis enhances global security services with the launch of intelligent security, critical next.js vulnerability let attackers compromise server operations, boeing confirms lockbit hackers demanded $200 million ransom after 2023 data breach, wavestealer malware delivered via telegram & discord messaging platforms.
- Public Sector
- Privileged Access Manager
- Secrets Manager
- Connection Manager
Every few seconds, a person or organization is victimized with ransomware.
Keeper will protect you.
- Business and Enterprise
- Personal and Family
- Military and Medical
- Password Management Protect and manage your organization's passwords, metadata and files
- Single Sign-On Security Seamlessly and quickly strengthen SAML-compliant IdPs, AD and LDAP
- Password Sharing Securely share passwords and sensitive information with users and teams
- Passwordless Authentication Enable passwordless authentication for fast, secure access to applications
- Secrets Management for DevOps Protect critical infrastructure, CI/CD pipelines and eliminate secret sprawl
- Credential Governance & Controls Achieve visibility, control and security across the entire organization
- Privileged Session Management Securely manage applications and services for users, teams and nodes
- SSH Key Management Manage and protect SSH keys and digital certificates across your tech stack
- Remote Infrastructure Access Initiate secure remote access with RDP, SSH and other common protocols
- Secure Remote Database Access Restrict secure access to authorized users with RBAC and policies
- Zero-Trust Security Strengthen your organization with zero-trust security and policies
- Industry Compliance & Reporting Achieve industry compliance and audit reporting including SOX and FedRAMP
- Password Rotation Automate credential rotation to drastically reduce the risk of credential-based attacks
- Resource Library
- Personal Dark Web Scan
- Business Dark Web Scan
- Secure Password Generator
- Secure Passphrase Generator
- Encrypted Messaging App
- Cyber Threats Database
- Passkeys Directory
- Keeper 101 Videos
- Documentation
- End-User Guides
- Enterprise Guide
- MSP Admin Guide
- Partners Portal
- Register a Deal
- Become a Reseller
- Find a Reseller
- Keeper for MSPs
- Affiliate Partner Program
- Our Partners
- Integrations
- Business Sales
- Press Inquiries
- Get a Quote Try It Free Try It Free Try It Free View Careers
- Admin Console
Safari Password Manager
Safari users everywhere protect and autofill their passwords and private data with Keeper, the world's most secure password manager and digital vault.
On any device where you use Safari, Keeper enables you to generate, store, protect and autofill strong passwords and passkeys that cybercriminals can’t access. Getting started with Keeper as your Safari password manager is easy—just download Keeper for Safari from the Mac App Store.
Managing Your Passwords on Safari Using Keeper
Keeper Security gives you the strongest possible system for managing passwords on Safari, keeping cybercriminals from gaining access to your money, private information and identity.
The KeeperFill browser extension for Safari can be downloaded directly from Apple’s App Store, and it automatically generates strong passwords and lets you autofill address and credit card information. Here are five reasons why your Safari browsing experience is even more secure with Keeper:
- Keeper is a streamlined, all-in-one platform for managing all your passwords and confidential information.
- Keeper helps you easily generate and store strong passwords everywhere you browse with Safari, on Apple devices or PCs.
- Keeper's autofill feature makes signing into websites easier across all your devices without compromising security.
- Keeper for Safari helps you protect confidential files, documents and other media in a secure, encrypted vault .
- Keeper lets you securely share individual passwords or files with people you trust and designate individuals who can access your vault in an emergency.
How Does Keeper Work With Safari?
When you use Keeper and Safari together, you'll never have to remember or worry about passwords again. With your master password that you use just for Keeper, you can manage all your other Safari passwords and logins and protect valuable data like credit card numbers, bank account numbers and other personal information stored on connected devices.
Safari users can also use Keeper to protect and securely access data such as answers to security questions and PINs . At the same time, you can easily share files and records with family members or other trusted parties using Keeper.
Keeper vs iCloud Keychain
Keeper has more features than iCloud Keychain allowing for more convenient management of all your confidential digital information.
Keeper syncs and is accessible across all devices, operating systems and browsers.
iCloud Keychain
iCloud Keychain is only accessible on Apple devices.
Keeper can store everything that iCloud Keychain can, plus it has custom record types, allowing users to store any kind of confidential information including medical cards, passports, driver's licenses, videos, documents and more.
iCloud Keychain can only store passwords, credit card numbers, security codes, notes and passkeys.
Keeper uses a unique master password to protect your information.
iCloud Keychain uses the same credentials as your device – therefore if someone has your device credentials they can also access your passwords.
Keeper has many organizational capabilities, including folders and color coding.
iCloud Keychain has no custom organizational capabilities.
Keeper has sophisticated record-sharing capabilities with different permissions types, time limits, the ability to revoke permissions and the ability to share with people that don’t have a Keeper account.
iCloud Keychain can only share passwords using AirDrop – so you can only share passwords with other Apple users who are physically nearby.
Why You Should Use Keeper Password Manager
Keeper makes managing passwords easy and straightforward. It gives you a secure encrypted location for storing passwords and other login information you don’t want others to access. Best of all, Keeper works on any device where you use Safari – Mac, PC, mobile and more.
Using Keeper Password Manager with Safari allows you to securely store and autofill unlimited passwords. It includes:
- Unlimited password storage
- Autofill passwords across devices
- Unlimited payment and identity info storage
- Fingerprint and Face ID login
- Access on multiple devices
Keeper Security: The Best Password Manager for Safari
Start your 30-day trial to see how Keeper can protect you wherever you're online.
- Americas & APAC +1 708 515 4062
- Federal & SLED +1 202 946 4575
- EMEA +353 21 237 5250
- Business (Americas) +1 312 226 4782
- Business (EMEA) +353 21 237 5250
- Business (APAC) +81 3 4520 3524
- English (US)
- English (UK)
- Português (BR)
Cookie Consent Preferences
Keeper Security uses 1st and 3rd party cookies to store and track information about your usage of our services and to provide a better website experience. We also may share this data in its aggregate form with advertisers, affiliates, and partners. Learn More
Withdraw Cookie Consent Cookie Consent Preferences
Chat with support.
You must accept cookies to use Live Chat.
Protect your company from cybercriminals.
Public Sector and FedRAMP
Protect your agency and educational institution from cybercriminals.
Protect your MSP organization, your end customers and add new revenue streams.
Protect yourself and your family from cybercriminals.
- Password Management
- Password Sharing
- Secrets Management for DevOps
- Privileged Session Management
- Remote Infrastructure Access
- Zero-Trust Security
- Single Sign-On Security
- Passwordless Authentication
- Credential Governance & Controls
- SSH Key Management
- Secure Remote Database Access
- Industry Compliance & Reporting
- Password Rotation
- White Papers
- Research Reports
- Security Architecture
- GDPR Compliance
- User Reviews
- Press and Media
Want to highlight a helpful answer? Upvote!
Did someone help you, or did an answer or User Tip resolve your issue? Upvote by selecting the upvote arrow. Your feedback helps others! Learn more about when to upvote >
Looks like no one’s replied in a while. To start the conversation again, simply ask a new question.
I received an apple security breach while on safari
I received an apple security breach while on safari and cant seem to get back in safari. Does anyone have any recommendations on how to fix my iphone?
iPhone 6, iOS 10
Posted on Apr 23, 2019 3:38 PM
Posted on Apr 23, 2019 7:28 PM
Try double clicking the Home button and swipe Safari upwards. Go to Settings/Safari and clear History and Website Data. Open Safari and test.
Safari - Clear the history and cookies on your iPhone, iPad, or iPod touch
Safari website data on your iPhone or iPad - How to clear
Similar questions
- Can my iPhone be hacked through Safari? I was browsing on Safari Private Mode and the website on my tab suddenly switched to the website I was previously on, and when I clicked to go forward it took me to a Google image search of cats. I turned off Wifi for a bit and restarted my device. I have an iPhone 11 and it is fully updated to the latest version of iOS (16.6). I checked all of my apps, files and activity, but I didn’t find anything suspicious. Should I be worried about this? Is there a chance that my phone been hacked? Thank you in advance for your help. [Re-titled by Moderator] 12141 8
- My safari is in dangerous How to protect my phone from hacker 255 4
- When I open Safari I get a notice that my Apple iPhone may be infected and to install an app. When I try to cancel the notice, I am taken to a site for Defendo: AdBlock and Security. How do I remove this from my iPhone7 so I can use Safari ? When I open Safari I get a notice that my Apple iPhone may be infected and to install an app. When I try to cancel the notice, I am taken to a site for Defendo: AdBlock and Security. How do I remove this from my iPhone7 so I can use Safari ? 596 3
Loading page content
Page content loaded
Apr 23, 2019 7:28 PM in response to Safari0419

How to clear the cache on your iPhone (and why you should)
How many tabs are open on your mobile browser right now? Go ahead, check -- you might be surprised by what you find.
Americans spend over five hours a day on their smartphones. That's over five hours of your phone potentially accessing, retrieving, and saving cache and cookies, which can negatively impact your iPhone's storage space .
What is cache?
Cache is the temporary storage of some data, like parts of a website from the last time you visited it, for example. Browser cache is content from a website that is stored on your phone during a browser session to help the browser execute faster the next time you visit that page.
Also: How to clear Google search cache on Android
Cache data can slow down your phone's overall browsing performance, however, since it takes up storage space on your device, so it's good to clear it out regularly. In this article, we mainly focus on clearing web browser cache on an iPhone, but you should know that other types of cache include mobile app cache and CPU cache.
How to clear cache on iPhone
What you'll need: Everything you need to clear your browser cache is within the iPhone's settings app or the Safari app, so grab your iPhone to get started.
Keep in mind that clearing the cache can clear private data, which can close all open tabs in Safari. This is also likely to log you out of all your websites, prompting you to sign in again the next time you open them.
How do I clear the cache from Chrome on iPhone?
If Google Chrome is your preferred browser, it may have a substantial amount of data stored on your device, which could also slow down performance.
To clear the cache in Chrome, open the Google Chrome app and follow these steps:
- Tap Settings .
- Go to Privacy and Security .
- Select Clear Browsing Data .
- Select the time from which to delete the data (if you want to delete all your browsing history, choose All Time ).
- Go through the items you'd like to delete, like your Browsing History, Cookies and Site Data, Cached Images and Files, Saved Passwords , and Autofill Data.
- Confirm by tapping Clear Browsing Data at the bottom of the screen.
- Tap Done when you've deleted the Chrome cache.
Also: Apple releases iOS 17.4 with podcast transcripts, new emojis, and EU app store changes
Clearing the browsing and cache data in Google Chrome doesn't close all open tabs, but it will refresh each tab and log you out of websites. Once you tap on one of the tabs you want to access, you'll have to log back in.
How can I browse on Safari without history?
If you're learning how to clear cache on an iPhone, you may also be wondering if there's a way to use Safari without saving any browsing history. You can turn on Private Browsing by following these steps:
- Open Safari .
- Tap on Tabs .
- Choose Private .
You can also enable private browsing by going to your iPhone Settings, finding Safari, and toggling on the private option.
How do I clear my app cache on my iPhone?
To clear the app cache from your iPhone Settings app, you can either delete the app and reinstall it, offload it, or try to clear the cache from within the app. Unfortunately, iOS apps don't have consistent settings across the board that would allow you to clear the cache of every app.
Also: Apple warns: Don't put your wet iPhone in rice. Do this instead
Apps like TikTok and CapCut, for example, have options to Clear Cache within their respective settings. Amazon lets users delete their browsing history, while the Reddit app can clear local history. It all depends on what the app's settings let you do.
Is "clear cache" the same as offloading?
Not exactly, though app offloading can help if your phone is slowed down by low storage. To offload an app means to uninstall an app without deleting any documents or data associated with it.
Also: Apple secures iMessage against threats from the future
To offload an app, go to Settings , then General , choose iPhone Storage and select the app to offload, then tap Offload App . If you ever download it again, you'll pick up where you left off for that app.
Are cookies and cache the same thing?
Cookies and cache are not the same. Cookies are data files that websites send to your phone, including things like saved passwords to keep you logged into an account or even the website preferences from the previous time you visited.
Also: I tested the best Mint alternatives, and this is my new favorite money app
Though they do sound harmless, cookies can also track how you browse the internet. They monitor patterns in your browsing and search history, even seeing what you clicked on or what your mouse hovered over. Ever made an innocuous search on Amazon only to find ads for it on all the apps you use? Cookies likely made that possible.
Can I block cookies on my iPhone?
While you can block cookies on Safari, the ranks are divided on whether you should. Blocking cookies entirely means that websites won't be able to get information from you, but it also means that some websites may not even work correctly on your browser. A lot of users actually enjoy a more personalized browsing experience, so cookies are a good thing for them.
If you'd like to block cookies in Safari, follow these steps:
- Go to Settings and select Safari .
- Tap on the toggle next to Block All Cookies .
There are also third-party extensions that help you block cookies and trackers in Google Chrome, like Ghostery and Disconnect .
How do I check iPhone storage?
On an iPhone, Settings can show you what's taking up most of your media storage, like photos, videos, and music. You can also see what each particular app's storage consumption is, which includes temporary data. To view the details of your iPhone's storage space, follow these steps:
- Go to the iPhone Settings .
- Tap on General .
- Select iPhone Storage .
- Scroll through to find the app you're looking for.
- Tap on the app to view storage status and options.
Unfortunately, you can't clear your iPhone cache for third-party apps by going into your Settings app, but this gives you a visual of your iPhone's storage and the option to delete or offload apps.
Also: Here's the fastest way to declutter your iPhone and free up Gigabytes of space
When you look at your device's storage space, you'll probably see recommended steps you can take to optimize your iPhone's storage, like offloading unused apps.
- How to better organize text messages on your iPhone, thanks to iOS 17
- How to transfer data from Android to an iPhone: 2 simple and fast ways
- How to turn on 80% charging limit on the iPhone 15 to save battery health
- How to leave a FaceTime voice or video message when your call goes unanswered
About the security content of Safari 17.5
This document describes the security content of Safari 17.5.
About Apple security updates
For our customers' protection, Apple doesn't disclose, discuss, or confirm security issues until an investigation has occurred and patches or releases are available. Recent releases are listed on the Apple security releases page.
Apple security documents reference vulnerabilities by CVE-ID when possible.
For more information about security, see the Apple Product Security page.

Safari 17.5
Released May 13, 2024
Available for: macOS Monterey and macOS Ventura
Impact: An attacker with arbitrary read and write capability may be able to bypass Pointer Authentication
Description: The issue was addressed with improved checks.
WebKit Bugzilla: 272750 CVE-2024-27834: Manfred Paul (@_manfp) working with Trend Micro's Zero Day Initiative
Additional recognition
Safari Downloads
We would like to acknowledge Arsenii Kostromin (0x3c3e) for their assistance.
Information about products not manufactured by Apple, or independent websites not controlled or tested by Apple, is provided without recommendation or endorsement. Apple assumes no responsibility with regard to the selection, performance, or use of third-party websites or products. Apple makes no representations regarding third-party website accuracy or reliability. Contact the vendor for additional information.
Start a discussion in Apple Support Communities
Home > News Tips
Safari Can't Establish a Secure Connection, Try These Solutions!
Updated on Monday, May 13, 2024

Approved by
To protect users' security and privacy, Apple enables websites to use strong encryption to provide a secure web connection, which makes Safari continuous to be one of the most secure browsers on Mac. However, if a webpage on a server doesn't meet Safari's secure cryptographic standards, the below warning message may show up:
- Safari can't open the page because Safari can't establish a secure connection to the server .
- Safari can't open the website because it's using weak encryption.
If you're facing the Safari won't open problem due to the unsafe connection to the server, just read along to learn how to fix Safari can't establish a secure connection on Mac.
Why can't Safari establish a secure connection?
There are many reasons why Safari can't establish a secure connection to the server you're trying to access. Namely, they're:
- The webpage you're trying to access is under low encryption.
- A third-party extension or add-on has been installed on your browser.
- Your browser has outdated cache data.
- The SSL certificate of a website is expired.
How to fix Safari can't establish a secure connection?
Now that you've understood the potential causes of Safari not establishing a secure connection to the server , it's time to look at how to fix it. Below are 8 solutions you can use to resolve the error.
Fix 1: Double-check the URL
The first thing you should do when Safari can't establish a secure connection is to check the URL again. Click the URL to view the full web address to make sure the web address is correct. Any small mistakes (like .cn should be .com) could bring you to a wrong and unsafe site.
Sometimes, the website you're trying to open isn't actually the one you want to visit. Fake websites are often designed to look like the real one to steal your precious personal data.
Fix 2: Check the current date and time
You may not know using the wrong date and time on your Mac can cause some unexpected issues. It might stop you from installing the latest software update, downloading new apps, or loading secure web pages. Thus, to fix the Safari not working issue you're facing, make sure the date & time you set is correct.
Click the Apple menu and go to System Preferences > Date & Time . Click the padlock to unlock changes, then tick the option named Set date and time automatically .
Fix 3: Disable iCloud Private Relay
If you're an iCloud+ subscriber, the iCloud Private Relay is automatically enabled for the Safari browser. iCloud Private Relay shields your online location and routes the traffic from an Apple-branded server. In that way, the website provider won't have your true location through the IP address.
However, the website may need your actual location to load. You need to disable iCloud Private Relay to fix Safari can't establish a secure connection . Simply open the Apple menu > System Preferences > Apple ID . Then, disable Private Relay from the list.
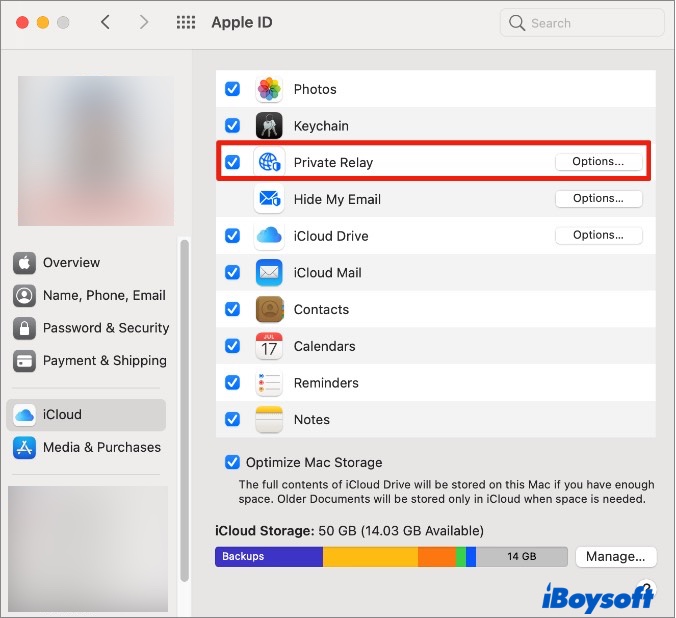
Fix 4: Disable your Safari browser extensions
An extension or add-on in your Safari browser may be conflicting with Safari's ability to connect to a site securely. Therefore, it may be helpful for troubleshooting the Safari issue if you disable all your browser extensions, especially those anti-virus programs and security-related extensions.
To do this, launch Safari first, then click Safari in the top menu bar and navigate to Preferences . Switch to the Extensions tab and cancel the checkmark next to the add-on name to disable it.
Fix 5: Clear the Safari browser history
As mentioned earlier, the outdated cache browser history may cause Safari can't establish a secure connection to the server . So let's see if clearing the browser history on Mac will resolve the Safari issue.
Step 1: Open Safari, and click on History from its menu bar.
Step 2: From the given list, select Clear History .
Step 3: A dialogue window shows up, select All History from the drop-down menu next to the word Clear . Then click Clear History again.
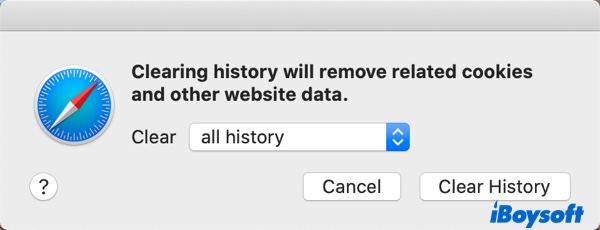
Fix 6: Change to a different DNS
If the error is still there, you may need to check your Domain Name Server (DNS) settings since issues with your DNS settings might be responsible for Safari can't establish a secure connection to the server. To see if this is the case (and resolve it), you can try using a different DNS address. For example, you could use Google's Public DNS.
- Go to Apple menu > System Preferences > Network .
- Select Advanced and switch to the DNS tab.
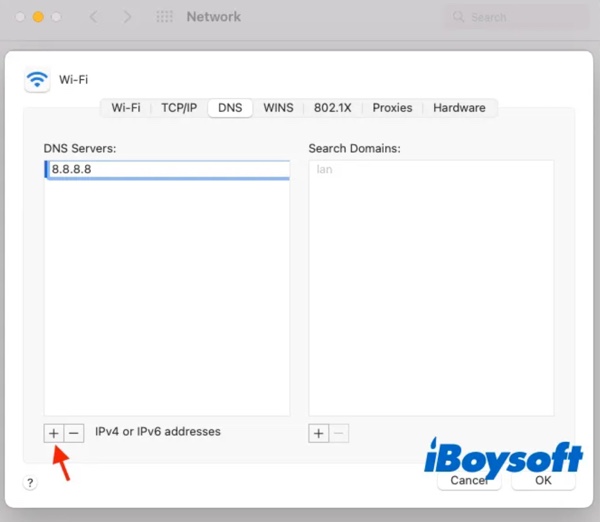
Fix 7: Disable IPv6 for your network
Internet Protocol (IP) controls how data moves across the internet. Its previous version was IPv4 and the latest one is IPv6. Some websites still use the IPv4 protocol and cause you to face the Safari can't establish a secure connection message. So you need to temporarily disable IPv6 on your Mac. Here's how to do it.
- Go to Apple menu > System Preferences > Network and select the Advanced menu at the bottom.
- Switch to TCP/IP this time and select Manually from the Configure IPv6 menu.
This should resolve the Safari issue if IPv6 were the problem. If not, there's one last fix you can try.
Fix 8: Make Keychain trust the certificate
Keychain Access in macOS is the application that stores your passwords, account details, and application certificates. It also keeps your data secure and can control which sites are trusted by your Mac device. Thus, you need to make sure that Keychain Access trusts the certificate of the site you're trying to open.
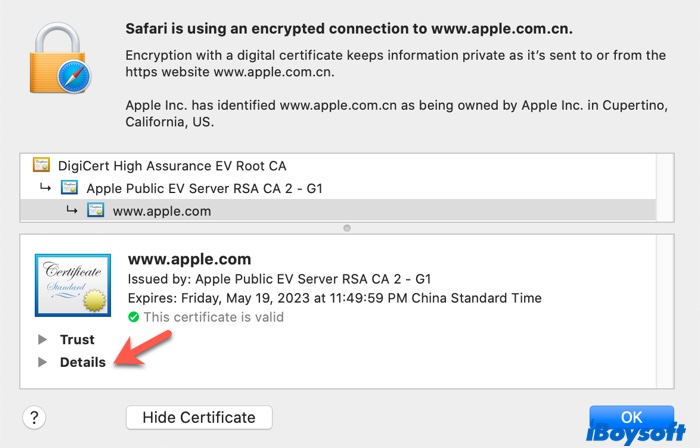
- With the Details panel expanded, click Command + Space keys to bring Spotlight Search bar, enter "Keychain" in the search field and open it.
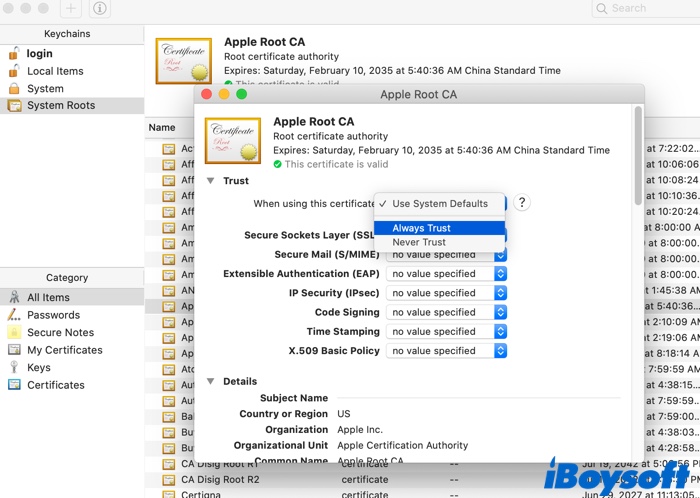
Anna Yuan is a professional tech editor at iBoysoft who specializes in writing articles related to software, macOS, Windows OS, Apple products, and Windows computers. Furthermore, she writes articles for some well-known tech websites. And as she has been a Mac user for many years, she's highly willing to share information on Mac utilities and tips.
Jessica Shee is a senior tech editor at iBoysoft. Throughout her 4 years of experience, Jessica has written many informative and instructional articles in data recovery, data security, and disk management to help a lot of readers secure their important documents and take the best advantage of their devices.
No. 308, 3/F, Unit 1, Building 6, No. 1700, Tianfu Avenue North, High-tech Zone
Copyright© 2024 iBoysoft ® . All Rights Reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In the Safari app on your Mac, use Security settings to turn security warnings on or off. Also enable or disable JavaScript. To change these settings, choose Safari > Settings, then click Security. Open Safari for me. Option.
Open the Safari app on your iPhone. Tap . Swipe right on the tab bar at the bottom of the screen until Private Browsing opens, then tap Unlock. To exit Private Browsing, tap , then swipe left to open a Tab Group from the menu at the bottom of your screen. The websites you have open in Private Browsing stay open, and Private Browsing locks.
Click the Security button. Check the box to Warn when visiting a fraudulent website . If you happen to run across one of these sites, Safari will put up a full-screen warning about the site before you can proceed.
Safari is the built-in browser on Mac, iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch. Fast and energy efficient, Safari delivers innovative features while also protecting user privacy. Safari is built to ... And Safari implements security best practices to protect user data. Protection from cross-site tracking .
Safari can detect when websites are suspicious or may appear fraudulent, and if you enable the setting, you can get a warning before visiting those sites. You can also just hit "Ignore" if you know the site is legit. Launch Settings from your Home screen. Tap Safari. You'll have to scroll down to find it.
To control links, go to Safari > Open Links. To use AutoFill, go to Settings > Safari > AutoFill > turn on Use Contact Info. To view saved passwords, go to Settings > Passwords & Accounts > Website & App Passwords. This article explains how to adjust Safari settings and security on your iPhone or iPad.
Here's a brief overview. Safari has two preference panes that are useful to stay safe when browsing. Chose Safari > Preferences, then click Security. It's probably safest to check all these options: The Fraudulent Sites option tells Safari to alert you when you visit a site that is known to be dangerous.
Safari is a well-built browser from a security perspective. However there are times when your privacy is compromised or the browser is hijacked. This can be very annoying.
On an iPhone or iPad, start the Settings app and then tap Safari. In the Search section, tap Search Engine and choose DuckDuckGo from the options. If you're using a Mac, start Safari and then ...
Safari Features for Better Security. In addition to keeping your information private, Safari also keeps you safe from hackers and malware as you browse the internet. 4. Safari's Password Manager. One of its major security features is its built-in password manager.
/en/safari/bookmarking-in-safari/content/ Safari privacy and security. Safari has several security features, including security indicators and malware protection.Because of its advanced security features, Safari offers a safe browsing experience.Safari also allows you to control what information you share online, keeping your personal information private.
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA Apple today announced its latest privacy and security innovations, including major updates to Safari Private Browsing, Communication Safety, and Lockdown Mode, as well as app privacy improvements. Additionally, Apple introduced new features designed with privacy and security at their core, including Check In, NameDrop, and Live Voicemail.
Now, here are 30 tricks to help you have a better experience when using Safari. 1. Navigate Tab Bar. (Credit: Lance Whitney / Apple) The jump to iOS 15 moved Safari's address bar to the bottom of ...
Safari doesn't include backwards compatibility for SSL, so you don't need to do anything about that security weakness. However, here are some actions you can take to make your Safari browser more secure. Click on Safari in the top menu bar and select Preferences. Select Security and then click on Manage Website Settings.
In the Safari app on your Mac, use Security settings to turn security warnings on or off. Also enable or disable JavaScript. To change these settings, choose Safari > Settings, then click Security. Open Safari for me. Option.
2. Reset Safari • Open the browser and go to Safari menu. Select Reset Safari in the drop-down list • Make sure all the boxes are ticked on the interface and hit Reset . Get rid of malware from Safari using Combo Cleaner automatic removal tool. The Mac maintenance and security app called Combo Cleaner is a one-stop tool to detect and remove ...
Reviewed by Min Shin and Alison DeNisco Rayome. Brave. Best browser for privacy overall. View at Brave. Mozilla Firefox. Most secure browser for tracking protection. View at Mozilla. The Tor ...
If these are sliding in the from the top right of the screen, a site you visited has given itself permission to send push notifications. Open Safari's preferences. Click on the Websites tab and then scroll down to Notifications. Clear any entries in the right hand window. You might find something similar in the Pop-up Windows heading below that.
Apple has released security updates to fix a zero-day vulnerability in the Safari web browser exploited during this year's Pwn2Own Vancouver hacking competition. The company addressed the security ...
Apple has released security updates to address a zero-day vulnerability in its Safari web browser that was exploited during this year's Pwn2Own Vancouver hacking competition. This issue, identified as CVE-2024-27834, was fixed by enhanced checks on macOS Monterey and macOS Ventura systems.
Safari warns you when a website that you're visiting isn't secure. In any of these cases, you may see a "Not Secure" or "Website Not Secure" message in Safari: The website is encrypted, but its certificate is expired or illegitimate. The website's certificate is valid but the version of TLS is not secure (TLS version 1.1 or earlier).
Mobile Android Device Browser (e.g. Samsung Galaxy 8+) • Chrome: 81 and higher . Mobile: Apple Devices (e.g. IPad Pro, IPhone 7) • Chrome: 81 and higher • Safari 13.7 and higher . Unsupported Browsers and Mobile Devices . Unsupported Browsers • IE 11 is no longer supported by SSA • Samsung Internet browser . Unsupported Devices
Apple has rolled out security updates to address a zero-day vulnerability in the Safari web browser that was exploited during the recent Pwn2Own Vancouver hacking competition, BleepingComputer ...
Keeper Security gives you the strongest possible system for managing passwords on Safari, keeping cybercriminals from gaining access to your money, private information and identity. The KeeperFill browser extension for Safari can be downloaded directly from Apple's App Store, and it automatically generates strong passwords and lets you ...
Try double clicking the Home button and swipe Safari upwards. Go to Settings/Safari and clear History and Website Data. Open Safari and test. Safari - Clear the history and cookies on your iPhone, iPad, or iPod touch. Safari website data on your iPhone or iPad - How to clear. I received an apple security breach while on safari. .
How to clear cache on iPhone. What you'll need: Everything you need to clear your browser cache is within the iPhone's settings app or the Safari app, so grab your iPhone to get started. Keep in ...
About the security content of Safari 17.5. This document describes the security content of Safari 17.5. About Apple security updates. For our customers' protection, Apple doesn't disclose, discuss, or confirm security issues until an investigation has occurred and patches or releases are available.
Fix 4: Disable your Safari browser extensions. An extension or add-on in your Safari browser may be conflicting with Safari's ability to connect to a site securely. Therefore, it may be helpful for troubleshooting the Safari issue if you disable all your browser extensions, especially those anti-virus programs and security-related extensions.
Google has issued another urgent update, bringing Chrome's Stable channel to 124..6367.207/.208 for Mac and Windows, as another zero day is anonymously reported and patched. Just as last week ...